 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851084
印度电动三轮车市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)India Electric Rickshaw - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
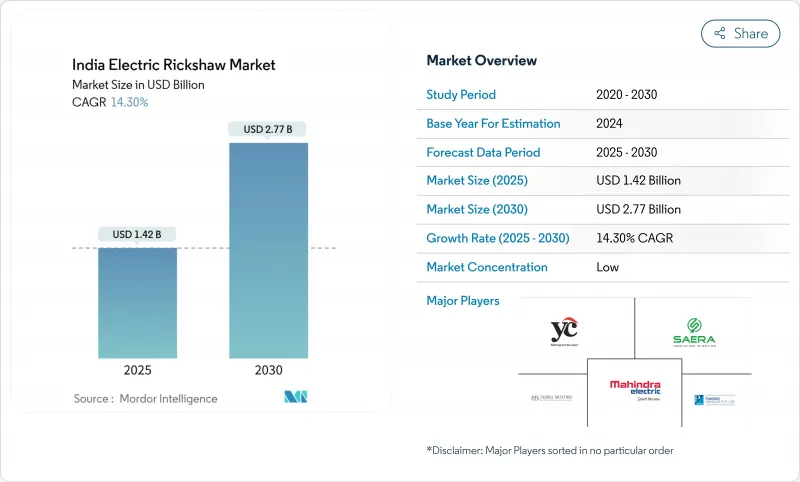
据估计,2025 年印度电动三轮车市场规模为 14.2 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 27.7 亿美元,预测期(2025-2030 年)复合年增长率为 14.30%。
这项快速扩张反映了政府奖励、积极的州级政策、不断增长的电子商务需求以及日益严格的都市区空气品质目标。客运企业的主导地位、铅酸电池强劲的回收利用经济效益以及电子商务物流向电动货运的快速转型,都支撑着这一成长势头。电池化学、模组化融资模式和动力传动系统效率的同步进步,正将目标市场从一线城市扩展到二线和三线城市。随着传统汽车製造商、创新新兴企业和全球汽车製造商投入资金和工程人才,试图抓住下一波成长浪潮,竞争日趋激烈。
印度电动三轮车市场趋势与洞察
FAME-II 拨款延期和州政府奖励加速二级标准的采用
联邦政府在延长的FAME-II计划和2024年电动出行促进计划之间保持了政策的连续性,维持了单车补贴不变,降低了主要城市以外地区驾驶员的准入门槛。马哈拉斯特拉邦、卡纳塔克邦和德里等邦政府提供的购车补贴和道路税减免等激励措施进一步降低了成本,使电动三轮车在销售时能够与燃油车型在价格上竞争。补贴力道与註册量密切相关,邦政府补贴力道每增加一个标准差,销售量就会增加46.16%。当地金融机构报告称,贷款回收期缩短,鼓励了更广泛的信贷参与。这些综合财政支持措施进一步推动印度电动三轮车市场进入对成本敏感的二线丛集,该市场非正式的转换需求正在激增。
快速都市化城市对最后一公里共用出行的需求日益增长
印度不断扩张的中型城市网路严重依赖电动三轮车来弥合公共交通的「最后一公里」和「首公里」差距。与汽油或CNG车辆每公里3-4卢比的营运成本相比,电动车的营运成本更低,每公里仅需0.50-0.70卢比,这使得车主能够快速获利。优步(Uber)和Rapido等共用出行平台正在引入电动三轮车,以满足市政清洁空气标准和乘客对价格的敏感度。高日利用率放大了燃料成本套利空间,加快了高额前期投资的报酬。便利的数位化预订提高了资产利用率,进一步提升了营运商的获利能力,并推动了印度电动三轮车市场的整体普及。
分散且非正式的融资管道阻碍了驾驶员的购买意愿。
由于缺乏充足的贷款管道,实际利率高企,贷款价值比低,这阻碍了依赖每日车费收入维持生计的独立司机购买电动三轮车的意愿。对技术风险的担忧导致许多金融机构将电动三轮车视为非标准资产,儘管其运作成本低廉,但贷款能力受到限制。非正规贷款机构填补了这一空白,但收取高额利息,抵消了电动三轮车的整体拥有成本优势。发展金融机构一直倡导建立混合融资池以降低零售贷款风险,但在主要城市以外的地区,这种模式的推广仍然缓慢。在主流银行规范电动三轮车贷款业务之前,在对前期投资和价格分布最敏感的细分市场,电动三轮车的成长可能仍将低于预期。
细分市场分析
目前,客运领域在印度电动三轮车市场占据主导地位,预计2024年将占总销售量的83.92%,巩固了其作为城市共享出行支柱的地位。密集的城市路线和全天候的使用使得驾驶员能够以每公里仅1元的能源成本运营,增强了该领域的韧性。然而,随着线上零售推动对轻便、零排放「最后一公里」配送的需求,货运电动三轮车的复合年增长率(CAGR)高达29.44%,成为成长最快的领域。亚马逊印度、Flipkart和其他电商平台正在与现有原始设备製造商(OEM)建立规范的采购管道,确保销售量的稳定成长。冷藏车等细分市场拓展了食品配送和医药领域的市场潜力。不断提升的有效负载容量和远端资讯处理技术的集成,使货运电动三轮车成为未来城市物流蓝图的重要组成部分。
从绝对数量来看,搭乘用型仍将主导印度电动三轮车市场,但由于高端配置的推出,货运车型的价值贡献有望稳步增长。针对商用车的税收优惠以及二线城市微型仓配中心的建设,可望提升货运车型的累积渗透率。随着城市拥堵费的日益严格,货运公司可能会更倾向于选择电动三轮车而非轻型卡车,从而巩固该细分市场的长期成长趋势。
以功率输出计算,1-1.5kW马达将占据印度电动三轮车市场份额的54.35%,预计到2024年将达到这一比例。此功率频宽非常适合典型的乘客出行,能够提供充足的扭矩,满足频繁启动的城市驾驶需求,同时还能延长电池寿命。营运商尤其青睐提案经济实惠的初始成本和实用的续航里程,尤其是在都市区高强度营运的情况下。
同时,印度电动三轮车市场中,功率超过1.5kW的动力传动系统成长最为迅猛,年复合成长率高达32.12%,这主要得益于市场对负载容量和更高爬坡能力的需求不断增长。此细分市场受益于电力驱动桥技术的进步,例如整合式马达控制器和IP防护等级机壳,这些技术提高了车辆在印度恶劣季风气候条件下的耐用性,并提升了车队的可靠性。
高功率的车型迎合了高端叫车市场的需求,该市场需要运输冷藏货物、应对更陡峭的坡道以及更快的周转时间。零件供应商正逐步实现磁铁和定子的本地化生产,从而减少进口并稳定价格分布。随着单车经济效益的提升,预计印度1.5kW以上功率等级的电动三轮车市场规模将扩大,市场份额也将随之成长,并催生以性能而非成本为核心的全新竞争格局。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- FAME-II 拨款延期和州政府奖励加速二级标准的采用
- 快速都市化城市对最后一公里共用出行的需求日益增长
- 电子商务物流引进电动三轮车进行市内配送
- 降低整体拥有成本的铅酸电池回收生态系统
- 电池即服务订阅模式降低了前期投资。
- 2030年,德里-NCR地区将强制逐步淘汰内燃机三轮车
- 市场限制
- 分散且非正式的资金筹措管道限制了驾驶员的购买。
- 乡村道路上底盘完整性的安全隐患
- 非正规铅酸电池供应链中的品质差异
- 可更换电池标准的缓慢推广阻碍了互通性
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监理与技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按车辆类型
- 客运公司
- 货运代理
- 透过输出
- 小于1千瓦
- 1~1.5 kW
- 1.5千瓦或以上
- 依电池类型
- 铅酸
- 锂离子(NMC/NCA)
- 锂离子电池(LFP)
- 其他化学物质(锂聚合物、镍氢化物)
- 按电池容量
- 小于3千瓦时
- 3~6 kWh
- 6度或以上
- 透过充电模式
- 插电式充电
- 更换电池
- 自有车型
- 私人车主司机
- 车队营运商
- 聚合器/出行即服务平台
- 按州
- 北方邦
- 德里
- 马哈拉斯特拉邦
- 比哈尔邦
- 拉贾斯坦邦
- 卡纳塔克邦
- 泰米尔纳德邦
- 旁遮普邦
- 特伦甘纳邦
- 印度其他地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Terra Motors India Corp.
- Piaggio Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- Mahindra Electric Mobility Ltd.
- Kinetic Green Energy & Power Solutions Ltd.
- ATUL Auto Ltd.
- Saera Electric Auto Pvt. Ltd.
- YC Electric Vehicle
- Goenka Electric Motor Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- Udaan E-Rickshaw
- Thukral Electric Bikes
- Mini Metro EV LLP
- E-Ashwa Automotive Pvt. Ltd.
- CityLife EV
- Adapt Motors Pvt. Ltd.
- Vani Electric Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.(Jezza Motors)
- Omega Seiki Mobility
- Euler Motors
- Lohia Auto Industries
- Bajaj Auto Ltd.(Electric 3W Division)
- Altigreen Propulsion Labs
- Gayam Motor Works
- Lectrix EV
- Saarthi E-Rickshaw
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Indian electric rickshaw market size is estimated at USD 1.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.77 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 14.30% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

This rapid expansion reflects government incentives, aggressive state-level policies, growing e-commerce demand, and heightened urban air-quality goals. Passenger carrier dominance, strong recycling economics for lead-acid batteries, and the swift pivot of e-commerce logistics toward electric cargo variants are sustaining volume momentum. Parallel advances in battery chemistry, modular finance models, and power-train efficiency are widening the total addressable base beyond Tier-I metros into Tier-II and Tier-III towns. Competitive rivalry intensifies as legacy OEMs, innovative start-ups, and global automakers commit capital and engineering talent to capture the next wave of growth.
India Electric Rickshaw Market Trends and Insights
FAME-II Subsidy Extension and State Incentives Accelerating Tier-II Adoption
Federal continuity between the extended FAME-II program and the Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme 2024 keeps per-vehicle subsidies intact, lowering acquisition cost barriers for drivers outside major metros. State top-ups-ranging from purchase rebates to road-tax waivers in Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Delhi-stack further savings, making electric three-wheelers price-competitive with ICE models at the point of sale. Subsidy density correlates strongly with registrations; assessments reveal a 46.16% sales uplift for each standard-deviation rise in state support intensity. Local financiers report shorter payback periods, encouraging broader credit participation. Combined, these fiscal levers push the Indian electric three-wheeler market deeper into cost-sensitive Tier-II clusters where informal transit demand is surging.
Rising Demand for Last-Mile Shared Mobility in Rapidly Urbanising Towns
India's expanding network of mid-sized cities relies heavily on auto-rickshaws to bridge first- and last-mile gaps in public transit. Electric variants cut running expenses to INR 0.50-0.70/km against INR 3-4/km for petrol or CNG, creating immediate earnings upside for owner-drivers. Shared-mobility aggregators such as Uber and Rapido are onboarding e-rickshaws to meet municipal clean-air mandates and rider price sensitivity. High daily utilization amplifies fuel-cost arbitrage, accelerating payback on the higher upfront purchase. Seamless digital booking elevates asset productivity, further reinforcing operator economics and boosting adoption across the Indian electric three-wheeler market.
Fragmented & Informal Financing Channels Constraining Driver Purchases
The lack of scale credit pipelines keeps effective interest rates high and loan-to-value ratios low, dampening uptake among independent drivers whose livelihood depends on daily fare receipts. Technology-risk perceptions lead many lenders to treat electric variants as non-standard assets, constricting credit lines despite lower running costs. Informal money-lenders bridge the gap but charge punitive rates, eroding total cost of ownership benefits. Development-finance institutions advocate blended-finance pools to de-risk retail lending, yet implementation remains slow outside major cities. Until mainstream banks normalize underwriting for electric three-wheelers, growth will undershoot potential in segments most sensitive to up-front affordability.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- E-Commerce Logistics Embracing Cargo E-Rickshaws for Intra-City Delivery
- Lead-Acid Battery Recycling Ecosystem Lowering Total Cost of Ownership
- Safety Concerns Over Chassis Integrity on Rural Roads
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
India electric rickshaw market share is currently dominated by the passenger carrier segment, which accounted for 83.92% of unit sales in 2024, cementing its role as the backbone of intra-city shared mobility. Dense urban routes and all-day utilization let drivers exploit penny-per-kilometer energy costs, reinforcing segment resilience. Goods carriers, however, are registering the fastest 29.44% CAGR as online retail pushes demand for nimble, emissions-free last-mile delivery. Amazon India, Flipkart, and quick-commerce players are formalizing procurement pipelines with established OEMs, ensuring predictable volume growth. Segment-specific designs such as refrigerated bodies widen addressable markets in food distribution and pharmaceuticals. Higher payload ratings and telematics integration make cargo e-rickshaws an essential piece of future city-logistics blueprints.
In absolute volume terms, passenger variants will continue to dominate the Indian electric three-wheeler market, yet the value contribution from cargo units will rise steadily through premium specification mixes. Tax breaks for commercial vehicles and dedicated micro-fulfillment hubs in Tier-II cities will push cumulative cargo penetration higher. As urban congestion charges tighten, freight operators will prefer electric three-wheelers over light trucks, cementing the segment's long-term upside.
India electric rickshaw market share by power output was led by the 1-1.5 kW motor segment, which accounted for 54.35% of total demand in 2024. This power band delivers sufficient torque for frequent stop-start city driving while conserving battery life, making it ideal for typical passenger operations. Operators value its balanced offering-affordable upfront cost with practical range-especially in high-usage urban duty cycles.
In contrast, powertrains rated above 1.5 kW are witnessing the fastest growth in the India electric rickshaw market, expanding at a 32.12% CAGR as payload demands and gradient-handling requirements rise. The segment is benefiting from advancements in e-axle technologies, including integrated motor controllers and IP-rated enclosures, which enhance durability during India's heavy monsoon conditions and boost fleet confidence.
The higher-powered bracket supports refrigerated cargo, steep-gradient hill-stations, and premium ride-hailing tiers that demand faster trip times. Component suppliers are localizing magnets and stators, cutting imported content and stabilizing price points. As unit economics improve, the Indian electric three-wheeler market size for the above-1.5 kW class is projected to widen its revenue share, ushering in a new competitiveness layer focused on performance rather than solely cost.
The India Electric Rickshaw Market Report is Segmented by Vehicle Type (Passenger Carriers and More), Power Output ( Up To 1 KW and More), Battery Type (Lead-Acid and More), Battery Capacity (Up To 3 KWh and More), Charging Mode (Plug-In Charging and More), Ownership Model (Individual Owner-Drivers and More), and States (Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Terra Motors India Corp.
- Piaggio Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- Mahindra Electric Mobility Ltd.
- Kinetic Green Energy & Power Solutions Ltd.
- ATUL Auto Ltd.
- Saera Electric Auto Pvt. Ltd.
- YC Electric Vehicle
- Goenka Electric Motor Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- Udaan E-Rickshaw
- Thukral Electric Bikes
- Mini Metro EV LLP
- E-Ashwa Automotive Pvt. Ltd.
- CityLife EV
- Adapt Motors Pvt. Ltd.
- Vani Electric Vehicles Pvt. Ltd. (Jezza Motors)
- Omega Seiki Mobility
- Euler Motors
- Lohia Auto Industries
- Bajaj Auto Ltd. (Electric 3W Division)
- Altigreen Propulsion Labs
- Gayam Motor Works
- Lectrix EV
- Saarthi E-Rickshaw
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 FAME-II Subsidy Extension and State Incentives Accelerating Tier-II Adoption
- 4.2.2 Rising Demand for Last-Mile Shared Mobility in Rapidly Urbanising Towns
- 4.2.3 E-Commerce Logistics Embracing Cargo E-Rickshaws for Intra-City Delivery
- 4.2.4 Lead-Acid Battery Recycling Ecosystem Lowering Total Cost of Ownership
- 4.2.5 Battery-as-a-Service Subscription Models Reducing Up-front Capex
- 4.2.6 Mandatory Phase-Out of ICE Three-Wheelers in Delhi-NCR by 2030
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented & Informal Financing Channels Constraining Driver Purchases
- 4.3.2 Safety Concerns Over Chassis Integrity on Rural Roads
- 4.3.3 Quality Variability in Unorganised Lead-Acid Battery Supply Chain
- 4.3.4 Slow Roll-Out of Swappable Battery Standards Hindering Interoperability
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory & Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Vehicle Type
- 5.1.1 Passenger Carriers
- 5.1.2 Goods Carriers
- 5.2 By Power Output
- 5.2.1 Up to 1 kW
- 5.2.2 1 - 1.5 kW
- 5.2.3 Above 1.5 kW
- 5.3 By Battery Type
- 5.3.1 Lead-Acid
- 5.3.2 Lithium-ion (NMC/NCA)
- 5.3.3 Lithium-ion (LFP)
- 5.3.4 Other Chemistries (Li-Polymer, Ni-MH)
- 5.4 By Battery Capacity
- 5.4.1 Up to 3 kWh
- 5.4.2 3 - 6 kWh
- 5.4.3 Above 6 kWh
- 5.5 By Charging Mode
- 5.5.1 Plug-in Charging
- 5.5.2 Battery Swapping
- 5.6 By Ownership Model
- 5.6.1 Individual Owner-Drivers
- 5.6.2 Fleet Operators
- 5.6.3 Aggregators / MaaS Platforms
- 5.7 By State
- 5.7.1 Uttar Pradesh
- 5.7.2 Delhi
- 5.7.3 Maharashtra
- 5.7.4 Bihar
- 5.7.5 Rajasthan
- 5.7.6 Karnataka
- 5.7.7 Tamil Nadu
- 5.7.8 Punjab
- 5.7.9 Telangana
- 5.7.10 Rest of India
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Terra Motors India Corp.
- 6.4.2 Piaggio Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.3 Mahindra Electric Mobility Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Kinetic Green Energy & Power Solutions Ltd.
- 6.4.5 ATUL Auto Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Saera Electric Auto Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.7 YC Electric Vehicle
- 6.4.8 Goenka Electric Motor Vehicles Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Udaan E-Rickshaw
- 6.4.10 Thukral Electric Bikes
- 6.4.11 Mini Metro EV LLP
- 6.4.12 E-Ashwa Automotive Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.13 CityLife EV
- 6.4.14 Adapt Motors Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Vani Electric Vehicles Pvt. Ltd. (Jezza Motors)
- 6.4.16 Omega Seiki Mobility
- 6.4.17 Euler Motors
- 6.4.18 Lohia Auto Industries
- 6.4.19 Bajaj Auto Ltd. (Electric 3W Division)
- 6.4.20 Altigreen Propulsion Labs
- 6.4.21 Gayam Motor Works
- 6.4.22 Lectrix EV
- 6.4.23 Saarthi E-Rickshaw
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment








