 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851584
动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM):市场占有率分析、产业趋势与成长预测(2025-2030 年)Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
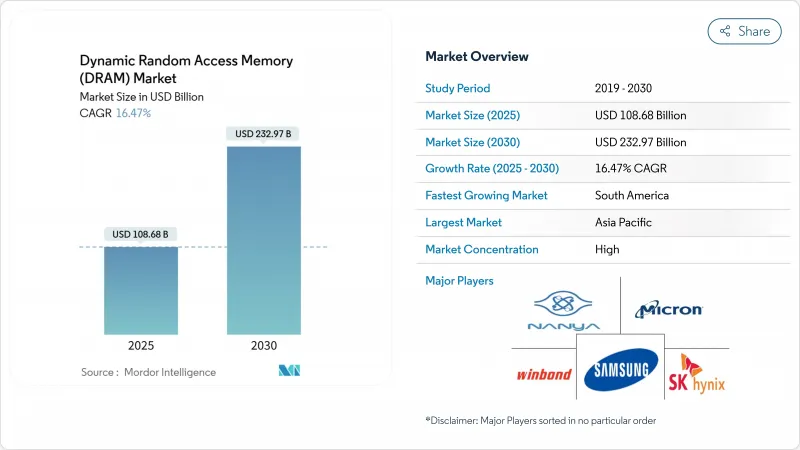
预计到 2025 年,动态随机存取记忆体 (DRAM) 市场规模将达到 1,086.8 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 2,329.7 亿美元,复合年增长率为 16.47%。
人工智慧伺服器的加速普及、高频宽记忆体的快速成长以及日益严格的汽车认证要求,正促使采购标准从单纯追求容量转向兼顾频宽、功耗和散热性能。超大规模云端运营商在2024年开始用DDR5和HBM3E模组更新其机架,而亚洲行动电话OEM厂商则将其大部分旗舰和中端产品组合迁移到LPDDR5X,并在2025年中期之前保持了95%以上的工厂使用率。随着分区架构取代传统的ECU网络,电动车的记忆体容量迅速成长,推动汽车DRAM需求进入多GB等级。同时,HBM3E产品线和传统DDR4产品线之间的供应分配竞争引发了价格上涨,并重塑了PC、智慧型手机和工业IoT闆卡的性价比格局。
全球动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场趋势与洞察
人工智慧和生成式人工智慧工作负载在超大规模资料中心的内容足迹不断扩大
NVIDIA 的 2025 年 Blackwell GP-AI 平台建立了超越传统 DDR 架构的频宽基准,将伺服器平均记忆体容量从 2024 年的 256GB 提升至 2025 年年中的数Terabyte部署。随着每个 HBM3E 堆迭的吞吐量超过 1TB/s,云端营运商围绕着以记忆体为中心的拓扑结构重新设计了机架。三星交付了可用于生产的 CXL 2.0 DRAM,使 Azure 和其他服务提供者能够跨主机共享内存,从而提高利用率,同时推迟添加计算节点的资本支出。因此,供应商将晶圆生产从 DDR4 转向 HBM,这导致传统等级的记忆体供应紧张,但加速了高端市场的利润成长。
亚太地区5G旗舰和中阶智慧型手机LPDDR采用率激增
美光的一年期LPDDR5X样品,运行速度高达9200 MT/s,将于2025年第一季交付给行动电话製造商,功耗降低20%,并将中国和印度机型的基准记忆体从8GB提升至12GB。小米、OPPO和传音等新兴品牌已签订长期合约,占用亚太地区晶圆厂的产能,迫使供应商调整行动和资料中心领域的产能分配。这种转变使得LPDDR自2015年LPDDR4量产以来,成为成长速度最快的行动记忆体。
週期性的供需关係导致平均售价出现剧烈波动
高利润率的HBM内存条的吸引力促使工厂将DDR4运作推迟到2025年初,导致5月份主流内存条现货价格上涨了50%。 DDR5记忆体的订单量也成长了15%至20%,促使OEM厂商重新设计材料清单或超额订购以避免价格进一步上涨。这种回馈循环加剧了市场波动,降低了生产计画的可视性,导致动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场的预期复合年增长率下降了2个百分点以上。
细分市场分析
到2024年,DDR5在动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场中所占比重仍然很小,但其预期复合年增长率(CAGR)将达到30.2%,成为成长最快的记忆体类型,这得益于JEDEC的JESD79-5C更新将其效能上限提升至8,800 Mbps。这项技术飞跃使得一级云端服务商能够运行DDR5-HBM3E混合配置,从而使每个插槽的有效频宽翻倍。美光的1Y DDR5将于2025年2月达到9,200 MT/s的效能,这项里程碑将促使伺服器OEM厂商加速平台更新换代。同时,由于企业IT预算仍倾向于成本优化配置,DDR4在2024年之前将维持45.3%的动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场占有率。随着工业和汽车设计向新标准的过渡,传统DDR3和DDR2的市占率持续缩小。
每当晶圆分配给DDR5晶片,用于PC的DDR4晶片就会减少,这导致中国笔记型电脑组装商的成本大幅上涨。持有长尾库存的拥有者利用套利机会,以2017年以来前所未有的更高的价格清仓DDR4库存。 JEDEC推出的新型CAMM2外形规格突破了SO-DIMM的高度限制,使笔记型电脑和边缘伺服器能够采用更高密度的单面堆迭式记忆体。这些封装技术的改进推动了动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场对更高频宽的需求,并带动了消费级和企业级设备的普及。
预计到2024年,19nm至10nm製程市场将占动态随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场规模的42.3%,并在2030年前以25.2%的年复合成长率成长。儘管采用EUV光刻技术的1Y製程晶片已于2025年第一季开始出货,但其产量比率仍比成熟的1z製程晶片低至少8个百分点。因此,许多装置製造商为了规避成本风险,续签了1z和1y製程晶片的合同,从而提高了中节点製程的产量。
SK海力士公布了垂直闸极DRAM蓝图,承诺从2027年起实现晶圆级堆迭,这标誌着其长期战略重心将从横向扩展转向三维架构。考虑到光罩模组、材料和折旧免税额成本,每次平面尺寸缩小带来的成本降低不到12%,这促使晶圆厂寻求架构重新设计,而不仅仅是缩小几何尺寸。移动和消费性电子产品对成本的敏感度使得20nm及以上製程节点对于价格敏感型产品而言仍然具有竞争力,这有助于晶圆厂实现产能多元化,并确保分层生产结构,从而支撑整体收入的稳定性。
动态随机存取记忆体市场按架构(DDR2 之前、DDR3、DDR4、DDR5、LPDDR、GDDR)、製程节点(20 奈米以下、19 奈米至 10 奈米、10 奈米以上)、容量(4 GB 以下、4-8 GB、8-16 GB、16 GB 以上)、容量(4 GB 以下、4-8 GB、8-16 GB、16 GB 以上)、PC和笔记型电脑、伺服器和超大规模资料中心、其他)以及地区(北美、欧洲、亚太地区、南美、中东和非洲)进行细分。
区域分析
亚太地区预计2024年营收将维持31.2%的成长,主要得益于韩国、台湾和中国当地晶圆厂的强劲发展。韩国供应商已承诺在2028年投资120兆韩元(约840亿美元)用于产能扩张,以确保其在HBM和传统DRAM生产领域的主导。同时,台湾代工组装也扩大了先进封装生产线,以满足日益增长的HBM4需求,并利用其在逻辑节点领域累积的前端技术,引入硅通孔技术以降低热阻。
北美成为最大的消费市场,超大规模资料中心建置商加快了机架更新换代,美国汽车製造商也整合了区域控制器。美光科技获得了《晶片法案》(CHIPS Act)61亿美元的资金,用于建造一座新的巨型晶圆厂,旨在规避地缘政治风险并缩短国内客户的前置作业时间。在欧洲,技术重点集中在汽车和工业应用领域,德国原始设备製造商(OEM)坚持以高价提供长寿命、高温保固。
预计南美洲将以22.2%的复合年增长率成长,这主要得益于巴西、阿根廷和墨西哥对电子组装生态系统的培育以及供应链在地化的推进。降低国产组装记忆体组件进口关税的政策诱因正在推动筹资策略渐进但意义深远的转变。中东和非洲地区实现了中等个位数的成长,这得益于波湾合作理事会资料中心的建设以及尼日利亚和肯亚智慧型手机普及率的提高,儘管政治不稳定仍然限制智慧型手机的普及。总而言之,这些区域趋势表明,在东亚製造地的背景下,充满活力的随机存取记忆体(DRAM)市场正在实现收入来源多元化。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 加速超大规模资料中心采用人工智慧和生成式人工智慧工作负载
- 亚太地区5G旗舰和中阶智慧型手机LPDDR采用率激增
- 汽车区域/网域控制器从 NOR 迁移到高温 DRAM
- 边缘人工智慧和工业IoT闆卡需要耐高温DRAM模组
- 云端服务供应商迁移到 CXL 连线记忆体池
- 市场限制
- 週期性的供需关係导致平均售价出现剧烈波动
- 10nm 和 Sub-EUV 节点产量比率下降的挑战
- 对中国的地缘政治出口限制阻碍了高密度伺服器DRAM的出货。
- 价值链分析
- 技术展望
- 监理展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 定价分析
- DRAM现货价格(每GB)
- 价格趋势分析
- 宏观经济影响分析
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 建筑设计
- DDR2之前
- DDR3
- DDR4
- DDR5
- LPDDR
- GDDR
- 依技术节点
- 20奈米或以上
- 19 nm-10 nm
- 小于 10 奈米(极紫外光)
- 按产能
- 4 GB 或更少
- 4-8 GB
- 8-16 GB
- 超过 16 GB
- 按最终用途
- 智慧型手机和平板电脑
- 桌上型电脑和笔记型电脑
- 伺服器和超大规模资料中心
- 图形和游戏机
- 汽车电子产品
- 消费性电子产品(机上盒、智慧型电视、VR/AR)
- 工业和物联网设备
- 其他的
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 法国
- 英国
- 北欧国家
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 台湾
- 韩国
- 日本
- 印度
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 智利
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- SK Hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc.(CXMT)
- Nanya Technology Corporation
- Winbond Electronics Corporation
- Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp.(PSMC)
- Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd.(JHICC)
- GigaDevice Semiconductor(Beijing)Inc.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc.(ISSI)
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc.(ESMT)
- Zentel Electronics Corporation
- Alliance Memory, Inc.
- AP Memory Technology Corp.
- Phison Electronics Corporation
- JSC Mikron(Mikron Group)
- AMIC Technology Corporation
- Utron Technology Inc.
- Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Dynamic Random Access Memory market size is valued at USD 108.68 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 232.97 billion by 2030, translating into a strong 16.47% CAGR.

Accelerated adoption of AI-centric servers, the steep ramp-up of high-bandwidth memory, and tighter automotive qualification requirements have shifted purchasing criteria from capacity alone to a balanced focus on bandwidth, power, and thermal performance. Hyperscale cloud operators began refreshing racks with DDR5 and HBM3E modules during 2024, while handset OEMs in Asia moved much of their flagship and mid-tier portfolios to LPDDR5X, collectively keeping fab utilization above 95% through mid-2025. Memory content per electric vehicle rose quickly as zonal architectures replaced traditional ECU networks, pushing automotive DRAM demand into multi-gigabyte territory. At the same time, supply allocation conflicts between lucrative HBM3E and legacy DDR4 lines triggered price surges that reshaped cost-performance trade-offs for PCs, smartphones, and industrial IoT boards.
Global Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) Market Trends and Insights
Ascending content footprint of AI and generative-AI workloads in hyperscale data centers
NVIDIA's 2025 Blackwell GP-AI platforms established bandwidth baselines that eclipsed conventional DDR architectures, lifting average server memory from 256 GB in 2024 to multi-terabyte deployments by mid-2025. With each HBM3E stack delivering more than 1 TB/s, cloud operators re-architected racks around memory-centric topologies. Samsung delivered production-ready CXL 2.0 DRAM that allowed Azure and other providers to pool memory across hosts, improving utilization while deferring capex on additional compute nodes. Suppliers consequently shifted wafer starts from DDR4 to HBM, triggering tightness in legacy grades but accelerating profit growth in the premium segment.
Soaring LPDDR adoption in 5G flagship and mid-tier smartphones across APAC
Micron's 1Y LPDDR5X samples running at 9,200 MT/s reached handset makers in Q1 2025, cutting power by 20% and raising baseline configurations in Chinese and Indian models from 8 GB to 12 GB RAM. Xiaomi, OPPO, and emerging brands such as Transsion are locked in forward contracts that consume a growing slice of APAC fab capacity, forcing suppliers to juggle commitments between mobile and datacenter lines. The shift gave LPDDR a steeper growth curve than any other mobile memory since LPDDR4 entered mass production in 2015.
Supply-demand cyclicality driving extreme ASP volatility
High-margin HBM pull-ins persuaded fabs to postpone DDR4 runs early in 2025, igniting a 50% spot-price jump for mainstream modules in May. DDR5 contracts also climbed 15-20%, prompting OEMs to re-engineer product bills of materials or over-order to hedge against further spikes. The feedback loop amplified volatility and cut visibility for production planning, knocking two-plus points from the Dynamic Random Access Memory market's forecast CAGR.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Automotive zonal and domain controllers migrating from NOR to high-temperature DRAM
- Edge-AI and industrial IoT boards requiring extended-temperature DRAM modules
- Yield-erosion challenges below 10 nm EUV nodes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
DDR5 accounted for a minimal share of the Dynamic Random Access Memory market in 2024, yet carried the fastest 30.2% forecast CAGR, underpinned by JEDEC's JESD79-5C update that lifted performance ceilings to 8,800 Mbps. That technical leap allowed tier-1 cloud builders to run mixed DDR5-HBM3E configurations that doubled per-socket effective bandwidth. Micron's 1Y DDR5 reached 9,200 MT/s in February 2025, a milestone that pushed server OEMs to pull forward platform refreshes. Meanwhile, DDR4 retained a 45.3% Dynamic Random Access Memory market share through 2024 because corporate IT budgets still favoured cost-optimized configurations. Legacy DDR3 and DDR2 footprints continued to shrink as industrial and automotive design-ins migrated to newer standards.
Suppliers confronted a balancing act: every wafer reassigned to DDR5 meant fewer DDR4 chips for PCs, driving cost spikes that flowed downstream to notebook assemblers in China. Holders of long-tail inventory exploited arbitrage trading, unloading stockpiled DDR4 at premiums unseen since 2017. JEDEC's new CAMM2 form factor removed the height constraints of SO-DIMMs, letting laptops and edge servers adopt denser single-sided stacks. Those packaging gains fed into the Dynamic Random Access Memory market's momentum toward higher-bandwidth norms across consumer and enterprise devices.
The 19 nm-10 nm bracket held 42.3% of the Dynamic Random Access Memory market size in 2024 and is projected to grow 25.2% through 2030 as suppliers squeeze additional dies per wafer without plunging into the yield-risk chasm of sub-10 nm. EUV-enabled 1Y production began shipping revenue units in Q1 2025, but line yields remained at least eight points below mature 1z lines. Consequently, many device makers renewed agreements for 1z and 1y grades to buffer cost risk, giving mid-node processes a volume boost.
SK Hynix laid out a vertical-gate DRAM roadmap that promises wafer-level stacking beyond 2027, signalling the long-term pivot from lateral scaling to 3D architectures. Each successive planar shrink delivers less than 12% cost reduction after mask set, materials, and depreciation are factored in, nudging fabs to look for structural redesigns rather than geometrical shrink alone. Cost sensitivity in mobile and consumer electronics kept >=20 nm nodes alive for price-focused SKUs, ensuring a stratified production mix that diversified fab output and underpinned overall revenue resiliency.
Dynamic Random Access Memory Market is Segmented by Architecture (DDR2 and Earlier, DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, LPDDR, and GDDR), Technology Node (>=20 Nm, 19 Nm-10 Nm, and <10 Nm), Capacity (<=4 GB, 4-8 GB, 8-16 GB, and >=16 GB), End-Use Application (Smartphones and Tablets, Pcs and Laptops, Servers and Hyperscale Data Centers, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained a 31.2% revenue position in 2024 on the strength of fabs clustered across South Korea, Taiwan, and mainland China. South Korean suppliers pledged KRW 120 trillion (USD 84 billion) for capacity build-outs through 2028, a figure intended to safeguard leadership in both HBM and traditional DRAM production. Taiwan's contract assembly houses, meanwhile, expanded advanced packaging lines to service rising HBM4 demand, leveraging front-end know-how from logic nodes to introduce Through-Silicon-Via innovations that reduce thermal resistance.
North America formed the largest consumption market as hyperscale builders accelerated rack refreshes and automakers in the United States integrated zonal controllers. Micron secured USD 6.1 billion CHIPS Act funding to construct a new megafab, a move aimed at de-risking geopolitical exposure and shortening lead times for domestic clients. Europe maintained a technology focus on automotive and industrial applications, with German OEMs insisting on extended temperature and longevity guarantees that fetched premium pricing.
South America is forecast to grow at a 22.2% CAGR as Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico nurture electronics assembly ecosystems to localize supply. Policy incentives cut import tariffs on memory components assembled domestically, creating modest but meaningful shifts in sourcing strategies. The Middle East and Africa displayed mid-single-digit growth anchored by data-center build-outs in Gulf Cooperation Council states and rising smartphone penetration in Nigeria and Kenya, yet political instability continued to temper wider adoption. Combined, these regional narratives underscore how the Dynamic Random Access Memory market diversifies revenue streams even as manufacturing remains concentrated in East Asia.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- SK Hynix Inc.
- Micron Technology Inc.
- ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. (CXMT)
- Nanya Technology Corporation
- Winbond Electronics Corporation
- Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp. (PSMC)
- Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd. (JHICC)
- GigaDevice Semiconductor (Beijing) Inc.
- Etron Technology Inc.
- Integrated Silicon Solution Inc. (ISSI)
- Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc. (ESMT)
- Zentel Electronics Corporation
- Alliance Memory, Inc.
- AP Memory Technology Corp.
- Phison Electronics Corporation
- JSC Mikron (Mikron Group)
- AMIC Technology Corporation
- Utron Technology Inc.
- Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Ascending Content Footprint of AI and Generative-AI Workloads in Hyperscale Data Centers
- 4.2.2 Soaring LPDDR Adoption in 5G Flagship and Mid-Tier Smartphones Across APAC
- 4.2.3 Automotive Zonal/Domain Controllers Migrating from NOR to High-Temperature DRAM
- 4.2.4 Edge-AI and Industrial IoT Boards Requiring Extended-Temperature DRAM Modules
- 4.2.5 Cloud Service Providers' Transition to CXL-attached Memory Pools
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Supply-Demand Cyclicality Driving Extreme ASP Volatility
- 4.3.2 Yield-Erosion Challenges Below 10 nm EUV Nodes
- 4.3.3 Geopolitical Export Controls on China Limiting High-density Server DRAM Shipments
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Pricing Analysis
- 4.8.1 DRAM Spot Price (Per GB)
- 4.8.2 Pricing Trends Analysis
- 4.9 Macroeconomic Impact Analysis
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Architecture
- 5.1.1 DDR2 and Earlier
- 5.1.2 DDR3
- 5.1.3 DDR4
- 5.1.4 DDR5
- 5.1.5 LPDDR
- 5.1.6 GDDR
- 5.2 By Technology Node
- 5.2.1 >=20 nm
- 5.2.2 19 nm - 10 nm
- 5.2.3 <10 nm (EUV)
- 5.3 By Capacity
- 5.3.1 <=4 GB
- 5.3.2 4 - 8 GB
- 5.3.3 8 - 16 GB
- 5.3.4 >=16 GB
- 5.4 By End-use Application
- 5.4.1 Smartphones and Tablets
- 5.4.2 PCs and Laptops
- 5.4.3 Servers and Hyperscale Data Centers
- 5.4.4 Graphics and Gaming Consoles
- 5.4.5 Automotive Electronics
- 5.4.6 Consumer Electronics (Set-top Boxes, Smart TV, VR/AR)
- 5.4.7 Industrial and IoT Devices
- 5.4.8 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 France
- 5.5.2.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.4 Nordics
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Taiwan
- 5.5.3.3 South Korea
- 5.5.3.4 Japan
- 5.5.3.5 India
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Chile
- 5.5.4.3 Argentina
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.2 SK Hynix Inc.
- 6.4.3 Micron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.4 ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc. (CXMT)
- 6.4.5 Nanya Technology Corporation
- 6.4.6 Winbond Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.7 Powerchip Semiconductor Manufacturing Corp. (PSMC)
- 6.4.8 Fujian Jinhua Integrated Circuit Co., Ltd. (JHICC)
- 6.4.9 GigaDevice Semiconductor (Beijing) Inc.
- 6.4.10 Etron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.11 Integrated Silicon Solution Inc. (ISSI)
- 6.4.12 Elite Semiconductor Memory Technology Inc. (ESMT)
- 6.4.13 Zentel Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.14 Alliance Memory, Inc.
- 6.4.15 AP Memory Technology Corp.
- 6.4.16 Phison Electronics Corporation
- 6.4.17 JSC Mikron (Mikron Group)
- 6.4.18 AMIC Technology Corporation
- 6.4.19 Utron Technology Inc.
- 6.4.20 Hua Hong Semiconductor Limited
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment









