 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1441484
日本通讯:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2024-2029)Japan Telecom - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
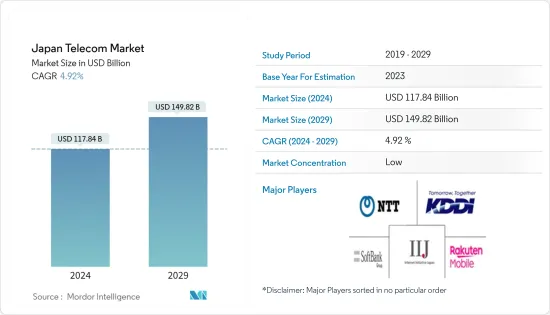
日本通讯市场规模预计 2024 年为 1,178.4 亿美元,预计到 2029 年将达到 1,498.2 亿美元,在预测期内(2024-2029 年)复合年增长率为 4.92% 增长。
日本拥有高度发达的基础设施,使人们能够保持联繫。除了网路普及高之外,日本还拥有庞大的行动网路用户群,反映出智慧型手机的日益普及。智慧型手机普及很高,预计未来几年将有更多人使用智慧型手机。
主要亮点
- 日本于2019年10月修订了《电讯商业法》,旨在促进行动领域的竞争并保护用户。此后,关于降价行动电话资费以减轻用户负担的讨论不断。内务部宣布了一项行动计划,旨在透过创建公平和竞争的行动市场来降低行动电话费用。到 2021 年 3 月,所有 MNO 公司都推出了新的低价品牌和收费系统,其中一些包括 20 GB资料。
- 儘管 6G通讯可能需要十年才能充分发挥其潜力,但日本已在建立自己的国内网路和技术基础设施。日本政府计划投资数十亿美元加速超高速通讯的发展。日本设备製造商 NEC 和富士通以及芬兰设备製造商诺基亚已宣布计划试验新的行动通讯技术,目标是到 2030 年商业推出 6G 服务。
- 儘管互联网不断发展系统和通讯协定,但行动网路的发展长期以来一直受到封闭文化和专有技术的限制。要成为各部门的重要基础设施,行动网路必须能够动态提供变化和动态设定。透过整合RESTful(表述性状态传输)应用程式介面(API),Softbank Corporation可以调整和修改其网络,以满足消费者的需求并提供更便捷的服务。
- COVID-19的感染疾病对日本经济产生了重大影响。采用数位技术对于提高疫情期间和之后的国家復原力至关重要。技术应用程式可以帮助企业及其员工与客户沟通、数位化营运、重新启动业务营运以及部署缓解物流瓶颈的技术,从而帮助企业及其员工从 COVID-19的感染疾病中恢復过来,帮助管理影响力。据信,日本 69% 的数位机会(价值 46.8 兆日圆(4,340 亿美元))来自帮助企业和员工应对疫情经济影响的技术。
日本通讯市场的动向
5G部署
- 根据GSMA报告,日本允许通讯业者在交通号誌上方安装5G基地台,加速全国5G部署。随着较小蜂窝的部署和网路密度的增加,21 个更高容量的用例可以蓬勃发展。日本的连接普及预计将从2021年的153%上升到2022年的154%。智慧型手机普及预计将从 2021 年的 71% 增加到 2025 年的 81%。日本的用户普及预计也将从 87 升至 87。 2021 年 % 至 2025 年 88%。
- 考虑到iPhone 12和13的降价和商店供应,该国5G部署的前景看起来更加乐观。最近,日本政府向该国三大行动电话提供商授予了 5G 频谱:NTT Docomo、KDDI au、Softbank Corporation以及最近加入的乐天移动。未来几年,这四家日本通讯业者预计将在基地台、伺服器和光纤等资本计划上投资超过140亿美元。惠誉研究显示,预计2026年5G将取代4G成为日本主要行动电话技术,到2029年将有约4,500万4G用户及超过1.51亿5G用户。
- 根据当地报道,日本通讯业者NTT Docomo 计划与其竞争对手一样,加快在全国部署 5G。报导称,NTT Docomo 计划在 2024 年 3 月为日本 90% 的人口提供服务,超过原定 80% 的目标。 2022年9月,NTT Docomo声称持有世界上第一个商用5G独立(SA)网路。这使得智慧型手机能够同时使用中频(6 GHz 以下)和毫米波频率,即 5G NR 双重连线。该公告是与无线技术公司高通联合发布的,该公司希望强调搭载该公司 Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 平台的智慧型手机可以充分利用新网路的全速。
- 日本客户可以利用各种毫米波设备,包括三星、索尼、夏普、富士通和谷歌的高阶智慧型手机,以及营运商对该技术的巨大推动力。其他OEM(包括较低层级设备製造商)预计也将在未来几个月内在日本推出毫米波智慧型手机。
- 2022年5月,Softbank Corporation公司开始在日本各地部署MEC伺服器,并宣布在关东地区启动5G MEC(多接取边缘运算)网站。 「软银5G MEC」采用5G SA(5G Stand Alone)商用服务,提供低延迟、高品质(低抖动)、高安全的服务体验。透过推动各种业务的数位转型(DX)并实现数位双胞胎*2,Softbank Corporation有望响应社会问题,并将行业发展为Beyond 5G的未来数位平台提供者。我是。
数位转型倡议
- 数位转型是 COVID-19 危机最明显加速的趋势 (DX) 之一。这种突然的变化可以改善企业和组织的运作方式,并对人们的生活产生广泛的正面影响。电讯(ITU)的一项研究显示,2020年,全球大都会圈有76%的人拥有网路接入,而农村地区这一比例为39%。日本设定了创造「新形式资本主义」的崇高目标,强调人与永续性,并将DX定位为实现成长和分配良性循环的重要组成部分。
- 当地私人企业可能会发现很难快速实现盈利,但与地方政府和部会的合作可以将创新想法付诸实行。此外,数位化在日本甚至农村地区并不新鲜。自 2016 年启动以来,内务部的区域物联网促进研究所计划已对日本 105 个地区的研究机构进行了奖励,奖励了最佳的新型物联网解决方案和公司,并鼓励当地计划和企业蓬勃发展和腾飞.我们已派出导师来支持您。
- 日本大型公司举办开放式创新会议和商业竞赛,透过利用其他组织的技术、概念、资产和资源来促进创新。儘管开放式创新在日本尚未像其他国家普及,但开放式创新在日本主要企业中正变得越来越普遍并不断成长。近年来,各领域举办了许多开放创新措施和商业竞赛。例如,NTTData在通讯领域开放创新。
- 2020 年 8 月,伊那市为每月支付费用的居民推出了全国首个使用无人机的购物服务「支援购物服务」。该服务透过有线电视提供,是与电信业者KDDI Corporation 合作开发的。客户可以使用电视遥控器订购并支付有线电视费用。由于该地区多山,标准电视讯号难以到达该地区,因此该市为户户提供有线电视,有线电视普及几乎达到100%。
- 当地私人企业可能会发现很难快速实现盈利,但与地方政府和部会的合作可以将创新想法付诸实行。此外,数位化在日本并不新鲜,即使在农村地区也是如此。根据经济产业省(METI)的报告,内务部推进研究所计划自 2016 年启动以来,已向日本 105 个地区的研究机构奖励最佳奖。全新物联网解决方案和杰出解决方案。已奖励。我们为企业提供导师,帮助当地计划和企业蓬勃发展。
日本通讯业概况
日本通讯市场本质上高度分散。该市场的主要企业包括日本电报电话公司、KDDI 公司、Softbank Group、乐天行动公司和 Internet Initiative Inc.。该市场还拥有其他网路服务供应商(ISP)、MVNO 和固定电话业者。一些日本电信业者在国际上具有强大的竞争力,在全球通讯领域拥有强大的地位。
- 2022 年 1 月,NTT Communications Corporation (NTT Com) 宣布即时推出 SDPF Edge,这是一种基于智慧资料平台的整合营运 (SDPF) 边缘运算解决方案。在主要服务于製造业的新 SDPF Edge 服务的帮助下,公司可以处理大量生产资料以保持品管并更快、更便宜地进行选择。
- 2022 年 2 月,KDDI 与三星和富士通一起宣布,全球首个由虚拟无线接取网路(vRAN) 提供支援的 5G 独立开放 RAN 站点将在神奈川县川崎市上线。借助 Open RAN 和 vRAN,这是 5G SA 的首次商业部署。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月分析师支持
目录
第一章 简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章市场洞察
- 市场概况
- 产业生态系统分析
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代产品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间的敌意强度
- COVID-19 对产业生态系统的影响
- 国内监理情况
第五章市场动态
- 市场驱动因素
- 加速5G设备普及及市场拓展
- 继续远距工作
- 市场限制因素
- 对竞争的担忧
- 基于连接性的市场分析(覆盖范围包括详细的趋势分析)
- 固定网路
- 宽频趋势(缆线数据机、有线光纤、有线DSL、固定Wi-Fi)、ADSL/VDSL、FTTP/B、缆线数据机、FWA、5G FWA
- 窄带
- 行动网路
- 智慧型手机和行动装置的普及
- 行动宽频
- 2G、3G、4G、5G 连接
- 智慧家庭、物联网、M2M 连接
- 固定网路
- 通讯铁塔分析(包括格子塔、支线塔、单极塔、隐形塔等不同类型铁塔的详细趋势分析)
第六章市场区隔
- 按服务细分(跨服务细分市场的每个用户平均收益、2020-2027 年期间每个细分市场的市场规模和估计,以及包括详细趋势分析的范围)
- 语音服务
- 有线
- 无线的
- 资料和通讯服务(网路和行动电话资料套餐,范围包括套餐折扣)
- OTT 和付费电视服务
- 语音服务
第七章 竞争形势
- 公司简介
- Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- KDDI Corporation
- SoftBank Group Corp.
- Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- JSAT Corporation
- TOKAI Communications Corporation
- Wowow Inc.
- Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- Z Holdings Corporation
第八章投资分析
第九章市场机会与未来趋势
The Japan Telecom Market size is estimated at USD 117.84 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 149.82 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 4.92% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

Japan has a highly developed infrastructure that allows its people to be constantly connected. Along with having a high internet penetration rate, Japan has a sizable mobile internet user base, which reflects the rising popularity of smartphones. Though the smartphone adoption rate is strong, more individuals are anticipated to utilize smartphones in the years to come.
Key Highlights
- In Japan, the Telecommunications Business Law was changed in October 2019 to encourage competition in the mobile sector and safeguard users. Since then, there have been conversations about reducing mobile phone fees to lessen the load on users. The Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications unveiled an action plan to lower mobile phone costs by creating a fair and competitive mobile market. By March 2021, all MNO companies introduced new, less-priced brands and pricing schemes, some of which included 20 GB of data.
- It might take a decade for 6G telecommunications to reach its full potential, but Japan is already establishing its own domestic network and technology foundation. The Japanese government plans to invest billions of dollars in promoting the development of ultra-high-speed communication. Japanese equipment manufacturers NEC and Fujitsu, as well as Finnish equipment manufacturer Nokia, announced plans to conduct experimental trials of new mobile communications technologies for the targeted commercial launch of 6G services by 2030.
- Though system and protocol evolution continued due to the Internet, the development of mobile networks was constrained by closed cultures and proprietary technologies for a very long time. Mobile networks must be able to offer modification and dynamic set up on the spot to be essential infrastructure for many different sectors. By integrating RESTful (Representational State Transfer) application programming interfaces (APIs), SoftBank tailors and modifies its network to meet the needs of consumers and offer more convenient services.
- The COVID-19 outbreak significantly impacted the Japanese economy. The adoption of digital technology was essential for the nation to become more resilient during and after the pandemic. Technology applications can help businesses and their employees manage the financial effects of COVID-19 by assisting them in contacting clients and conducting business digitally, restarting business operations, and implementing technologies that reduce logistical bottlenecks. A sizable 69% of Japan's digital opportunity, valued at JPY 46.8 trillion (USD 434 billion), was thought to be sourced from technology that assists companies and employees in managing the effects of the pandemic on the economy.
Japan Telecom Market Trends
5G Rollouts
- According to a GSMA report, Japan allows operators to mount 5G base stations atop traffic signals, accelerating 5G deployments nationwide. 21 higher-capacity use cases can flourish when tiny cells are put into place, and network density is raised. The connection penetration in Japan is expected to rise from 153% in 2021 to 154% in 2022. The projected increase in smartphone adoption rate is from 71% in 2021 to 81% in 2025. Subscriber penetration in Japan is also expected to rise from 87% in 2021 to 88% in 2025.
- Given the price reductions and the availability of the iPhone 12 and 13 in stores, the prospects for 5G adoption in the nation seem more promising. Recently, the Japanese government granted the 5G spectrum to the country's top three mobile providers, NTT Docomo, KDDI au, Softbank, and a recent entrant, Rakuten Mobile. Over the following years, these four Japanese carriers are anticipated to invest more than USD 14 billion in capital projects, including base stations, servers, and fiber optics. According to Fitch Research, by 2026, 5G will overtake 4G as the primary cellular technology in Japan, and by 2029 there will be around 45 million 4G subscribers and more than 151 million 5G subscribers.
- According to the local press, Japanese carrier, NTT Docomo, plans to quicken the speed of its 5G rollout nationwide while competitors do the same. The same article claims that NTT Docomo plans to provide coverage to 90% of the Japanese population, up from its earlier target of 80%, by March 2024. In September 2022 NTT Docomo claimed to have the world's first commercial 5G Standalone (SA) network that enables smartphones to simultaneously use mid-band (sub-6 GHz) and mmWave frequencies, known as 5G NR Dual Connectivity. The announcement was made with wireless technology company Qualcomm, which was keen to showcase that smartphones powered by its Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 platform can exploit the full speed of the new network.
- Japanese customers have access to a wide range of mmWave devices, including high-end smartphones from Samsung, Sony, Sharp, Fujitsu, and Google, and significant carrier momentum for the technology. Other OEMs, including those from lower tiers, are expected to introduce mmWave smartphones in Japan in the coming months.
- In May 2022, SoftBank Corp. declared beginning the statewide deployment of MEC servers in Japan and launching a 5G MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) site in the Kanto area. Using 5G SA (5G Stand Alone) commercial services, SoftBank 5G MEC offers low-latency, high-quality (low-jitter), and highly secure service experience. By encouraging the digital transformation (DX) of various businesses and achieving Digital Twin*2, SoftBank is expected to address societal concerns and advance the industry as a digital platform provider in the Beyond 5G future.
Digital Transformation Initiatives
- Digital transformation is one of the trends that the COVID-19 crisis has most visibly hastened (DX). This abrupt change can improve business and organization operations and have a wide range of positive effects on people's lives. In metropolitan regions throughout the world, 76% of people had internet access in 2020, compared to 39% in rural areas, according to research by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). With the lofty objective of creating a "New Form of Capitalism" that would be both people- and sustainability-focused, Japan has positioned DX as a key component of its initiatives for a virtuous cycle of growth and distribution.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may be able to make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural regions. Since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 areas around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
- Large Japanese firms host Open Innovation conferences and business competitions to foster innovation by employing other organizations' technology, concepts, assets, and resources. Open innovation is still not as prevalent in Japan as it is in other countries, but it is becoming more common among major Japanese corporations, and it is growing. Over the past several years, numerous open innovation initiatives and business competitions have been held in various sectors. For example, NTTData Open Innovation for the telecom sector.
- Ina City introduced a "Mutual Support Shopping Service" in August 2020, which is Japan's first drone-delivered shopping service for residents who pay a monthly subscription fee. The service is delivered via cable TV and was developed in collaboration with the telecom company KDDI Corp. Customers can use the TV remote control to place orders and pay their cable bill. As a result of the city providing cable TV to households due to poor signal reception for standard television broadcasts due to the area's mountainous terrain, cable TV has almost 100% penetration.
- Private businesses in rural locations may find it difficult to reach profitability quickly, but collaboration with regional authorities and ministries may make novel ideas workable. Additionally, digitalization is nothing new in Japan, not even in rural areas. As per the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) report, since its inception in 2016, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication's Local IoT Acceleration Laboratories project has recognized labs in 105 regions around Japan, awarded the finest new IoT solutions and enterprises, and sent mentors to help regional projects and ventures flourish and take off.
Japan Telecom Industry Overview
The Japanese telecom market is highly fragmented in nature. Some major players in the market include Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation, KDDI Corporation., SoftBank Group Corp., Rakuten Mobile, Inc, and Internet Initiative Japan, Inc. The market also hosts other Internet service providers (ISPs), MVNOs, and fixed-line service providers. Some Japanese telecommunication companies are very competitive internationally and hold strong ground in the global telecom space.
- In January 2022, on its Smart Data Platform, NTT Communications Corporation (NTT Com) announced the immediate launch of "SDPF Edge," an edge-computing solution with integrated operations (SDPF). With the help of the new SDPF Edge service, which primarily serves the manufacturing sector, companies may process massive volumes of production data to maintain quality control and make choices more quickly and inexpensively.
- In February 2022, KDDI, along with Samsung and Fujitsu, announced the world's first 5G Standalone Open RAN site, powered by a virtualized Radio Access Network (vRAN), will go online in Kawasaki, Kanagawa. With Open RAN and vRAN, this happened to be the first commercial deployment of 5G SA.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness-Porter's Five Force Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.4 Impact of COVID-19 on the Industry Ecosystem
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape in the Country
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 5G Device Penetration and Accelerated Expansion of Market
- 5.1.2 Continuation of Remote Work
- 5.2 Market Restrains
- 5.2.1 Concerns on Competition
- 5.3 Analysis of the Market based on Connectivity (Coverage to include In-depth Trend Analysis)
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.3.1.1 Broadband (Cable modem, wireline-fiber, wireline DSL, fixed Wi-Fi ), Trends regarding ADSL/VDSL, FTTP/B, cable modem, FWA, and 5G FWA )
- 5.3.1.2 Narrowband
- 5.3.2 Mobile Network
- 5.3.2.1 Smartphone and Mobile Penetration
- 5.3.2.2 Mobile Broadband
- 5.3.2.3 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G connections
- 5.3.2.4 Smart Home, IoT, and M2M connections
- 5.3.1 Fixed Network
- 5.4 Analysis of Telecom Towers (Coverage to include in-depth trend analysis of various types of towers, like, lattice, guyed, monopole, and stealth towers)
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 Segmentation by Services (Coverage to include Average Revenue Per User for the overall Services segment, Market size and Estimates for each segment for the period of 2020-2027 and in-depth Trend Analysis)
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
- 6.1.1.1 Wired
- 6.1.1.2 Wireless
- 6.1.2 Data and Messaging Services (Coverage to include Internet & Handset Data packages, Package Discounts)
- 6.1.3 OTT and Pay-tv Services
- 6.1.1 Voice Services
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation
- 7.1.2 KDDI Corporation
- 7.1.3 SoftBank Group Corp.
- 7.1.4 Rakuten Mobile, Inc.
- 7.1.5 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.6 JSAT Corporation
- 7.1.7 TOKAI Communications Corporation
- 7.1.8 Wowow Inc.
- 7.1.9 Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
- 7.1.10 Z Holdings Corporation













