 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1693922
日本资料中心伺服器市场:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Japan Data Center Server - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
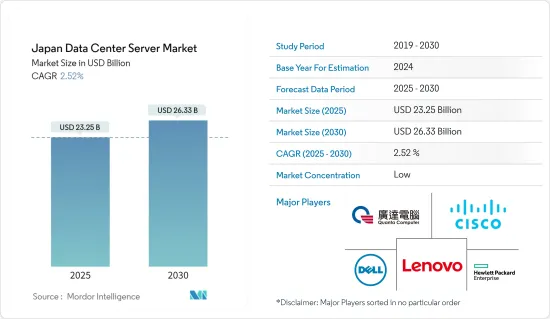
日本资料中心伺服器市场规模预计在2025年为232.5亿美元,预计到2030年将达到263.3亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030年)的复合年增长率为2.52%。
日本对资料中心的需求正在快速成长,使其成为一个越来越有吸引力的商业市场。解决环境问题的努力、政府对当地资料中心的支持、产业结构的变化以及由于技术进步而导致的生活方式的改变都在日本资料中心市场中发挥着重要作用,导致对伺服器的需求不断增长。
关键亮点
- 市场成长的主要动力是日本地区对超大规模建筑的需求不断增长。大阪的优势在于其集中了多种产业,包括环境、新能源、製药和製造业。这个充满活力的生态系统促进了超大规模资料中心与推动全球永续性和技术进步的产业之间的独特合作。大阪府人口为880万,国内生产毛额达3,600亿美元,经济规模与挪威相当。
- 日本被广泛认为是网路普及率最先进的经济体之一。截至2023年,日本网路使用率(个人)为82.9%,光纤发展率为99.3%。宽频用户数4,380万户,其中FTTH用户3,660万户,CATV网路用户650万户,行动宽频用户(4G、5G)1.84亿户。
- 排放在2050 年实现净零碳排放的目标,而云端资料中心的能源效率对于减少日本的碳足迹可以发挥关键作用。
- 日本政府认识到云端技术可以为日本带来的好处以及它对刺激创新和培育非传统经营模式的积极影响,因此推出了一系列倡议来推广云端运算,作为进一步实现国家数位化的更广泛计划的一部分。
- 要建立伺服器,您首先必须购买各个元件。您需要组装伺服器并安装必要的软体。客製化、拥有和维护伺服器需要资源。适合长期计划和内部知识累积。
日本资料中心伺服器市场趋势
刀锋型伺服器外形尺寸市场预计将显着成长
- 刀锋型伺服器是一种小型计算机,用于在电脑或系统网路内託管和分发资料。它充当电脑、应用程式、程式和系统之间的连结。据Cloudscene称,截至2023年9月,日本共有218个资料中心。由于需要最大限度地提高空间和电源效率,刀锋型伺服器通常用于大型资料中心。
- 日本已确认拥有近 40 个大型资料中心设施,预计未来几年还会有更多。日本政府计划透过分散海底电缆登陆基地、多样化登陆点的方式,在全国各地建造多个新的资料中心。海底电缆主要铺设在日本东太平洋沿岸,其中许多集中在东京、志摩等特定地区。政府计划将登陆基地分散到其他地区,以增强经济安全。这可能会导致新的集中区域的大型资料中心部分显着增长,从而刺激对刀锋型伺服器的需求。
- 首都地区的土地和电力限制推高了建筑成本,有可能减缓新开发,并加剧来自国内外参与企业的竞争。资料中心建设公司正在日本稀缺的土地上投资建造新的资料中心,但由于需求量大,这些资料中心很可能具有很高的运算能力。在这种情况下,刀锋型伺服器刀锋型伺服器的优势在于其有限的运算元件允许客户将更多的伺服器安装到更小的机架区域,从而提高密度。
- 一些亚洲国家,例如日本,不支援 110V 电力基础设施。因此,我们无法达到美国所享有的功率密度。例如,美国一个采用三相220V电源的资料中心可以支援15kW的机架。然而,支援这种功率密度需要专门的冷却解决方案。如果您的电源限制为 110V,那么无论供应商是谁,刀片都不是一个可行的解决方案。例外的是部门解决方案,例如 HP BladeSystem C3000 和 IBM BladeCenter S。
- 此外,刀锋型伺服器专为高效能处理而设计。与机架伺服器不同,刀锋型伺服器是可热插拔的。这意味着您可以移除和更换丛集中的刀锋型伺服器,而无需关闭整个丛集。当管理员需要更换刀锋型伺服器刀锋型伺服器将其移出丛集进行维护时,这大大减少了停机时间。
- 了解刀锋型伺服器技术的过去、现在和未来对于日本各种规模的组织都至关重要,这样IT基础设施做出明智的决策。凭藉其紧凑的设计、高效能和可扩展性,随着技术的不断发展,刀锋型伺服器预计在未来许多年内仍将是基础设施的重要组成部分。
IT 和通讯作为最终用户产业将快速成长
- 日本的资讯和通讯技术 (ICT) 产业处于创新的前沿,推动着显着的进步并创造了面向未来的环境。 ICT 领域正在利用最尖端科技开闢一个充满可能性的世界,同时面临决定其成长的挑战。
- 日本 ICT 市场的成长主要得益于物联网 (IoT) 设备在家用电子电器、军事、农业和建筑等各个领域的日益广泛的使用。日本拥有一些世界领先的 ICT 公司,包括索尼、松下、富士通、NEC 和东芝公司,这些公司在日本发展成为 ICT 中心的过程中发挥关键作用。政府增加支出以维持一流和先进的基础设施,以及许多现代化和改进计划的成功实施,都促进了市场的扩张。
- 由于电子日本策略的快速扩张,日本的ICT市场预计将实现成长,该策略专注于地方电子政府计划,包括公民参与、自我评估和对线上政务服务的回馈。
- 日本拥有高品质的基础设施和服务,包括ICT基础设施、通讯技术、教育和医疗保健,以及高度的商业和社会稳定性。日本政府正在采取措施支持私营部门的数位转型和中小企业的崛起。
- 智慧城市是日本政府实现社会5.0的关键倡议之一。第六个策略技术基础设施(STI)计画涉及1000多个组织,包括地方政府、区域团体和私人公司,并设定了2025年实施100项措施的目标。智慧城市官民合作关係平台将取代地方的、分散的数位环境,以促进官民合作关係关係并发展区域计划。具体措施包括到2030年集中实施「我的号码」(公民身分证)系统并制定资料库註册标准。
- 此外,日本电信业者正在投资6G。 6G系统不仅超越5G,还提供更快的速度、更高的容量、更低的延迟、新的高频率频段(100GHz及以上)、扩展到空中、海上和太空的通讯范围,以及超低功耗和超低成本的通讯。根据内务部,截至2023年3月,日本5G合约数量约6,980万份。 2022 年 6 月,NEC、富士通和诺基亚宣布将合作测试新的行动通讯技术,目标是到 2030 年实现 6G 服务商业化。
- 因此,政府为促进 IT 产业发展而采取的倡议,以及科技公司整体投资的增加和国家资料中心的成长,可能会促进日本伺服器市场的发展。
日本资料中心伺服器产业概况
日本的资料中心伺服器市场高度细分,主要公司包括戴尔科技公司、惠普企业、思科系统、联想集团有限公司和广达电脑公司。该市场的参与企业正在采取合作和收购等策略来加强其产品供应并获得可持续的竞争优势。
- 2023年12月-富士通宣布将依照该策略在日本成立专门的硬体业务公司,以进一步加强以伺服器和储存解决方案为主的硬体业务的管理。
- 2023 年 8 月 - 惠普企业宣布,phoenixNAP 将透过采用 Ampere Computing 节能处理器的云端原生 HPE ProLiant RL300 Gen11 伺服器扩展其实机云端平台。扩展的服务将支援人工智慧推理、云端游戏和其他云端原生工作负载,并提高效能和能源效率。
- 2023 年 7 月-富士通宣布推出新伺服器 BS2,000 SE730/SE730B。最新的 SE 代伺服器被视为管理大量资料的高阶效能平台。它提供了极高的可用性,是关键任务应用程式的理想平台。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场洞察
- 市场概览
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买家的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
- 产业价值链分析
第五章市场动态
- 市场驱动因素
- 新建资料中心增加,网路基础建设发展加快
- 云端和物联网服务的采用率不断提高
- 市场问题
- 初期投资高
- COVID-19影响评估
第六章市场区隔
- 按外形尺寸
- 刀锋型伺服器
- 机架式伺服器
- 塔式伺服器
- 按最终用户
- 资讯科技/通讯
- BFSI
- 政府
- 媒体娱乐
- 其他的
第七章竞争格局
- 公司简介
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Lenovo Group Limited
- Quanta Computer Inc.
- Super Micro Computer Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Fujitsu Limited
- NEC Corporation
- IBM Corporation
第八章投资分析
第九章 市场机会与未来趋势
The Japan Data Center Server Market size is estimated at USD 23.25 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 26.33 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 2.52% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Japan's demand for data centers is proliferating and becoming more attractive as a business market. Environmental initiatives, government support for local data centers, changes in industrial structure, and changing lifestyles due to technological advancements all play a significant role in the Japanese data center market, resulting in major demand for the server market.
Key Highlights
- The major driver for the market growth is the growing demand for hyperscale construction in the Japanese region. Osaka's strength lies in its diverse concentration of industries, encompassing environmental, new energies, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing sectors. This vibrant ecosystem fosters a unique coaction between hyperscale data centers and industries driving global sustainability and technological advancement. With a population of 8.8 million, Osaka Prefecture has a GDP of USD 360 billion, similar to the size of Norway's economy.
- Japan is widely regarded as one of the most advanced economies in terms of Internet penetration. As of 2023, Japan's Internet usage rate (individuals) was 82.9%, and the development rate of optical fiber was 99.3%. The number of broadband subscribers was 43.8 million, which includes 36.6 million FTTH subscribers and 6.5 million CATV Internet subscribers, while the number of mobile broadband subscribers (4G and 5G) was 184 million.
- The energy efficiency of cloud data centers can play a crucial role in reducing Japan's carbon footprint to achieve the Japanese government's goal of net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
- Having recognized the benefits cloud technologies can provide to the country and their positive effect on encouraging innovation and fostering non-conventional business models, the Japanese government has been launching numerous initiatives to promote the cloud as part of the broader plans to digitalize the country further.
- To build a server, one must buy individual components first. They have to assemble the server and install the necessary software. It is resource-intensive to customize, own, and maintain a server. It is well-suited for long-term projects and knowledge-building within the company.
Japan Data Center Server Market Trends
Blade Server Form Factor Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth
- A blade server is a small computer used to host and distribute data within a network of computers and systems. It acts as a link between computers, applications, programs, and systems. According to Cloudscene, as of September 2023, there were 218 data centers in Japan. A blade server is typically used in larger data centers due to the need to maximize space and power utilization and efficiency, have high computing needs, and support higher thermal and electrical loads.
- There are close to 40 data centers in Japan that are identified as extensive data center facilities and are expected to increase in the coming years. The Japanese government plans to build several new data centers nationwide by decentralizing landing bases for submarine cables to diversify landing points. Submarine cables are laid mainly on Japan's eastern Pacific Ocean side, with many concentrated in certain areas, such as Tokyo and Shima. The government intends to disperse landing bases in other areas and strengthen economic security. This may lead to significant growth in the large DC segments in newer concentrated areas, boosting the demand for blade servers.
- Constraints on land and power in the greater Tokyo area result in higher construction costs, possible delays for new developments, and fierce competition from domestic and foreign players. DC construction companies are investing in new data centers to build new data centers on scarce land in Japan, but as the demand is high, these data centers are likely to have high computing power. The advantage of blade servers in this situation is that, due to the limited computing components of blade servers, customers can fit more servers into a smaller rack area to increase the density.
- Some Asian countries, such as Japan, do not support 110 V power infrastructure. As a result, they are unable to achieve the power density enjoyed in the United States. For example, a 3-phase 220V power data center in the United States can support a 15 kW rack. However, special cooling solutions are needed to support this power density. Blades are not a viable solution in cases where power is restricted to 110V, no matter the vendor. An exception to this would be a departmental solution, such as the HP BladeSystem C3000 or IBM BladeCenter S.
- Further, blade servers are designed for high-performance processing. Unlike rack servers, blade servers can be hot-swapped. This means that one can remove and replace a blade server in a cluster without powering down the whole cluster. This significantly reduces downtime when an administrator needs to swap out a blade server or move a blade server out of the cluster for maintenance.
- Understanding blade server technology's past, present, and future is essential for organizations of all sizes in Japan to make informed decisions regarding their IT infrastructure. Due to their compact design, high performance, and scalability, blade servers are expected to remain a key component of that infrastructure for many years as they continue to evolve and evolve with the ever-evolving world of technology.
IT and Telecommunication to be the Fastest Growing End-user Industry
- Japan's Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector is at the forefront of innovation, driving remarkable progress and creating a future-proof environment. The ICT sector opens up a world of possibilities by utilizing state-of-the-art technologies while facing the challenges that define its growth.
- The growth of the Japanese ICT market is mainly driven by the growing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices across various sectors, such as consumer electronics, military, agriculture, and construction. Japan is home to some of the most prominent ICT organizations in the world, such as Sony, Panasonic, Fujitsu, NEC, and Toshiba (Toshiba), which are playing an important role in the growth of Japan as an ICT hub. The increasing government spending on maintaining the top-of-the-line and advanced infrastructure and the proper implementation of many modernization and improvement projects contribute to the market's expansion.
- Japan's ICT market is expected to grow due to the rapid expansion of E-Japan's strategy, which focuses on local e-government projects, such as citizen participation, self-assessment, and feedback on online government services.
- Japan has a high level of stability in business and society, as well as high-quality infrastructure and services such as ICT infrastructure, communication technology, education, healthcare, and more. The Japanese government is taking steps to support the private sector's digital transformation and the emergence of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Smart Cities are one of the Japanese government's key initiatives to bring Society 5.0 to life. The 6th Strategic Technology Infrastructure (STI) plan set a goal of 100 initiatives10 to be implemented by 2025 with the participation of 1000+ organizations from local government, regional organizations, and private enterprises. The "Smart City Public-Private Partnership platform" will replace the local and dispersed digital landscape to promote public-private partnerships and develop regional projects. Specific initiatives include centralizing the MyNumber (citizens ID) system and developing database registry standards by 2030.
- Further, the telecom companies in Japan are investing in 6G. The 6G system will not only outperform 5G, but it will also offer high speed, high capacity, low latency, new high-frequency bands (above 100 GHz), extend communication coverage to the sky, sea, and space, and provide ultra-low power consumption and ultra-low-cost communications. According to the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, about 69.8 million 5G subscriptions were counted in Japan as of March 2023. In June 2022, NEC (NEC), Fujitsu (Fujitsu), and Nokia (Nokia) joined forces to test new mobile communication technologies to launch 6G services commercially by 2030.
- Thus, with the overall increase in investment by tech companies, government initiatives to improve the IT industry development and growth in data centers in the country would boost the server market in Japan.
Japan Data Center Server Industry Overview
The Japan data center server market is highly fragmented with the presence of major players like Dell Technologies Inc., Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Cisco Systems Inc., Lenovo Group Limited, and Quanta Computer Inc. Players in the market are adopting strategies such as partnerships and acquisitions to enhance their product offerings and gain sustainable competitive advantage.
- December 2023 - Fujitsu announced the launch of a dedicated company for the hardware business in Japan in alignment with this strategy and to further strengthen the management of its hardware business, which primarily focuses on servers and storage solutions.
- August 2023 - Hewlett Packard Enterprise announced that phoenixNAP is expanding its Bare Metal Cloud platform with cloud-native HPE ProLiant RL300 Gen11 servers, using energy-efficient processors from Ampere Computing. The expanded services support AI inferencing, cloud gaming, and other cloud-native workloads with enhanced performance and energy efficiency.
- July 2023 - Fujitsu announced a new server, BS2000 SE730/SE730B. The servers of the latest SE generation are a valued platform in the high-end performance range for managing the largest data volumes. The servers offer extremely high availability and serve as an ideal platform for mission-critical applications.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumption and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Increase in Construction of New Data Centers, Development of Internet Infrastructure
- 5.1.2 Increasing Adoption of Cloud and IoT Services
- 5.2 Market Challenge
- 5.2.1 High Initial Investments
- 5.3 Assessment of COVID-19 Impact
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Form Factor
- 6.1.1 Blade Server
- 6.1.2 Rack Server
- 6.1.3 Tower Server
- 6.2 By End User
- 6.2.1 IT and Telecommunication
- 6.2.2 BFSI
- 6.2.3 Government
- 6.2.4 Media and Entertainment
- 6.2.5 Other End Users
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Dell Technologies Inc.
- 7.1.2 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- 7.1.3 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 7.1.4 Lenovo Group Limited
- 7.1.5 Quanta Computer Inc.
- 7.1.6 Super Micro Computer Inc.
- 7.1.7 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- 7.1.8 Fujitsu Limited
- 7.1.9 NEC Corporation
- 7.1.10 IBM Corporation










