 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851073
货运代理:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Freight Forwarding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
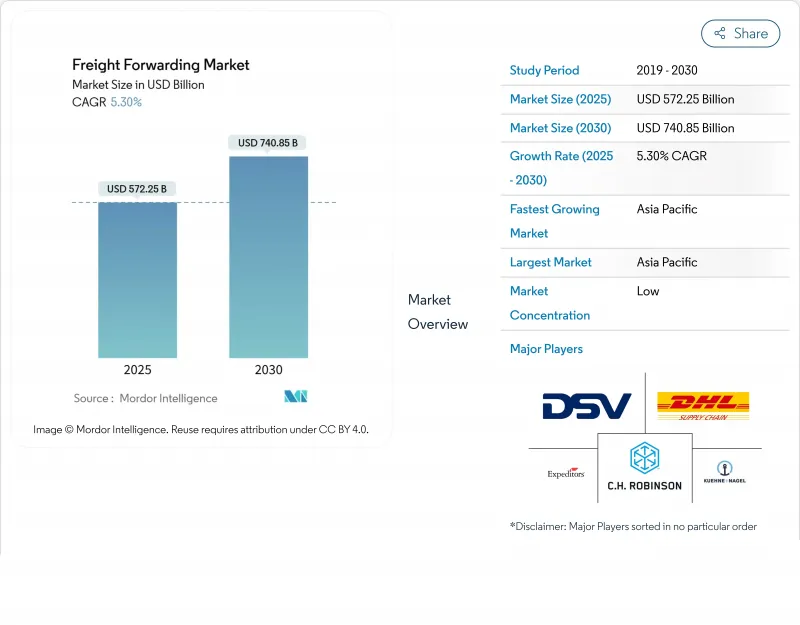
预计到 2025 年,货运市场规模将达到 5,722.5 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 7,408.5 亿美元,年复合成长率为 5.3%。
儘管地缘政治紧张局势加剧,供应链屡遭衝击,但货运量仍持续上升,这得益于数位化平台、高韧性的多式联运网络以及持续的电子商务流动。对小包裹跨境包裹货运的需求不断增长,对温控运力的持续投资,以及向近岸外包的结构性转型,都在推动各大贸易航线的货运量增长。其他影响因素包括技术应用加速、以即时视觉为核心的新型高端服务层级涌现,以及货运代理商为寻求规模优势而进行的整合。以DSV在2025年以159亿美元收购DB Schenker为首的併购活动,充分展现了规模和数据密度如何支撑货运代理市场的竞争地位。
全球货运市场趋势与洞察
跨境电子商务小包裹量快速成长
亚洲创纪录的线上消费持续推动小小包裹涌入北美市场。货运代理商正将现有设施改造为小包裹分拣中心,整合海关预清关流程,并迭加预测性关税计算工具,以消除购买环节的摩擦。如今,服务速度而非单纯的成本已成为路线选择的主要驱动因素,承运商正在扩大每週跨太平洋特快专线的营运规模。诸如小包裹层级的同位素可视性和品牌退货等增值功能,正帮助现有企业抵御纯粹的小包裹整合商的竞争,捍卫市场份额。
近岸外包主导的製造业转型
墨西哥、波兰和土耳其的邻近製造业正促使货运量从远距海运转向更短的多式联运。预计到2024年,美国墨之间的跨境卡车运输需求将实现两位数成长,这将刺激对简化边境清关软体和保税内陆港口的投资。精通海关的货运代理能够利用复杂的关税制度获利,而铁路和公路联运的综合解决方案与海运相比,可将门到门运输时间缩短35%。
港口拥挤和货柜数量不平衡
泊位排队时间延长、设备短缺、船期难以预测,导致运输时间更加不稳定。与2023年相比,亚洲主要港口的平均停留时间增加了一倍以上,在几条主要贸易航线上,设备重新部署现在需要额外18天。货运代理商提前数週预订货柜舱位,协商优先闸口窗口,并租用辅助支线船舶以绕过拥挤的枢纽港。 2025年初,亚欧航线的即期运价飙升了255%,迫使托运人重新审视其货源,否则就只能承受更高的成本。
细分市场分析
由于跨洋散货运输的每标准箱(TEU)运输成本最低,海运在2024年仍维持了62%的货运代理市场份额。大型船舶的部署、自动化码头的建设以及干线支线网路的扩展,都使得舱位成本保持在较低水平,从而推动了海运业务的发展。儘管海运规模庞大,但其服务仍面临瓶颈,一旦船期延误,托运人就会倾向选择铁路或空运服务。因此,多式联运解决方案(即货运代理将海运、铁路和公路运输整合起来,以缩短亚欧航线2至4天的前置作业时间)的复合年增长率达到了6.4%。预计2024年欧亚走廊的铁路货运量将成长10.7%,进一步分散运输风险。空运仍然主导着对时间要求严格的药品、电子产品和时尚产品的运输,随着航线网络的重组,其运力正在逐步恢復。陆运可确保区域配送和最后一公里履约,但由于燃油额外费用和司机短缺推高了干线货运价格,其成本仍然较为敏感。能够协调多式联运路线的货运代理商在所有货运市场区域都能获得更高的市场份额和更深的客户留存率。
预计到2030年,多模态货运市场规模将以6.4%的复合年增长率成长。整合式控制塔平台、统一报价引擎和整列火车包车服务提升了营运灵活性和利润率。纯粹的海运和空运专家现在正与多式联运铁路营运商合作,以防止客户更换营运商。科技正发挥核心作用,实现海关放行数位化、货柜设施自动分配以及在单一控制面板上发布到货通知。市场领导报告称,端到端的多式联运合约可将客户维繫提高22%,凸显了货运市场中编配的服务组合的黏性。
到2024年,大型企业将占据货运代理市场70%的份额,它们每年利用超过5万个标准箱的竞标量来授予与指数挂钩的海运和空运合约。这些企业的采购部门要求采用统一的全球关键绩效指标(KPI)和碳计量,这促使货运代理在其营运资料之上建立分析层。过去,小型出口商缺乏议价能力,但如今,数位市场汇集了中小企业的需求,并将竞标给承运商进行每日现货采购,从而降低了12%的货运支出。这种趋势将推动中小企业在货运代理市场实现6.6%的复合年增长率。货运平台与中小企业的现金流週期相契合,提供即时报价、里程碑提醒和整合的贸易融资模组。
中小企业的参与也凸显了合规要求,因为新手托运人容易申报货物资讯不实,从而招致罚款。数位化单证工具透过标记限制物品和预先填写标准表格,可将海关扣留率降低19%。货运代理正透过将保险、退税申请和电子发票等服务打包成订阅套餐来实现收入多元化。虽然大型工业客户仍然主导着重型计划货物和工厂搬迁业务,但中小企业在电子商务补货和特色成品运输方面也提供了新的成长动力。因此,随着资源受限的出口商需求加速成长,货运代理市场可能会逐渐呈现出更均衡的客户组成。
区域分析
亚太地区将在2024年以36%的营收份额引领全球货运市场,并在2030年之前维持7.8%的复合年增长率。随着品牌商对冲采购风险,製造业多元化发展至越南、印尼和印度将推动区域销售量飙升。上海、深圳和新加坡等主要港口正大力投资自动化起重机和智慧闸门技术以缩短卡车週转时间,但泊位利用率仍接近历史最高水准。杜拜环球港务集团(DP World)预测,到2027年,亚太地区港口的总合吞吐量将达到20万个标准箱,这进一步巩固了该地区在全球供应链中的关键地位。
北美在全球货运量中排名第二,这主要得益于美国强劲的消费需求和日益增长的近岸外包业务,预计到2024年,美国墨跨境货运量将增长10%。对横跨德克萨斯州和亚利桑那州的双层货柜铁路走廊的投资将加速远距公路运输向多式联运的模式转换,从而缓解卡车司机运力瓶颈。温哥华和鲁珀特王子港的加拿大门户将扩大铁路装卸能力,以分流亚洲货物,避免美国西海岸码头拥挤。
欧洲航运网络面临许多挑战,包括司机短缺、排放法规日益严格、边境管制措施不统一。然而,对附加价值服务(尤其是药品和高科技机械)的持续需求,确保了收入稳定。鹿特丹、汉堡和安特卫普等主要枢纽正在进行海关数位化改造,并实施岸电解决方案,以符合「适航55」目标。南美洲正受惠于「摩羯座BI」海上走廊的蓬勃发展,该走廊预计将于2027年建成,届时南方共同市场内部的运输成本将降低高达40%。中东正在扩建杰贝阿里港和阿卜杜拉国王港,从而搭建东西方贸易的桥樑。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 亚洲至北美跨境电子商务货运量快速成长
- 製造业向近岸外包转移推动了墨西哥-美国公路货运需求。
- 需要国际小包裹履约的直接面向消费者(D2C)品牌数量激增
- 扩大冷藏运输能力以支援温控药品运输
- 按需杂货和食材自煮包服务提升了低温运输和当日送达能力。
- 消费者对即时可见性的期望正促使零售商转向精通技术的货运代理。
- 市场限制
- 港口拥塞和货柜失衡加剧了航运的不确定性。
- 全球司机短缺推高了北美和欧洲的公路货运价格。
- 时尚产品退货週期的加速给货运代理商带来了成本和利润压力。
- 价值/供应链分析
- 行业法规和政策
- 市场技术发展
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 地缘政治事件如何影响市场
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 透过交通工具
- 海运货运代理
- FCL
- LCL
- 公路货运代理
- FCL
- LCL
- 空运代理
- 铁路货运代理
- 多模态和联运交通运输
- 海运货运代理
- 按公司规模
- 小型企业
- 大公司
- 透过前向器模型
- 传统轻资产货运代理
- 数位化优先/线上货运平台
- 其他的
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 工业和製造业
- 零售与电子商务
- 医疗保健和製药
- 石油、天然气和能源
- 饮食
- 车
- 化学
- 其他最终用户
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 智利
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 新加坡
- 越南
- 印尼
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 土耳其
- 以色列
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 奈及利亚
- 肯亚
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Kuehne+Nagel International AG
- DHL Global Forwarding
- DSV A/S(DSV Panorama)
- CH Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- Bollore Logistics
- Nippon Express Co. Ltd.
- CEVA Logistics(SCX)
- GEODIS SA
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics SE
- Dachser SE
- Kerry Logistics Network Ltd.
- Yusen Logistics Co. Ltd.
- Agility Logistics
- Maersk Logistics and Services(incl. Damco)
- FedEx Logistics
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- Sinotrans Ltd.
- XPO Logistics
- Uber Freight LLC
- Lineage Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- LX Pantos
- CIMC Wetrans Logistics
- Toll Group
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The freight forwarding market is valued at USD 572.25 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 740.85 billion by 2030, expanding at a 5.3% CAGR.

The upward trajectory continues despite geopolitical tensions and repeated supply-chain shocks because digital platforms, resilient multimodal networks, and sustained e-commerce flows keep volumes intact. Heightened demand for parcel-sized cross-border shipments, steady investment in temperature-controlled capacity, and a structural pivot toward near-shoring all lift volumes in every major trade lane. Second-order effects include faster technology adoption, new premium service tiers built around real-time visibility, and an observed tilt toward consolidation as forwarders strive for scale advantages. M&A activity, spearheaded by DSV's USD 15.9 billion takeover of DB Schenker in 2025, illustrates how scale and data density now underpin competitive positioning in the freight forwarding market.
Global Freight Forwarding Market Trends and Insights
Surging Cross-Border E-commerce Parcel Volumes
Record online spending in Asia continues to drive small-parcel flows toward North American consumers. Freight forwarders are repurposing existing facilities into parcel sortation hubs, integrating customs pre-clearance, and layering predictive duty-tax calculators to remove purchase friction. Service speed rather than simple cost now determines routing decisions, encouraging carriers to expand weekly sailings on trans-Pacific express lanes. Value-added features, such as isotopic parcel-level visibility and branded returns, help incumbents defend share against pure-play parcel integrators.
Near-shoring-Led Manufacturing Shifts
Proximity manufacturing in Mexico, Poland, and Turkiye pulls freight volumes from long-haul ocean to shorter multimodal corridors. Cross-border truckload demand on the US-Mexico lane grew double digits in 2024, stimulating investments in streamlined border-clearance software and bonded inland ports. Forwarders with customs brokerage depth monetize complex tariff regimes, while integrated rail-truck solutions shorten door-to-door time by 35% compared with ocean alternatives.
Port Congestion & Container Imbalances
Extended berth queues, equipment shortages, and unpredictable sailing schedules inflate transit variability. Average dwell time at major Asian ports more than doubled versus 2023, and equipment repositioning now adds an 18-day buffer on several head-haul trades. Forwarders pre-book container slots weeks ahead, negotiate priority gate windows, and charter supplemental feeders to bypass gridlocked hubs. Spot rates on Asia-Europe lanes spiked 255% in early 2025, forcing shippers to rebalance sourcing or absorb cost surges.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Direct-to-Consumer Brand Proliferation
- Reefer Capacity Expansion for Pharma
- Global Driver Shortage
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Ocean freight retained a 62% freight forwarding market share in 2024 because it offers the lowest cost per TEU for high-volume goods moving across oceans. The segment benefits from megavessel deployments, automated terminals, and expanded mainline-feeder networks that keep slot costs low. Despite its scale, ocean services face chokepoints, motivating shippers to add rail or air legs when schedule integrity falters. Multimodal solutions therefore log a 6.4% CAGR, as forwarders bundle ocean, rail, and road to shave lead times by two to four days on Asia-Europe lanes. Rail volumes on the Eurasian corridor climbed 10.7% in 2024 and continue to diversify routing risk. Air forwarding still dominates time-critical pharma, electronics, and fashion drops, with capacity rebounding as belly-hold networks rebuild. Road forwarding secures regional distribution and last-mile fulfilment but remains cost-sensitive because fuel surcharges and driver scarcity inflate line-haul rates. Forwarders that orchestrate mode-agnostic routing enjoy higher wallet share and deeper client lock-in across every freight forwarding market region.
The freight forwarding market size for multimodal services is forecast to expand at a CAGR of 6.4% by 2030. Integrated control-tower platforms, unified quoting engines, and block-train charters enhance operational agility and margin retention. Pure ocean or air specialists now partner with intermodal rail operators to keep customers from switching providers. Technology that digitises customs hand-offs, auto-allocates container equipment, and releases arrival notifications in a single dashboard plays a central role. Market leaders report that end-to-end multimodal contracts lift client retention by 22%, highlighting the stickiness of an orchestrated service bundle in the freight forwarding market.
Large enterprises captured 70% of the freight forwarding market size in 2024, leveraging yearly tender volumes above 50,000 TEUs to lock in index-linked ocean and air contracts. Their procurement departments demand unified global KPIs and carbon accounting, driving forwarders to build analytics layers atop operational data. Smaller exporters historically lacked negotiating power, but digital marketplaces now aggregate SME demand and auction it to carriers in daily spot buys, cutting freight spends by 12%. This dynamic pushes the SME slice of the freight forwarding market to a 6.6% CAGR. Freight platforms offer instant quotes, milestone alerts, and integrated trade-finance modules that align with SME cash-flow cycles.
SME participation also sharpens compliance needs because novice shippers may misdeclare cargo, inviting fines. Digital documentation wizards flag restricted commodities and pre-populate standard forms, reducing customs holds by 19%. Forwarders diversify revenue by bundling insurance, duty-drawback filing, and e-invoicing into subscription tiers. Large industrial clients still dominate heavyweight project cargo and plant relocation work, but the incremental growth momentum lies with SMEs shipping e-commerce replenishment and niche finished goods. The freight forwarding market will therefore exhibit a progressively balanced customer portfolio as demand from resource-constrained exporters accelerates.
The Freight Forwarding Market Report is Segmented by Mode of Transport (Air Freight Forwarding, Ocean Freight Forwarding, and More), by Enterprise Size (Small & Medium Enterprises, and More), by Forwarder Model (Traditional Asset-Light Forwarders, and More), by End-User Industry (Industrial and Manufacturing, and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led the freight forwarding market with a 36% revenue share in 2024 while expanding at a 7.8% CAGR through 2030. Manufacturing diversification into Vietnam, Indonesia, and India spikes regional volumes as brands hedge sourcing risk. Major ports in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Singapore invest heavily in automated cranes and smart-gate technology that shortens truck turnaround times, yet berth utilizations still hover near record highs. DP World expects Asia-Pacific ports collectively to handle 200,000 TEUs annually by 2027, affirming the region's anchoring role in global supply chains.
North America ranks second in the freight forwarding market, bolstered by the United States' strong consumer demand and ongoing near-shoring that boosts US-Mexico cross-border traffic by 10% in 2024. Railroad investments in double-stack corridors across Texas and Arizona accelerate modal shift from long-haul truck to intermodal, easing driver-capacity bottlenecks. Canadian gateways in Vancouver and Prince Rupert expand rail-mount capacity to redirect Asia cargo away from crowded US West Coast terminals.
Europe's network faces compounded challenges from driver shortages, stringent emissions mandates, and patchwork border regulations. However, sustained demand for value-added services, especially in pharma and high-tech machinery, preserves revenue. Leading hubs in Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Antwerp digitize customs and deploy shore-power solutions to comply with the Fit-for-55 goals. Beyond the tri-continent core, South America grows rapidly on the back of the Capricorn BI oceanic Corridor, which promises to cut intra-Mercosur transit costs by up to 40% once completed in 2027. The Middle East expands Jebel Ali and King Abdullah Port to position itself as a bridging node between East-West trade, while African corridors benefit from Chinese-financed rail revamps that unlock inland commodity flows.
- Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- DHL Global Forwarding
- DSV A/S (DSV Panorama)
- C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- Bollore Logistics
- Nippon Express Co. Ltd.
- CEVA Logistics (SCX)
- GEODIS SA
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics SE
- Dachser SE
- Kerry Logistics Network Ltd.
- Yusen Logistics Co. Ltd.
- Agility Logistics
- Maersk Logistics and Services (incl. Damco)
- FedEx Logistics
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- Sinotrans Ltd.
- XPO Logistics
- Uber Freight LLC
- Lineage Logistics
- Kintetsu World Express
- LX Pantos
- CIMC Wetrans Logistics
- Toll Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging Cross-Border E-commerce Parcel Volumes Across Asia-Origin to North America
- 4.2.2 Near-shoring-Led Manufacturing Shifts Driving Mexico-US Road Freight Demand
- 4.2.3 Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) brand proliferation demanding international small-parcel fulfilment
- 4.2.4 Reefer Capacity Expansion Supporting Temperature-Controlled Pharma Shipments
- 4.2.5 On-demand grocery and meal-kit services fuelling cold-chain and same-day freight volumes
- 4.2.6 Consumer expectation for real-time visibility pushing retailers toward tech-heavy forwarders
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Port Congestion and Container Imbalances Escalating Transit Uncertainty
- 4.3.2 Global Driver Shortage Inflating Road Freight Rates in North America and Europe
- 4.3.3 Accelerated fashion return cycles adding cost drag and margin pressure on forwarders
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Industry Policies and Regulations
- 4.6 Technological Developments in the Market
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Geopolitical Events on the Market
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.1.1 Ocean Freight Forwarding
- 5.1.1.1 Full Container Load (FCL)
- 5.1.1.2 Less-Than-Container Load (LCL)
- 5.1.2 Road Freight Forwarding
- 5.1.2.1 Full Truck Load (FTL)
- 5.1.2.2 Less-Than-Truck Load (LTL)
- 5.1.3 Air Freight Forwarding
- 5.1.4 Rail Freight Forwarding
- 5.1.5 Multimodal and Intermodal Forwarding
- 5.1.1 Ocean Freight Forwarding
- 5.2 By Enterprise Size
- 5.2.1 Small and Medium Enterprises
- 5.2.2 Large Enterprises
- 5.3 By Forwarder Model
- 5.3.1 Traditional Asset-Light Forwarders
- 5.3.2 Digital-First / Online Freight Platforms
- 5.3.3 Others
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Industrial and Manufacturing
- 5.4.2 Retail and E-commerce
- 5.4.3 Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- 5.4.4 Oil, Gas and Energy
- 5.4.5 Food and Beverages
- 5.4.6 Automotive
- 5.4.7 Chemicals
- 5.4.8 Other End-users
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Chile
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Spain
- 5.5.3.5 Italy
- 5.5.3.6 Netherlands
- 5.5.3.7 Russia
- 5.5.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Singapore
- 5.5.4.6 Vietnam
- 5.5.4.7 Indonesia
- 5.5.4.8 Australia
- 5.5.4.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.4 Israel
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.6 Africa
- 5.5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.5.6.2 Egypt
- 5.5.6.3 Nigeria
- 5.5.6.4 Kenya
- 5.5.6.5 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- 6.4.2 DHL Global Forwarding
- 6.4.3 DSV A/S (DSV Panorama)
- 6.4.4 C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- 6.4.5 Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- 6.4.6 Bollore Logistics
- 6.4.7 Nippon Express Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.8 CEVA Logistics (SCX)
- 6.4.9 GEODIS SA
- 6.4.10 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics SE
- 6.4.11 Dachser SE
- 6.4.12 Kerry Logistics Network Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Yusen Logistics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Agility Logistics
- 6.4.15 Maersk Logistics and Services (incl. Damco)
- 6.4.16 FedEx Logistics
- 6.4.17 UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- 6.4.18 Sinotrans Ltd.
- 6.4.19 XPO Logistics
- 6.4.20 Uber Freight LLC
- 6.4.21 Lineage Logistics
- 6.4.22 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.4.23 LX Pantos
- 6.4.24 CIMC Wetrans Logistics
- 6.4.25 Toll Group









