 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906096
微型菜苗:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Microgreens - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
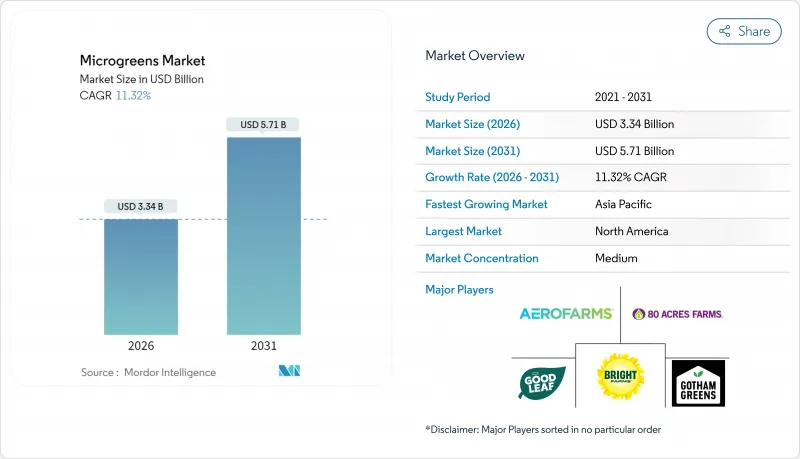
预计到 2025 年,微型菜苗市场价值将达到 30 亿美元,到 2031 年将达到 57.1 亿美元,高于 2026 年的 33.4 亿美元。
预计在预测期(2026-2031 年)内,复合年增长率将达到 11.32%。
消费者对营养丰富的农产品的需求、种植者向高产室内种植系统的转型以及零售商将优质微型菜苗作为差异化生鲜食品专区进行扩张,共同推动了微型蔬菜市场的持续增长。微型菜苗市场在机能性食品领域中保持着强劲的地位,科学证据表明,某些特定品种的维生素和抗氧化剂含量是成熟品种的5-40倍。技术融合也推动了市场成长,人工智慧控制的LED照明方案可达到高达32%的节能效果,垂直种植系统的产量密度比田间种植高出390倍。缩短供应链和减少废弃物的在地化策略进一步增强了微型菜苗市场将继续超越整个可控环境农业领域,并在未来几年内保持两位数的成长。
全球微型菜苗市场趋势与洞察
越来越多的健康意识消费者正在寻找营养食品。
微型菜苗是一种豆科植物,每100克含有80.45毫克抗坏血酸(维生素C),远高于成熟植株的含量。其8-21天的生长週期使其可以全年采收。面临微量营养素缺乏的居住者将这种高含量视为一种优质选择。健康专家在推荐符合预防保健预算的机能性食品时,也越来越多提及微型菜苗。人口老化扩大了愿意投资于经证实有效的营养产品的消费者群体。同行评审的研究表明,每日食用微型蔬菜与心血管功能和血糖值指标的改善有关,这促使注重健康的消费者重复购买。这些因素共同确保了营养倡导仍然是微型菜苗行销讯息的核心。
引进城市、室内和垂直农业基础设施
阿联酋计划在五年内部署超过500座垂直农场,预计到2030年,该领域的成长潜力将达到62亿美元。微型菜苗作为旗舰作物,将充分利用其短週期优势。荷兰创新企业PlantLab于2024年完成了资金筹措,用于扩大其在欧洲的生产能力,这印证了投资者对其可扩展模式的信心。物联网感测器可在植物层面调节湿度、二氧化碳水平和气流,从而提高产量稳定性并降低人事费用。可再生能源驱动的冷却系统和热交换循环系统可降低生命週期成本,并解决碳足迹问题。旨在缩短食品运输距离的市政激励措施进一步支持了城市中心生产的经济效益。这些因素共同为成熟市场和新兴市场的产能扩张奠定了坚实的基础。
因卫生条件不佳导致食品安全召回
与豆芽相关的沙门氏菌和大肠桿菌集体爆发影响了监管机构对类似生产方法的看法。然而,1998年至2017年间,未有微型菜苗引发确诊疾病的报告(extension.unr.edu)。美国食品药物管理局(FDA)收紧的有机农业法规将于2024年生效,该法规要求制定书面危害分析计画并实现批次级可追溯性,增加了合规成本。种植者目前正在使用抗菌根区清洁剂和紫外线C温室棚来防止污染。 GlobalGAP和SQF等认证已成为进入零售通路的实际通行证。农场自动化减少了人为接触点和出错的可能性。同时,最初为轨道营养液膜栽培技术设计的太空作物卫生通讯协定正回馈到地面农场,提供检验的病原体控制方法。
细分市场分析
就微型菜苗市场规模而言,西兰花微型菜苗预计到2025年将占据27.45%的市场份额,这主要得益于其高总酚含量(825.53毫克GAE/100克),这也支撑了其较高的价格分布。芝麻菜将保持14.70%的市场份额,其独特的风味深受厨师喜爱,常用于沙拉和披萨中。萝卜将占21.10%的市场份额,尤其是在水耕渠道,其快速发芽的特性使其能够进行高密度种植。
罗勒微型菜苗预计将以14.57%的复合年增长率推动市场成长,这得益于其在烹饪中的熟悉度和浓郁的香气,零售客户能够迅速识别。生菜和菊苣将占12.55%的市场份额,其温和的口味能够吸引初次购买者。茴香、豌豆、酸模以及仍有争议的麻微型菜苗等特色产品,保持了产品种类的多样性,并鼓励消费者尝试新口味。持续的育种工作以及与种子生产商的合作,使得每个种植季节都能推出新的品种,从而保持消费者的好奇心并维持价格稳定。
截至2025年,室内农场占据了微型菜苗市场45.30%的份额,这主要得益于气候可控的种植室,这些种植室能够提供均匀的二氧化碳浓度、光照和营养供应。在这样的环境下,微型蔬菜的叶片质地和颜色保持一致,这对于要求产品单品(SKU)品质可预测性的零售商至关重要。
垂直农场预计在2031年实现19.74%的年复合成长率,成为成长最快的产业之一,其优势在于提高了单位面积产量。位于亚利桑那州的AutoStore和OnePointOne的全自动化农场,将托盘排列成立方体网格,15天后即可收穫产品,用水量比田间种植减少95%。混合型温室,即在半透明屋顶下堆迭多层塔架的温室,因其能够弥补资本投资缺口,而备受中端市场投资者的青睐。同时,货柜农场则可在杂货店后院或校园食堂等场所实现在地化生产,从而缓解「最后一公里」配送难题。
区域分析
亚太地区预计将成为成长的主要驱动力,到2031年将维持12.85%的复合年增长率,主要得益于都市化进程、收入成长以及政府对粮食安全的津贴。中国1.34兆美元的果蔬市场蕴藏着巨大的成长潜力,上海和深圳等特大城市目前正在城市地区试办垂直农场,以缩短运输时间。新加坡经营高科技室内设施,并向马来西亚和印尼出口微型菜苗,使其成为区域创新中心。澳洲因干旱和盐碱化问题,支持在城郊地区建造太阳能温室丛集。同时,针对连锁饭店的小型货架农场在印度班加罗尔地区正逐渐成为主流。
北美仍将是微型菜苗市场最大的贡献者,到2025年将占全球市场规模的42.40%。这反映了零售渗透率的不断提高以及餐饮服务业的强劲需求。 AeroFarms、Gotham Greens和Bowery Farming等业者为数千家门市供货,而GoodLeaf则以新的资金筹措,将在加拿大的业务拓展至2,700家门市。墨西哥正利用其低廉的电力成本和与美国买家的接近性,达成合资供应协议,从而避免跨境运输瓶颈。有机水耕的区域性法规的明确有助于提升其高端定位,但标准的分散也为州际物流带来了挑战。在欧洲,城市农业补贴和碳排放边境调节机制正在推动当地生产,年复合成长率达8.05%。荷兰先驱PlantLab持续开发全封闭式“植物生产单元”,而德国则利用可再生能源信用额度来抵消温室气体排放。义大利的「从农场到餐桌」餐厅因其以微型菜苗为特色的菜餚而深受美食游客的喜爱。欧盟有机认证的数位化将于2025年生效,这可能成为一种软性贸易壁垒,鼓励超级市场从当地采购。同时,中东地区正在调动主权财富基金,Pure Harvest计划在2024年筹集1.805亿美元,用于建造气候适应设施。在非洲,冷链走廊向二线城市的扩展已推动市场以11.10%的速度成长。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 越来越多的健康意识消费者正在寻找营养食品。
- 城市、室内和垂直农业基础设施的采用情况
- 世界各地高级餐饮和高端美食的兴起
- 零售连锁店开发自有品牌微型菜苗
- 奈米技术强化培养基可提高产量和营养价值
- 被选中用于太空生命维持系统和太空人菜单
- 市场限制
- 收穫后保存期限短和低温运输缺陷
- 受控环境农业的单位生产成本高
- 因卫生缺陷导致的食品安全召回
- 标准碎片化延缓了全球有机认证进程。
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 绿色花椰菜
- 生菜和菊苣
- 芝麻菜
- 罗勒
- 茴香
- 红萝卜
- 向日葵
- 萝卜
- 豌豆
- 其他类型
- 透过栽培方法
- 室内农业
- 垂直农业
- 商业温室
- 其他耕作方法
- 透过生长培养基
- 泥炭藓
- 土壤
- 椰壳纤维
- 棉纸
- 其他生长介质
- 透过分销管道
- 大卖场和超级市场
- 餐厅
- 其他频道
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 智利
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 荷兰
- 西班牙
- 德国
- 法国
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 新加坡
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 奈及利亚
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- AeroFarms LLC(Dream Holdings, Inc.)
- BrightFarms(Cox Enterprises)
- GoodLeaf Farms(TrueLeaf)
- Farmbox Greens(Charlie's Produce)
- Gotham Greens Farms LLC
- 80 Acres Farms
- Chef's Garden Inc.
- 2BFresh(Teshuva Agricultural Projects)
- Metro Microgreens
- Farm.One, Inc.
- Living Earth Farm
- Ibiza Microgreens
- UnsFarms(Speedex group)
- Badia Farms
- Greeneration
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The microgreens market was valued at USD 3.0 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 3.34 billion in 2026 to reach USD 5.71 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 11.32% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Sustained demand stems from consumers seeking nutrient-dense produce, producers upgrading to high-yield indoor systems, and retailers adding premium microgreen assortments to differentiate fresh-food aisles. Scientific evidence confirming that certain varieties hold 5-40 times the vitamin and antioxidant content of their mature counterparts keeps the microgreens market firmly positioned within functional foods. Technology convergence is another lift: AI-directed LED recipes are delivering energy savings close to 32% while vertical stacks achieve production densities up to 390-fold above field output. Localization strategies that shorten supply chains and reduce spoilage further reinforce the economic appeal, and lunar agriculture trials scheduled for 2026 are catalyzing new precision-growing tools for terrestrial use. Altogether, the microgreens market continues to outpace broader controlled-environment agriculture segments and is on track for another multi-year run of double-digit expansion.
Global Microgreens Market Trends and Insights
Rising Health-Conscious Consumers Demanding Nutrient-Dense Foods
Bean microgreens supply 80.45 mg/100 g of ascorbic acid-well above mature-plant levels-while their 8-21-day growth cycle supports year-round harvests. Urban dwellers facing micronutrient gaps view this concentration as worth a premium. Healthcare professionals increasingly cite microgreens when recommending functional foods that dovetail with preventive health budgets. Aging demographics magnify the pool of customers willing to invest in proven nutrition. Peer-reviewed links between routine intake and improved cardiovascular as well as glycemic markers spur repeat purchases among wellness-minded buyers. Together, these factors keep nutrition advocacy central to microgreens market messaging.
Uptake of Urban, Indoor, and Vertical Farming Infrastructures
The UAE's plan to deploy more than 500 vertical farms inside five years signals a USD 6.2 billion upside by 2030, with microgreens positioned as anchor crops thanks to quick cycles. Dutch innovator PlantLab closed EUR 20 million (USD 20 million) in 2024 to widen European capacity, underscoring investor belief in scalable models. IoT sensors now adjust humidity, CO2, and airflow at the plant level, raising yield consistency while shrinking labor. Renewable-powered chillers and heat-exchange loops improve lifetime operating costs and answer carbon-footprint critiques. Municipal incentives that target food-miles reduction further tilt economics in favor of city-center production. Collectively, these inputs build a durable foundation for capacity expansion across both mature and emerging markets.
Food-Safety Recalls Linked to Poor Sanitation Practices
Sprout outbreaks of Salmonella and E. coli color regulators' perception of similar production methods, even though no microgreens illnesses were logged from 1998-2017 extension.unr.edu. The FDA's stronger organic enforcement, activated in 2024, adds documented hazard-analysis plans and lot-level traceability, raising compliance costs. Growers now deploy antimicrobial root-zone washes and UV-C cabin tunnels to pre-empt contamination. Certifications such as GlobalGAP and SQF have become de facto tickets to retail distribution. On-farm automation reduces human touchpoints, cutting the probability of lapses. In parallel, space-crop sanitation protocols-originally devised for nutrient film technique in orbit-feed back to earth farms, offering validated pathogen-control blueprints.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Fine-Dining and Premium Culinary Adoption Worldwide
- Retail-Chain Private-Label Microgreen Launches
- Fragmented Standards Delaying Global Organic Certification
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Broccoli microgreens controlled 27.45% of 2025 revenue within the microgreens market size, buoyed by 825.53 mg GAE/100 g total phenolics that support premium price points. Arugula retains a 14.70% share, leveraging its peppery kick that chefs prize for salads and pizzas. Radish lines capture 21.10%, especially in hydroponic channels, where quick germination validates aggressive planting densities.
Basil microgreens headline growth with a forecast 14.57% CAGR, reflecting culinary familiarity and aromatic punch that retail shoppers recognize quickly. Lettuce and chicory add 12.55%, offering gentle flavors that help first-time buyers. Specialty entries, fennel, pea, sorrel, and the still-controversial hemp microgreen, keeping SKUs dynamic and inviting experimentation. Continuous breeding and seed-house collaborations open fresh cultivar cycles every season, keeping consumer curiosity alive and pricing resilient.
Indoor farms held 45.30% microgreens market share in 2025, anchored by climate-tight rooms that deliver uniform CO2, lighting, and nutrient flow. These conditions produce leaves with consistent texture and color, vital for retailers who demand SKU-level predictability.
Vertical farms promise the fastest 19.74% CAGR through 2031 by multiplying square-foot output. AutoStore and OnePointOne's fully robotic Arizona site packs trays into cubic lattices and snips product after 15 days, using 95% less water than field cultivation. Hybrid greenhouses that stack tiered towers beneath translucent roofing split the difference on capex, appealing to mid-tier investors. Meanwhile, container farms allow on-premise production at grocery backlots and campus food halls, shrinking last-mile challenges.
The Microgreens Market Report Segments the Industry Into Type (Broccoli, Lettuce and Chicory, Arugula, Basil, Fennel, and More), Farming (Indoor Farming, Vertical Farming, and More), Growth Medium (Peat Moss, Soil, Coconut Coir, and More), Distribution Channel (Hypermarkets/Supermarkets, Restaurants, and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific is the growth engine, logging a 12.85% CAGR through 2031 as urbanization and rising incomes align with government food-security grants. China's USD 1.34 trillion fruit-and-vegetable economy offers a vast runway, and megacity pilots in Shanghai and Shenzhen now place vertical farms within city blocks to slash travel time. Singapore operates high-tech indoor hubs that export microgreens to Malaysia and Indonesia, cementing the city-state as a regional innovation lab. Australia, spurred by drought and salinity concerns, backs solar-powered greenhouse clusters in peri-urban zones, while India's Bengaluru cluster champions low-capex rack farms aimed at hotel chains.
North America retained the largest contribution to the microgreens market size at 42.40% in 2025, reflecting mature retail penetration and robust food-service demand. Operators like AeroFarms, Gotham Greens, and Bowery Farming serve thousands of stores, and fresh financing helped GoodLeaf add 2,700 Canadian doors. Mexico leverages lower power costs and proximity to U.S. buyers, securing joint-venture supply agreements that bypass cross-border bottlenecks. Regional regulatory clarity on organic hydroponics supports premium positioning, although fragmented standards still challenge interstate logistics. Europe is advancing at an 8.05% CAGR on the back of urban-agriculture subsidies and carbon-border adjustments that favor local production. Dutch pioneers such as PlantLab iterate on fully enclosed "Plant Production Units," while Germany's renewable-energy credits offset greenhouse inputs. Italy's farm-to-table restaurants tout microgreens-topped dishes to culinary tourists. EU organic certificate digitization, active from 2025, may erect soft trade barriers that push supermarkets to source within the bloc. Elsewhere, the Middle East marshals sovereign-wealth capital, evidenced by a USD 180.5 million Pure Harvest raise in 2024 to build climate-tough facilities, and Africa is starting its 11.10% ascent as cold-chain corridors reach secondary cities.
- AeroFarms LLC (Dream Holdings, Inc.)
- BrightFarms (Cox Enterprises)
- GoodLeaf Farms (TrueLeaf)
- Farmbox Greens (Charlie's Produce)
- Gotham Greens Farms LLC
- 80 Acres Farms
- Chef's Garden Inc.
- 2BFresh (Teshuva Agricultural Projects)
- Metro Microgreens
- Farm.One, Inc.
- Living Earth Farm
- Ibiza Microgreens
- UnsFarms (Speedex group)
- Badia Farms
- Greeneration
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising health-conscious consumers demanding nutrient-dense foods
- 4.2.2 Uptake of urban, indoor, and vertical farming infrastructures
- 4.2.3 Fine dining and premium culinary adoption worldwide
- 4.2.4 Retail-chain private-label microgreen launches
- 4.2.5 Nanotechnology-enhanced substrates boost yield and nutrition
- 4.2.6 Microgreens selected for space life support and astronaut menus
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Short post-harvest shelf life and cold-chain gaps
- 4.3.2 High unit production costs for controlled-environment farming
- 4.3.3 Food-safety recalls linked to poor sanitation practices
- 4.3.4 Fragmented standards delaying global organic certification
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Broccoli
- 5.1.2 Lettuce and Chicory
- 5.1.3 Arugula
- 5.1.4 Basil
- 5.1.5 Fennel
- 5.1.6 Carrots
- 5.1.7 Sunflower
- 5.1.8 Radish
- 5.1.9 Peas
- 5.1.10 Other Types
- 5.2 By Farming Method
- 5.2.1 Indoor Farming
- 5.2.2 Vertical Farming
- 5.2.3 Commercial Greenhouses
- 5.2.4 Other Farming Methods
- 5.3 By Growth Medium
- 5.3.1 Peat Moss
- 5.3.2 Soil
- 5.3.3 Coconut Coir
- 5.3.4 Tissue Paper
- 5.3.5 Other Growth Media
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Hypermarkets and Supermarkets
- 5.4.2 Restaurants
- 5.4.3 Other Channels
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Chile
- 5.5.2.3 Argentina
- 5.5.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Netherlands
- 5.5.3.2 Spain
- 5.5.3.3 Germany
- 5.5.3.4 France
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Singapore
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.6 Africa
- 5.5.6.1 South Africa
- 5.5.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.5.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AeroFarms LLC (Dream Holdings, Inc.)
- 6.4.2 BrightFarms (Cox Enterprises)
- 6.4.3 GoodLeaf Farms (TrueLeaf)
- 6.4.4 Farmbox Greens (Charlie's Produce)
- 6.4.5 Gotham Greens Farms LLC
- 6.4.6 80 Acres Farms
- 6.4.7 Chef's Garden Inc.
- 6.4.8 2BFresh (Teshuva Agricultural Projects)
- 6.4.9 Metro Microgreens
- 6.4.10 Farm.One, Inc.
- 6.4.11 Living Earth Farm
- 6.4.12 Ibiza Microgreens
- 6.4.13 UnsFarms (Speedex group)
- 6.4.14 Badia Farms
- 6.4.15 Greeneration









