 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1690902
日本电力 -市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Japan Power - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
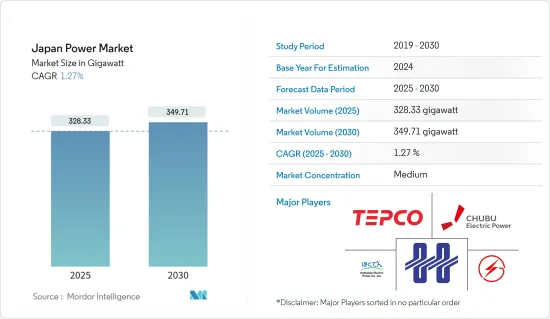
日本电力市场规模预计在 2025 年为 328.33 吉瓦,预计在 2030 年达到 349.71 吉瓦,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 1.27%。
关键亮点
- 从中期来看,太阳能光电系统价格和安装成本的下降、可再生能源技术的进步以及政府的支持措施预计将推动日本电力市场的发展。
- 预计液化天然气成本的波动和较高的进口依赖度将影响天然气发电,并在预测期内阻碍市场成长。
- 日本离岸风力发电领域的发展可能为未来日本电力市场创造许多机会。
日本电力市场的趋势
火力发电预计将占据市场主导地位
- 截至2023年,火力发电将占日本总设备容量的近46.96%,并将成为日本能源结构的最大贡献者。根据跨地区输电业者协调组织(OCCTO)预测,到2023年,日本火力发电装置容量将达到近1,506万千瓦,涵盖481多个地点。
- 根据经济产业省的资料,日本持有火力发电资产的发电公司约有214家。但日本火力发电市场主要由原一般电力公司所持有,火力发电总合装置容量超过3GW的公司仅有十家,其中包括北海道电力、东北电力、JERA、北陆电力、关西电力等大公司。
- 日本火力发电领域以液化天然气发电厂为主,占总发电量的近53.1%。根据经济产业省统计,日本共有发电厂69座,平均装置容量为110万千瓦。其次是燃煤发电厂,有近95台机组,总设备容量的32.2%。
- 然而,自俄乌衝突爆发以来,日本液化天然气供应情况日益恶化。例如,日本的合约液化天然气供应量预计将在 2023 年下降近 8%,每年近 600 万吨(MTPA)的长期液化天然气供应合约将到期。
- 日本公司已与主要液化天然气供应商协商了2023年和2024年的新合同,以扭转这一趋势。例如,2024年5月,澳洲石油天然气公司桑托斯与日本北海道燃气公司签署了液化天然气(LNG)长期供购协议(SPA)。根据协议,北海道天然气将在10年内每年供应高达40万吨液化天然气。
- 因此,由于上述因素,预计火力发电将成为预测期内电力市场最大的组成部分。
可再生能源技术的进步和政府支援措施
- 在政府大力推动向清洁能源来源转型以及可再生能源技术不断进步的推动下,日本可再生能源电力产业有望大幅成长。日本製定了雄心勃勃的气候变迁目标,力争实现碳中和。
- 日本第六个战略能源计画的目标是到2030年将可再生能源在其能源结构中的比例从36%提高到38%。在逐步摆脱核能的同时,日本也越来越多地采用太阳能、风能和潮汐能等再生能源,旨在减少对外国能源的依赖,促进国内能源创新。
- 此外,日本经济产业省的「绿色成长策略」旨在2050年实现碳中和。该战略概述了对再生能源、核能復兴以及采用低碳氢化合物、先进核子反应炉和碳回收等最尖端科技的雄心勃勃的推动。这些发展必将加速可再生技术的进步。
- 根据经济产业省资源能源厅统计,截至2023年9月,日本全国可再生能源发电发电厂约有4,730座,与前一年同期比较增加了458座。由于政府的支持性策略和政策预计将导致再生能源计划可再生能源发电可再生能源发电厂的数量预计将会增加。
- 例如,2024年5月,总部位于阿布达比的主权投资者穆巴达拉投资公司(Mubadala)投资了PAG的亚太可再生能源平台。该平台的战略重点是为日本企业提供太阳能解决方案。
- 在政府的强力支持下,包括政策、机构和雄心勃勃的可再生能源目标,日本的可再生能源市场预计将在未来几年内实现成长。
日本电力业概况
日本的电力市场适度细分。市场的主要企业包括东京电力公司、东北电力公司、北海道电力公司、中部电力公司和北陆电力公司。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究范围
- 市场定义
- 调查前提
第二章执行摘要
第三章调查方法
第四章 市场概述
- 介绍
- 日本发电量及截至2029年的预测
- 日本发电量及预测(截至2029年)
- 2023年日本可再生能源结构
- 近期趋势和发展
- 政府法规和政策
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 太阳能发电系统价格与安装成本下降
- 可再生能源技术的进步和政府支援措施
- 限制因素
- 液化天然气成本波动和高进口依赖度影响天然气发电
- 驱动程式
- 供应链分析
- PESTLE分析
第五章市场区隔
- 发电源
- 火力
- 水力发电
- 核能
- 可再生能源
- 输配电(T&D)
第六章竞争格局
- 併购、合资、合作与协议
- 主要企业策略
- 公司简介
- Hokkaido Electric Power Company
- Tohoku Electric Power Company
- Tokyo Electric Power Company
- Chubu Electric Power Company
- Hokuriku Electric Power Company
- Kansai Electric Power Company
- Chugoku Electric Power Company
- Shikoku Electric Power Company
- Kyushu Electric Power Company
- Okinawa Electric Power Company
- 市场排名/份额(%)分析
第七章 市场机会与未来趋势
- 日本离岸风力发电领域的发展
简介目录
Product Code: 72379
The Japan Power Market size is estimated at 328.33 gigawatt in 2025, and is expected to reach 349.71 gigawatt by 2030, at a CAGR of 1.27% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- In the medium period, the declining price and installation cost of solar PV systems, advancements in renewable energy technologies, and supportive government initiatives are expected to drive the Japanese power market.
- Volatility in LNG costs and high reliance on imports impact natural gas power generation and are expected to hinder the market's growth during the forecast period.
- Nevertheless, the progress in the Japanese offshore wind power sector is likely to create several opportunities for the Japanese power market in the future.
Japan Power Market Trends
Thermal Power Generating Source is Expected to Dominate the Market
- As of 2023, the thermal power plant sector was the largest contributor to Japan's power mix, accounting for nearly 46.96% of the country's total installed capacity. In 2023, according to the Organization of Cross-Regional Coordination of Transmission Operators (OCCTO), the country had nearly 150.06 GW of installed thermal capacity from more than 481 power plants.
- According to Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) data, Japan has nearly 214 electricity generation companies that own thermal electricity generation assets. However, the Japanese thermal power market is dominated by former general electric utilities, with only ten companies having a total installed thermal capacity exceeding 3 GW, which include major companies such as Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Tohoku Electric Power Co., JERA, Hokuriku Electric Power Co., and Kansai Electric Power Co.
- The Japanese thermal power sector is dominated by LNG-fired plants, which account for nearly 53.1% of the total power capacity. According to METI statistics, Japan has 69 plants, with an average installed capacity of 1.1 GW. This is followed by coal-fired power plants, which account for nearly 95 plants and 32.2% of the total installed capacity.
- However, since the start of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, Japan's LNG supply situation has become increasingly dire. For instance, in 2023, nearly 6 million tonnes/year (MTPA) of long-term LNG supply contracts expired, which was expected to reduce the country's contractual LNG supply by nearly 8%.
- Japanese companies negotiated new deals with major LNG-supplying nations to reverse this trend in 2023 and 2024. For instance, in May 2024, Santos, an Australian oil and gas company, made a long-term liquified natural gas (LNG) supply and purchase agreement (SPA) with Japan's Hokkaido Gas. As per the deal, the company will supply up to 0.4 million tonnes of LNG annually over ten years.
- Therefore, owing to the factors mentioned above, the thermal source for power generation is expected to be the largest segment of the power market during the forecast period.
Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies and Supportive Government Initiatives
- Japan's renewable power sector is poised for significant growth, driven by robust government initiatives to transition toward cleaner energy sources and ongoing advancements in renewable technology. The nation has set ambitious climate targets, aiming for carbon neutrality.
- Japan's Sixth Strategic Energy Plan outlines a goal of elevating the share of renewable energy in its energy mix from 36% to 38% by 2030. With a shift away from nuclear power, Japan is increasingly embracing renewables like solar, wind, and tidal power, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign energy and foster domestic energy innovation.
- Further, the Japanese Green Growth Strategy by the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry aims for carbon neutrality by 2050. The strategy outlined an ambitious push for renewables, a revival of nuclear power, and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like low-carbon hydrogen, advanced nuclear reactors, and carbon recycling. These developments are poised to drive advancements in renewable technologies.
- As per the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry of Japan, as of September 2023, there were around 4.73 thousand renewable power stations in Japan, an annual increase of 458 power stations compared to the previous year. With the surge in the upcoming investments in renewable energy projects due to supportive government strategies and policies, the number of renewable power plants is expected to increase during the forecast period.
- For instance, in May 2024, Mubadala Investment Company (Mubadala), a sovereign investor based in Abu Dhabi, invested in PAG's Asia Pacific renewable energy platform. This platform is strategically centered on delivering solar power solutions to businesses in Japan.
- Given this strong government backing, including policies, schemes, and ambitious renewable targets, the renewable energy market in Japan is poised for growth in the coming years.
Japan Power Industry Overview
The Japanese power market is moderately fragmented. Some of the key players in the market are Tokyo Electric Power Company, Tohoku Electric Power Company, Hokkaido Electric Power Company, Chubu Electric Power Company, and Hokuriku Electric Power Company.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Installed Power Generation Capacity and Forecast, till 2029
- 4.3 Electricity Generation and Forecast, Japan, till 2029
- 4.4 Renewable Energy Mix, Japan, 2023
- 4.5 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.6 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.7 Market Dynamics
- 4.7.1 Drivers
- 4.7.1.1 Declining Price and Installation Cost of Solar PV Systems
- 4.7.1.2 Advancements in Renewable Energy Technologies and Supportive Government Initiatives
- 4.7.2 Restraints
- 4.7.2.1 Fluctuating LNG Costs and High Reliance on Imports Impact Natural Gas Power Generation
- 4.7.1 Drivers
- 4.8 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.9 PESTLE Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Power Generation Source
- 5.1.1 Thermal
- 5.1.2 Hydroelectric
- 5.1.3 Nuclear
- 5.1.4 Renewable
- 5.2 Power Transmission and Distribution (T&D)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Hokkaido Electric Power Company
- 6.3.2 Tohoku Electric Power Company
- 6.3.3 Tokyo Electric Power Company
- 6.3.4 Chubu Electric Power Company
- 6.3.5 Hokuriku Electric Power Company
- 6.3.6 Kansai Electric Power Company
- 6.3.7 Chugoku Electric Power Company
- 6.3.8 Shikoku Electric Power Company
- 6.3.9 Kyushu Electric Power Company
- 6.3.10 Okinawa Electric Power Company
- 6.4 Market Ranking/Share (%) Analysis
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Progress in Japan's Offshore Wind Power Sector
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219













