 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851966
印度农业拖拉机:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)India Agricultural Tractor - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
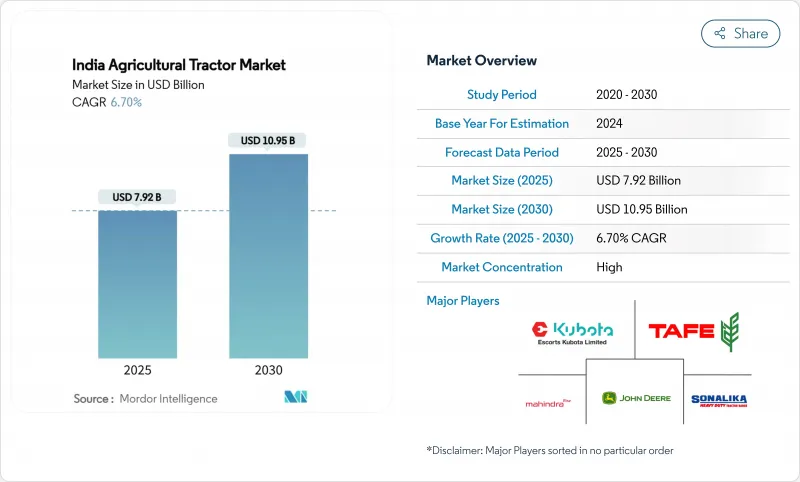
印度农业拖拉机市场规模预计在 2025 年达到 79.2 亿美元,在 2030 年达到 109.5 亿美元,年复合成长率为 6.70%。
成长与直接福利转移计画、排放合规期限以及政府支持的机械化基金密切相关,这些因素共同塑造了采购週期。太阳能水泵覆盖范围的扩大、二手设备平台的快速数位化以及精密农业的普及正在扩大基本客群,而日益紧缩的信贷环境则抑制了增长势头。区域需求高度集中在北部平原地区,而西部各州近期经历了最快速的增长,因为多元化的作物组合使得高端设备更具吸引力。
印度农业拖拉机市场趋势与洞察
直接发放「总理农民收入支持计画」(PM-Kisan)补贴后,与补贴相关的需求激增
2025年8月,PM-Kisan季度补贴2,050亿卢比(约25亿美元)注入流动性,六週内拖拉机融资申请量激增。受益农民近期对31-50马力拖拉机支付了高达20%的首付,进一步强化了生产者与补贴发放週期同步的周期性需求成长。因此,印度拖拉机产业正更加密切地关注资金流动以及作物季节性变化。製造商透过将生产划分为中阶和高端市场来对冲波动。数位化支付管道减少了资金流失,提高了销售预测的可靠性。只要每年600亿卢比(约7,200万美元)的补贴维持不变,印度拖拉机产业就可能迎来一波可预测的流动性成长。
甘蔗种植区快速拖拉机电气化试点项目
在PM E-DRIVE(PM电动驱动创新车辆升级计画)计画的支持下,政府采集费用提供高达40%的补贴,并已启动试点计画。在这些试验计画中,甘蔗合作社测得每小时燃料节省量达60-70%。在马哈拉斯特拉邦和北方邦,由于甘蔗种植密度高,电动拖拉机的使用率很高,投资回报前景可观。早期用户正在维修棚屋,安装30kW的充电桩,并连接到非尖峰时段电价。零件製造商表示,国内用于牵引电池、温度控管和小型逆变器的生态系统仍在发展中。印度拖拉机产业将电气化视为规避排放法规并吸引註重环境、社会和治理(ESG)的买家的一种途径。虽然目前的试点车队规模较小,仅有几百台,但预计到2027年电池成本将大幅下降,这将使25-35马力范围内的拖拉机成为主流,尤其是在太阳能水泵已经改善农村负载率的地区。
更严格的非道路排放气体法规(TREM-V),以及虚高的价格标籤
针对功率超过37千瓦的发动机,第五阶段排放法规将增加排放气体后处理系统,将使工厂成本增加8-12%。主要目标商标产品製造商(OEM)正在本地新建生产线上生产柴油氧化触媒(DOC)和柴油颗粒过滤器(DPF)模组,例如FPT位于诺伊达的F28工厂。规模较小的品牌则面临退出市场或寻求契约製造的风险。农民会优先购买早期阶段的拖拉机,可能导致2024-2025年出现需求激增,随后出现低谷。信贷机构将错开贷款期限,并将残值与法规规定的报废期限挂钩。随着供应商扩大过滤器基板和感测器的生产规模,成本转嫁最终会趋于正常,但短期内的价格缺口将抑製印度拖拉机产业的成长。
细分市场分析
31-50马力频宽占据印度拖拉机市场46%的份额,主要面向1-3公顷的耕地,在这些耕地上,多功能性比专业动力更为重要。尤其是在柴油价格上涨之后,农民们更青睐那些在购置成本和燃油效率之间取得良好平衡的引擎。随着多种作物种植和打包机的普及,对更高扭力的需求日益增长,51-80马力区间的拖拉机将以9.3%的复合年增长率增长。 TREM-V技术的推广将加速优质化,使入门级车型的价格接近配置丰富的车型。 GPS导航、CAN总线控制的农具以及更长的保养週期正逐渐成为50马力及以上拖拉机的标配。马恆达进军30马力以下细分市场表明,微型农地的需求仍然存在,但资金筹措障碍限制了其成长。 80马力以上的拖拉机主要面向承包商和出口作物种植园,但在市场整合加剧之前,仍将保持小众市场地位。
中阶拖拉机越来越多地配备远端资讯处理系统,用于追踪工作小时数、负载容量和燃油量,从而帮助贷款机构进行风险评估。随着二手拖拉机交易平台日趋成熟,31-50马力拖拉机的残值不断提升,进一步检验了其经济性。田间试验显示,在印度恆河平原的稻麦耕耘机可使生产率提高12%。更高马力的拖拉机采用机器人换檔变速箱和电液转向系统来减轻操作员的疲劳,但其普及程度取决于工资增长和定製作业的密度。因此,印度拖拉机产业呈现功率等级分层的趋势:中型拖拉机保值性高,高阶拖拉机技术创新强劲,而小型拖拉机则面临价格压力。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 总理农民补贴直接支付后,与补贴相关的需求激增
- 甘蔗种植带拖拉机车队快速电气化试点项目
- 规范二手拖拉机市场将改善升级週期。
- 最低支援价格(MSP)下滑有利于中型马力拖拉机的销售
- 无人机辅助挂钩系统促进交叉销售
- 农场太阳能水泵计画旨在提高拖拉机动力输出轴(PTO)的利用率
- 市场限制
- 由于更严格的非道路排放法规(TREM-V)导致价格上涨
- 面积小于一公顷的土地持续零散分布
- 远端资讯处理技术普及率低限制了资金筹措创新
- 非银行金融公司流动性危机后,农村信贷成长疲软。
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特的五力模型
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按引擎输出
- 小于30马力
- 31-50 HP
- 51-80 HP
- 超过 80 匹马力
- 按驱动类型
- 两轮驱动
- 四轮驱动
- 透过使用
- 高地农用拖拉机
- 果园拖拉机
- 其他用途
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Mahindra&Mahindra Ltd.
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- Escorts Kubota Limited.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- Sonalika Group(International Tractors Limited(ITL))
- VST Tillers Tractors Limited
- Same Deutz-Fahr India Private Limited(SDF Group SpA)
- Indo Farm Equipment Limited
- Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.
- Action Construction Equipment Limited
- Preet Tractors Private Limited
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The India agricultural tractor market size stands at USD 7.92 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 10.95 billion by 2030, advancing at a 6.70% CAGR.

Growth is tied to direct-benefit transfer programs, emission compliance deadlines, and state-backed mechanization funds that shape procurement cycles. Expanding solar pump coverage, rapid digitalization of used-equipment platforms, and precision-agriculture adoption are widening the customer base, while a gradually tightening credit environment tempers momentum. Regional demand is highly concentrated in the northern plains, and western states have recently registered the quickest expansion as diversified crop portfolios justify premium equipment.
India Agricultural Tractor Market Trends and Insights
Subsidy-Linked Demand Spikes After PM-Kisan Direct Benefit Transfers
Quarterly PM-Kisan disbursements of INR 20,500 crore (USD 2.5 billion) in August 2025 infused liquidity that lifted tractor finance applications within six weeks Beneficiary farmers recently cover up to 20% of a down payment on 31-50 HP models, reinforcing cyclical surges that producers synchronize with payment calendars. The tractor industry in the Indian market, therefore, tracks fiscal flows more closely than crop-seasonality alone. Manufacturers hedge volatility by splitting production runs between mid-range volumes and premium variants, while dealers preload inventory before each installment release. Digital payment rails shrink leakages and make sales forecasting more reliable. As long as the annual INR 6,000 (USD 72) benefit stays intact, the tractor industry in the Indian market is likely to ride predictable liquidity waves.
Rapid Tractor Fleet Electrification Pilots in Sugar-Cane Belts
Subsidies covering up to 40% of e-tractor acquisition costs under the PM E-DRIVE (PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement) program have triggered pilots where cane cooperatives measure 60-70% fuel-cost savings per hour. Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh leverage dense cane clusters that assure high utilization, boosting payback prospects. Early adopters retrofit sheds with 30 kW chargers linked to off-peak tariffs. Component makers report a nascent domestic ecosystem for traction batteries, thermal management, and compact inverters. The tractor industry in the Indian market sees electrification as an avenue to sidestep emission penalties and win ESG-minded buyers. While current pilot numbers are in the low hundreds, battery cost declines projected for 2027 could unlock mainstream uptake in the 25-35 HP range, especially where solar pumps already improve rural load factors.
Tightening Non-Road Emission Standards (TREM-V), Inflating Price Tags
Stage V limits for engines above 37 kW add emission after-treatment systems that raise factory costs by 8-12%. Larger OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) localize DOC-DPF modules at new lines such as FPT's F28 plant in Noida. Smaller brands risk market exit or seeking contract manufacturing. Farmers front-load purchases of pre-stage tractors, causing a demand pull-forward in 2024-25 and a potential trough thereafter. Credit financiers split loan tenors so residual values align with regulatory obsolescence. Over time, cost pass-through will normalize as suppliers scale filter substrates and sensors, but an interim affordability gap dampens the tractor industry in the Indian market's growth.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Formalization of Used-Tractor Marketplaces Improving Upgrade Cycles
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) indexation favoring mid-HP tractor sales
- Low Telematics Adoption is Limiting Financing Innovation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The 31-50 HP band owns 46% of the tractor industry in India market share, anchored in plots of 1-3 hectares where versatility trumps specialized power. Farmers gravitate to engines that balance purchase price with fuel efficiency, especially after diesel price spikes. The 51-80 HP segment expands at a 9.3% CAGR as multi-crop rotations and baler adoption demand higher torque. Premiumization gathers pace because TREM-V compliance pushes base-model prices closer to feature-rich trims. GPS guidance, CAN-enabled implement control, and longer service intervals are becoming standard above 50 HP. Mahindra's thrust into sub-30 HP niches illustrates residual demand for micro-plots, yet financing hurdles temper growth. Above 80 HP units cater to contractors and export-crop estates but remain niche until consolidation advances.
Mid-range tractors increasingly embed telematics that capture hours, load, and fuel, assisting lenders with risk scoring. As used-tractor portals mature, residual values for 31-50 HP units strengthen, further validating ownership economics. Field trials show a 12% productivity lift when mid-HP tractors pair with minimal-tillage implements, especially in rice-wheat systems across the Indo-Gangetic plain. High-HP modules leverage robotic shift transmissions and electro-hydraulic steering to cut operator fatigue, but adoption hinges on wage inflation and custom-hiring density. The tractor industry in the Indian market thus sees power-band stratification: value retention in mid-range, innovation in upper tiers, and affordability pressure in sub-compact classes.
The India Tractor Market Report is Segmented by Engine Power (Less Than 30 HP, 31-50 HP, and More), by Drive Type (Two-Wheel Drive and Four-Wheel Drive), and by Application (Row Crop Tractors, Orchard Tractors, and Other Applications). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Mahindra&Mahindra Ltd.
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- Escorts Kubota Limited.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- Sonalika Group (International Tractors Limited (ITL)
- VST Tillers Tractors Limited
- Same Deutz-Fahr India Private Limited (SDF Group S.p.A.)
- Indo Farm Equipment Limited
- Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.
- Action Construction Equipment Limited
- Preet Tractors Private Limited
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Subsidy-linked demand spikes after PM-Kisan Direct Benefit transfers
- 4.2.2 Rapid tractor fleet electrification pilots in sugar-cane belts
- 4.2.3 Formalization of used-tractor marketplaces improving upgrade cycles
- 4.2.4 Minimum Support Price (MSP) indexation favoring mid-HP tractor sales
- 4.2.5 Drone-ready hitching systems boosting cross-selling
- 4.2.6 On-farm solar-pump schemes raising tractor PTO (Power take-off) utilization
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Tightening non-road emission standards (TREM-V) inflating price tags
- 4.3.2 Persistent land-holding fragmentation below 1 hectare
- 4.3.3 Low telematics adoption limiting financing innovation
- 4.3.4 Stagnant rural credit growth post-NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company) liquidity crunch
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porters Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Engine Power
- 5.1.1 Less than 30 HP
- 5.1.2 31-50 HP
- 5.1.3 51-80 HP
- 5.1.4 Above 80 HP
- 5.2 By Drive Type
- 5.2.1 Two-wheel Drive
- 5.2.2 Four-wheel Drive
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Row-Crop Tractors
- 5.3.2 Orchard Tractors
- 5.3.3 Other Applications
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Mahindra&Mahindra Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Tractors and Farm Equipment Limited
- 6.4.3 Escorts Kubota Limited.
- 6.4.4 Deere & Company
- 6.4.5 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.6 Sonalika Group (International Tractors Limited (ITL)
- 6.4.7 VST Tillers Tractors Limited
- 6.4.8 Same Deutz-Fahr India Private Limited (SDF Group S.p.A.)
- 6.4.9 Indo Farm Equipment Limited
- 6.4.10 Captain Tractors Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Action Construction Equipment Limited
- 6.4.12 Preet Tractors Private Limited







