 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851090
小型基地台5G网路:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030年)Small Cell 5G Network - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
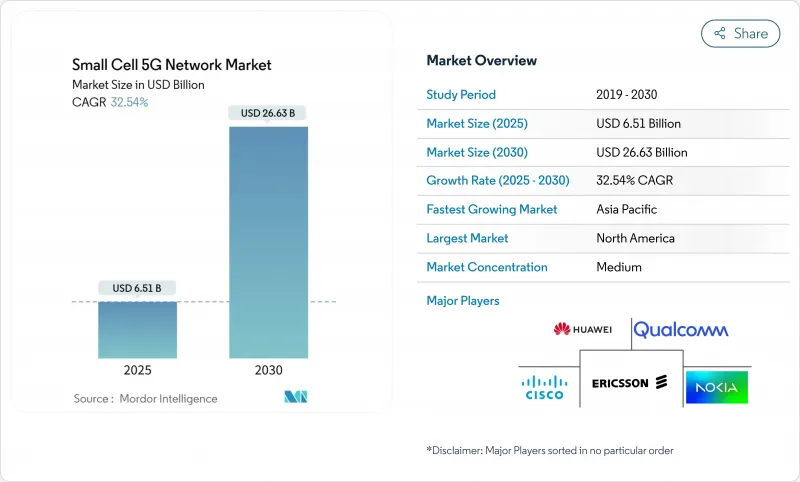
预计到 2025 年,小型基地台5G 网路市场规模将达到 65.1 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 266.3 亿美元,预测期(2025-2030 年)复合年增长率为 32.54%。
城市走廊的日益密集化、企业数位化以及人工智慧原生网路管理系统的部署,正在加速通讯业者和私人网路的普及。微微型基地台、中立主机模型以及Release-17 NR-U功能,透过缓解频谱和站点限制,拓展了可应用场景。亚太地区因其基础设施规模的扩张而备受关注,而北美则更有效地将基础设施转化为高额收入。竞争格局促使人工智慧晶片製造商和开放式无线存取网(Open RAN)专家开闢新的市场,而传统无线设备供应商则转向软体定义架构。
全球小型基地台5G网路市场趋势与洞察
都市区5G部署需要快速密集化
通讯业者已证实,仅靠大型基地台无法满足人口密集城市的 5G 服务等级协定 (SLA)。 EE 在英国运作1000 多个小型基地台,其中伦敦的 25 个站点每週资料传输量达 7.5TB,有效缓解了传统网路的拥塞。 Virgin Media O2 部署了英国首个 5G 独立组网小型基地台,实现了宏基地台无法实现的网路切片和低延迟。小型基地台内部的部分频率復用提高了频谱利用率,这对于扩增实境和工业IoT等上行链路密集型应用的普及至关重要。市政当局已运作繁琐的审批流程,全球已有超过 100 个中立主机投入营运。这些因素共同推动了中期内 5G 网路密集化的必要性。
企业(製造、物流)对专用网路的需求
政府政策和工业4.0蓝图正推动工厂和物流场所转型为确定性无线连接。中国已建成约4,000个5G工厂网络,并计画在2027年达到10,000个。诺基亚预计到2024年第四季将拥有850个5G住宅用户,仅一个季度就新增了55个。一家泰国家电工厂报告称,透过5G自动化,其生产效率提高了15%至20%。目前已有七个欧洲国家获得了26GHz频段的本地许可,另有六个国家分配了3.4-3.8GHz频段的100MHz频谱,这使得企业更容易获取频谱资源。小型基地台仍然是首选的无线层,因为它们能够实现严格的覆盖范围、整合边缘运算并支援同时进行网路切片。
郊区和农村地区光纤/回程传输的经济挑战
在郊区,架空光纤的建造成本为每英里6万至17万美元,导致人口密度较低地区的获利能力较差。 Crown Castle公司在意识到回程传输成本计算不利后,搁置了在美国建设的7000个小型基地台基站,从而节省了8亿美元的未来资本支出。微波和卫星回程传输虽然可以降低资本支出,但仍无法满足5G的容量和延迟目标。美国联邦公路管理局的数据显示,即使采用微型沟槽技术,郊区的损益平衡点也需要六到八年。因此,在下一代无线回程传输被证明具有商业性可行性之前,营运商不愿在盈利的大都会圈进行大规模部署。
细分市场分析
到2024年,微微微型基地台将占总收入的41%,这证实了它们适用于拥挤的城市走廊中100-200公尺的覆盖区域。随着中频段频谱和多用户MIMO技术的普及,单一站点的容量不断提升,小型基地台微微型基地台网路的市场规模预计将迅速扩大。诸如EdgeQ的晶片级基地台等硅晶片创新技术,整合了人工智慧,从而降低了功耗、成本和占地面积。
毫微微基地台微微蜂窝基地台满足住宅和小办公室的特定需求,但正面临来自 Wi-Fi 7 的竞争压力;而微蜂窝基地台则支援大型郊区,在这些地区,部署微微型基地台基地台的成本过高。康巴电信符合 ORAN 标准的微型无线电单元体现了标准化、多厂商生态系统的发展趋势。随着人工智慧驱动的最佳化缩小外形规格之间的效能差距,营运商可以灵活地满足每个站点的容量需求,而无需牺牲营运效率。
到2024年,室内部署将占总部署量的63%,因为中频段5G讯号会逐渐被现代建材吸收而衰减。中立主机系统和智慧建筑管理将使室内投资对那些希望在办公室、体育场和工厂等场所提供优质服务的企业保持吸引力。随着市政审批流程的加快、Release-17 NR-U标准的发布以及共用基础设施的普及,室外部署将以33.01%的复合年增长率加速成长,从而降低安装阻力。 Virgin Media O2在曼彻斯特市中心建造的户外基地台等专案就凸显了这个趋势。
Freshwave 将英国四家通讯业者的网路整合到一个室内外小型基地台机壳中,与先前的系统相比,成本降低了 65%,能耗降低了 60%。室内业者现在必须捍卫 Wi-Fi 7 的市场地位,因为 Wi-Fi 7 的理论速度高达 46Gbps,而 Wi-Fi 7 在这些方面却有所不足。
小型基地台5G 网路市场报告按蜂窝类型(毫微微基地台、微微型基地台、微型蜂窝、区域基地台)、运行环境(室内、室外)、频段(6 GHz 以下、毫米波 [24 GHz 以上]、1 GHz 以下)、最终用户(通讯业者、企业、住宅)和地区进行细分。
区域分析
亚太地区预计到2024年将占全球收入的38%,到2030年复合年增长率将达到32.60%。这主要得益于中国440万个5G基地台的建设,以及300个城市5G-Advanced网路建设投入的30亿元人民币资金。中国联通北京和华为在1000万人口区域实现了11.2Gbps的下行峰值速度,为未来的高密度网路建设树立了标竿。日本和韩国正在大力推动企业级毫米波技术,而印度则在竞标后透过官民合作关係为网路密集化发展提供了空间。
北美地区展现了卓越的营收实现效率。爱立信在北美地区凭藉与AT&T签订的价值140亿美元的合同,营收年增55%,展现了强劲的投资回报。美国已有超过50个基于CBRS的中立主机计划投入运营,而加拿大电信公司TELUS部署了首个商用虚拟化开放式无线接入网(Open RAN),使该地区在云端原生无线接入网路(RAN)实验领域处于领先地位。然而,Crown Castle部署计画的放弃凸显了郊区经济模式的持续挑战。
欧洲拥有清晰的频谱政策,但独立组网的5G覆盖率却落后于其他地区,预计2024年底渗透率仅2%。儘管Virgin Media O2和EE正在扩大其小型基地台的覆盖范围,但许多营运商仍在等待设备普及率的提升,以推动商业发展。在中东,阿联酋的通讯速度已达30.5Gbps,du已投资20亿迪拉姆建置超大规模资料中心。在拉丁美洲,巴西的Brisanet和乌拉圭的Antel正在扩展公共5G网络,但宏观经济限制和频谱资源的匮乏阻碍了小型基地台的部署。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 都市区5G部署的快速密集化需求
- 企业(製造、物流)对专用网路的需求
- Release 17 5G NR-U 支援免授权小型基地台频谱
- 中立主机经营模式获得监理支持
- 人工智慧驱动的自优化网路可降低营运成本(未充分通报)
- 市场限制
- 郊区和农村地区的光纤/回程传输经济挑战
- 地方政府土地征收延误及费用
- 围绕开放式无线接取网路(RAN)小型基地台的持续性(且未被充分通报的)安全隐患
- 供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争的激烈程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按细胞类型
- 毫微微基地台
- 微微型基地台
- 微细胞
- 区域基地台
- 透过使用环境
- 室内的
- 户外的
- 按频宽
- 6 GHz 以下频段
- 毫米波(24 GHz 以上)
- 低于1 GHz
- 最终用户
- 电讯营运商
- 公司
- 住宅
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Nokia Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- CommScope Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Baicells Technologies Co. Ltd
- Qucell Inc.
- JMA Wireless
- Parallel Wireless
- Mavenir Systems
- Casa Systems
- Corning Inc.
- Sercomm Corporation
- Comba Telecom Systems Holdings Ltd
- American Tower Corporation
- Boingo Wireless Inc.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Small Cell 5G Network Market size is estimated at USD 6.51 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 26.63 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 32.54% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Ongoing densification in urban corridors, enterprise digitalization, and the roll-out of AI-native network management systems are accelerating uptake across telecom operators and private-network deployments. Picocells, neutral-host models, and Release-17 NR-U capabilities are expanding addressable use cases by easing spectrum and site constraints. Asia Pacific commands attention through infrastructure scale, yet North America converts infrastructure into premium revenue more efficiently, while Europe's regulatory clarity promises a delayed but sizable second wave of growth. Competitive dynamics feature established radio vendors pivoting toward software-defined architectures even as AI-enabled chipmakers and Open RAN specialists carve out niches.
Global Small Cell 5G Network Market Trends and Insights
Rapid densification needs in urban 5G rollouts
Operators have confirmed that macro cells alone cannot satisfy 5G service-level agreements in dense cities. EE has activated more than 1,000 small cells across the United Kingdom, with 25 London sites moving 7.5 TB of data each week, easing congestion in traditional sectors. Virgin Media O2 introduced the first UK 5G standalone small cells, unlocking network slicing and lower latency that macro sites cannot match. Fractional frequency reuse within small cells improves spectrum utilization, which is critical as uplink-heavy applications such as AR and industrial IoT become mainstream. Municipalities are cutting red tape, and more than 100 neutral-host installations are now live worldwide. Combined, these factors reinforce the densification imperative over the medium term.
Enterprise private-network demand (manufacturing, logistics)
Government policy and Industry 4.0 roadmaps are pushing factories and logistics sites toward deterministic wireless connectivity. China already hosts roughly 4,000 5G factory networks and targets 10,000 by 2027. Nokia counted 850 private 5G customers by Q4 2024, adding 55 in a single quarter. Operational outcomes are compelling: a Thai appliance plant reported 15-20% productivity gains after 5G-enabled automation. Seven European states now license the 26 GHz band locally, and six allocate 100 MHz in the 3.4-3.8 GHz range, making spectrum procurement easier for enterprises. Small cells remain the preferred radio layer because they enforce tight coverage boundaries, integrate edge compute, and support concurrent network slices.
Challenging fiber/backhaul economics in suburban and rural zones
Aerial fiber construction costs between USD 60,000 and USD 170,000 per mile in suburbs, depressing returns where population density is low. Crown Castle shelved 7,000 U.S. small-cell sites, preserving USD 800 million in future capital spending, after recognizing unfavorable backhaul math. Microwave and satellite backhaul trim capex but cannot yet meet 5G capacity or latency targets. Federal Highway Administration data show that using micro-trenching still leaves a six-to-eight-year breakeven in suburban settings. Consequently, operators hesitate to densify beyond profitable metros until next-generation wireless backhaul proves commercially viable.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Release-17 5G NR-U enabling unlicensed small-cell spectrum
- AI-driven self-optimizing networks cutting OpEx
- Persistent security concerns around Open RAN small cells
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Picocells contributed 41% of 2024 revenue, confirming their suitability for 100-200 m coverage zones in crowded downtown corridors. The Small Cell 5G Network market size for picocells is on course to expand sharply as mid-band spectrum and multi-user MIMO raise per-site capacity. mmWave picocells show the sharpest 36.51% CAGR, propelled by private networks and fixed wireless access that exploit 28 GHz and 39 GHz to deliver multi-gigabit throughput. Silicon innovation, such as EdgeQ's base-station-on-a-chip, brings integrated AI that shrinks power, cost, and footprint.
Femtocells hold niche residential and small-office positions but face pressure from Wi-Fi 7, while microcells support wider suburban blocks where picocell density is cost-prohibitive. ORAN-compliant micro-radio units from Comba Telecom reflect a drift toward standardized multi-vendor ecosystems. As AI-enabled optimization narrows performance gaps between form factors, operators gain flexibility to match each site's capacity requirements without sacrificing operating efficiency.
Indoor sites represented 63% of 2024 deployments, since mid-band 5G signals fade through modern building materials. Neutral-host systems and smart-building management keep indoor investments compelling for enterprises seeking quality-of-service across offices, stadiums, and factories. The outdoor category is accelerating at a 33.01% CAGR as faster municipal permitting, Release-17 NR-U, and shared infrastructure lower siting friction. Initiatives such as Virgin Media O2's outdoor cells in central Manchester underline this pivot.
Hybrid solutions are emerging, with Freshwave integrating all four UK carriers into a single outdoor-indoor small cell enclosure, cutting costs by 65% and energy by 60% relative to earlier systems. Indoor providers must now defend against Wi-Fi 7, which advertises 46 Gbps theoretical speeds, by highlighting deterministic latency, security, and slice management that Wi-Fi cannot match.
The Small Cell 5G Network Market Report is Segmented by Cell Type (Femtocell, Picocell, Microcell, and Metrocell), Operating Environment (Indoor and Outdoor), Frequency Band (Sub-6 GHz, Mmwave [More Than 24 GHz], and Sub-1 GHz), End-User (Telecom Operators, Enterprises, and Residential), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific owns 38% of 2024 revenue and tracks a 32.60% CAGR to 2030, propelled by China's 4.4 million 5G base stations and CNY 3 billion earmarked for 5G-Advanced overlays in 300 cities. China Unicom Beijing and Huawei achieved downlink peaks of 11.2 Gbps across a population of 10 million, setting a reference point for future dense overlays. Japan and South Korea push enterprise mmWave, and India's post-auction build-out supplies scope for densification through public-private partnerships.
North America showcases revenue realization efficiency. Ericsson's regional revenue climbed 55% year over year on the back of AT&T's USD 14 billion contract, underlining robust investment returns. More than 50 U.S. neutral-host projects operate in CBRS, and Canada's TELUS is rolling out the first commercial virtualized Open RAN, positioning the region at the forefront of cloud-native RAN experimentation. Still, Crown Castle's canceled deployments highlight suburban economics as a persistent hurdle.
Europe enjoys a clear spectrum policy yet lags in standalone 5G coverage, reaching only 2% penetration by late 2024. Virgin Media O2 and EE are ramping small-cell footprints, but many operators wait for a business-case inflection once device penetration rises. In the Middle East, the UAE logged record 30.5 Gbps 5G speeds, and du committed AED 2 billion to hyperscale data centers, signaling that Gulf operators will leapfrog directly to 5G-Advanced. Latin America sees Brazil's Brisanet and Uruguay's Antel expanding public 5G, though macroeconomic constraints and spectrum scarcity temper small-cell rollouts.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Nokia Corporation
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- ZTE Corporation
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- CommScope Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Baicells Technologies Co. Ltd
- Qucell Inc.
- JMA Wireless
- Parallel Wireless
- Mavenir Systems
- Casa Systems
- Corning Inc.
- Sercomm Corporation
- Comba Telecom Systems Holdings Ltd
- American Tower Corporation
- Boingo Wireless Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid densification needs in urban 5G roll-outs
- 4.2.2 Enterprise private-network demand (manufacturing, logistics)
- 4.2.3 Release-17 5G NR-U enabling unlicensed small-cell spectrum
- 4.2.4 Neutral-host business models gaining regulatory support
- 4.2.5 AI-driven self-optimizing networks cutting OpEx (under-reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Challenging fiber/backhaul economics in suburban and rural zones
- 4.3.2 Municipal site-acquisition delays and fees
- 4.3.3 Persistent security concerns around Open RAN small-cells (under-reported)
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Cell Type
- 5.1.1 Femtocell
- 5.1.2 Picocell
- 5.1.3 Microcell
- 5.1.4 Metrocell
- 5.2 By Operating Environment
- 5.2.1 Indoor
- 5.2.2 Outdoor
- 5.3 By Frequency Band
- 5.3.1 Sub-6 GHz
- 5.3.2 mmWave (More than 24 GHz)
- 5.3.3 Sub-1 GHz
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Telecom Operators
- 5.4.2 Enterprises
- 5.4.3 Residential
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Russia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 UAE
- 5.5.5.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.6 Africa
- 5.5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.5.6.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.2 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- 6.4.4 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.5 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd
- 6.4.6 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.7 Airspan Networks Inc.
- 6.4.8 CommScope Inc.
- 6.4.9 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.10 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.11 Baicells Technologies Co. Ltd
- 6.4.12 Qucell Inc.
- 6.4.13 JMA Wireless
- 6.4.14 Parallel Wireless
- 6.4.15 Mavenir Systems
- 6.4.16 Casa Systems
- 6.4.17 Corning Inc.
- 6.4.18 Sercomm Corporation
- 6.4.19 Comba Telecom Systems Holdings Ltd
- 6.4.20 American Tower Corporation
- 6.4.21 Boingo Wireless Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment










