 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906917
机器视觉系统(MVS):市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Machine Vision Systems (MVS) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
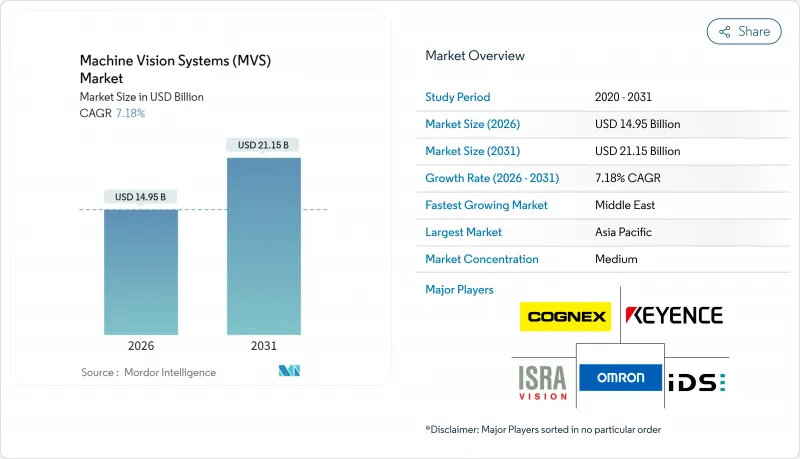
预计机器视觉系统(MVS)市场将从 2025 年的 139.5 亿美元成长到 2026 年的 149.5 亿美元,到 2031 年将达到 211.5 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 7.18%。
这种加速成长反映了对零缺陷製造日益增长的需求、人工智慧与工业成像技术的融合,以及在汽车、半导体、物流和医疗等行业不断扩展的应用场景。曾经在硬体规格上竞争的供应商,如今正透过深度学习软体、云端连线和订阅定价模式来脱颖而出,企业也在寻求端到端的品质保证,以降低保固风险。儘管基于云端的部署仍占少数,但可扩展处理和远端管理的优势正迫使供应商加强其网路安全和资料管治框架。区域成长模式显示,亚太地区保持着製造业的主导地位,中东地区正在扩大新的自动化计划,而北美和欧洲则实施了有利于认证视觉架构的严格责任规则。
全球机器视觉系统(MVS)市场趋势与洞察
对零缺陷製造的需求日益增长
在汽车电池製造和先进电子产品组装,即使是单一缺陷也是不可接受的。因此,生产商正在放弃统计抽样,转而采用100%在线连续检测。配备高光谱遥测相机的机器视觉系统(MVS)能够以亚毫米级分辨率识别材料和结构异常,从而避免代价高昂的召回和保固责任。欧盟的监管变化强化了财务责任,推动了对高解析度感测器和人工智慧分类器的投资。云端连接的仪錶板为工厂管理人员提供即时缺陷图,加快了根本原因调查。随着零缺陷专案的日益成熟,提供承包分析、边缘推理和坚固耐用的工业硬体的供应商正在机器视觉系统(MVS)市场中占据越来越大的份额。
视觉引导机器人的应用日益普及
机器人搭载的摄影机引导机械手臂随机放置零件,以实现以往由管线工人完成的拣货、组装和组装任务。康耐视透过客户案例进一步展示了生产力的提升:人工智慧视觉技术将汽车零件的换型时间从数小时缩短至数分钟。搭载相机的边缘处理器支援即时抓取规划,而碰撞规避演算法则可减少废弃物。在仓库中,视觉引导的移动机器人正被整合到系统中,用于定位库存和了解包装状况,为无人值守的履约中心奠定基础。在劳动力持续短缺的背景下,视觉引导的机器人技术正在增加灵活的生产能力,并加速机器视觉系统 (MVS) 市场在离散製造和物流领域的成长。
熟练的机器视觉整合技术人员短缺
复杂的视觉系统实现需要光学、照明、影像处理、神经网路调优和工业网路等技术,但将这些技术作为单一学科进行教授的工程课程却寥寥无几。中小企业将计划外包,而係统整合商的订单仍排得订单,导致前置作业时间延长,总成本上升。供应商认证计画分散,阻碍了人才流动,并限制了新兴市场的劳动力资源。实施延迟延长了投资回收期,并限制了机器视觉系统(MVS)在新兴经济体的市场渗透率,尤其是在价格敏感型应用领域。儘管产学合作旨在规范课程设置,但预计中期内供应仍将持续超过需求。
细分市场分析
到2025年,硬体仍将占据机器视觉系统(MVS)市场60.15%的份额,巩固其在工业环境影像撷取中的基础性作用。相机、镜头、照明设备和影像撷取卡构成了资本密集的基础组件,但商品化压力和标准介面正在挤压利润空间。软体将以7.42%的复合年增长率成长,透过深度学习推理、资料集管理和低程式码应用程式建构器创造价值。斑马技术公司的「Aurora」软体在2024年新增了预训练神经网络,降低了准入门槛并推动了经常性收入。原始设备製造商(OEM)正越来越多地将边缘硬体与终身软体订阅捆绑销售,转向基于年金的经营模式,这正在重塑机器视觉系统市场的获利模式。
这种转变正云端协作、模型版本控制和网路安全成为日益重要的企业采购标准。提供整合软体堆迭的整合商有可能取代以硬体为中心的竞争对手,而感测器供应商则透过与人工智慧框架合作来保持竞争力。随着终端用户寻求全机队分析,软体正成为异质摄影机环境的控制基础,加速了从销售零件到提供功能的转变。
到2025年,基于PC的安装方案将占机器视觉系统(MVS)市场规模的57.35%,因其适用于计算密集型演算法和多摄影机编配而备受青睐。然而,将光学、照明和处理能力整合到坚固耐用模组中的智慧摄影机将以7.24%的复合年增长率(CAGR)实现最快的成长。像Hailo-10H这样的汽车边缘加速器将变压器网路和生成式人工智慧引入摄影机模组,从而缩小了机柜的面积。仓库业者正在绕过外部PC,采用即插即用的智慧摄影机进行条码解码、体积测量和损坏侦测。智慧摄影机供应商正在提供基于浏览器的配置功能,将部署时间从几天缩短到几小时,从而巩固了其在整个机器视觉系统(MVS)市场小型化应用领域的领先地位。
儘管边缘运算技术取得了长足进步,但在需要Terabyte级吞吐量的研究机构、半导体代工厂和多频谱环境中,PC后端仍然至关重要。混合架构正在兴起,智慧相机执行初步推断,而PC则聚合更深入的分析,这表明两者可以共存,而非完全替代。
机器视觉系统 (MVS) 报告按组件(硬体、软体)、产品类型(基于 PC、基于智慧型相机)、成像类型(2D、3D、高光谱遥测和频谱)、部署模式(本地部署、边缘/嵌入式、云端部署)、终端用户产业(电子与半导体、食品饮料、物流与零售等)以及地区进行细分。市场预测以美元 (USD) 为以金额为准。
区域分析
到2025年,亚太地区将占全球收入的40.25%,这主要得益于中国强大的电子组装能力、日本的机器人技术以及韩国的储存晶片製造工厂。区域各国政府正在资助智慧工厂升级改造,而契约製造製造商也积极采用视觉技术以满足严格的出口品质标准。印度正受益于与生产连结奖励计画,以吸引全球行动电话和电池製造商,从而提振当地对在线连续检测的需求。东南亚国家正在汽车线束和晶片封装领域开拓利基市场,推动视觉技术的普及和供应商生态系统的不断深化。
北美正利用电动车和半导体工厂的退货政策和激励措施。美国食品药物管理局(FDA) 和国家公路交通安全管理局 (NHTSA) 的监管推动了对可产生审核追踪的检验视觉生产线的投资。加拿大安大略省和魁北克省的先进製造群正在整合人工智慧视觉和机器人技术以填补劳动力短缺,而墨西哥的汽车产业走廊则正在部署价格适中的智慧摄影机生产线以维持原始设备製造商 (OEM) 的核准。
欧洲注重品质的中型製造商和严格的责任法律持续推动工业4.0技术的稳定普及。德国和义大利正在完善其工业4.0项目,融合视觉技术、机器人技术和製造执行系统(MES)。中东地区正经历最快的复合年增长率(CAGR),达到8.22%,这主要得益于沙乌地阿拉伯和阿联酋将主权财富基金投入非石油製造业,包括食品加工、消费品和可再生能源。土耳其的汽车出口和埃及的包装工厂正在推动该地区工业4.0技术的普及。
南美洲的机器视觉系统应用与出口型农业企业和汽车生产密切相关,但宏观经济波动限制了其普及。非洲仍处于发展中,但南非的汽车产业中心和摩洛哥的电子组装基地为供应商在不断扩张的机器视觉系统(MVS)市场中站稳了脚跟。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 对零缺陷製造的需求日益增长
- 扩大视觉引导机器人技术的应用
- 电子设备小型化导致对3D视觉的需求不断增长
- 食品和药品的严格品质标准
- 设备端人工智慧推理晶片的普及
- VaaS(视觉即服务)订阅模式的兴起
- 市场限制
- 熟练的机器视觉整合商短缺
- 高解析度和高光谱遥测相机的高成本
- 云端连结视觉系统中的网路安全风险
- 影像感测器半导体供应链波动性
- 产业生态系分析
- 宏观经济因素的影响
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按组件
- 硬体
- 视觉系统
- 相机
- 光学和照明系统
- 影像撷取卡
- 其他硬体
- 软体
- 硬体
- 依产品类型
- 基于PC
- 智慧型摄影机底座
- 按影像类型
- 二维成像
- 三维成像
- 高光谱遥测和频谱成像
- 透过部署模式
- 本地部署
- 边缘/嵌入式
- 基于云端的
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 车
- 电子装置和半导体
- 食品/饮料
- 医疗和药品
- 物流与零售
- 其他终端用户产业
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 印度
- 中东
- 土耳其
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Cognex Corporation
- Keyence Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
- Sony Group Corporation
- Atlas Copco AB(ISRA Vision)
- IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
- National Instruments Corporation
- MVTec Software GmbH
- Basler AG
- Allied Vision Technologies GmbH
- TKH Group NV(LMI Technologies)
- FLIR Systems Inc(Teledyne)
- Intel Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc
- Sick AG
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Stemmer Imaging AG
- Zebra Technologies Corporation
- Hitachi Ltd
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The machine vision systems market is expected to grow from USD 13.95 billion in 2025 to USD 14.95 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 21.15 billion by 2031 at 7.18% CAGR over 2026-2031.

The acceleration reflects rising demand for zero-defect production, the fusion of artificial intelligence with industrial imaging, and expanding use cases across automotive, semiconductor, logistics, and healthcare operations. Vendors that once competed on hardware specifications now differentiate through deep-learning software, cloud connectivity, and subscription pricing, while enterprises pursue end-to-end quality assurance to limit warranty exposure. Cloud-based deployment, still a minority, benefits from scalable processing and remote management, pushing vendors to harden cybersecurity and data-governance frameworks. Regional growth patterns show Asia-Pacific retaining manufacturing primacy, the Middle East scaling greenfield automation projects, and North America and Europe enforcing tighter liability rules that favor certified vision architectures.
Global Machine Vision Systems (MVS) Market Trends and Insights
Rising Need for Zero-Defect Manufacturing
Automotive battery manufacturing and advanced electronics assemblies cannot tolerate single-point defects, leading producers to abandon statistical sampling in favor of 100% inline inspection. Machine vision systems equipped with hyperspectral cameras identify material or structural anomalies at sub-millimeter resolution, preventing costly recalls and warranty liabilities. Regulatory amendments in the European Union reinforce financial accountability, motivating investment in higher-resolution sensors and AI classifiers. Cloud-linked dashboards give plant managers real-time defect maps that shorten root-cause investigations. As zero-defect programs mature, vendors that deliver turnkey analytics, edge inference, and hardened industrial hardware capture incremental share within the machine vision systems market.
Increasing Adoption of Vision-Guided Robotics
Robot-mounted cameras now guide grippers through random part orientations, enabling bin-picking, kitting, and assembly tasks once reserved for line workers. Cognex reported customers trimming automotive changeover time from hours to minutes using AI-enabled vision, strengthening the productivity case. Edge processors inside the camera support real-time grasp planning, while collision-avoidance algorithms reduce scrap. Warehouses integrate vision-guided mobile robots that localize inventory and capture package condition, forming the backbone of lights-out fulfillment hubs. As labor scarcity persists, vision-guided robotics adds flexible capacity and accelerates the machine vision systems market across discrete and logistics sectors.
Lack of Skilled Machine Vision Integrators
Complex vision deployments span optics, lighting, image processing, neural-network tuning, and industrial networking, skills that engineering programs seldom teach as a single discipline. Small and medium enterprises outsource projects, yet system integrators remain over-booked, raising lead times and total cost. Vendor certification tracks are fragmented, making talent portability difficult and limiting labor pools in emerging markets. Delayed rollouts widen the return-on-investment horizon, especially for price-sensitive applications, constraining uptake of the machine vision systems market in growth economies. Academic-industry partnerships are forming to standardize curricula, but supply will lag demand through the medium term.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Demand for 3D Vision in Electronics Miniaturization
- Stringent Quality Rules for Food and Pharmaceuticals
- High Cost of High-Resolution and Hyperspectral Cameras
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hardware retained a 60.15% machine vision systems market share in 2025, underscoring its foundational role in capturing images across industrial environments. Cameras, lenses, lighting, and frame grabbers form a capital-intensive base, but commoditization pressures and standard interfaces squeeze margins. Software, advancing at a 7.42% CAGR, captures value through deep-learning inference, dataset management, and low-code application builders. Aurora software from Zebra Technologies added ready-trained neural networks in 2024, lowering entry barriers and pushing recurring revenue. OEMs increasingly package lifetime software subscriptions with edge hardware, pivoting to an annuity model that reshapes profit pools within the machine vision systems market.
The shift elevates cloud orchestration, model versioning, and cybersecurity as corporate procurement criteria. Integrators that offer unified software stacks stand to displace hardware-centric competitors, while sensor vendors partner with AI frameworks to remain relevant. As end users pursue fleet-wide analytics, software becomes the control plane over heterogeneous camera footprints, accelerating the transition from component sales to capability delivery.
PC-based installations represented 57.35% of the machine vision systems market size in 2025, favored for compute-intensive algorithms and multi-camera orchestration. However, smart cameras, compressing optics, lighting, and processing into a rugged module, record the fastest 7.24% CAGR. Automotive-qualified edge accelerators such as Hailo-10H bring transformer networks and generative AI to the camera pod, shrinking cabinet footprints. Warehouse operators adopt plug-and-play smart cameras for barcode decoding, volumetric measurement, and damage detection, bypassing external PCs. Smart-camera vendors package browser-based configuration that cuts deployment days to hours, tightening their grip on small-form-factor applications across the machine vision systems market.
Despite edge advances, PC back-ends remain indispensable in research labs, semiconductor fabs, and multi-spectral setups requiring terabytes of throughput. Hybrid architectures emerge in which smart cameras perform preliminary inference while PCs aggregate deeper analytics, illustrating coexistence rather than outright displacement.
The Machine Vision Systems Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, and Software), Product Type (PC-Based, and Smart Camera-Based), Imaging Type (2D, 3D, and Hyperspectral and Multispectral), Deployment Mode (On-Premise, Edge/Embedded, and Cloud-Based), End-User Industry (Electronics and Semiconductors, Food and Beverage, Logistics and Retail, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific accounted for 40.25% of 2025 revenue, anchored by China's electronics assembly capacity, Japan's robotics expertise, and South Korea's memory-chip fabs. Regional governments fund smart-factory upgrades, while contract manufacturers embed vision to meet stringent export quality criteria. India benefits from production-linked incentives that draw global handset and battery makers, boosting local demand for inline inspection. Southeast Asian nations carve out niches in automotive wiring and chip packaging, raising vision penetration and deepening supplier ecosystems.
North America leverages reshoring policies and incentives for electric-vehicle and semiconductor plants. Regulatory oversight by the U.S. FDA and NHTSA spurs investments in validated vision lines that generate audit trails. Canada's advanced-manufacturing clusters in Ontario and Quebec integrate AI vision with robotics to offset labor constraints, while Mexico's automotive corridor deploys affordable smart-camera lines to maintain OEM approvals.
Europe combines quality-obsessed midsize manufacturers with rigorous liability statutes, sustaining steady uptake. Germany and Italy refine Industrie 4.0 programs that merge vision, robotics, and MES integration. The Middle East delivers the fastest 8.22% CAGR as Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates channel sovereign wealth into non-oil manufacturing, including food processing, consumer goods, and renewables. Turkey's automotive exports and Egypt's packaging plants widen regional installations.
South America shows sporadic adoption tied to export agribusiness and vehicle production, though macroeconomic volatility tempers volume. Africa remains nascent, but South Africa's automotive hubs and Morocco's electronics assemblies offer footholds for suppliers in the expanding machine vision systems market.
- Cognex Corporation
- Keyence Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
- Sony Group Corporation
- Atlas Copco AB (ISRA Vision)
- IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
- National Instruments Corporation
- MVTec Software GmbH
- Basler AG
- Allied Vision Technologies GmbH
- TKH Group NV (LMI Technologies)
- FLIR Systems Inc (Teledyne)
- Intel Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc
- Sick AG
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- Stemmer Imaging AG
- Zebra Technologies Corporation
- Hitachi Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Need for Zero-Defect Manufacturing
- 4.2.2 Increasing Adoption of Vision-Guided Robotics
- 4.2.3 Growing Demand for 3D Vision in Electronics Miniaturisation
- 4.2.4 Stringent Quality Rules for Food and Pharmaceuticals
- 4.2.5 Surge in On-Device AI Inference Chips
- 4.2.6 Emergence of Vision-as-a-Service Subscription Models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Lack of Skilled Machine Vision Integrators
- 4.3.2 High Cost of High-Resolution and Hyperspectral Cameras
- 4.3.3 Cybersecurity Risks in Cloud-Connected Vision Systems
- 4.3.4 Supply Chain Volatility of Image Sensor Semiconductors
- 4.4 Industry Ecosystem Analysis
- 4.5 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
- 4.6 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.7 Technological Outlook
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.1.1 Vision Systems
- 5.1.1.2 Cameras
- 5.1.1.3 Optics and Illumination Systems
- 5.1.1.4 Frame Grabbers
- 5.1.1.5 Other Hardwares
- 5.1.2 Software
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.2 By Product Type
- 5.2.1 PC-Based
- 5.2.2 Smart Camera-Based
- 5.3 By Imaging Type
- 5.3.1 2D Imaging
- 5.3.2 3D Imaging
- 5.3.3 Hyperspectral and Multispectral Imaging
- 5.4 By Deployment Mode
- 5.4.1 On-Premise
- 5.4.2 Edge/Embedded
- 5.4.3 Cloud-Based
- 5.5 By End-User Industry
- 5.5.1 Automotive
- 5.5.2 Electronics and Semiconductors
- 5.5.3 Food and Beverage
- 5.5.4 Healthcare and Pharmaceutical
- 5.5.5 Logistics and Retail
- 5.5.6 Other End-User Industries
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Mexico
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Turkey
- 5.6.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Egypt
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cognex Corporation
- 6.4.2 Keyence Corporation
- 6.4.3 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.4 Teledyne Technologies Incorporated
- 6.4.5 Sony Group Corporation
- 6.4.6 Atlas Copco AB (ISRA Vision)
- 6.4.7 IDS Imaging Development Systems GmbH
- 6.4.8 National Instruments Corporation
- 6.4.9 MVTec Software GmbH
- 6.4.10 Basler AG
- 6.4.11 Allied Vision Technologies GmbH
- 6.4.12 TKH Group NV (LMI Technologies)
- 6.4.13 FLIR Systems Inc (Teledyne)
- 6.4.14 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.15 Qualcomm Technologies Inc
- 6.4.16 Sick AG
- 6.4.17 Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- 6.4.18 Stemmer Imaging AG
- 6.4.19 Zebra Technologies Corporation
- 6.4.20 Hitachi Ltd
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment











