|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1635525
亚太地区太阳能逆变器市场:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030)Asia Pacific Solar PV Inverters - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
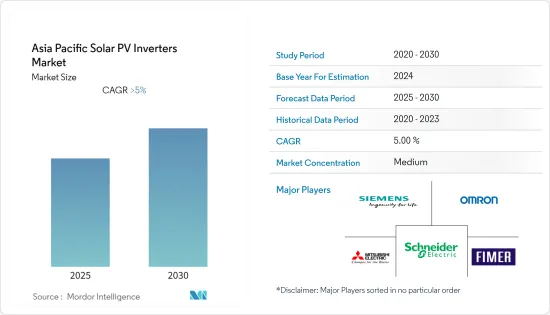
预计亚太地区太阳能逆变器市场在预测期内的复合年增长率将超过 5%。
2020 年市场受到 COVID-19 大流行的负面影响。目前市场处于大流行前的水平。
主要亮点
- 从中期来看,增加投资和雄心勃勃的太阳能目标预计将推动市场成长。
- 另一方面,组串式逆变器的技术缺陷预计将阻碍太阳能逆变器在预测期内的成长。
- 太阳能逆变器的产品创新和最新技术的采用预计将在预测期内为亚太地区太阳能逆变器市场提供利润丰厚的成长机会。
- 中国在市场上占据主导地位,并可能在预测期内保持最高的复合年增长率。这一增长是由投资增加和政府支持措施推动的。
亚太太阳能逆变器市场趋势
中央逆变器市场预计将出现高成长
- 中央逆变器是一个大型电网馈线。常用于额定输出100kWp以上的太阳能发电系统。通常,落地式或地面安装式逆变器将从太阳能电池阵列收集的直流电转换为交流电以用于并联型。这些设备的容量约为50kW至1MW,可在室内或室外使用。
- 通常,中央逆变器由一个直流-交流转换级组成。一些逆变器具有 DC-DC 升压级,以扩展 MPP(最大功率点)电压范围。低频变压器有时用于升高交流电压并隔离输出。然而,这会降低效率并增加逆变器的尺寸、重量和成本。
- 2021年,中国新增太阳能光电装置容量占全球的31%,占比最大。相比之下,印度太阳能发电装置容量约占全球的7%。
- 2022年3月,中国逆变器製造商阳光电源开始扩大在印度的产能。该公司已将其印度工厂开发并扩大至每年 10 吉瓦的产能,为印度和全球客户提供更短的前置作业时间和更好的服务体验。在竣工仪式上,我们发布了新的组串式逆变器和集中式逆变器产品,包括SG350HX和1+X模组化逆变器。
- 因此,电力需求的增加、政府对电力产业脱碳的努力以及中央逆变器成本的下降预计将在未来几年推动这一领域的发展。
中国主导市场
- 中国几乎拥有全球所有最大的光伏(PV)面板和设备製造商及设施,约占中国太阳能光电总产能的70%。这些公司也控制着太阳能供应链中的其他业务。例如,製造多晶硅、硅锭、面板晶圆以及逆变器和相关硬体等设备。
- 中国是全球太阳能发电的主要市场之一,也是太阳能逆变器最大的市场之一。根据IRENA统计,2021年,中国总设备容量为306.97GW。 2021年,中国太阳能装机约5,000万千瓦。
- 中国市场正在大幅成长。根据工业信部统计,2022年4月至5月,全国太阳能逆变器产量31GW。推动市场的关键因素之一是国内需求的快速成长。
- 根据中国光伏产业协会(CPIA)统计,2021年我国太阳能发电装置容量总合5488万千瓦,与前一年同期比较增长13.9%,预计2022年将成长75至9000万千瓦。此外,2021年中国製造产品出口额创历史新高,超过280亿美元,与前一年同期比较去年同期成长72%。这显示海外对中国製造的逆变器等太阳能硬体的需求强劲。
- 人事费用和采购成本降低等宏观经济因素推动了经济扩张,导致中国企业的太阳能硬体(包括逆变器)的全球成本趋势下降。因此,国内价格处于全球最低水平,降低了国际逆变器成本。
- 因此,基于上述因素,中国可望继续保持全球最大的太阳能及设备市场的地位。预计在预测期内,太阳能逆变器的需求将稳定成长。
亚太地区太阳能逆变器产业概况
亚太地区太阳能逆变器市场较为分散。市场主要企业包括(排名不分先后)FIMER SpA、施耐德电机、西门子、三菱电机和欧姆龙。
其他好处
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月分析师支持
目录
第一章简介
- 调查范围
- 市场定义
- 研究场所
第 2 章执行摘要
第三章调查方法
第四章市场概况
- 介绍
- 至2027年市场规模及需求预测(单位:十亿美元)
- 最新趋势和发展
- 政府法规和措施
- 市场动态
- 促进因素
- 抑制因素
- 供应链分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间敌对关係的强度
第五章市场区隔
- 按逆变器类型
- 中央逆变器
- 组串式逆变器
- 微型逆变器
- 按用途
- 住宅
- 商业和工业
- 实用规模
- 按地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 其他亚太地区
第六章 竞争状况
- 併购、合资、联盟、协议
- 主要企业策略
- 公司简介
- FIMER SpA
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- General Electric Company
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- Delta Energy Systems Inc.
- Enphase Energy Inc.
- Genus Innovation Limited
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
第七章 市场机会及未来趋势
简介目录
Product Code: 93042
The Asia Pacific Solar PV Inverters Market is expected to register a CAGR of greater than 5% during the forecast period.

The market was negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Presently, the market has reached pre-pandemic levels.
Key Highlights
- Over the medium term, increasing investments and ambitious solar energy targets are expected to drive the market's growth.
- On the other hand, technical drawbacks of the string inverters are expected to hamper the growth of solar PV inverters during the forecast period.
- Nevertheless, product innovation and adaptation of the latest technologies in solar PV inverters are likely to create lucrative growth opportunities for the Asia-Pacific solar PV inverters market in the forecast period.
- China dominates the market and is also likely to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing investments, coupled with supportive government policies.
APAC Solar PV Inverters Market Trends
Central Inverters Segment Expected to Witness High Growth
- A central inverter is a large grid feeder. It is often used in solar photovoltaic systems with rated outputs over 100 kWp. Typically, floor or ground-mounted inverters convert DC power collected from a solar array into AC power for grid connection. These devices range in capacity from around 50 kW to 1 MW and can be used indoors or outdoors.
- Generally, a central inverter consists of one DC-AC conversion stage. Some inverters also have a DC-DC boost stage to increase their MPP (Maximum Power Point) voltage range. Low-frequency transformers are sometimes used to boost the AC voltage and provide isolation at the output. However, this reduces efficiency and increases the inverter's size, weight, and cost.
- In 2021, China installed the largest share of the world's new solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity, at 31% of the total capacity. In comparison, India accounted for about 7% of the world's solar PV installed capacity.
- In March 2022, Chinese inverter manufacturer Sungrow inaugurated its expanded scale of manufacturing capacity in India. The company developed and scaled the India factory to 10 GW/annum capacity for its customers locally and globally with lesser lead time and better service experience. At the inauguration ceremony, Sungrow launched new products in the string and central inverter categories, including models SG350HX and 1+X modular inverter.
- Therefore, the growing electricity demand, the government's efforts to decarbonize the power sector, and the declining costs of central inverters are expected to drive the segment in the coming years.
China to Dominate the Market
- China is home to nearly all the largest solar photovoltaic (PV) panel and equipment manufacturing companies and facilities globally, with about 70% of China's global solar PV manufacturing capacity. These companies also dominate other businesses in the solar energy supply chain. For example, the manufacture of polysilicon, ingot, and wafers for panels and equipment, such as inverters and related hardware.
- China is one of the major solar PV markets globally, and it is one of the largest markets for solar inverters. According to IRENA, in 2021, China had a total installed solar capacity of 306.97 GW. In 2021, China installed nearly 50 GW of solar power.
- The Chinese market has been growing considerably. According to the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), from April to May 2022, the country produced 31 GW of solar PV inverters. One of the primary factors driving the market is the burgeoning domestic demand.
- According to the China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA), China installed a total of 54.88 GW solar capacity in 2021, up 13.9% year-on-year, and is expected to grow by 75-90 GW in 2022. Additionally, in 2021, Chinese-made products' export value hit a historic high at over USD 28 billion, witnessing a 72% year-on-year growth. It demonstrates the overseas demand for Chinese solar PV hardware, such as inverters.
- Due to several macroeconomic factors, such as lower labor and procurement costs enabling larger scales of economies, Chinese companies have driven down the global cost trends in solar PV hardware, including inverters. Due to this, domestic prices are among the lowest in the world, driving down international inverter costs.
- Hence, due to the above factors, China is expected to remain the world's largest solar energy and equipment market. The demand for solar inverters is expected to rise steadily during the forecast period.
APAC Solar PV Inverters Industry Overview
The Asia-Pacific solar PV inverters market is fragmented in nature. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) include FIMER SpA, Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and Omron Corporation.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD billion, till 2027
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Inverter Type
- 5.1.1 Central Inverters
- 5.1.2 String Inverters
- 5.1.3 Micro Inverters
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 5.2.3 Utility-scale
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 China
- 5.3.2 India
- 5.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 FIMER SpA
- 6.3.2 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.3.3 Siemens AG
- 6.3.4 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.3.5 Omron Corporation
- 6.3.6 General Electric Company
- 6.3.7 SMA Solar Technology AG
- 6.3.8 Delta Energy Systems Inc.
- 6.3.9 Enphase Energy Inc.
- 6.3.10 Genus Innovation Limited
- 6.3.11 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219