 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1850217
行动回程:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Mobile Backhaul - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
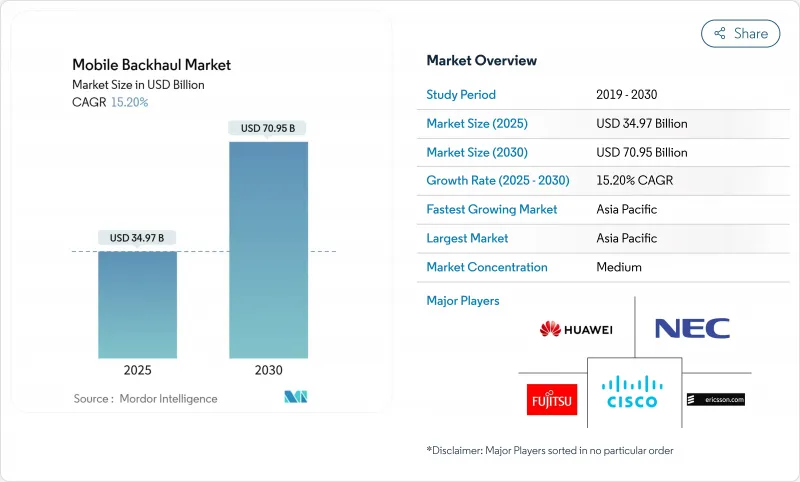
预计到 2025 年,行动回程市场规模将达到 349.7 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 709.5 亿美元,预测期(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 15.20%。
智慧型手机普及率的提高、影片串流媒体的爆炸式增长以及密集部署的5G网路正推动着5G市场的发展,这些部署对每个基地台每个小区10Gbps乃至即将达到100Gbps的容量提出了更高的要求。营运商正在用光纤和高容量无线链路取代铜线,而中立主机模式则减少了重复建设,预计2020年至2025年间,5G投资将超过1.1兆美元。开放式架构、软体定义传输和边缘运算对回程传输的效能和安全性提出了新的要求,而现成的硬体则可以降低生命週期成本。亚太地区以35%的收入贡献位居榜首,并维持着17.3%的最快复合年增长率,这主要得益于中国、日本、韩国和印度部署了数百万个小型基地台。通讯业者目前正在将光纤的规模优势与微波、毫米波和低地球轨道(LEO)卫星传输相结合,以填补覆盖盲点并加速部署。
全球行动回程市场趋势与洞察
行动数据流量增加和智慧型手机的广泛普及
预计智慧型手机用户每月平均数据使用量将从2023年的21GB激增至2029年的56GB,其中影片流量占行动流量的75%。区域差异日益显现:北美用户每月数据使用量可能达到66GB,而撒哈拉以南非洲用户则接近23GB,这迫使营运商设计针对不同国家的专用回程传输链路组合。将光纤干线与高频宽微波链路连接的混合拓扑结构目前在都市区高密度化建设中占据主导地位,因为它们无需耗费大量时间进行道路挖掘即可满足容量需求。小型基地台的普及增加了数千条短距离链路,并刺激了对能够即时调整每个站点容量的自动化网路管理平台的新投资。
快速部署 5G 推动容量需求
5G丛集将基地台密度从每平方公里4-5个站点提高到每平方公里40-50个站点,回程传输终端数量也在增加。光是中国预计就将兴建超过60万个5G大型基地台台和小型基地台,是4G基地台数量的1.3-1.5倍。每个5G小区现在需要10Gbps的上行链路和低于5毫秒的严格延迟,这加速了基于70/80GHz E频段无线电和光纤的时序敏感型网路(TSN)的普及。资金压力促使许多业者转向共用基地台和租赁暗纤,以降低初始成本,同时确保向100Gbps介面的升级路径。
光纤和频谱成本方面的高资本投资
在人口密集的城市地区铺设光纤的成本可能超过每公里10万美元,而道路通行证稀缺地区的成本更是飙升。此外,4G和5G频宽重迭时,不断上涨的电价也会导致宏基地台的电力消耗翻倍,进而推高营运成本。在新兴经济体,低利率融资管道有限,减缓了光纤部署速度,迫使通讯业者即使从长远经济角度来看光纤更具优势,也只能依赖微波技术。结果是城乡网路体验品质不均,阻碍了数位包容的目标实现。
细分市场分析
凭藉其无与伦比的容量和低延迟,光纤链路将在2024年占据行动回程市场55%的份额。这一份额在2024年192亿美元的行动回程市场规模中占据最大份额。然而,受都市区密集化和突发事件的推动,预计到2030年,这一差距将缩小,复合年增长率将达到16.4%,因为这些事件需要快速推出。通讯业者正在将70/80 GHz E波段无线电与租用的暗纤干线进行网状连接,在避免昂贵的土木工程的同时,实现单跳10 Gbps的传输速率。
混合架构如今已成为主流。虽然光纤仍然是核心聚合的首选介质,但微波和毫米波正服务于边缘的小型基地台和企业设施,在这些地方,由于授权或地理限制,无法进行沟槽铺设。新兴的W波段和D波段链路预计在1-2公里范围内实现多千兆Gigabit的吞吐量,与光纤形成互补,适用于高密度群集。在人口密度较低的地区,营运商正在将低地球轨道卫星回程传输熔接至微波环网中,以在不超出预算限制的情况下实现连续覆盖。这种灵活性有助于营运商在长期内保持市场竞争力。
微波无线电技术将在2024年占据行动回程市场41%的份额,这反映了其数十年来在实际应用中久经考验的可靠性。供应商已采用链路聚合技术来聚合非连续通道,并将频谱效率提升至16 bps/Hz。目前小型基地台回程传输设备收入占比很小,但随着体育场馆、购物中心和交通枢纽等场所采用室内5G网络,预计其年复合成长率将达到17.4%。
行动回程市场正向整合接取回回程传输节点。捆绑自组织网路软体的供应商正在赢得竞标,因为它可以减少负载容量并优化复杂环境中的链路对齐。
行动回程市场报告按配置(有线[光纤/光纤、铜缆/DSL]、无线[微波、毫米波、其他])、设备类型(路由器和交换器、微波无线电、其他)、服务类型(专业服务、託管服务、其他)、网路架构(大型基地台回程传输、其他)、最终用户(行动通讯业者、主机和主机
区域分析
亚太地区占据行动回程市场35%的份额,并正以17.3%的复合年增长率快速增长,这主要得益于对5G的大量投资、政府补贴以及密集的城市人口。中国、日本和韩国已在主要城市实现了独立组网(SA)5G的全面覆盖,从而刺激了对绕过钻井瓶颈的10Gbps微波链路的需求。印度近期举行的频谱竞标释放了高速公路沿线和二线城市的光纤部署热潮,营运商正在试点卫星-微波混合方案,以覆盖喜马拉雅山脉和岛屿地区。政府为农村光纤建设提供的补贴计画也进一步推动了这一趋势。
儘管北美地区规模较小,但在虚拟化无线存取网路 (RAN) 和暗纤聚合领域却处于创新领先地位。 Verizon 和 T-Mobile 于 2024 年收购了区域光纤营运商,以增强其光纤网路覆盖范围,并确保可扩展的回程传输,从而支援固定无线存取部署。美国联邦通讯委员会 (FCC) 设立的 90 亿美元 5G 基金将激励偏远地区的行动通信基地台升级,并指导在地形不适合开挖的情况下投资微波和卫星回程传输。随着营运商将光纤重复用于Gigabit宽频和行动通信基地台链路,固移融合将加速,资本回报率也将提高。
成熟的欧洲市场正在努力平衡严格的监管改革与泛欧5G走廊的建设。基础设施共用框架正在减少重复的资本支出,而官民合作关係则为跨境光纤线路提供资金,这对于互联货运等低延迟服务至关重要。同时,中东正快速推进其智慧城市愿景,该愿景依赖密集的小型基地台;非洲通讯业者则利用低地球轨道卫星群为偏远地区的网路回程传输传链路。 5G已在17个拉丁美洲国家推出,通讯业者组成联盟,租赁海底光缆的容量,并透过微波链路将其分发到内陆,从而增强国家网路的韧性。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 行动数据流量不断成长,智慧型手机普及率不断提高。
- 快速部署5G网路增加了容量需求
- 云端原生和开放式无线接取网路架构
- 用于农村地区的卫星低地球轨道回程传输
- 公共产业光纤租赁和专用LTE网络
- 市场限制
- 光纤和频谱方面的高资本投资
- 微波频谱授权的复杂性
- 超低延迟同步的挑战
- SDN回程传输网路安全风险
- 价值链/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 投资分析
- 新冠疫情对市场的影响
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 透过部署
- 有线
- 光纤
- 铜线/DSL
- 无线的
- 微波
- 毫米波(E波段和V波段)
- 卫星
- 自由空间光
- 有线
- 透过装置
- 路由器和交换机
- 微波无线电
- 光纤传输设备
- 小型基地台回程传输设备
- 其他的
- 按服务类型
- 专业服务
- 託管服务
- 安装与集成
- 维护和支援
- 透过网路架构
- 大型基地台回程传输
- 小型基地台回程传输
- 云端无线存取网/去程传输
- 最终用户
- 行动网路营运商
- 中立主机和铁塔公司
- 网际网路服务供应商
- 私人公司和公共产业
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东
- GCC
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介(包括全球概览)
- Market level overview
- Huawei Technologies Co.
- Ericsson AB
- Nokia Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Cisco Systems
- Fujitsu Limited
- Aviat Networks
- Ceragon Networks Ltd.
- BridgeWave Communications
- ATandT Inc.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Juniper Networks
- Siklu Communication Ltd.
- Infinera Corporation
- CommScope Holding Company
- Telefonica SA
- Intelsat SA
- Parallel Wireless
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Mobile Backhaul Market size is estimated at USD 34.97 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 70.95 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.20% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Growth is propelled by escalating smartphone penetration, the sharp rise in video streaming, and dense 5G rollouts that demand 10 Gbps and soon 100 Gbps per cell per site capacity. Operators are swapping copper lines for fiber and high-capacity wireless links, while neutral-host models reduce duplication as 5G investments top USD 1.1 trillion between 2020 and 2025. Open architectures, software-defined transport, and edge compute place new performance and security pressures on backhaul, yet they can lower life-cycle costs through commercial off-the-shelf hardware. Asia Pacific leads with a 35% revenue contribution and shows the fastest regional CAGR at 17.3% as China, Japan, South Korea, and India install millions of small cells. Operators everywhere now blend fiber's scale with microwave, millimeter-wave, and low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellite hops to fill coverage gaps and accelerate rollouts.
Global Mobile Backhaul Market Trends and Insights
Growing Mobile Data Traffic & Smartphone Adoption
Average monthly data per smartphone is forecast to soar from 21 GB in 2023 to 56 GB by 2029, with video expected to account for 75% of mobile traffic. Regional divergence is emerging: North American users may hit 66 GB per month while Sub-Saharan Africa lingers near 23 GB, forcing operators to engineer country-specific backhaul mixes. Hybrid topologies that splice fiber trunks with high-band microwave hops now dominate urban densification because they meet capacity needs without prolonged street-dig permitting. Small-cell proliferation adds thousands of short-haul links, prompting fresh investment in automated network-management platforms that can tune capacity per site in real time.
Rapid 5G Rollout Driving Capacity Needs
Base-station density is climbing from 4-5 to 40-50 sites per km2 in 5G clusters, multiplying backhaul terminations. China alone is building more than 600,000 5G macro and small cells, a count projected to outstrip 4G by 1.3-1.5 times . Each 5G cell now requires 10 Gbps uplinks and stringent latency of sub-5 ms, accelerating the adoption of 70/80 GHz E-band radios and time-sensitive networking over fiber. Capital stress is nudging many operators toward shared towers and leased dark fiber, lowering up-front costs while ensuring upgrade paths to 100 Gbps interfaces.
High Capex for Fiber & Spectrum Costs
Fiber trenching in dense cities can run beyond USD 100,000 per Kilometer, a figure that climbs sharply where road-opening permits are scarce. Rising electricity prices also double macro-site power draw when 4G and 5G bands overlap, inflating operational overhead. In developing economies, limited access to low-interest financing delays fiber build-outs, forcing carriers to rely on microwave even where long-term economics favor fiber. The result is uneven quality-of-experience across urban and rural divides, hindering digital-inclusion goals.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cloud-Native & Open RAN Architectures
- Satellite LEO Backhaul for Rural Reach
- SDN Backhaul Cybersecurity Risks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fiber-based links constituted 55% of the mobile backhaul market in 2024 due to their unrivalled capacity and low latency. This share translates to the largest deployment slice of the mobile backhaul market size at USD 19.2 billion in 2024. Wireless alternatives, however, are set to post a 16.4% CAGR through 2030, narrowing the gap as urban densification and pop-up events demand rapid turn-ups. Operators mesh 70/80 GHz E-band radios with leased dark fiber trunks, delivering 10 Gbps per hop while avoiding costly civil works.
Hybrid architectures are now standard: fiber remains the preferred medium for core aggregation, but microwave and millimeter-wave serve edge small cells and enterprise venues where permits or geography stall trenching. Emergent W-band and D-band links promise multi-gigabit throughput over 1-2 km, complementing fiber for dense clusters. In sparsely populated regions, operators splice LEO satellite backhaul into microwave rings, creating contiguous coverage without exceeding budget ceilings. This flexibility underpins the long-term competitiveness of the mobile backhaul market.
Microwave radios held 41% of the mobile backhaul market size in 2024, reflecting decades of field-proven reliability. Vendors have pushed spectral efficiency to 16 bps/Hz while adding link-bonding schemes that aggregate non-contiguous channels. Small cells backhaul gear, though only a fraction of revenue today, is set for a 17.4% CAGR as stadiums, malls, and transport hubs adopt indoor 5G.
The mobile backhaul market is witnessing a pivot toward integrated access and backhaul (IAB), where a 28 GHz radio simultaneously serves user devices and relays traffic upstream. This reduces rooftop congestion and simplifies zoning. Millimeter-wave chipset advances cut power draw by 30% since 2023, enabling pole-mount and window-mount nodes that require minimum site work. Vendors that bundle self-organizing-network software are winning tenders because they lower truck rolls and optimize link alignment in cluttered environments.
The Mobile Backhaul Market Report is Segmented by Deployment (Wired [Fiber/Optical and Copper/DSL], Wireless [Microwave, Millimetre-Wave, and More]), Equipment Type (Routers and Switches, Microwave Radios, and More), Service Type (Professional Services, Managed Services, and More), Network Architecture (Macro-Cell Backhaul, and More), End-User (Mobile Network Operators, Neutral-Host and Tower Companies, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific commands 35% of the mobile backhaul market, expanding at 17.3% CAGR thanks to outsized 5G investments, state subsidies, and dense urban populations. China, Japan, and South Korea already blanket major cities with standalone 5G, driving steep demand for 10 Gbps microwave hops that skirt excavation bottlenecks. India's recent spectrum auctions have unleashed a fiber-laying spree along highways and into tier-2 cities, while operators also pilot satellite-plus-microwave hybrids for Himalayan and island coverage. Government schemes that underwrite rural fiber further sustain momentum.
North America, while smaller by volume, leads innovation in virtualized RAN and dark-fiber aggregation. Verizon and T-Mobile bolstered their optical footprints by acquiring regional fiber players in 2024, locking in scalable backhaul to support fixed-wireless access rollouts. The Federal Communications Commission's USD 9 billion 5G Fund incentivizes cell-site upgrades in remote counties, channeling investments toward microwave and satellite backhaul where terrain hampers trenching. Fixed-mobile convergence accelerates as operators reuse fiber for both gigabit broadband and cell-site uplinks, amplifying return on capital.
Europe's mature markets balance stringent regulatory reviews with a push for pan-EU 5G corridors. Infrastructure-sharing frameworks lower duplicate capex, while public-private partnerships finance cross-border fiber routes vital for low-latency services such as connected freight. Meanwhile, the Middle East fast-tracks smart-city visions that rely on dense small-cell grids, and African carriers tap LEO constellations to backhaul remote coverage islands. Latin America sees 5G launches in 17 countries, with carriers forming consortia to lease submarine-cable capacity and distribute it inland via microwave chains, weaving resilience into national networks.
- Market level overview
- Huawei Technologies Co.
- Ericsson AB
- Nokia Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Cisco Systems
- Fujitsu Limited
- Aviat Networks
- Ceragon Networks Ltd.
- BridgeWave Communications
- ATandT Inc.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Juniper Networks
- Siklu Communication Ltd.
- Infinera Corporation
- CommScope Holding Company
- Telefonica S.A.
- Intelsat S.A.
- Parallel Wireless
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing mobile data traffic and smartphone adoption
- 4.2.2 Rapid 5G rollout driving capacity needs
- 4.2.3 Cloud-native and Open RAN architectures
- 4.2.4 Satellite LEO backhaul for rural reach
- 4.2.5 Fiber leasing by utilities and private LTE networks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capex for fiber and spectrum costs
- 4.3.2 Microwave spectrum licensing complexity
- 4.3.3 Ultra-low-latency synchronisation challenges
- 4.3.4 SDN backhaul cybersecurity risks
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
- 4.9 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment
- 5.1.1 Wired
- 5.1.1.1 Fiber/Optical
- 5.1.1.2 Copper/DSL
- 5.1.2 Wireless
- 5.1.2.1 Microwave
- 5.1.2.2 Millimetre-Wave (E- and V-band)
- 5.1.2.3 Satellite
- 5.1.2.4 Free-Space Optics
- 5.1.1 Wired
- 5.2 By Equipment Type
- 5.2.1 Routers and Switches
- 5.2.2 Microwave Radios
- 5.2.3 Optical Transport Equipment
- 5.2.4 Small-Cell Backhaul Equipment
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Service Type
- 5.3.1 Professional Services
- 5.3.2 Managed Services
- 5.3.3 Installation and Integration
- 5.3.4 Maintenance and Support
- 5.4 By Network Architecture
- 5.4.1 Macro-Cell Backhaul
- 5.4.2 Small-Cell Backhaul
- 5.4.3 Cloud RAN/Fronthaul
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Mobile Network Operators
- 5.5.2 Neutral-Host and Tower Companies
- 5.5.3 Internet Service Providers
- 5.5.4 Private Enterprises and Utilities
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Spain
- 5.6.3.5 Italy
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 GCC
- 5.6.5.2 Turkey
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.6.3 Egypt
- 5.6.6.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview
- 6.4.1 Market level overview
- 6.4.2 Huawei Technologies Co.
- 6.4.3 Ericsson AB
- 6.4.4 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.5 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.6 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.7 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.8 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.4.9 Aviat Networks
- 6.4.10 Ceragon Networks Ltd.
- 6.4.11 BridgeWave Communications
- 6.4.12 ATandT Inc.
- 6.4.13 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.14 Ciena Corporation
- 6.4.15 Juniper Networks
- 6.4.16 Siklu Communication Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Infinera Corporation
- 6.4.18 CommScope Holding Company
- 6.4.19 Telefonica S.A.
- 6.4.20 Intelsat S.A.
- 6.4.21 Parallel Wireless
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment










