 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1644949
半导体物流:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Semiconductor Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
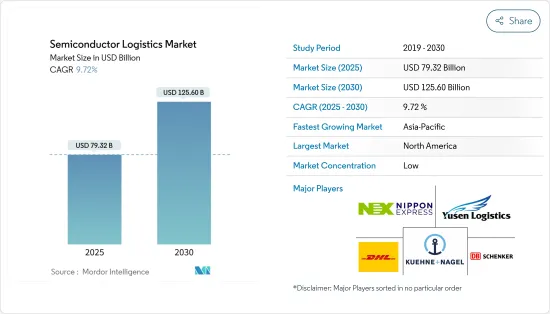
预计预测期内半导体物流市场将以超过 7% 的复合年增长率成长。
主要亮点
- 对智慧型设备的需求不断增长、对永续生产方法的需求、人才发展的重要性以及亚太地区不断增长的半导体市场占有率将塑造半导体物流行业。然而,新冠疫情造成的供应链和劳动力中断已导致全球晶片短缺,而持续的美国贸易紧张局势以及俄罗斯的衝突则加剧了这一短缺。科技进步的步伐可能会加快。 5G网路和物联网的建置已经为互联互通和自动化奠定了基础。
- 缺乏满足市场需求的製造能力是贯穿半导体供应链诸多方面的主要主题趋势。半导体是许多可再生能源应用、电动车、智慧型手机和其他个人电子产品、资料中心甚至防御性武器的重要组成部分。但在幕后,现今的半导体公司面临许多挑战。即使工厂满载运作,也无法满足需求,导致产品前置作业时间长达六个月或更长时间。持续的半导体短缺经常成为头条新闻,特别是因为它迫使汽车OEM製造商推迟汽车生产。此外,半导体公司还面临日益复杂的设计、人才短缺和疫情相关问题,所有这些都扰乱了连接不同市场参与者的复杂的全球供应链。
- 半导体产业必须以过去两年的物流挑战为警钟,意识到需要采取严厉措施。当新冠疫情爆发时,许多企业的销售额大幅下降。汽车业失去了80%的买家,导致半导体需求急剧下降。预计全球半导体短缺状况将持续至2024年。据估计,2020年至2022年间,此类短缺已造成全球经济超过5,000亿美元的损失。比直接的经济影响更严重的是,这些供不应求暴露了半导体供应链的不足。一些明显的缺陷已经暴露出来,解决这些问题需要的不仅仅是赶上订单。
- 半导体公司的未来取决于找到应对物流挑战的方法,这是一个需要采取严厉措施的讯号。随着对半导体的需求不断增长,能够更有效地将这些产品送到最终用户的公司将成为未来几年最大的受益者。半导体价值链极为复杂,依赖全球材料和设备供应商网路。这使得有效的供应链管理变得极其困难,导致库存过剩和常规瓶颈。货物管理就是一个很好的例子。从港口拥堵到货柜短缺,货物问题导致前置作业时间延长和航运延误延长。影响供应链的其他因素包括湿度、衝击和窃盗。但由于缺乏准确的资料和有关货运进度的 GPS 跟踪,领导者经常在黑暗中业务。
半导体物流市场趋势
半导体需求不断成长推动市场
自2020年以来,全球晶片短缺现象加剧,价格上涨成为半导体产业的必然趋势。上游材料、设备厂商面临供不应求,晶片厂商加大投资扩大产品线,下游半导体公司则获得巨额利润。整体来看,面板驱动IC、消费性MCU、记忆体晶片等供不应求开始缓解,预示价格开始下滑。然而,部分功率半导体晶片仍处于供不应求的状态,尤其是用于汽车、工业控制和物联网等领域的晶片。
其主要原因是受市场週期性波动影响,DRAM价格突然开始下滑。全球最大记忆体晶片生产国韩国的晶片库存增幅创四年来最大。根据韩国统计厅2022年6月发布的统计数据,该国晶片库存较2021年同期成长53.4%,并从2021年10月开始持续稳定增加。随着智慧型手机、个人电脑和消费应用的需求下降,全球对电子产品使用的记忆体晶片的需求也在下降。虽然伺服器需求较为强劲,但由于库存水准高企,2022年下半年记忆体晶片价格可能仍将持续下跌。
消费市场的下滑趋势会加速储存市场的週期性变化,这也会对MCU晶片带来影响。以行动电话、个人电脑为代表的消费性电子产品近年来呈现下滑趋势,2022年全年负成长的可能性很高。针对这些趋势,今年 4 月有消息称,家电设备晶片的订单订单可能高达 30%,这给争相准备产品的设备製造商和供应链带来了巨大的库存压力。消费性电子设备订单取消现在也影响了晶片製造商。
使用先进技术和附加价值服务将推动市场
半导体供应链和物流的透明度低会导致决策失误。随着卡车市场的分化和货柜运输成本的飙升,领导者必须能够看清他们的选择,并比较不同的行动方案。但要做到这一点,你需要集中的、可靠的、即时的资料。儘管 83% 的企业表示,他们比疫情前更意识到交通封锁带来的风险,但他们仍需要找到能够为他们提供正确视觉性的正确技术。这次疫情表明,单一事件可能会造成多大的破坏,并对整个半导体供应链产生连锁反应。这凸显了供应链灵活性的重要性——调整材料采购、生产水准和运输能力以满足需求的能力。但这很难实现。
在半导体供应链中,过度依赖单一合作伙伴是有问题的。为了确保供应链的弹性,半导体公司需要接触多个合作伙伴,无论是材料供应商、製造地或承运商。另一方面,要获得多个合作伙伴并不容易。尤其是当许多仲介存在隐藏的偏见时。这意味着领导者必须自己驾驭高度复杂的多个市场,或找到能够完全公正地将他们与供应商联繫起来的合作伙伴。另一个问题是信任。为了确保灵活性,公司需要有多个可依赖的供应商来遵守法规。这意味着公司必须进行广泛的实质审查,或找到可以完全透明地委託这项责任的合作伙伴。
半导体物流行业概况
半导体物流市场竞争激烈且分散,有大量本地、区域和少数全球参与者参与市场。主要参与者包括 DHL、日本通运、Yusen 物流、DB Schenker 和 Kuehne+Nagel。采用适当且先进的技术来明确半导体供应链和物流,很可能会对企业产生重大影响。与地区和本地参与者相比,全球参与者由于服务的可用性而占据了该市场的很大份额。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章 简介
- 调查前提条件
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究阶段
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态
- 当前市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 限制因素
- 机会
- 价值链/供应链分析
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 购买者/消费者的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
- COVID-19 对市场的影响
第五章 市场区隔
- 按功能
- 运输
- 路
- 铁路
- 水路和海路
- 航空
- 仓储和配送
- 附加价值服务(包装、清关、货运经纪及其他服务)
- 运输
- 目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
第六章 竞争格局
- 市场集中度概览
- 公司简介
- DHL
- Nippon Express
- Yusen Logistics
- DB Schenker
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Omni Logistics
- Dimerco
- CEVA Logistics
- HOYER Group
- MAERSK
- Dintec Shipping Express
第七章:市场的未来
第 8 章 附录
The Semiconductor Logistics Market is expected to register a CAGR of greater than 7% during the forecast period.

Key Highlights
- There has been an increasing demand for smart devices, the need for sustainable production methods, the importance of cultivating a talent pool, and growth in APAC's semiconductor market share will shape the semiconductor logistics industry. However, supply chain and labour disruptions caused by COVID-19 had resulted in a worldwide chip shortage crisis, which had been exacerbated by ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, as well as conflict in Russia. The pace of technological advancement will quicken. The construction of 5G networks and the Internet of Things has already laid the groundwork for connectivity and automation.
- Insufficient manufacturing capacity to meet market demand is a key thematic trend permeating many facets of the semiconductor supply chain. Semiconductors are essential components in many renewable energy applications, electric vehicles, smartphones and other personal electronics, data centres, and even defence weapons. However, behind the scenes, today's semiconductor companies are facing a slew of challenges. Even at full capacity, fabs have been unable to meet demand, resulting in product lead times of six months or longer. The ongoing semiconductor shortage is now making headlines regularly, especially when it forces automotive OEMs to delay vehicle production. Furthermore, semiconductor firms are dealing with increased design complexity, a talent shortage, and pandemic-related issues, all of which are disrupting the complex, global supply chain that connects players in different markets.
- The semiconductor industry must see the logistical challenges of the last two years as a wake-up call that drastic action is required. When COVID-19 went into effect, many businesses saw a significant drop in sales. The automotive industry lost 80% of its buyers, resulting in a sharp drop in semiconductor demand. Some predict a global semiconductor shortage that will last until 2024. Between 2020 and 2022, it was estimated that these shortages cost the global economy more than USD 500 billion. Worse than the immediate financial impact, these shortages have revealed that semiconductor supply chains are inadequate. Several obvious flaws have been exposed, and addressing them requires more than simply catching up on order backlogs.
- The future of semiconductor companies is dependent on finding a way to compete with logistical challenges as a signal that drastic action is required. Because the demand for semiconductors is only going to increase, those who can get them to end users more efficiently will be the ones to benefit the most in the coming years. The semiconductor value chain is unusually complex, relying on a global network of material and equipment suppliers. This makes efficient supply chain management extremely difficult, resulting in excess stock and routine bottlenecks. A good example is freight management. Freight issues, ranging from port congestion to container shortages, can result in longer lead times and longer shipment delays. Other factors influencing the supply chain include humidity, shock impact, and theft. But without precise data on the progress of shipments and GPS tracking, leaders are often left operating in the dark.
Semiconductor Logistics Market Trends
Increasing demand for semiconductor driving the market
Since 2020, the global chip shortage has worsened, with price increases being the semiconductor industry's defining trend. Upstream material and equipment manufacturers are facing supply shortages, chipmakers have increased investments to expand their product lines on occasion, and downstream semiconductor companies have made significant profits. Overall, the supply shortage of panel drive IC, consumer-grade MCU, memory chips, and other products have begun to ease, signalling the start of a price decrease. However, some power semiconductor chips, particularly those used in automotive, industrial control, IoT, and other fields, remain scarce.
The primary reason for this is that DRAM has quickly entered a downward price trend as the market undergoes cyclical changes. South Korea, the world's largest memory chip producer, has seen the largest increase in chip inventory in more than four years. According to statistics released by the South Korean statistics office in June 2022, the country's chip inventory increased by 53.4% over the same period in 2021 and has been steadily increasing since October 2021. As demand for smartphones, PCs, and consumer applications falls, global demand for memory chips used in electronic products falls. Despite relatively strong server demand, memory chip prices will continue to fall in the second half of 2022 as a result of high inventory levels.
The consumer market's downward trend has accelerated the cyclical changes in the storage market, and MCU chips are also affected. Consumer electronics, as represented by mobile phones and computers, have shown a downward trend in recent years, with likely negative growth in the entire year of 2022. According to this trend, news circulated in April of this year that terminal chips for consumer electronics could face up to 30% order cancellations, putting huge inventory pressure on the supply chain and terminal manufacturers who were busy preparing goods. Order cancellations from consumer electronic terminals have now gradually spread to chip manufacturers.
Increasing use of advanced technology and value-added services driving the market
Key decisions are made with insufficient insight as there is less visibility in the semiconductor supply chain and logistics. Leaders must be able to see their options and compare different courses of action as truck markets fragment and shipping container costs spiral. However, this requires centralized, dependable real-time data. While 83% of businesses say they are more aware of the risks associated with transportation blockades than they were before the pandemic, they still need to find the right technology to enable proper visibility. The pandemic exemplified how disruptive a single event can be, causing cascading effects across entire semiconductor supply chains. This highlights the critical importance of supply chain flexibility - the ability to adjust material purchases, production levels, and transportation capacity to meet demand. However, acknowledging this proves extremely tough.
Overreliance on single partners in semiconductor supply chains is a problem. To ensure the resilience of their supply chains, semiconductor companies require access to multiple partners, whether it's a material supplier, manufacturing base, or freight provider. Gaining access to multiple partners, on the other hand, is not so simple, especially when many brokers have hidden biases. This means that leaders must either navigate multiple highly complex markets on their own or find a partner who can connect them with providers with complete impartiality. Another issue is trust: flexibility necessitates companies having multiple providers they can trust to comply with regulations. This means they must either conduct extensive due diligence or find a partner to whom they can delegate this responsibility in complete transparency.
Semiconductor Logistics Industry Overview
The Semiconductor Logistics Market is highly competitive and fragmented with a large number of local, regional and a few global players penetrating the market. Major players are DHL, Nippon Express, Yusen Logistics, DB Schenker, Kuehne+Nagel, and many more. The use of proper and advanced technology to bring clarity in the semiconductor supply chain and logisitcs is going to bring a difference between the companies. Global players hold a good share in this market due to availibility of services compared to the regional and local players.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Method
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Overview
- 4.3 Market Dynamics
- 4.3.1 Drivers
- 4.3.2 Restraints
- 4.3.3 Opportunities
- 4.4 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Impact of the COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Function
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.1.1 Roadways
- 5.1.1.2 Railways
- 5.1.1.3 Water and Seaways
- 5.1.1.4 Airways
- 5.1.2 Warehousing and Distribution
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Packaging, Customs Clearance, Freight Brokerage, and Other Services)
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.2 By Destination
- 5.2.1 Domestic
- 5.2.2 International
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 DHL
- 6.2.2 Nippon Express
- 6.2.3 Yusen Logistics
- 6.2.4 DB Schenker
- 6.2.5 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.2.6 Omni Logistics
- 6.2.7 Dimerco
- 6.2.8 CEVA Logistics
- 6.2.9 HOYER Group
- 6.2.10 MAERSK
- 6.2.11 Dintec Shipping Express*









