 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1435880
日本低温运输物流:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2024-2029)Japan Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
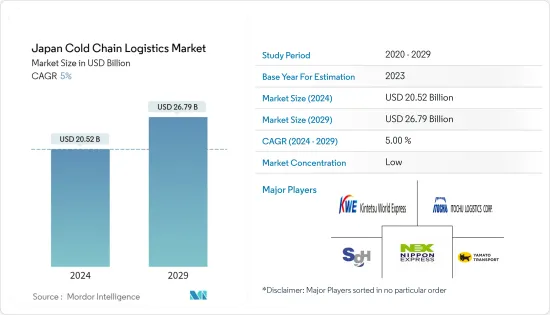
日本低温运输物流市场规模预估2024年为205.2亿美元,预估至2029年将达267.9亿美元,在预测期间(2024-2029年)成长5%,复合年增长率为%。
由于COVID-19的影响,日本贸易省报告称,2020年3月药妆店销售额与前一年同期比较增长了7.5%。与此一致,日本超级市场协会宣布,为了因应自我隔离和自行做饭的需求,2020年3月超级市场食品的需求和销售量与前一年同期比较增加了7.4%。这些因素都对日本低温运输物流市场产生了负面影响。 COVID-19 影响了日本的低温运输业务,包括日益增加的食品安全问题。
日本被认为是成熟的低温运输物流市场,由多家参与者主导。由于生物製药和再生医学的快速发展,日本对冷药品连锁店的需求最近有所增加。随着 COVID-19感染疾病和其他治疗方法的推出,这一趋势预计将持续下去。日本的低温运输物流最初是针对生鲜食品、冷藏食品、冷冻食品产业而建立的。低温运输物流的重点是在持续控制的温度和湿度环境下及时交付产品。
日本的冷库设施大部分由大型低温运输公司拥有和经营,只有少量设施可供租赁。随着冷冻冷藏产品电商使用的增加,有潜在需求的地区冷库建设将加快。
冷库数量的增加和製药业的成长等因素预计将推动日本低温运输物流市场的成长。市场面临的挑战包括冷库容量分配不规范、缺乏足够的物流连接支援以及需要大量的资本投资。
日本低温运输物流市场趋势
现代家庭引发对冷冻食品的需求
随着老年人的独立、双收入家庭和单身人数的增加、食品浪费危机以及食品人手不足现代家庭的解决方案,冷藏和冷冻食品的需求不断增加食品整个食品工业。饮料业。
日本生产的热门冷冻食品包括饺子(gyoza)、炸丸子和麵条(乌龙麵)。近年来,日本食品尤其是农产品在世界各地爆普及。
在人口老化的日本,向健康的预期寿命过渡是支持冷冻食品销售的人们的通用。超级市场、超级市场、药局也大幅成长。由于冷冻技术的进步以及新冠病毒 (COVID-19 ) 的感染疾病导致对家常饭菜的需求增加,日本的冷冻食品已经多样化。
来自名店的昂贵美食和来自海外的正宗复製品已经蔓延到市场,百货公司和超市也加快了扩大销售范围的步伐。
日本製药业的成长
日本是世界上最大的医药市场之一,这主要是由于其人口老化。在政府积极推广学名药的支持下,该公司也是先进医疗设施的领先製造商和进口商之一。
该国的本土生技药品产业仅次于美国。再加上政府对支持低成本仿冒品的重视,这为生物相似药提供了巨大的机会。创新製药公司长期以来一直受益于日本慷慨的独占期,但该国在学名药普及方面正在追赶其他成熟市场。
对这一体系的信心体现在国内製药公司越来越多地将其产品分销到全球的事实中。日本企业的海外销售份额稳定上升,对低温运输储运设施的需求也增加。引起人们对日本製药业兴趣的另一个重要因素是需要加强日本的药物发现生态系统。
该国 COVID-19感染疾病人数的增加增加了对处方药和疫苗的需求。它影响了药品的需求。由于 COVID-19感染疾病进口增加,药品需求增加。例如,2021年5月,日本政府与辉瑞-BioNTech签署协议,在年终进口1.94亿剂(133万美元)疫苗。根据 IQVIA 的数据,2021 年日本处方药市值约为 10.6 兆日圆(800 亿美元),高于 2020 年的约 10.4 兆日圆(790 亿美元)。
日本低温运输物流产业概况
市场相对分散,国内外参与者众多,包括日本通运、雅玛多运输、佐川急便、伊藤忠物流株式会社和近铁世界通运。市场竞争与成本、仓储费、空间以及包装和包装材料价格的上涨有关。服务供应商继续致力于开发提供流程标准化的功能。缺乏与储存温度和操作程序相关的标准化是该行业面临的进一步重大挑战。可用冷库空间的品质和弹性是一个主要问题。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月分析师支持
目录
第一章简介
- 研究成果
- 调查先决条件
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章市场动态与洞察
- 目前的市场状况
- 市场动态
- 促进因素
- 医疗保健产业的重要性
- 消费者对生鲜食品的需求增加
- 抑制因素
- 如果包装不充分或产品损坏
- 温控混乱
- 机会
- 创新
- 促进因素
- 技术趋势和自动化
- 政府法规和倡议
- 产业价值链/供应链分析
- 专注环境温度/温控存储
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代产品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间的敌意强度
- 排放标准法规对低温运输产业的影响
- 新型冠状病毒感染疾病(COVID-19)对市场的影响
第五章市场区隔
- 按服务
- 贮存
- 交通设施
- 附加价值服务(冷冻、标籤、库存管理等)
- 按温度类型
- 冷藏
- 冷冻的
- 按用途
- 园艺(新鲜水果和蔬菜)
- 乳製品(牛奶、冰淇淋、奶油等)
- 肉、鱼、家禽
- 加工过的食品
- 製药、生命科学、化学
- 其他用途
第六章 竞争形势
- 市场集中度概况
- 公司简介
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Sagawa
- Kintetsu World Express
- Itochu Logistics Corp.
- DHL
- Kuehne Nagel
- K line Logistics
- Nichirei Logistics Group, Inc.
- Sojitz Corporation
- CEVA Logistics
- Kokubu Goup
- Agility
- SF Express*
第七章 日本低温运输物流市场的未来
第8章附录
The Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 20.52 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 26.79 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

With COVID-19 in effect, the Japanese Trade Ministry reported a 7.5% Y-o-Y increase in the sale of drugstores in March 2020. Along with this, the Japan Supermarkets Association, in response to the self-imposed quarantines and the need to cook at home, reflected a 7.4% Y-o-Y increase in the demand and sales of groceries at the supermarkets in March 2020. All these factors led to a negative impact on the cold chain logistics market in Japan. COVID-19 impacted Japan's cold chain operations, including increased food safety concerns.
Japan is regarded as a mature market for cold chain logistics and is dominated by several players. Rapid advancements in biopharmaceuticals and regenerative medicine recently increased the demand for the cold pharmaceutical chain in Japan. This trend is expected to continue with the COVID-19 vaccines introduction and other treatments. Cold chain logistics in Japan was initially established for the fresh, refrigerated, and frozen food industries. Cold chain logistics focuses on the timely distribution of products within a constantly controlled temperature and humidity environment.
Most cold storage facilities in Japan are owned and operated by major cold chain corporations, with only a small number available for lease. Advances in using e-commerce to sell frozen and chilled goods will accelerate cold storage development in areas with latent needs.
Factors such as an increase in the number of refrigerated warehouses and growth in the pharmaceutical sector are expected to drive the growth of Japan's cold chain logistics market. Some of the challenges in the market are the irregular distribution of cold storage capacity, lack of proper logistical connectivity support, and the need for high capital investment.
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends
Modern Households Leading to Demand for Frozen Foods
The demand for chilled/frozen foods is increasing as a solution for modern-age families, such as independent elderly citizens, increase in dual-income households and single people, along with the danger of food loss and increasing overall labor shortages in the food and beverage industry.
In 2021, the consumption volume of frozen food in Japan amounted to about 2.9 million tons (USD 0.020 million tons). Popular frozen food products manufactured in Japan include dumplings (gyoza), croquettes, and wheat-flour noodles (udon). In recent years, Japanese food also exploded worldwide, especially agricultural products.
As the Japanese population ages, the shift to healthy life expectancy is a common desire of the people aiding the sale of frozen products. It also significantly increased in supermarkets, hypermarkets, and drugstores. Frozen food items in Japan became more diverse due to advances in refrigeration technology and growing demand for eat-at-home products amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
High-priced delicacies from well-known restaurants and authentic reproductions of food from abroad grew across the market, prompting department stores and supermarkets to speed up efforts to expand sales spaces.
Growth of Pharmaceutical Sector in Japan
Japan is one of the largest pharmaceutical markets in the world, primarily due to its aging population. It is also among the major producers and importers of advanced medical facilities backed by active government initiatives to promote generic drugs.
The country's native biologics sector is second after the USA. Coupled with the government's focus on supporting lower-cost copycat products, this entails a massive opportunity for bio-similars. While innovative drugmakers long benefited from generous exclusivity periods in Japan, the country is catching up with other mature markets regarding generics penetration.
The confidence in the system is reflected by the fact that domestic drugmakers are increasingly going global with their products. With the share of top Japanese companies' overseas sales rising steadily, the demand for cold chain storage and transportation facilities is also increasing. Another critical factor for increased interest in Japan's pharmaceuticals sector is the need to enhance Japan's drug discovery ecosystem.
The increased COVID-19 infection cases in the country increased the demand for prescription drugs and vaccines. It impacted the pharmaceutical product demand. The increasing import of COVID-19 vaccines increased the pharmaceutical product demand. For instance, in May 2021, the Japanese government signed a contract with Pfizer-BioNTech to import 194 million (USD 1.33 million)vaccine doses by the end of 2021. In 2021, the Japanese prescription drug market was valued at approximately JPY 10.6 trillion (USD 0.080 Trillion), up from about JPY 10.4 trillion (USD 0.079 Trillion) in 2020, according to IQVIA.
Japan Cold Chain Logistics Industry Overview
The market is relatively fragmented, with many local and international players, including Nippon Express, Yamato, Sagawa Express Co., Ltd, Itochu Logistics Corp., and Kintetsu World Express. The competition in the market pertains to costs, storage fees, and space, along with the rising prices of packing and packaging materials. The service providers are still working on developing the ability to provide standardization in the processes. Lack of standardization related to storage temperature and operating procedures are a few more significant challenges the industry faces. The quality and flexibility of available cold warehousing space are a considerable concern.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Criticality of the healthcare sector
- 4.2.1.2 Increased consumer demand for fresh foods
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Inadequate packaging or damaged products
- 4.2.2.2 Disrupted temperature control
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Technological Innovations
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Technological Trends and Automation
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.5 Industry Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Spotlight on Ambient/Temperature-controlled Storage
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Emission Standards and Regulations on Cold Chain Industry
- 4.9 Impact of COVID - 19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Services
- 5.1.1 Storage
- 5.1.2 Transportation
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Blast Freezing, Labeling, Inventory Management, etc.)
- 5.2 By Temperature Type
- 5.2.1 Chilled
- 5.2.2 Frozen
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Horticulture (Fresh Fruits & Vegetables)
- 5.3.2 Dairy Products (Milk, Ice-cream, Butter, etc.)
- 5.3.3 Meats, Fish, Poultry
- 5.3.4 Processed Food Products
- 5.3.5 Pharma, Life Sciences, and Chemicals
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Nippon Express
- 6.2.2 Yamato Holdings
- 6.2.3 Sagawa
- 6.2.4 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.2.5 Itochu Logistics Corp.
- 6.2.6 DHL
- 6.2.7 Kuehne Nagel
- 6.2.8 K line Logistics
- 6.2.9 Nichirei Logistics Group, Inc.
- 6.2.10 Sojitz Corporation
- 6.2.11 CEVA Logistics
- 6.2.12 Kokubu Goup
- 6.2.13 Agility
- 6.2.14 SF Express*













