 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906060
拉丁美洲乘用车:市场份额分析、行业趋势和统计数据、成长预测(2026-2031 年)Latin America Passenger Car - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
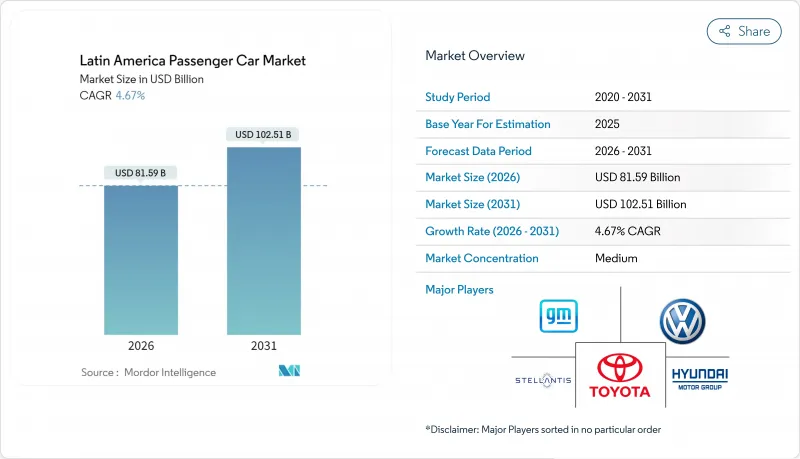
预计到 2026 年,拉丁美洲乘用车市场价值将达到 815.9 亿美元。
这代表着从 2025 年的 779.5 亿美元成长到 2031 年的 1,025.1 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 4.67%。
儘管汇率波动和贸易政策变化,强劲的家庭需求、加速的电气化以及汽车生产的回流仍然支撑着这一增长。製造商正在扩大区域生产规模,以符合美国墨加协定(USMCA)和南方共同市场(Mercosur)的在地采购要求。同时,政府奖励,例如巴西的“Mover计划”,正在刺激国内电动车的生产。中国品牌正抓住这一趋势,迫使现有汽车製造商重新评估产品系列和定价策略,推出具有成本竞争力的车型。此外,半导体供应的稳定性正在恢復生产节奏,使汽车製造商能够解决因2021年至2023年供不应求订单。
拉丁美洲乘用车市场趋势及分析
疫情后家庭汽车拥有率的韧性
随着疫情限制措施的逐步解除,私家车拥有率显着上升。这一激增主要受工作模式转变、共用出行依赖性降低以及大量人口向郊区迁移的推动。在墨西哥,这种转变导致轻型汽车销售大幅成长,预计在经济復苏的支撑下,这一趋势将持续到2025年。同时,在巴西,近期的经济復苏提振了消费者信心,促使人们开始购买先前推迟的汽车,尤其是在农村地区。有限的公共运输基础设施也使得汽车展示室客流量稳定,从而维持了对私家车出行方式的持续需求。
中国汽车製造商资本的快速流入和低成本电动车进口
凭藉强大的国内电池供应链和政府支持的资金筹措,中国汽车製造商正逐步进军拉丁美洲市场。例如,比亚迪透过将生产转移到巴西本地,迅速扩大了在巴西的市场份额。这项策略不仅规避了进口关税,也增强了其价格竞争力。随后,长城汽车和奇瑞等品牌也纷纷效仿,加剧了该地区的价格竞争。虽然日益激烈的竞争扩大了消费者可选择的经济型电动车的范围,但也给现有汽车製造商带来了压力,挤压了它们的利润空间,并改变了竞争格局。
披索和雷亚尔贬值推高进口成本
宏观经济压力正在削弱拉丁美洲主要市场汽车的价格竞争力。巴西面临外贸失衡,阿根廷的工业产能仍未充分利用,这两点都凸显了更广泛的经济紧张。同时,疲软的该地货币推高了进口零件的成本。为因应这一局面,汽车製造商纷纷提高车辆价格,这可能会延长更换週期,并抑制非必要升级的需求。这些倡议有可能拖慢成长预期,并使维持长期市场扩张的努力变得更加复杂。
细分市场分析
预计到2025年,SUV/跨界车将占拉丁美洲乘用车市场的40.85%,在预测期(2026-2031年)内以4.88%的复合年增长率超越其他车型。小型车和B级车的日益普及推动了入门价格的下降。更高的离地间隙(非常适合未铺设路面和易涝道路)以及消费者普遍认为更高的安全性是推动市场需求的主要因素。丰田的混合动力SUV策略不仅充分利用了现有的乙醇基础设施,而且符合排放气体法规。与此同时,新兴的中国汽车製造商正在推出价格与传统紧凑型轿车相当的多功能跨界车,这促使偏好转向更高车身的车型。
在都市区拥挤和燃油效率是购车决策关键因素的地区,轿车和掀背车仍然占有一席之地,尤其是在巴西沿海城市。然而,随着家庭在车辆更换週期中升级换代,它们的总合份额正在下降。多用途汽车(MPV)仍然是一个小众市场,主要面向农村车队营运商和大家庭,在这些地区,载客量比燃油效率更为重要。
2025年,入门级A/B级车型占拉丁美洲乘用车市场的47.83%,预计在预测期(2026-2031年)内将以5.08%的复合年增长率增长,这主要得益于紧凑型汽车融资渠道的便利性和政府的税收优惠政策。巴西和墨西哥融资管道的改善提高了汽车的可负担性,同时汽车製造商正透过平台通用降低单位成本。
中型C级车迎合了不断壮大的中产阶级的需求,但随着消费者直接转向紧凑型SUV,它们面临着被替代的风险。豪华D/E级车目前主要针对富裕的都市区专业人士和政府用车,但电动车正在开拓一个新的高端消费群体。比亚迪的Dolphin Mini就是一个很好的例子,它展示了价格亲民的小型电动车,加上税收优惠政策,如何加速科技的普及应用。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 疫情后家庭汽车拥有量呈现强劲反弹
- 中国整车厂资本快速涌入和低成本电动车进口
- 为规避美墨加协定/南方共同市场关税上涨,汽车製造商纷纷重返日本市场
- 汽车製造商恢復对灵活燃料的投资计划
- 巴西和哥伦比亚的电动车税收优惠政策
- 稳定半导体供应链,使生产能赶上需求
- 市场限制
- 由于披索和雷亚尔贬值,进口成本上升。
- 加速大都会区快速公车系统(BRT)的扩张
- 主要都会区以外地区公共充电基础设施密度不足
- 加强区域二氧化碳排放平均目标(2027年)
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模及成长预测(以金额为准/数量)
- 按车辆类型
- 掀背车
- 轿车
- SUV/跨界车
- 多用途汽车(MPV)
- 按车辆类别
- 入门级(A/B)
- 中型车(C)
- 全尺寸(D/E)
- 按推进/燃料类型
- 汽油
- 柴油引擎
- 弹性燃料汽车
- 油电混合车
- 电池式电动车
- 按销售管道
- 厂商直营店
- 独立经销商
- 按国家/地区
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- 智利
- 秘鲁
- 其他拉丁美洲地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- General Motors Company
- Volkswagen AG
- Stellantis NV
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Ford Motor Company
- Nissan Motor Corporation
- Renault SA
- Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- Kia Corporation
- BMW AG
- Daimler AG(Mercedes-Benz)
- Chery Automobile
- BYD Auto
- SAIC-GM-Wuling
- Subaru Corporation
- Mazda Motor Corporation
- Geely Auto
- Audi AG
- Suzuki Motor Corporation
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
Latin America passenger car market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 81.59 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 77.95 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 102.51 billion, growing at 4.67% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Robust household demand, accelerating electrification, and on-shoring of vehicle production continue to underpin this growth despite currency volatility and shifting trade policies. Manufacturers are scaling regional plants to comply with USMCA and Mercosur content rules, while government incentives-led by Brazil's Mover program-stimulate domestic EV output. Chinese brands capitalize on these dynamics with cost-effective models that pressure incumbent OEMs to update product portfolios and pricing strategies. Meanwhile, stabilizing semiconductor supplies restores production rhythm, enabling automakers to address deferred orders accumulated during 2021-2023 shortages.
Latin America Passenger Car Market Trends and Insights
Resilient Post-Pandemic Rebound in Household Car Ownership
As pandemic restrictions eased, personal vehicle ownership saw a notable uptick. This surge was fueled by changing work habits, a diminished reliance on shared mobility, and a notable migration trend towards suburban areas. In Mexico, this shift has led to a pronounced increase in light-vehicle sales, a momentum that's projected to persist into 2025, buoyed by an improving economy. Meanwhile, in Brazil, a recent economic upswing has rekindled consumer confidence, prompting many to make vehicle purchases they had previously postponed. Notably, demand is particularly robust in secondary cities. Here, a limited public transportation infrastructure has resulted in consistent showroom traffic and a sustained appetite for personal mobility solutions.
Rapid Inflow of Chinese OEM Capital and Low-Cost EV Imports
Chinese automakers, bolstered by robust domestic battery supply chains and state-backed financing, are making significant inroads into Latin America. BYD, for instance, has swiftly captured market share in Brazil by localizing its production. This strategy not only sidesteps import tariffs but also allows for more competitive pricing. Following suit, brands like GWM and Chery are amplifying price competition in the region. While this surge in competition offers consumers a wider array of affordable electric vehicle choices, it simultaneously strains established manufacturers, squeezing their profit margins and altering the competitive dynamics.
Peso and Real Depreciation Inflating Import Costs
Key Latin American markets are feeling the pinch of macroeconomic pressures, impacting automotive affordability. Brazil grapples with external trade imbalances, and Argentina's industrial capacity remains underutilized, both highlighting broader economic strains. Concurrently, local currency weaknesses are inflating the costs of imported components. In response, automakers are hiking vehicle prices, potentially elongating replacement cycles and curbing demand for non-essential upgrades. Such dynamics could temper growth forecasts and complicate efforts to maintain long-term market expansion.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- OEM On-Shoring to Skirt USMCA/Mercosur Tariff Escalation
- Resumption of Automaker Flex-Fuel Investment Programs
- Acceleration of BRT Expansion in Major Metros
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
SUVs/Crossovers accounted for 40.85% of the Latin America passenger car market in 2025 and are forecast to outpace all other body styles at a 4.88% CAGR during the forecast period (2026-2031). Buoyed by the increasing availability of sub-compact and B-segment variants, entry prices have seen a decline. Demand is driven by the vehicles' higher ground clearance, making them suitable for unpaved or flood-prone roads, and a prevailing perception of enhanced safety. Toyota's hybrid-flex SUV initiative not only leverages the current ethanol infrastructure but also tackles emissions caps. Meanwhile, Chinese newcomers are introducing feature-rich crossovers, priced similarly to traditional compacts, swaying consumer preference towards these taller vehicles.
Sedans and hatchbacks maintain relevance where urban congestion and fuel economy dominate decision factors, particularly across Brazil's coastal cities. However, their combined share continues to decline as households upgrade during replacement cycles. Multi-purpose vehicles remain niche, catering mainly to fleet operators and large families in rural areas where passenger capacity trumps efficiency.
Entry-level A/B models captured 47.83% of the Latin America passenger car market share in 2025, and with a 5.08% CAGR during the forecast period (2026-2031). Driven by competitive financing and governmental tax credits for compact cars. Credit access improvements in Brazil and Mexico expand the eligible buyer pool, while OEMs utilize platform commonality to cut per-unit costs.
Mid-size C-segment offerings cater to an expanding middle class, yet they face substitution risk as consumers transition directly to compact SUVs. Premium D/E classes stay limited to affluent urban professionals and government fleets, although EV variants add a new aspirational layer. BYD's Dolphin Mini illustrates how low-priced electric compacts can accelerate technology diffusion when paired with tax exemptions.
The Latin America Passenger Car Market Report is Segmented by Vehicle Type (Hatchback, Sedan, and More), Vehicle Class (Entry-Level (A/B), Mid-Size (C), and More), Propulsion/Fuel Type (Gasoline, Diesel, and More), Sales Channel (OEM-Owned Stores and Independent Dealers), and Country. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- General Motors Company
- Volkswagen AG
- Stellantis N.V.
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Hyundai Motor Company
- Ford Motor Company
- Nissan Motor Corporation
- Renault S.A.
- Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- Kia Corporation
- BMW AG
- Daimler AG (Mercedes-Benz)
- Chery Automobile
- BYD Auto
- SAIC-GM-Wuling
- Subaru Corporation
- Mazda Motor Corporation
- Geely Auto
- Audi AG
- Suzuki Motor Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Resilient Post-Pandemic Rebound in Household Car Ownership
- 4.2.2 Rapid Inflow of Chinese OEM Capital and Low-Cost EV Imports
- 4.2.3 OEM On-Shoring to Skirt USMCA/Mercosur Tariff Escalation
- 4.2.4 Resumption of Automaker Flex-Fuel Investment Programs
- 4.2.5 EV-Friendly Fiscal Credits in Brazil and Colombia
- 4.2.6 Stabilizing Semiconductor Supply Chain Enabling Production Catch-Up
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Peso and Real Depreciation Inflating Import Costs
- 4.3.2 Acceleration of BRT Expansion in Major Metros
- 4.3.3 Limited Public Charging Density Outside Tier-1 Cities
- 4.3.4 Tightening Regional CO2 Fleet-Average Targets by 2027
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value and Volume)
- 5.1 By Vehicle Type
- 5.1.1 Hatchback
- 5.1.2 Sedan
- 5.1.3 SUV / Crossover
- 5.1.4 Multi-Purpose Vehicle (MPV)
- 5.2 By Vehicle Class
- 5.2.1 Entry-Level (A/B)
- 5.2.2 Mid-Size (C)
- 5.2.3 Full-Size (D/E)
- 5.3 By Propulsion / Fuel Type
- 5.3.1 Gasoline
- 5.3.2 Diesel
- 5.3.3 Flex-Fuel
- 5.3.4 Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- 5.3.5 Battery-Electric Vehicle
- 5.4 By Sales Channel
- 5.4.1 OEM-Owned Stores
- 5.4.2 Independent Dealers
- 5.5 By Country
- 5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Argentina
- 5.5.4 Colombia
- 5.5.5 Chile
- 5.5.6 Peru
- 5.5.7 Rest of Latin America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 General Motors Company
- 6.4.2 Volkswagen AG
- 6.4.3 Stellantis N.V.
- 6.4.4 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 6.4.5 Hyundai Motor Company
- 6.4.6 Ford Motor Company
- 6.4.7 Nissan Motor Corporation
- 6.4.8 Renault S.A.
- 6.4.9 Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Kia Corporation
- 6.4.11 BMW AG
- 6.4.12 Daimler AG (Mercedes-Benz)
- 6.4.13 Chery Automobile
- 6.4.14 BYD Auto
- 6.4.15 SAIC-GM-Wuling
- 6.4.16 Subaru Corporation
- 6.4.17 Mazda Motor Corporation
- 6.4.18 Geely Auto
- 6.4.19 Audi AG
- 6.4.20 Suzuki Motor Corporation
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment










