 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1849919
服务机器人:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Service Robotics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
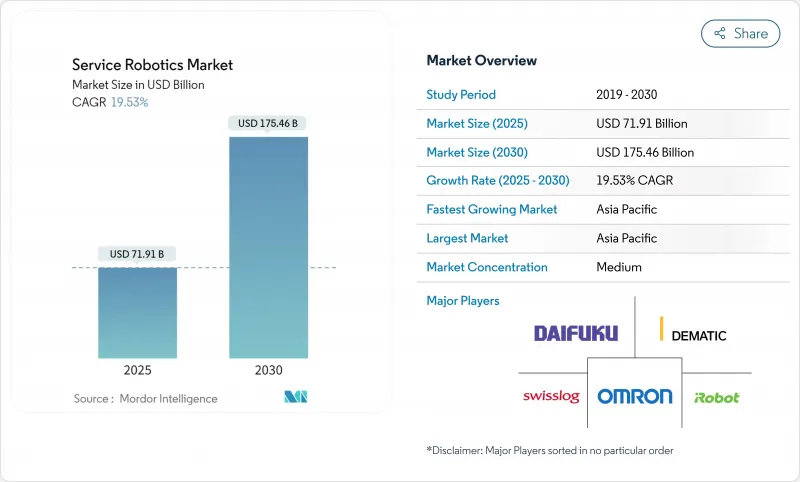
预计2025年服务机器人市场规模将达到719.1亿美元,到2030年将扩大到1,754.6亿美元,2025年至2030年的复合年增长率为19.53%。
新兴经济体劳动力供应紧张、机器人总拥有成本下降以及消除前期投资障碍的「机器人即服务」(RaaS)计画的普及推动了这些发展。主要技术供应商的策略性收购标誌着自动化预算从可自由支配的转向核心基础设施支出,而协同工作监管的明确性正在加速从先导计画到企业范围推广的转变。辅助机器人和移动机器人专利数量的不断增长,凸显出即使在宏观经济不确定的情况下,创新週期也可能保持两位数的成长。
全球服务机器人市场趋势与洞察
医疗保健、物流和农业领域对自动化的需求不断增长
受手术精度需求和更严格的感染控制通讯协定推动,预计 2024 年医疗机器人交付将增加 36%,达到约 6,100 台。物流业者正在加速部署微型仓配中心,预计到 2030 年全球安装量将超过 6,600 个,创造 360 亿美元的额外可用资金池。在农业领域,由于生产商努力应对长期劳动力短缺,预计到 2030 年手眼协作机器人将达到 3,590 万台。随着这三个产业推动投资报酬率,服务机器人市场正从成本抵销转向重塑营运模式的生产力平台。更广泛的应用范围也使收益来源多样化,并降低了经济波动的风险。跨部门交叉学习将进一步加速软体重复使用和组件标准化,缩短开发週期并维持价格下降。
劳动力短缺和人口老化
预计到2040年,日本将面临1,100万劳动力短缺,而65岁及以上人口的比例将上升至40%。预计到2025年,欧洲医疗保健领域将面临38万的人员短缺,促使医院测试辅助机器人和人工智慧分诊系统。欧洲汽车产业的自动化普及率已达36%,而所有产业的自动化普及率仅为6%,这显示其他产业仍有成长空间。因此,劳动力短缺支撑了服务机器人市场的结构性需求,因为企业追求的是韧性而非单纯的成本削减。人口老化也正在扩大老年护理和復健领域的消费应用,从而扩大了市场的社会意义。这些人口现实超越了经济週期,为投资者和供应商提供了长期视角。
高资本支出和维护成本
儘管硬体价格下降,但建筑案例研究表明,儘管生产率提高了近三倍,但从纯成本指标来看,机器人仍不如传统方法。生命週期的不确定性,包括电池更换、感测器重新校准和软体许可,使非专业人士的预算变得复杂。移动平檯面临地图绘製和定位的额外成本,特别是在雷射雷达和视觉 SLAM 基础设施稀少的地方。缺乏多年的投资报酬率框架导致许多中小型企业采取保守的投资立场,减缓了在价格敏感地区的采用。虽然供应商透过标准化组件和捆绑预测性维护分析来应对,但对领先成本风险的普遍认识继续阻碍服务机器人市场的发展。
細項分析
到2024年,专业服务机器人将占据服务机器人市场的72%,并在物流、清洁和检查等领域拥有成熟的投资报酬率。在这一细分市场中,医疗机器人预计将达到最高成长率,到2030年复合年增长率将达到23.4%,主要得益于医院对微创手术和严格感染控制通讯协定的需求。医疗机器人将受益于保险报销范围的扩大以及越来越多的临床证据表明机器人可以降低併发症率,从而缩短医院的投资回收期。个人和家用机器人虽然体型较小,但仍将继续被用于地板保养和陪伴等角色,这将进一步提升消费者对机器人技术的接受度。
辅助技术专利数量的不断增长表明,医疗保健应用频谱正在不断拓宽,从復健外骨骼到人工智慧辅助诊断设备,不一而足。这些创新管道表明,一旦监管瓶颈得到缓解,医疗细分领域的服务机器人市场规模可能会超过整体市场规模。工业和临床开发团队之间的交叉整合也提高了组件的通用,有助于降低成本并提高供应商的利润率。因此,医疗设备的部署正在从实验性资产发展成为关键任务医院基础设施。
硬体仍将是主要的收益驱动力,到2024年将占服务机器人市场规模的65.3%。感测器、致动器和电池占据了材料清单,推动了大规模生产的大部分成本节约。然而,随着云端运行时环境、伫列编配层和AI推理引擎成为关键的差异化因素,预计到2030年,软体的复合年增长率将达到22.1%。
这种转变反映了企业IT的趋势,即经常性授权费用超过了一次性硬体利润。提供专有作业系统的供应商能够获得更稳定的收益,并收集数据以不断改进其演算法。随着整合复杂性的降低,买家正在根据软体灵活性而非有效载荷容量来评估平台。在预测期内,RaaS、预测性维护和工作流程优化等服务预计将发展成为服务机器人市场的第三大价值支柱,与硬体和软体形成互补。
区域分析
到2024年,北美将占据全球服务机器人市场的34.5%,这得益于其成熟的自动化基础设施、优惠的税收优惠政策以及强劲的创业投资资金将达到64亿美元。企业用户正在从试点车队转向整栋大楼的部署,新的RaaS模式正在加速中型製造商的采用。监管机构正在明确协作机器人的安全要求,减少合规方面的模糊性,并鼓励缩短采购週期。公共部门的需求也正在透过国防和基础设施现代化项目逐渐形成,这些项目需要自主检查能力。
预计亚太地区将实现最快的复合年增长率,达到19.6%。中国服务机器人产量预计在2024年年增18%,达到871万台。政府推出政策,推动2025年53.3%的工业机器人国产化,为出口扩张提供了强大的国内市场平台。日本的服务机器人产业预计在2029年将成长两倍,因为严重的劳动力短缺和文化认同推动了老年护理和旅馆业的应用。韩国企业集团正在利用其在消费性电子产品领域的专业知识,开发低成本的国产机器人,将该地区定位为製造中心和需求中心。
欧洲拥有庞大的安装基数,但由于严格的监管,成长正在放缓。 ISO 10218 和欧盟医疗设备法规的更新将增加合规支出,同时也将为欧洲供应商在出口市场树立全球标竿。德国拥有 79% 的专业应用服务机器人供应商,预计到 2028 年将引领欧洲服务机器人的普及。该地区的竞争优势在于其精密工程和功能安全专业知识,这使其能够在受监管的行业中获得高利润。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- 医疗保健、物流和农业领域对自动化的需求不断增长
- 劳动力短缺和人口老化加剧
- 人工智慧与感测器的快速整合降低了机器人TCO
- 机器人即服务 (RaaS) 订阅推动中小企业采用
- 护理辅助机器人的养老保险报销
- 暗店微型仓配热潮需要 AMR
- 市场限制
- 资本投资和维护成本高
- 安全和网路安全合规的负担
- 锂电池运输规则限制移动机器人
- 解决消费机器人Start-Ups的创投资金问题
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管格局
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 替代品的威胁
第五章市场规模及成长预测
- 按应用领域
- 专业的
- 现场机器人
- 专业清洁
- 检查和维护
- 建筑和拆除
- 物流系统
- 医疗机器人
- 救援和安全
- 防御机器人
- 水下系统
- 动力人类体外骨骼
- 公关机器人
- 个人/家庭
- 家用机器人
- 娱乐机器人
- 老年人和残障人士支持
- 专业的
- 按组件
- 硬体
- 感应器
- 致动器
- 控制器和驱动器
- 电力系统
- 软体
- 作业系统和中介软体
- 人工智慧和分析演算法
- 服务(RaaS、整合、维护)
- 硬体
- 按运转环境
- 地面以上
- 航空摄影/无人机
- 海洋/水下
- 行动性
- 移动/自主
- 固定型
- 按最终用户产业
- 医疗保健和医学
- 物流与仓储
- 农业
- 建筑和拆除
- 国防和安全
- 饭店和零售
- 教育和娱乐
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 印度
- 澳洲
- ASEAN
- 其他亚太地区
- 中东和非洲
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 肯亚
- 其他非洲国家
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争态势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- iRobot Corporation
- Dematic Corp.
- Daifuku Co. Ltd.
- Swisslog Holding AG(KUKA)
- Omron Corporation
- SoftBank Robotics Group Corp.
- Pudu Robotics
- Boston Dynamics Inc.
- DJI Technology Co. Ltd.
- ABB Ltd.
- Seegrid Corporation
- Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- JBT Corporation
- SSI Schaefer AG
- Grenzebach GmbH
- Smith and Nephew plc
- Stryker Corporation
- Knightscope Inc.
- Kollmorgen Corporation
- Brokk AB
- Husqvarna AB
- Construction Robotics LLC
- Ecovacs Robotics
- Neato Robotics
- Transbotics Corporation
- Medtronic plc
- Northrop Grumman Corp.
- BAE Systems plc
- UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- SMP Robotics Systems
- Vision Robotics Corporation
- Naio Technologies SAS
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The service robotics market size reached USD 71.91 billion in 2025 and is forecast to advance to USD 175.46 billion in 2030, reflecting a 19.53% CAGR during 2025-2030.

Growth is powered by tightening labor supply in developed economies, falling robot total cost of ownership, and wider availability of Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) plans that eliminate up-front capital hurdles. Professional deployments in logistics, healthcare, and agriculture are scaling rapidly as AI-enabled perception modules lift precision and reliability benchmarks while shortening commissioning cycles.Strategic acquisitions by large technology vendors signal a transition from discretionary automation budgets to core infrastructure spending, and regulatory clarity around collaborative operation is accelerating the shift from pilot projects to enterprise-wide rollouts. A growing pipeline of patents in assistive and mobile robotics underscores an innovation cycle that is likely to sustain double-digit expansion even through macroeconomic volatility.
Global Service Robotics Market Trends and Insights
Growing Demand for Automation in Healthcare, Logistics & Agriculture
Medical robot deliveries rose 36% in 2024 to about 6,100 units on the back of surgical precision requirements and stricter infection-control protocols. Logistics operators accelerated micro-fulfillment centre rollouts, with global installations projected to top 6,600 by 2030, creating an incremental USD 36 billion addressable pool.In agriculture, hand-eye coordinated robots are forecast to reach 35.9 million units by 2030 as growers tackle chronic labour shortages. As these three verticals anchor return-on-investment cases, the service robotics market is shifting from cost offsetting toward productivity platforms that re-shape operating models. The breadth of applications also diversifies revenue exposure, insulating suppliers against cyclical swings. Cross-learning between sectors further accelerates software reuse and component standardisation, compressing development cycles and sustaining price declines.
Rising Labour Shortages & Ageing Population
Japan anticipates an 11 million worker gap by 2040 while its over-65 cohort climbs toward 40% of the population. European healthcare faces a projected 380,000 staffing shortfall by 2025, prompting hospitals to pilot care-support robots and AI triage systems. Automation penetration stands at 36% in Europe's automotive sector versus 6% across all industries, illuminating the headroom for other verticals. Labour scarcity, therefore, underpins structural demand for the service robotics market as companies pursue resilience rather than pure cost savings. Population ageing also expands consumer-facing applications in eldercare and rehabilitation, widening the market's societal relevance. These demographic realities stretch beyond economic cycles, providing long-run visibility for investors and vendors alike.
High CAPEX & Maintenance Costs
Despite declining hardware prices, construction case studies show robots can trail conventional methods on pure cost metrics even while delivering nearly threefold productivity gains. Lifecycle uncertainties around battery replacement, sensor recalibration, and software licensing complicate budgeting for non-specialists. Mobile platforms face additional expenses for mapping and localisation, particularly where LiDAR or visual SLAM infrastructure is sparse. Many SMEs lack multi-year ROI frameworks, leading to conservative investment postures that slow penetration in price-sensitive regions. Vendors are countering by standardising components and bundling predictive-maintenance analytics, but widespread perception of upfront cost risk remains a drag on the service robotics market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid AI-Sensor Convergence Lowers Robot TCO
- Robot-as-a-Service Subscriptions Unlock SME Adoption
- Safety-Cybersecurity Compliance Burden
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Professional service robots controlled 72% of the service robotics market in 2024, anchored by proven ROI in logistics, cleaning, and inspection assignments. Within this cohort, medical robots are set to capture the highest growth at a 23.4% CAGR to 2030, buoyed by hospital demand for minimally invasive surgery and stringent infection-control protocols. The segment benefits from expanding insurance reimbursements and growing clinical evidence that robots reduce complication rates, which collectively shortens hospital payback periods. Personal and domestic units, while smaller, continue to find adoption in floor-care and companionship roles that prime consumer familiarity with robotics.
Growing patent volumes in assistive technologies point to a widening spectrum of healthcare applications, from rehabilitation exoskeletons to AI-enabled diagnostic aides. This innovation pipeline suggests that the service robotics market size for medical subsegments could outpace the broader aggregate once regulatory bottlenecks ease. Cross-pollination between industrial and clinical development teams is also raising component commonality, helping lower costs and lifting vendor margins. Consequently, medical deployments are evolving from experimental assets into mission-critical hospital infrastructure
Hardware remained the revenue backbone with a 65.3% share of the service robotics market size in 2024. Sensors, actuators, and batteries dominate the bill of materials and still account for most cost reductions achieved via scale manufacturing. Yet, software is projected to surge at a 22.1% CAGR through 2030 as cloud runtime environments, fleet-orchestration layers, and AI inference engines become primary differentiators.
The shift mirrors enterprise IT trends where recurring licences eclipse one-time hardware margins. Vendors offering proprietary operating systems unlock stickier revenue and gather data to refine algorithms continuously. As integration complexities shrink, buyers increasingly evaluate platforms on software flexibility rather than payload capacity. Over the forecast horizon, services such as RaaS, predictive maintenance, and workflow optimisation are expected to evolve into a third value pillar that complements hardware and software in the service robotics market.
The Service Robotics Market is Segmented by Field of Application (Professional, Personal/Domestic), Component (Hardware, Software, and More), Operating Environment (Ground, Aerial / UAV, and More), Mobility (Mobile / Autonomous, Stationary / Fixed-Base), End-User Industry (Healthcare and Medical, Logistics and Warehousing, and More), and by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America held 34.5% of the global service robotics market in 2024, underpinned by mature automation infrastructure, favourable tax incentives, and robust venture funding that hit USD 6.4 billion in 2024. Enterprise users are migrating from pilot fleets to building-wide rollouts, and new RaaS models are accelerating penetration among mid-sized manufacturers. Regulatory agencies have clarified collaborative-robot safety expectations, reducing compliance ambiguity and encouraging faster procurement cycles. Public-sector demand is also materialising through defence and infrastructure modernisation initiatives that require autonomous inspection capabilities.
Asia-Pacific is projected to record the fastest 19.6% CAGR, led by China's production of 8.71 million service robots in 2024, an 18% year-on-year increase. Government policies promoting 53.3% localisation of industrial robots by 2025 provide a strong home-market platform for export expansion. Japan's service robotics industry is on course to triple by 2029 as acute labour shortages and cultural acceptance drive adoption across eldercare and hospitality. South Korean conglomerates are funneling consumer electronics expertise into low-cost domestic robots, positioning the region as both a manufacturing hub and a demand centre.
Europe accounts for a sizeable installed base but grows at a steadier pace given stringent regulatory regimes. The updated ISO 10218 and EU Medical Device Regulation increase compliance spending, yet they also set global benchmarks that European vendors leverage in export markets. Germany hosts 79% of its service-robot suppliers in professional applications and is projected to lead European service-robotics adoption by 2028. The region's competitive edge lies in high-precision engineering and functional-safety know-how, which fetches premium margins in regulated industries.
- iRobot Corporation
- Dematic Corp.
- Daifuku Co. Ltd.
- Swisslog Holding AG (KUKA)
- Omron Corporation
- SoftBank Robotics Group Corp.
- Pudu Robotics
- Boston Dynamics Inc.
- DJI Technology Co. Ltd.
- ABB Ltd.
- Seegrid Corporation
- Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- JBT Corporation
- SSI Schaefer AG
- Grenzebach GmbH
- Smith and Nephew plc
- Stryker Corporation
- Knightscope Inc.
- Kollmorgen Corporation
- Brokk AB
- Husqvarna AB
- Construction Robotics LLC
- Ecovacs Robotics
- Neato Robotics
- Transbotics Corporation
- Medtronic plc
- Northrop Grumman Corp.
- BAE Systems plc
- UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- SMP Robotics Systems
- Vision Robotics Corporation
- Naio Technologies SAS
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing demand for automation in healthcare, logistics and agriculture
- 4.2.2 Rising labour shortages and ageing population
- 4.2.3 Rapid AI-sensor convergence lowers robot TCO
- 4.2.4 Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) subscriptions unlock SME adoption
- 4.2.5 Eldercare insurance reimbursements for assistive robots
- 4.2.6 Dark-store micro-fulfilment boom needs AMRs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX and maintenance costs
- 4.3.2 Safety-cybersecurity compliance burden
- 4.3.3 Lithium-battery shipping rules limit mobile robots
- 4.3.4 VC funding correction for consumer-robotics start-ups
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7.5 Threat of Substitutes
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Field of Application
- 5.1.1 Professional
- 5.1.1.1 Field Robots
- 5.1.1.2 Professional Cleaning
- 5.1.1.3 Inspection and Maintenance
- 5.1.1.4 Construction and Demolition
- 5.1.1.5 Logistics Systems
- 5.1.1.6 Medical Robots
- 5.1.1.7 Rescue and Security
- 5.1.1.8 Defense Robots
- 5.1.1.9 Underwater Systems
- 5.1.1.10 Powered Human Exoskeletons
- 5.1.1.11 Public-Relation Robots
- 5.1.2 Personal / Domestic
- 5.1.2.1 Domestic Task Robots
- 5.1.2.2 Entertainment Robots
- 5.1.2.3 Elderly and Handicap Assistance
- 5.1.1 Professional
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.2.1.1 Sensors
- 5.2.1.2 Actuators
- 5.2.1.3 Controllers and Drives
- 5.2.1.4 Power Systems
- 5.2.2 Software
- 5.2.2.1 Operating Systems and Middleware
- 5.2.2.2 AI and Analytics Algorithms
- 5.2.3 Services (RaaS, Integration, Maintenance)
- 5.2.1 Hardware
- 5.3 By Operating Environment
- 5.3.1 Ground
- 5.3.2 Aerial / UAV
- 5.3.3 Marine / Underwater
- 5.4 By Mobility
- 5.4.1 Mobile / Autonomous
- 5.4.2 Stationary / Fixed-Base
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Healthcare and Medical
- 5.5.2 Logistics and Warehousing
- 5.5.3 Agriculture
- 5.5.4 Construction and Demolition
- 5.5.5 Defense and Security
- 5.5.6 Hospitality and Retail
- 5.5.7 Education and Entertainment
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 APAC
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 ASEAN
- 5.6.4.7 Rest of APAC
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 UAE
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Kenya
- 5.6.5.2.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 iRobot Corporation
- 6.4.2 Dematic Corp.
- 6.4.3 Daifuku Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Swisslog Holding AG (KUKA)
- 6.4.5 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.6 SoftBank Robotics Group Corp.
- 6.4.7 Pudu Robotics
- 6.4.8 Boston Dynamics Inc.
- 6.4.9 DJI Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.10 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Seegrid Corporation
- 6.4.12 Intuitive Surgical Inc.
- 6.4.13 JBT Corporation
- 6.4.14 SSI Schaefer AG
- 6.4.15 Grenzebach GmbH
- 6.4.16 Smith and Nephew plc
- 6.4.17 Stryker Corporation
- 6.4.18 Knightscope Inc.
- 6.4.19 Kollmorgen Corporation
- 6.4.20 Brokk AB
- 6.4.21 Husqvarna AB
- 6.4.22 Construction Robotics LLC
- 6.4.23 Ecovacs Robotics
- 6.4.24 Neato Robotics
- 6.4.25 Transbotics Corporation
- 6.4.26 Medtronic plc
- 6.4.27 Northrop Grumman Corp.
- 6.4.28 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.29 UBTECH Robotics Inc.
- 6.4.30 SMP Robotics Systems
- 6.4.31 Vision Robotics Corporation
- 6.4.32 Naio Technologies SAS
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment











