|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1583179
智慧工厂介绍:2024Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024 |
|||||||
本报告是 IoT Analytics 正在进行的工业物联网和工业 4.0 研究的一部分,该研究基□□于对企业营运商进行的调查结果。目的是为参赛者提供有关智慧工厂用例和製造商技术采用现状的资讯。
本报告从以下六个角度检视智慧工厂的引进。
6 个镜头:
- 1.范式
- 2.技术
- 3.预算
- 4.作业
- 5.投资前景
- 6.投资报酬率
四个深层详细分析:
- 1.工业人工智慧与边缘人工智慧
- 2.工业资料运营
- 3.设备管理
- 4.OT 容器化
为什么製造商致力于让他们的工厂变得更聪明?
保持成本竞争力:
保持成本竞争力对于生存至关重要,尤其是在价格敏感的行业。一个显着的例子是德国太阳能电池製造业的崩溃。德国的太阳能电池产业一度领先世界,但在2000年代末,廉价的中国太阳能组件进入市场,削弱了像SolarWorld这样的国内製造商,该公司最终走到了破产的地步。类似的情况目前可能正在电动车(EV)产业上演。
缓解劳力短缺与技能差距:
许多高收入国家正在经历出生率下降,并且在退休时面临失去许多专业人员的边缘。这也对製造业造成沉重打击。光是在美国,未来十年就可能有 190 万个製造业职缺,而自动化和数位化可以帮助缓解这些课题。

为了解决永续性和监管压力:
许多监管机构正在透过推出相关法规来应对气候变迁的课题。例如,欧盟现已开始要求大公司以及上市中小企业报告其碳足迹和相关主题。如果没有技术基础,准确的追踪和报告是困难的。

为了获得更大的灵活性和客製化:
汽车产业目前向电动车的转变是製造灵活性重要性的一个很好的例子。为内燃机汽车建造的传统生产线通常缺乏灵活性,无法适应电动车所需的各种零件和配置。此外,电动车的需求波动很大,因此汽车製造商在能够灵活调整生产以满足当前需求方面具有显着优势。因此,实施更具适应性和可扩展性的製造解决方案以应对客户偏好、产品设计和材料的变化将是未来的关键。
问题解答
- 智慧工厂的现况如何?
- 对于部署智慧工厂策略的製造商来说,哪些技术最重要?
- 哪些製造商在采用数位技术方面被认为是 "先进" 的?
- 製造商模式正在发生怎样的变化?
- 製造商正在部署哪些人工智慧用例?
- AI 模型训练和推理在哪里进行?
- 选择 DataOps 解时主要考虑哪些因素?
- 製造商使用什么类型的软体来管理设备?
- 用于边缘容器化的主要容器化工具有哪些?
提及的公司
|
|
|
"The Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024" is part of IoT Analytics' ongoing coverage of Industrial IoT & Industry 4.0. The information presented in this report is based on the results of a survey of 500 manufacturers between February 2024 to March 2024. The purpose is to inform other market participants about the current state of adoption of smart factory use cases and technology across manufacturers. Survey participants were selected randomly, and their knowledge was verified independently. To ensure complete objectivity, IoT Analytics did not alter or supplement any survey results and did not accept participants who were suggested by third parties (e.g., customers from specific vendors).
INFOGRAPHICS


This report highlights smart factory adoption through
6 lenses
- 1. Paradigms
- 2. Technologies
- 3. Budgets
- 4. Challenges
- 5. Investment outlooks
- 6. ROI
INFOGRAPHICS


and 4 deep dives
- 1. Industrial AI & edge AI
- 2. Industrial DataOps
- 3. Device management
- 4. Containerization of OT
INFOGRAPHICS


Why do manufacturers look to make factories smarter?
To stay (cost-)competitive.
Especially in industries where price sensitivity is high, maintaining cost competitiveness is crucial for survival. A stark example is the collapse of the German solar manufacturing industry. Once a global leader, Germany's solar sector struggled when cheaper Chinese solar modules flooded the market in the late 2000s, undercutting domestic producers like SolarWorld, which eventually declared insolvency. A similar scenario may currently be unfolding in the electric vehicle (EV) industry.
To mitigate labor shortages and skill gaps.
Many high-income countries are experiencing declining birth rates and stand on the brink of losing a large chunk of experts as they transition into retirement. This is also harming manufacturing companies. In the US alone, 1.9 million manufacturing jobs could remain unfilled in the next 10 years. Automation and digitalization can help to mitigate these challenges.
INFOGRAPHICS

To address sustainability and regulatory pressures.
Many regulatory bodies have reacted to climate change challenges by introducing related regulations. The European Union, for example, now requires a broad set of large companies, as well as listed SMEs, to start reporting on carbon footprint and related topics. The new rules are first coming into effect in the 2024 financial year, for reports published in 2025. Accurate tracking and reporting will not be difficult without the technological foundation.
INFOGRAPHICS

To achieve greater flexibility and customization.
The automotive industry's current shift towards EVs is a good example of why manufacturing flexibility matters. Traditional production lines built for internal combustion engine vehicles often lack the flexibility to accommodate the variety of components and configurations required for EVs. Additionally, with EV demand highly fluctuating, automotive manufacturers that can flexibly adjust their manufacturing setup to the current demand have massive advantages. That is why implementing more adaptive and scalable manufacturing solutions to handle changes in customer preferences, product design, and materials will be key in the future.
Questions answered:
- What is the current state of smart factories?
- Which technologies are most important for manufacturers who roll out a smart factory strategy?
- Which manufacturers are considered "leading" when it comes to adoption of digital technologies?
- How are the paradigms of manufacturers changing?
- Which AI use cases are manufacturers rolling out?
- Where are training and inference of AI models happening?
- What are key considerations when choosing a DataOps solution?
- Which type of software are manufacturers using to manage devices?
- What are the leading containerization tools used for containerization at the edge?
Companies mentioned:
A selection of companies mentioned in the report.
|
|
|
Table of Tables
1. Executive Summary
- 1. Executive summary
- 2. This report highlights smart factory adoption through 6 lenses and 4 deep dives
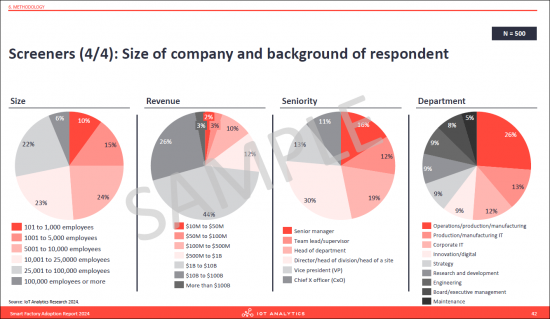
- 3. 500 people participated in this research that represent a variety of different manufacturers
- 4. The Smart Factory Adoption Report 2024 is part of IoT Analytics' ongoing coverage of Industry 4.0 and IIoT
2. Introduction
- 1. Recap: In 2022, manufacturers had or were in the process to develop a smart factory strategy
- 2. Why do manufacturers look to make factories smarter?
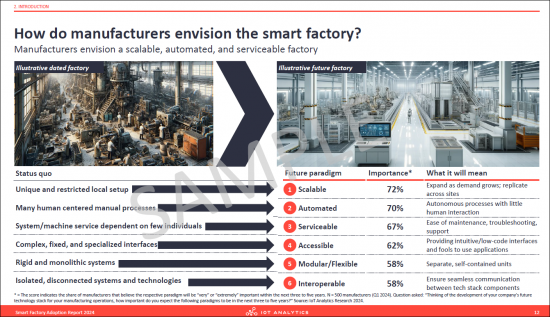
- 3. How do manufacturers envision the smart factory?
- 4. Technology plays a key role for smart factories
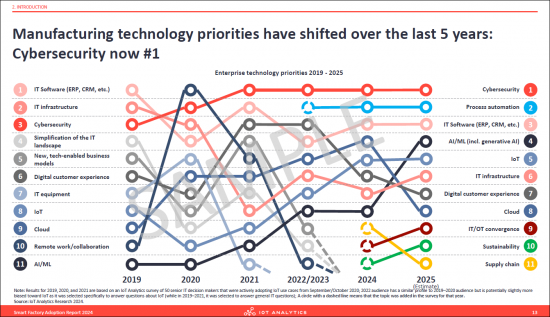
- 5. Manufacturing technology priorities have shifted over the last 5 years
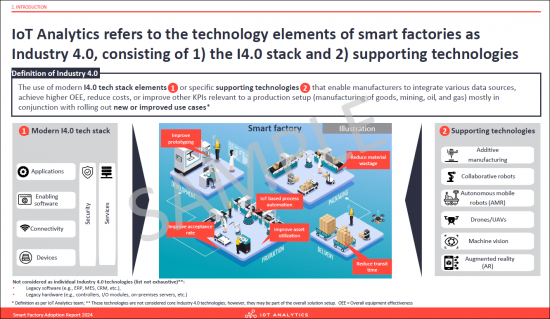
- 6. IoT Analytics refers to the technology elements of smart factories as Industry 4.0
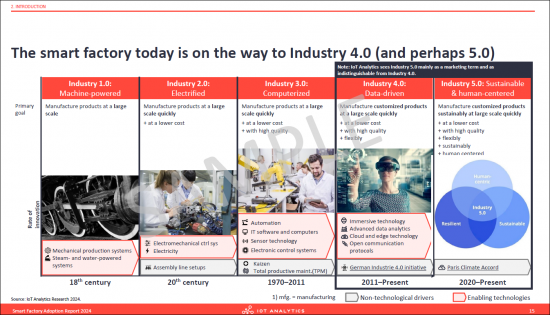
- 7. The smart factory today is on the way to Industry 4.0 (and perhaps 5.0)
- 8. The Industry 4.0 tech stack is forecasted to reach by 2030
- 9. The four deep-dives in chapter 4 have been trending in public search interest in the last 3-4 years
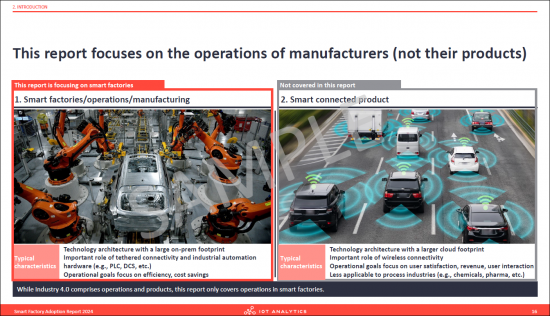
- 10. This report focuses on the operations of manufacturers (not their products)
3. State of smart factories in 2024
- 1. Chapter 3: State of smart factories 2024 - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. State of smart factories 2024: Focus on scalability and security
- 3. How do manufacturers envision the smart factory?
- 4. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (1/3)
- 5. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (2/3) - By region/industry/company size
- 6. Importance of smart factory paradigms in the next 3-5 years (3/3) - By function
- 7. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (1/3) - Overview
- 8. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (2/3) - By type
- 9. Importance of technologies in the next 3-5 years (3/3) - By department
- 10. Severity of challenges (1/3) - Overview
- 11. Severity of challenges (2/3) - By region/industry/company size
- 12. Severity of challenges (3/3) - By department
- 13. Example: Why cybersecurity is so important - 3 recent notable breaches
4. Leading smart factory adopters 2024
- 1. Chapter 4: Leading smart factory adopters 2024 - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Leading smart factory adopters - Top 25
- 3. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (1/3)
- 4. Example: Tesla Giga Berlin is often regarded as the most advanced Tesla factory
- 5. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (2/3)
- 6. Why these manufacturers are seen as leading adopters (3/3)
- 7. Extensive list of all companies mentioned by respondents
5. a) Selected deep-dives: Overview
- 1. Chapter 5: Selected deep-dives - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Smart factory technology deep-dives: Overview
- 3. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (1/3): Overview
- 4. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (2/3): By vertical
- 5. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (3/3): By region
- 6. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (in $M) (1/2): Budget by topic
- 7. Budgets for smart factory topics in 2024 (in $M) (2/2): Budget
- 8. Expected budget change between 2024 and 2026 (1/2): Overview
- 9. Expected budget change between 2024 and 2026 (2/2): By company type
- 10. Severity of challenges by type of technology
- 11. Return on investment by type of technology (1/3): Overview
- 12. Return on investment by type of technology (2/3): By company type
- 13. Return on investment by type of technology (3/3): By department
5. b) Selected deep-dives: Industrial AI & edge AI
- 1. Chapter 5b: Deep-dive on Industrial & Edge AI - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Importance of AI use cases (1/3): Overview
- 3. Importance of AI use cases (2/3): By company type
- 4. Importance of AI use cases (3/3): By function
- 5. Training and inferencing of AI use cases 2 years from now (1/2): Overview
- 6. Training and Inferencing of AI use cases 2 years from now (2/2): Deep-dive
- 7. Example: Machine vision training and inference of AI models is happening across the edge-cloud continuum
5. c) Selected deep-dives: Industrial DataOps
- 1. Chapter 5c: Deep-dive on industrial DataOps - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (1/3): Overview
- 3. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (2/3): By company type
- 4. Importance of industrial DataOps themes (3/3): By function
- 5. Finding: Combined IT/OT data platform is crucial - Example: Vendors react
- 6. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (1/3): Overview
- 7. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (2/3): Vendors
- 8. How manufacturers implement industrial DataOps (3/3): In-house
- 9. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (1/3)
- 10. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (2/3): By company type
- 11. Challenges when adopting industrial DataOps (3/3): By department
5. d) Selected deep-dives: Device management
- 1. Chapter 5d: Deep-dive on device management - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (1/3): Overview
- 3. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (2/3): Third party
- 4. How manufacturers procure device management solutions (3/3): Device manufacturer
- 5. Importance of aspects in device management (1/3): Overview
- 6. Importance of aspects in device management (2/3): By company type
- 7. Importance of aspects in device management (3/3): By function
- 8. How manufacturers manage and update of devices on the shopfloor
- 9. Management of devices on the shopfloor: By company type
- 10. Update of devices on the shopfloor: By company type
- 11. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (1/3)
- 12. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (2/3): By company type
- 13. Most challenging aspects when adopting device management (3/3): By function
5. e) Selected deep-dives: Containerization of OT
- 1. Chapter 5e: Deep-dive on containerization of OT - Overview & key takeaways
- 2. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (1/3): Overview
- 3. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (2/3)
- 4. Containerization of manufacturing software (next 3 years) (3/3)
- 5. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (1/3): Overview
- 6. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (2/3): By company type
- 7. Mitigation of challenges by using containerization (3/3): By department
- 8. Usage of container management solutions (1/2): Overview
- 9. Usage of container management solutions (2/2): By company type
- 10. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (1/3): Overview
- 11. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (2/3): By company
- 12. Reasons to use container management tools at the edge (3/3): By function
- 13. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (1/3): Overview
- 14. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (2/3): By company type
- 15. Usage of containerized workloads today and in the future (3/3): By function
- 16. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (1/3): Overview
- 17. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (2/3): By company type
- 18. Most challenging aspects when adopting containerization (3/3): By function











