 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1850361
行动卫星服务:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Mobile Satellite Services - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
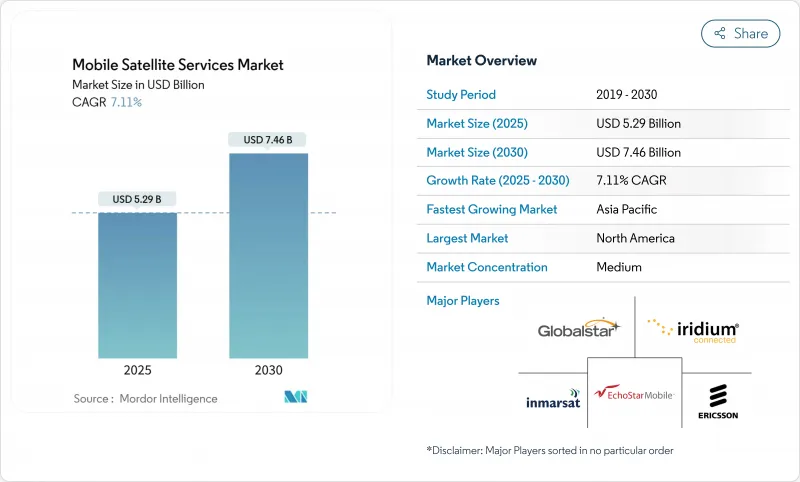
预计到 2025 年,行动卫星服务市场规模将达到 52.9 亿美元,到 2030 年将扩大到 74.6 亿美元,年复合成长率为 7.12%。
从以语音为中心的链路到宽频和直接设备间连接的快速转变正在重塑需求模式,同时降低对地面电波回程传输的依赖。 3GPP 非地面网路标准的商业化、低地球轨道 (LEO)卫星群发射成本的急剧下降,以及农村和沿海地区持续存在的连接缺口,都在扩大移动卫星服务的市场机会。随着安全主权链路从可自由支配的支出转变为战略基础设施,政府采购週期正在加快;企业数位化专案也开始将通讯容量纳入预算,作为应对光纤和行动电话中断的标准保障。此外,来自垂直整合的 LEO 营运商日益激烈的竞争,正迫使传统的地球静止轨道卫星营运商对其卫星群技术进行现代化改造,采用软体定义有效载荷,并将多轨道容量打包到基本契约中。
全球行动卫星服务市场趋势与洞察
卫星网路和地面移动网路的融合日益加深
主要亮点
- 随着美国联邦通讯委员会(FCC) 于 2024 年采纳「太空补充覆盖」框架,允许在地面移动频段开展二次性卫星业务,天基网路与地面网路之间的无缝切换已从概念迈向早期商业性现实。 AT&T 和 Verizon 已开启使用 AST Space Mobile 的L波段和 S 波段有效载荷进行全国漫游试验的大门,以便在基地台故障时提供简讯服务。卫星通讯业者的批发收益得以增加,而通讯业者无需资本支出即可增强其覆盖范围。由此形成良性循环,模糊了地面电波网路和非地面电波网路之间的传统界限,并扩大了行动卫星服务的市场。
政府和国防部门对安全链路的需求日益增长
在多次地缘政治衝突暴露了对外国业者的依赖之后,对自主连结的需求激增。欧盟委员会核准了106亿欧元(113亿美元)的多轨道IRIS2项目,该项目将为政府机构、紧急服务部门和关键基础设施提供加密宽频。美国、日本和印度也有类似的采购计划,这些计划都明确要求采用抗量子加密和多轨道冗余技术。 SES于2025年初完成了对国际通讯卫星组织(Intelsat)的收购,交易金额达31亿美元,此举增强了其政府业务组合,并透过单一管道合约提供了地球同步轨道、城域轨道和低地球轨道三层网路容量。因此,高利润的政府合约支撑着卫星群的升级,并扩大了行动卫星服务市场的潜在收益来源。
传统MSS系统之间缺乏互通性
由于L波段、S波段和Ku波段闸道之间缺乏互通性,拥有跨洲机队的公司仍依赖多个终端。儘管行动卫星服务协会(MSSA)于2024年成立,旨在倡导漫游标准,但晶片组碎片化问题依然存在,推高了货运公司和航空公司在多个地区的总体拥有成本。如果没有无缝漫游,行动卫星服务市场的价值仍然低于地面电波行动电话,后者只需一张SIM卡即可提供全球存取。多模终端正在兴起,但认证、天线设计的妥协以及有限的生产规模都减缓了其普及速度。
细分市场分析
到2024年,数据连接将占总收入的63.4%,这表明宽频和串流媒体服务在行动卫星服务市场中正成为客户预算的核心。各公司正在预留高吞吐量电路用于回程传输,例如视讯监控、船员社会福利存取和远端软体更新等,这些服务原本无法使用。语音服务在海上遇险和驾驶座安全领域仍占有一席之地,但按频宽的合约正在取代按分钟收费。物联网/机器对机器(IoT/M2M)合约成长最快,到2030年复合年增长率将达到12.4%,这主要得益于农业、采矿和公共产业不断扩大其远端感测器丛集。每个新的感测器模组都能增加收益,而卫星营运成本却微乎其微。因此,儘管每个设备的平均收益较低,但物联网终端的行动卫星服务市场规模预计将显着成长。
视讯和数据的成长正推动营运商采用再生有效载荷,使其能够在卫星上处理流量并减少地面瓶颈。中国发射了12颗人工智慧增强型低地球轨道卫星,吞吐量达744 TOPS,展示了轨道边缘运算技术。该技术透过提高频谱效率,使营运商无需额外频谱分配即可自由出售额外的吞吐量。灵活的软体定义枢纽使得容量能够在几分钟内从季节性航道重新部署到飓风灾后重建区,从而提高利用率。向容量即服务合约的转变也激励奖励提供效能保证,而不是像云端处理那样提供尽力而为的连结。总而言之,这些转变巩固了数据的主导地位,并支持了到2030年数据将占行动卫星服务市场60%的预测。
行动卫星服务市场报告按服务类型(语音、数据、宽频、其他)、频率类型( L波段、S 波段、其他)和最终用户垂直行业(海事、航空、政府和国防、其他)进行细分。
区域分析
2024年,北美在行动卫星服务市场维持了38.1%的份额,这主要得益于国防部的一项大型合约、完善的监管机制以及早期进行的直接设备连接试验。美国占了该地区收益的大部分,这主要得益于能源管道和紧急应变网路中的卫星广播服务。加拿大透过在其北部地区推行普遍服务指令扩大了需求,而墨西哥则利用共用卫星容量连接山区社区。区域C波段卫星补给增加了下行频宽,使营运商无需发射新的太空船即可扩展面向消费者的宽频服务。
亚太地区预计将以10.2%的复合年增长率成为所有地区中最快的,这主要得益于各国政府追求数位主权以及私人企业集团推进物流数位化。卫星发射率保持强劲,KDDI等区域企业已将「au Starlink Direct」商业化,向日本山区一般智慧型手机用户发送讯息。中国透过增设高通量Ka波段卫星来提升通讯能力,以支持其「一带一路」倡议;印度对Bharti Airtel与SpaceX达成协议以扩大农村宽频覆盖范围表示欢迎。东南亚群岛国家签署了一项采购框架协议,将灾害救援、渔业监测和学校网路连接等能力整合到一份主权合约中。
在欧洲,IRIS2安全计画推动了强劲的机构需求。欧洲全球导航卫星系统局加快了对量子安全上行链路研究的津贴,SpaceRISE联盟开始建立一个结合地球同步轨道(GEO)、中地球轨道(MEO)和低地球轨道(LEO)的多轨道网路。中东通讯业者与欧洲船队合作,在红海新航线上提供海上通讯;非洲通讯业者从欧洲供应商采购Ka波段容量,以弥补国内光纤网路的不足。拉丁美洲在飓风区部署了抗灾卫星网路;安第斯山脉国家则采用L波段手持通讯电话,用于微波链路无法覆盖的地区进行紧急应变。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 卫星和地面移动网路融合的进展
- 政府和国防当局对安全链路的需求日益增长
- 远端物联网/机器对机器资产的连接需求日益增长
- 抗灾通讯计画的激增
- 3GPP-NTN 标准支援直接向设备发送 MSS 讯号
- 低地球轨道窄频星座可减少延迟和成本。
- 市场限制
- 传统MSS系统之间缺乏互通性
- 加强对频谱和轨道槽位的监管
- 相位阵列天线会增加用户终端成本。
- 太空碎片减缓规则增加了发射保险成本
- 价值链分析
- 监管格局
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 透过服务
- 嗓音
- 数据
- 宽频
- IoT/M2M
- 按频宽
- L波段
- S波段
- Ku波段
- Ka波段
- 按最终用户产业
- 海上
- 航空
- 政府和国防部
- 商业与能源
- 陆运
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- ASEAN
- 其他亚太地区
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 其他非洲国家
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Inmarsat plc
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- Globalstar Inc.
- EchoStar Mobile Ltd
- Thuraya Telecommunications Co.
- Intelsat SA
- ORBCOMM Inc.
- ViaSat Inc.(Incl. ViaSat UK)
- Ericsson(Satellite IoT)
- SES SA
- Eutelsat Group
- Hughes Network Systems
- OneWeb
- AST SpaceMobile
- Ligado Networks
- Telesat Lightspeed
- Skylo Technologies
- Qualcomm Inc.(Snapdragon Satellite)
- SpaceX-Starlink Direct-to-Cell
- Thales Alenia Space
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The mobile satellite services market reached USD 5.29 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise to USD 7.46 billion by 2030, advancing at a 7.12% CAGR.

Rapid migration from voice-centric links to broadband and direct-to-device connectivity is reshaping demand patterns while lowering reliance on terrestrial backhaul. Commercialisation of 3GPP non-terrestrial network standards, the sharp drop in launch costs for Low-Earth-Orbit (LEO) constellations, and persistent connectivity gaps across rural and maritime zones are expanding the mobile satellite services market opportunity. Government procurement cycles are accelerating because secure sovereign links have moved from discretionary spend to strategic infrastructure, and enterprise digitalisation programmes now budget satellite capacity as standard insurance against fibre or cellular outages. Intensifying competition from vertically integrated LEO operators is also pressuring legacy geostationary incumbents to modernise fleet technologies, adopt software-defined payloads and bundle multi-orbit capacity into usage-based contracts.
Global Mobile Satellite Services Market Trends and Insights
Rising Integration of Satellite-Terrestrial Mobile Networks
Key Highlights
- Seamless handover between space-based and ground networks moved from concept to early commercial reality after the Federal Communications Commission adopted its Supplemental Coverage from Space framework in 2024, allowing secondary satellite operations within terrestrial mobile spectrum.Mobile operators now embed satellite capacity as an automated fallback layer so subscribers retain service on the same handset when fibre backhaul, microwave, or cellular radios fail. AT&T and Verizon opened the door to nationwide roaming trials that use AST SpaceMobile's L- and S-Band payloads to provide texting when towers are down. Satellite operators gain incremental wholesale revenue, while telcos strengthen coverage maps without capital outlay. The result is a virtuous cycle that enlarges the mobile satellite services market by blurring the historical boundary between terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks.
Escalating Government and Defense Demand for Secure Links
Sovereign connectivity requirements surged after several geopolitical flashpoints exposed reliance on foreign operators. The European Commission approved EUR 10.6 billion (USD 11.3 billion) for the multi-orbit IRIS2 programme that will furnish encrypted broadband to institutions, first responders, and critical infrastructure.Similar procurement tracks in the United States, Japan, and India specify quantum-resistant encryption and multi-orbit redundancy. SES completed its USD 3.1 billion acquisition of Intelsat in early 2025 to strengthen its government portfolio and offer layered GEO-MEO-LEO capacity under single-throat contracts. High-margin government deals therefore underpin fleet upgrades and expand the reachable revenue pool for the mobile satellite services market.
Lack of Interoperability Among Legacy MSS Systems
Enterprises with transcontinental fleets still juggle multiple terminals because L-Band, S-Band, and Ku-Band gateways do not interoperate. The Mobile Satellite Services Association formed in 2024 to champion roaming standards, yet chipset fragmentation persists and drives higher total cost of ownership for shippers and airlines that traverse many footprints. Without seamless roaming, the perceived value of the mobile satellite services market remains lower than terrestrial cellular, where a single SIM offers worldwide access. Multimode terminals are emerging, but certification, antenna design compromises, and limited production scale have slowed adoption.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Connectivity Needs for Remote IoT/M2M Assets
- Surge in Disaster-Resilient Communications Programmes
- High User-Terminal Cost Due to Phased-Array Antennas
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Data connectivity accounted for 63.4% of 2024 revenue, underscoring how broadband and streaming now anchor customer budgets in the mobile satellite services market. Enterprises book high-throughput circuits to backhaul video surveillance, crew welfare access, and remote software updates that would otherwise be impossible. Voice retains a niche in maritime distress and cockpit safety, yet bandwidth-driven contracts are eclipsing per-minute billing. IoT/M2M subscriptions grew fastest and are forecast to post 12.4% CAGR to 2030 as agriculture, mining, and utilities scale remote sensor fleets. Each new sensor module adds incremental revenue at negligible satellite operating cost, making the segment strategically significant for margin expansion. The mobile satellite services market size for IoT endpoints is therefore poised to rise meaningfully despite lower average revenue per device.
Video and data growth pushes operators to adopt regenerative payloads so traffic can be processed onboard, reducing ground bottlenecks. China's launch of 12 AI-enhanced LEO satellites that execute 744 TOPS showcases orbital edge computing, where spectral efficiency gains free additional throughput for sale without extra spectrum allocation. Flexible software-defined hubs let capacity be redeployed from seasonal maritime lanes to hurricane recovery zones within minutes, improving utilisation. The transition to capacity-as-a-service contracts also incentivises operators to provide performance guarantees rather than best-effort links, a model imported from cloud computing. These shifts collectively reinforce data's primacy and validate the expectation that data will still exceed 60% of the mobile satellite services market by 2030.
The Mobile Satellite Services Market Report is Segmented by Service (Voice, Data, Broadband, and More), Frequency (L-Band, S-Band, and More), End-User Industry (Maritime, Aviation, Government and Defense, and More),
Geography Analysis
North America retained 38.1% share of the mobile satellite services market in 2024 because of large Department of Defense contracts, well-established regulatory pathways, and early direct-to-device pilots. The United States accounted for most regional revenue, buoyed by fleet broadcasts across energy pipelines and first-responder networks. Canada increased demand through universal service mandates in its northern territories, and Mexico leveraged shared satellite capacity to connect mountainous communities. Regional C-band refarming provided additional downlink bandwidth, allowing operators to widen consumer broadband offers without launching new spacecraft.
Asia Pacific is set to post a 10.2% CAGR, the fastest among all regions, as governments pursue digital sovereignty and private conglomerates digitise logistics chains. Launch rates remain brisk, and regional players such as KDDI commercialised "au Starlink Direct" to bring messaging to standard smartphones across Japan's mountainous topography. China expanded national capacity by adding high-throughput Ka-Band satellites that will serve Belt and Road shipping routes, while India welcomed agreements between Bharti Airtel and SpaceX to widen rural broadband. Southeast Asian archipelagos signed procurement frameworks that bundle capacity for disaster-relief, fisheries monitoring, and school connectivity into a single sovereign contract.
Europe experienced robust institutional demand anchored by the IRIS2 security programme. The European GNSS Agency fast-tracked grants for quantum-safe uplink research, and the SpaceRISE consortium began constructing a multi-orbit network with combined GEO, MEO, and LEO segments. Middle East operators collaborated with European fleet owners to provide maritime coverage along new Red Sea shipping lanes, and African telcos sourced Ka-Band capacity from European providers to bridge national fibre gaps. Latin America pursued disaster-resilient satellite overlays in hurricane zones, and Andean nations adopted L-Band handheld satellite phones for emergency response in terrain where microwave links are infeasible.
- Inmarsat plc
- Iridium Communications Inc.
- Globalstar Inc.
- EchoStar Mobile Ltd
- Thuraya Telecommunications Co.
- Intelsat S.A.
- ORBCOMM Inc.
- ViaSat Inc. (Incl. ViaSat U.K.)
- Ericsson (Satellite IoT)
- SES S.A.
- Eutelsat Group
- Hughes Network Systems
- OneWeb
- AST SpaceMobile
- Ligado Networks
- Telesat Lightspeed
- Skylo Technologies
- Qualcomm Inc. (Snapdragon Satellite)
- SpaceX - Starlink Direct-to-Cell
- Thales Alenia Space
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising integration of satellite-terrestrial mobile networks
- 4.2.2 Escalating government and defense demand for secure links
- 4.2.3 Growing connectivity needs for remote IoT/M2M assets
- 4.2.4 Surge in disaster-resilient communications programs
- 4.2.5 3GPP-NTN standard enabling direct-to-device MSS
- 4.2.6 LEO narrow-band constellations lowering latency and cost
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Lack of interoperability among legacy MSS systems
- 4.3.2 Tightening spectrum and orbital slot regulations
- 4.3.3 High user-terminal cost due to phased-array antennas
- 4.3.4 Space-debris mitigation rules raising launch insurance
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Voice
- 5.1.2 Data
- 5.1.3 Broadband
- 5.1.4 IoT / M2M
- 5.2 By Frequency Band
- 5.2.1 L-Band
- 5.2.2 S-Band
- 5.2.3 Ku-Band
- 5.2.4 Ka-Band
- 5.3 By End-User Industry
- 5.3.1 Maritime
- 5.3.2 Aviation
- 5.3.3 Government and Defense
- 5.3.4 Enterprise and Energy
- 5.3.5 Land Mobile
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 South America
- 5.4.2.1 Brazil
- 5.4.2.2 Argentina
- 5.4.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.3.1 Germany
- 5.4.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.3.3 France
- 5.4.3.4 Russia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.4.4.1 China
- 5.4.4.2 India
- 5.4.4.3 Japan
- 5.4.4.4 South Korea
- 5.4.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.4.5 Middle East
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.3 Turkey
- 5.4.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.4.6 Africa
- 5.4.6.1 South Africa
- 5.4.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.4.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Inmarsat plc
- 6.4.2 Iridium Communications Inc.
- 6.4.3 Globalstar Inc.
- 6.4.4 EchoStar Mobile Ltd
- 6.4.5 Thuraya Telecommunications Co.
- 6.4.6 Intelsat S.A.
- 6.4.7 ORBCOMM Inc.
- 6.4.8 ViaSat Inc. (Incl. ViaSat U.K.)
- 6.4.9 Ericsson (Satellite IoT)
- 6.4.10 SES S.A.
- 6.4.11 Eutelsat Group
- 6.4.12 Hughes Network Systems
- 6.4.13 OneWeb
- 6.4.14 AST SpaceMobile
- 6.4.15 Ligado Networks
- 6.4.16 Telesat Lightspeed
- 6.4.17 Skylo Technologies
- 6.4.18 Qualcomm Inc. (Snapdragon Satellite)
- 6.4.19 SpaceX - Starlink Direct-to-Cell
- 6.4.20 Thales Alenia Space
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment













