 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1844443
越南电力:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Vietnam Power - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
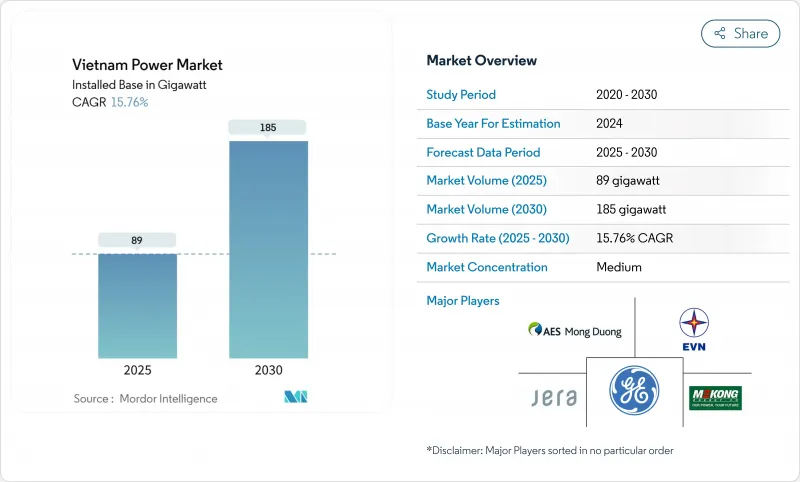
越南电力市场规模预计将从 2025 年的 89 吉瓦成长到 2030 年的 185 吉瓦,预测期间(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 15.76%。
越南电力市场正处于快速扩张的轨道上。这项加速发展得益于《第八号电力发展计画》(PDP-8)下1,360亿美元的政策推动,该计画的目标是到2030年将可再生能源占比提高到28-36%,到2050年提高到74-75%。从2023年起,工业电气化、资料中心的广泛部署以及停电期间的能源安全将推动资本投资,而新的直接购电协议(DPPA)规则允许私人可再生能源营运商直接与大用户交易。输电网的改进,特别是500千伏及以上主干网的改进,将解决电网瓶颈问题。这些瓶颈曾阻碍了越南一半的装置容量,并迫使该国在2024年从中国进口25.6亿度电的电力。随着国际开发商进入离岸风力发电试点和液化天然气计划,由国营越南电力公司(EVN)主导的竞争格局正在改变。
越南电力市场趋势与洞察
快速工业化导致电力需求激增
预计2024年工业生产将成长8.4%,5月底全国用电量将达到10亿度,促使越南电力公司实施需求响应计画。预计到2024年,光是半导体产业产值就将达182.3亿美元,年复合成长率为11.48%。这是越南「硅谷Delta」计画的成果,该计画旨在2030年实现45%的产量来自高科技产品。韩国在2025年初重新夺回了最大投资地位,SK集团向液化天然气和小型核子反应炉拨款数十亿美元。为实现政府2025年8%的GDP目标,年发电量成长率需要达到12-16%,而越南的电力市场则依赖快速发展的电网计划。外国投资者现在将稳定的电力供应作为位置高科技工厂的先决条件。
政府可再生能源目标及上网电价
修订后的 PDP-8 将越南 2030 年的电力消耗目标设定为 5,044 亿至 5,578 亿千瓦时,同时要求可再生能源占比达到 28% 至 36%,标誌着越南将不再以煤炭为主导。新的价格上限分别为北部陆上风电 1,959.4 越南盾/千瓦时(0.078 美元)和海上计划1,987.4 越南盾/千瓦时(0.079 美元),在多年指导价停滞之后,恢復了投资者的可见性。然而,与此同时,追溯性电价削减可能会影响价值 130 亿美元的运作中太阳能和风能资产,引发国际开发商的抗议。第 57/2025 号法令引入了 DPPA,允许私人电力生产商绕过 EVN 并直接与合格消费者进行交易。这一转变使越南与东协电网愿景一致,即在 2030 年实现该地区 50% 的电力来自清洁能源。
PPA核准缓慢且监管不明确
审核发现上网电价 (FIT) 有不当应用,并暂停了新的待审批购电协议 (PPA),约有价值 130 亿美元的风电和太阳能资产面临风险。儘管越南表面上计划在 2030 年将发电量翻一番,但这导致 Enel、Equinor 和 Austed 退出。最新的 PDP-8 草案删除了 6 吉瓦的离岸风力发电区,加剧了人们对政策不确定性的担忧。电网核准也同样被推迟,政府数据显示,16 个强制性电网计划中,只有两个在 2024 年的最后期限前完成。这些延误在短期内限制了越南电力市场的发展步伐。
細項分析
同时,到2030年,风发电工程的复合年增长率将达到16.5%,随着3.4吉瓦海上联合循环发电厂的投入运作,风电将逐渐取代火力发电的主导地位。到2035年,越南计画新建15座发电厂,总合装置容量达22吉瓦。首座发电厂是越南国家石油公司(PetroVietnam)的812兆瓦仁泽三号(Nhon Trach 3),该发电厂已于2025年1月投入营运。如果竞标按计画进行,到2020年,越南的风电市场规模可能超过20吉瓦。
水力发电仍然是电力可靠性的关键支柱,但季节性因素降低了发电的稳定性,这促使人们开展电池试验,并于2025年2月在宁顺省核准了该国首个1.2吉瓦的抽水蓄能水力发电项目。在电价调整后,太阳能光电发电的普及率回升,生质能也获得了发展动力,一座20兆瓦的稻壳发电厂每年可减少36,800吨二氧化碳排放。长期搁置的核能发电方案透过与俄罗斯、日本和美国的可行性谈判重新提上日程,这可能会重塑越南2030年代的电力市场。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- 快速工业化导致电力需求激增
- 政府可再生能源目标及上网电价
- PDP-8主导外商直接投资流入发电与输电网络
- 电网现代化基金(亚洲开发银行、日本国际协力机构)
- 解锁离岸风电竞标渠道
- 资料中心繁荣推动弹性发电需求
- 市场限制
- PPA核准延迟和监管不确定性
- ESG主导的煤炭资金筹措紧缩
- 太阳能发电厂的土地征用问题
- 高压设备依赖进口
- 供应链分析
- 监管状况
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- PESTLE分析
第五章市场规模及成长预测
- 按发电源分类
- 火力
- 水力发电
- 太阳热
- 风力发电(陆上和海上)
- 生物质和垃圾焚化发电
- 其他电源
- 依输配电电压等级(仅定性分析)
- 500千伏及以上
- 220~330 kV
- 110~220 kV
- 低于110千伏
- 按最终用户
- 住房
- 商业和工业
- 公共产业
第六章 竞争态势
- 市场集中度
- 策略性倡议(併购、伙伴关係、购电协议)
- 市场占有率分析(主要企业的市场排名/份额)
- 公司简介
- Vietnam Electricity(EVN)
- PetroVietnam Power Corporation(PV Power)
- AES Corporation(Vietnam)
- JERA Co., Inc.
- Trung Nam Group
- Mekong Energy Company Ltd
- Vietnam Sunergy Joint Stock Company
- Sharp Energy Solutions Corporation
- B.Grimm Power(Vietnam)
- Siemens Energy Vietnam
- General Electric Vietnam
- Vestas Vietnam
- Orsted Vietnam
- Sunseap/EDP Renewables APAC
- Trina Solar Vietnam
- T&T Group Power
- Bamboo Capital Group(BCG Energy)
- Hitachi Energy Vietnam
- SP Group Vietnam
- Power Engineering Consulting JSC 2(PECC2)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Vietnam Power Market size in terms of installed base is expected to grow from 89 gigawatt in 2025 to 185 gigawatt by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.76% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The Vietnam power market is on a rapid build trajectory. A USD 136 billion policy push under Power Development Plan 8 (PDP-8) underpins this acceleration, targeting 28-36% renewable energy by 2030 and 74-75% by 2050. Industrial electrification, data-center proliferation, and post-2023 blackout energy-security pledges are lifting capital spending, while new Direct Power Purchase Agreement (DPPA) rules open space for private renewable producers to transact directly with large users. Transmission upgrades-the above 500 kV backbone in particular-remove the grid bottlenecks that once stranded half of the installed capacity and forced 2.56 billion kWh of imports from China in 2024. A moderate competitive landscape dominated by state-owned EVN is evolving as international developers anchor offshore-wind pilots and LNG projects.
Vietnam Power Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Industrialisation-Led Electricity Demand Surge
Industrial production jumped 8.4% 2024, lifting nationwide electricity use to 1 billion kWh in late May and prompting EVN to deploy demand-response programs. The semiconductor sector alone is valued at USD 18.23 billion in 2024 and is expanding at 11.48% CAGR, an outcome of Vietnam's "Silicon Delta" policy that targets 45% of output from high-tech goods by 2030. South Korea reclaimed the top-investor slot in early 2025, with SK Group allocating multibillion-dollar budgets to LNG and small-modular reactors. Meeting the government's 8% GDP objective for 2025 requires 12-16% yearly additions to generation, magnifying the Vietnam power market dependency on fast-track grid projects. Foreign investors now cite a stable electricity supply as a precondition for high-tech plant siting.
Government Renewable-Energy Targets & FITs
The revised PDP-8 sets a 500.4-557.8 billion kWh consumption band for 2030 while mandating that renewables claim 28-36% of the mix, signaling a pivot away from coal dominance. New price caps place onshore wind at VND 1,959.4/kWh (USD 0.078) in the north and near-shore projects at VND 1,987.4/kWh (USD 0.079), restoring investor visibility after years of stalled guidance.Yet simultaneous retroactive tariff cuts threaten USD 13 billion in operating solar and wind assets, sparking protests from international developers. Decree 57/2025 introduced DPPAs, allowing private generators to bypass EVN and transact directly with qualified consumers, a reform expected to lower state-budget strain and quicken renewable deployment. These shifts align Vietnam with the ASEAN Power Grid vision that foresees clean sources covering up to 50% of regional output by 2030.
Slow PPA Approval & Regulatory Uncertainty
Around USD 13 billion in wind and solar assets are at risk after auditors found mis-applied FIT rules and suspended new PPAs pending review, prompting exits by Enel, Equinor, and Orsted despite Vietnam's headline plan to double capacity by 2030. A 6 GW offshore-wind zone was removed from the latest PDP-8 draft, deepening perceptions of policy volatility. Transmission approvals are equally sluggish; government data show only 2 of 16 mandated grid projects met 2024 timelines. These delays restrain the Vietnam power market's tempo in the short run.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- PDP-8-Driven FDI Inflow in Generation & Grid
- Grid-Modernisation Funding (ADB, JICA)
- ESG-Driven Coal-Financing Squeeze
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Thermal plants controlled 45% of the Vietnam power market share in 2024, anchored by coal units that stabilized the grid during drought-triggered hydro outages that removed 5,000 MW from service.At the same time, wind projects are on a 16.5% CAGR track through 2030, positioning the segment to chip away at thermal primacy as 3.4 GW offshore complexes come online. LNG is the mid-transition bridge; 15 new plants totaling 22 GW are scheduled by 2035, beginning with PetroVietnam's 812 MW Nhon Trach 3 unit launched in January 2025. The Vietnam power market size for wind generation could top 20 GW by decade-end if auctions clear on schedule.
Hydropower remains the reliability linchpin, but seasonality undermines consistency, prompting battery trials and the nation's first 1,200 MW pumped-storage scheme in Ninh Thuan, approved in February 2025. Solar deployment has rebounded after tariff resets, while biomass gained traction with a 20 MW rice-husk plant that eliminates 36,800 tons of CO2 annually. Emerging nuclear options, long tabled, re-entered debate via feasibility talks with Russia, Japa,n and the United States, potentially resizing the Vietnam power market in the 2030s.
The Vietnam Power Market Report is Segmented by Generation Source (Thermal, Hydro, Solar, Wind, Biomass and Waste-To-Energy, and Other Sources), T&D Voltage Level (Above 500 KV, 220 To 330 KV, 110 To 220 KV, and Below 110 KV), and End-User (Residential, Commercial and Industrial, and Utilities). The Market Size and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Installed Capacity (GW).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Vietnam Electricity (EVN)
- PetroVietnam Power Corporation (PV Power)
- AES Corporation (Vietnam)
- JERA Co., Inc.
- Trung Nam Group
- Mekong Energy Company Ltd
- Vietnam Sunergy Joint Stock Company
- Sharp Energy Solutions Corporation
- B.Grimm Power (Vietnam)
- Siemens Energy Vietnam
- General Electric Vietnam
- Vestas Vietnam
- Orsted Vietnam
- Sunseap / EDP Renewables APAC
- Trina Solar Vietnam
- T&T Group Power
- Bamboo Capital Group (BCG Energy)
- Hitachi Energy Vietnam
- SP Group Vietnam
- Power Engineering Consulting JSC 2 (PECC2)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid industrialisation-led electricity demand surge
- 4.2.2 Government renewable-energy targets & FITs
- 4.2.3 PDP-8-driven FDI inflow in generation & grid
- 4.2.4 Grid-modernisation funding (ADB, JICA)
- 4.2.5 Offshore-wind auction pipeline unlock
- 4.2.6 Data-centre boom raising flexible-generation need
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Slow PPA approval & regulatory uncertainty
- 4.3.2 ESG-driven coal-financing squeeze
- 4.3.3 Land-acquisition conflicts for solar farms
- 4.3.4 Import-dependency for high-voltage equipment
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porters Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 PESTLE Analysis
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Generation Source
- 5.1.1 Thermal
- 5.1.2 Hydro
- 5.1.3 Solar
- 5.1.4 Wind (Onshore and Offshore)
- 5.1.5 Biomass and Waste-to-Energy
- 5.1.6 Other Sources
- 5.2 By T&D Voltage Level (Qualitative analysis only)
- 5.2.1 Above 500 kV
- 5.2.2 220 to 330 kV
- 5.2.3 110 to 220 kV
- 5.2.4 Below 110 kV
- 5.3 By End-User
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 5.3.3 Utilities
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (M&A, Partnerships, PPAs)
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis (Market Rank/Share for key companies)
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Vietnam Electricity (EVN)
- 6.4.2 PetroVietnam Power Corporation (PV Power)
- 6.4.3 AES Corporation (Vietnam)
- 6.4.4 JERA Co., Inc.
- 6.4.5 Trung Nam Group
- 6.4.6 Mekong Energy Company Ltd
- 6.4.7 Vietnam Sunergy Joint Stock Company
- 6.4.8 Sharp Energy Solutions Corporation
- 6.4.9 B.Grimm Power (Vietnam)
- 6.4.10 Siemens Energy Vietnam
- 6.4.11 General Electric Vietnam
- 6.4.12 Vestas Vietnam
- 6.4.13 Orsted Vietnam
- 6.4.14 Sunseap / EDP Renewables APAC
- 6.4.15 Trina Solar Vietnam
- 6.4.16 T&T Group Power
- 6.4.17 Bamboo Capital Group (BCG Energy)
- 6.4.18 Hitachi Energy Vietnam
- 6.4.19 SP Group Vietnam
- 6.4.20 Power Engineering Consulting JSC 2 (PECC2)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment












