 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906918
绿建筑材料:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Green Building Materials - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
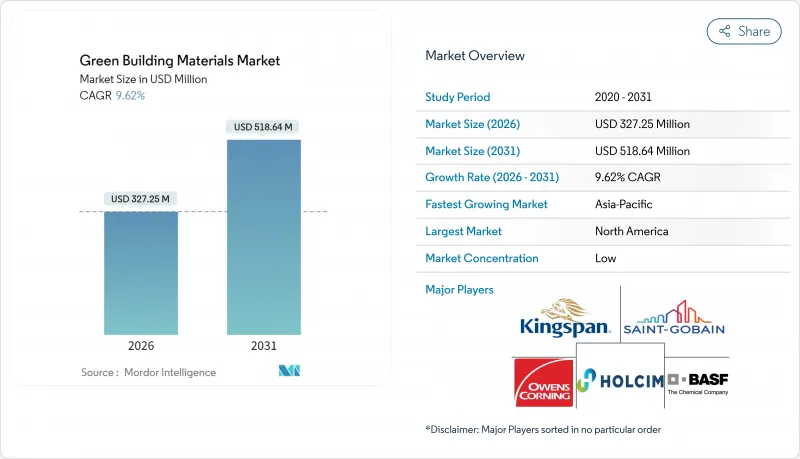
绿色建筑材料市场预计将从 2025 年的 2.9852 亿美元成长到 2026 年的 3.2725 亿美元,预计到 2031 年将达到 5.1864 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 9.62%。
这一前景反映了政府持续施压推动零排放建筑,企业对净零排放目标的承诺日益增强,以及低碳建筑材料技术的快速普及。欧盟、美国和其他主要经济体的监管协调正在打破传统的碎片化局面,使全球製造商能够实现规模经济并加速产品创新。财政奖励进一步支撑了市场需求,缩小了绿色建筑材料与传统产品之间的价格差距,而数位化材料追踪工具也开始将废旧材料的价值链货币化。这些因素共同作用,造就了绿建材市场前所未有的快速引进週期。
全球绿建筑材料市场趋势与洞察
加强强制性节能标准
世界各地的建筑规范正从自愿性指南转向具有约束力的性能标准。在欧洲,修订后的《建筑能源性能指令》要求所有新建建筑到2030年实现零现场石化燃料排放,现有住宅存量也必须在同年维修,达到最低E级能源效率标准。美国也紧接着,2024年版《国际节能规范》(IECC)简化了各州采纳该规范的流程,并增加了生命週期碳排放的规定。更严格的标准推动了对高性能隔热材料、低碳混凝土和先进建筑幕墙的需求,并有利于那些能够透过数位化合规平台检验其产品永续性的供应商。执法力度的加强进一步提高了传统建筑材料的合规成本,从而为经过认证的替代产品创造了可持续的竞争优势。
政府奖励和认证计划
税额扣抵、绿色债券和优惠融资正在改变计划的经济格局。美国《通货膨胀控制法》第45L条规定,符合条件的住宅最高可获得5000美元的补贴,而179D税收抵免政策的适用范围已扩大至大规模商业维修。加拿大已拨款100亿加币用于清洁能源基础建设,刺激了对认证材料的投资。 LEED、WELL和能源之星等认证项目,加上优惠融资,使开发商能够抵消先进产品15%至25%的溢价。这些激励措施加速了成本敏感市场对先进产品的采用,并为拥有现代化认证组合的製造商创造了稳定的收入来源。
认证材料的初始成本较高
认证产品通常会因检测成本、特殊加工和小批量生产而产生15%至25%的溢价。这种溢价在住宅建筑领域尤其显着,因为买家主要关注初始成本,往往忽略了潜在的全生命週期成本节约。诸如负碳混凝土和生物基隔热材料等新型产品也需要投入研发成本。虽然随着产量增加和碳定价缩小成本差距,这些成本正在下降,但高昂的初始成本仍然是短期内推广应用的障碍,尤其是在缺乏强有力奖励机制的发展中地区。
细分市场分析
到2025年,低碳混凝土和水泥将占绿色建材市场24.17%的份额,凸显了该产业迫切需要将全球温室气体排放传统水泥减少8%。突破性技术,例如矿物碳化製程(可在保持强度的同时封存45%的二氧化碳),正从试验阶段走向有限的商业化规模。海德堡材料公司位于伦福特的计划每年将捕获7万吨二氧化碳,展现了其作为主流技术的潜力。由于结构钢通常含有93%的废料,且在报废时可达到98%的回收率,因此对再生金属的需求保持稳定。工程木製品,特别是交错层压木材(CLT),随着开发商利用其快速组装、轻质基础和现场碳储存等优势,市场持续成长。矿物棉隔热材料凭藉其新型不燃产品系列,持续保持领先地位。同时,得益于可再生原料和优异的隔热性能,纤维素和生物泡沫隔热材料正以10.17%的复合年增长率成长。由于生命週期评估中对微塑胶脱落问题的担忧,再生塑胶复合复合材料的成长更加谨慎,而木质聚合物板材则继续渗透到外墙和建筑幕墙细分市场。
不同材料的成长前景各不相同。低碳黏合剂受益于航空碳捕获补贴,并将随着碳定价的扩大而加速成长。大宗木材市场依赖于认证林业的扩张和建筑规范中高度限制的修订。纤维素的成长轨迹取决于能否确保充足的消费后废纸原料供应以及酵素加工厂的规模化建设。总体而言,材料创新正在增强竞争优势,并迫使现有企业将循环经济特性、检验的碳足迹和数位护照等资讯整合到其所有产品线中。
区域分析
到2025年,北美将占全球绿色建材市场规模的40.35%,这主要得益于北美长期以来推行的能源之星(ENERGY STAR)和LEED认证项目,以及各州实施的零能耗建筑法规。根据《通膨控制法案》,联邦税额扣抵将加强全国范围内的协调一致,而加州2025年的建筑规范预计将进一步限制产品的碳含量。加拿大的「绿色家园倡议」 (Greener 住宅 Initiative)正在为维修提供低利率贷款,从而刺激了对纤维素和矿物棉隔热材料的需求。
在欧洲,《建筑能源性能指令》和即将实施的碳边境调节机制透过提高高碳进口成本并鼓励国内低碳生产,维持了较高的采纳率。斯堪地那维亚国家已要求所有大型建筑物进行生命週期碳排放评估,从而刺激了对数位通行证和大型木材的需求。德国和法国在公共部门采购低碳混凝土方面处于主导,而英国正在试点循环建筑中心,以回收都市区拆除工程中的可重复使用材料。
亚太地区预计到2031年将以10.95%的复合年增长率成长,这主要得益于快速的都市化和不断发展的绿色建筑标准。中国将要求所有新计画在2025年前至少达到基础级绿建筑认证标准,并且一些省份已经引入了製造业碳排放基准值。印度的节能建筑规范和印尼的绿建筑委员会评级体係正在推动绿建筑标准的早期应用,但各城市间执行力度的不平衡将限制短期内的需求成长。澳洲和新加坡的绿色建筑系统已经成熟,它们正在向全部区域输出专业知识,推动供应链在地化并加强区域认证标准。
儘管南美洲、中东和非洲仍处于发展阶段,但由于基础设施投资不断增长,这些地区已成为极具吸引力的市场。巴西的「Procel Edifica」认证系统和阿联酋的「Estidama Pearl」评级系统正鼓励材料供应商在当地生产,以满足特定的气候性能要求。虽然资金筹措仍然是一个主要障碍,但越来越多的多边银行绿色债券流入这些市场,正为在下一个规划週期内加速推广绿色环保奠定基础。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 加强强制性节能标准
- 政府奖励和认证计划
- 企业净零排放目标与碳包容性采购
- 老旧建筑维修工程蓬勃发展
- 利用数位材料护照实现报废价值货币化
- 市场限制
- 认证材料的初始成本较高
- 区域认证和绩效复杂性
- 2027年起生物基原料供应短缺
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依材料类型
- 低碳混凝土和水泥
- 回收金属
- 加工木材/再生木材
- 矿棉隔热材料
- 纤维素和生物泡沫隔热材料
- 再生塑胶复合复合材料
- 透过使用
- 框架
- 隔热材料
- 屋顶材料
- 墙板
- 室内装修
- 其他用途
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 住宅
- 商业的
- 工业和公共设施
- 基础设施
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- BASF
- Binderholz GmbH
- Cemex SAB de CV
- Coromandel International Ltd.
- DuPont
- Heidelberg Materials
- Holcim Ltd
- Interface Inc.
- Kingspan Group
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc
- Rockwool A/S
- Saint-Gobain
- Sika AG
- SmartLam
- Steico SE
- Weyerhaeuser Company
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Green Building Materials Market is expected to grow from USD 298.52 million in 2025 to USD 327.25 million in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 518.64 million by 2031 at 9.62% CAGR over 2026-2031.

The outlook reflects sustained policy pressure for zero-emission construction, rising corporate net-zero commitments and rapid scaling of low-carbon material technologies. Regulatory alignment between the European Union, the United States and other major economies is eliminating historical fragmentation, enabling global manufacturers to capture scale efficiencies and accelerate product innovation. Demand is further supported by financial incentives that narrow the price gap with conventional products, while digital material-tracking tools are beginning to monetise end-of-life value streams. Together, these forces are triggering the fastest adoption cycle the green building materials market has experienced to date.
Global Green Building Materials Market Trends and Insights
Mandatory Energy-Efficiency Codes Tightening
Worldwide building codes are shifting from voluntary guidelines to binding performance standards. In Europe, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive requires all new buildings to achieve zero on-site fossil-fuel emissions by 2030, and existing residential stock must upgrade to at least an E rating by the same year. The United States is following with the 2024 International Energy Conservation Code, which streamlines state adoption and adds life-cycle carbon provisions. Stricter codes boost demand for high-performance insulation, low-carbon concrete and advanced facades, rewarding suppliers that can verify product sustainability through digital compliance platforms. Enhanced enforcement further raises compliance costs for traditional materials, creating durable competitive advantages for certified alternatives.
Government Incentives and Certification Schemes
Tax credits, green bonds and preferential financing are transforming project economics. The US Inflation Reduction Act's Section 45L offers up to USD 5,000 per qualifying housing unit, and the 179D deduction now covers larger commercial upgrades. Canada has earmarked CAD 10 billion for clean-energy infrastructure, funnelling capital toward certified materials. With programs such as LEED, WELL and ENERGY STAR now linked to discounted financing, developers can offset the 15-25% price premium associated with advanced products. These incentives accelerate adoption in cost-sensitive segments and create reliable revenue streams for manufacturers that maintain up-to-date certification portfolios.
High Upfront Cost of Certified Materials
Certified products typically command 15-25% price premiums owing to testing, specialised processing and smaller production runs. The premium is most acute in residential construction, where buyers focus on first-cost and may overlook lifecycle savings. Novel products such as carbon-negative concrete or bio-based insulation also carry R&D amortisation charges. While declining as volumes rise and carbon pricing narrows cost differentials, elevated upfront expense remains a near-term adoption barrier, particularly in developing regions without robust incentive programs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Corporate Net-Zero, Embodied-Carbon Procurement
- Retrofit Wave for Ageing Building Stock
- Certification and Performance Complexity Across Regions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Low-carbon concrete and cement captured 24.17% of green building materials market share in 2025, underscoring industry urgency to abate the 8% of global greenhouse-gas emissions linked to conventional cement. Breakthrough technologies such as mineral-carbonation processes that sequester 45% CO2 while preserving strength have transitioned from pilot to limited commercial scale. Heidelberg Materials' Lengfurt project will capture 70,000 t of CO2 per year, signalling mainstream viability. Recycled metals retain reliable demand as structural steel routinely contains 93% scrap content and achieves 98% recovery rates at end-of-life. Engineered wood products, notably cross-laminated timber, are expanding as developers capitalise on faster assembly, lighter foundations and on-site carbon storage. Mineral-wool insulation remains a staple thanks to new non-combustible product lines, while cellulose and bio-foam insulation is progressing at a 10.17% CAGR, supported by renewable feedstocks and high thermal performance. Recycled-plastic composites are growing more selectively as lifecycle assessments raise concerns over micro-plastic shedding, although wood-polymer boards continue to penetrate exterior decking and facade niches.
Growth prospects vary across materials. Low-carbon binders benefit from inflight carbon-capture subsidies and will accelerate once carbon pricing regimes scale. Mass-timber markets hinge on expanded certified forestry capacity and revisions to height limits in building codes. Cellulose's trajectory depends on securing sufficient post-consumer paper streams and scaling enzymatic treatment plants. Overall, material innovation reinforces competitive differentiation, compelling incumbents to integrate circular-economy features, verified carbon footprints and digital passports into every product line.
The Green Building Materials Market Report is Segmented by Material Type (Low-Carbon Concrete and Cement, Recycled Metals, and More), Application (Framing, Insulation, and More), End-Use Industry (Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Institutional, and Infrastructure), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle-East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 40.35% of the green building materials market size in 2025, reflecting long-standing ENERGY STAR and LEED programmes and state-level zero-energy-ready building mandates. Federal tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act strengthen national alignment, while California's 2025 code cycle is expected to tighten embodied-carbon limits further. Canada's Greener Homes Initiative funnels low-interest loans into retrofit upgrades, stimulating demand for cellulose and mineral-wool insulation.
Europe maintains a high adoption baseline due to the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive and the forthcoming Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, which together raise the cost of high-carbon imports and incentivise domestic low-carbon production. Scandinavian countries have already mandated whole-life-carbon assessments for all large buildings, accelerating demand for digital passports and mass timber. Germany and France lead public-sector procurement of low-carbon concrete, while the United Kingdom pilots circular-construction hubs to harvest reusable materials from urban demolition.
Asia-Pacific is forecast to expand at an 10.95% CAGR through 2031 as rapid urbanisation meets evolving green-building codes. China requires all new projects to achieve at least Basic Grade green certification by 2025, while several provinces have introduced embodied-carbon benchmarks. India's Energy Conservation Building Code and Indonesia's Green Building Council rating system are driving early adoption, though fragmented municipal enforcement tempers near-term volumes. Australia and Singapore, already mature, are exporting expertise across the region, reinforcing supply-chain localisation and regional certification standards.
South America and the Middle East and Africa remain nascent but attractive as infrastructure investment expands. Brazil's Procel Edifica labelling system and the United Arab Emirates' Estidama Pearl Rating System are encouraging material suppliers to localise production to meet climate-specific performance needs. Financing remains the principal hurdle; however, multilateral banks increasingly channel green bonds into these markets, setting the stage for accelerated uptake during the next planning cycle.
- BASF
- Binderholz GmbH
- Cemex S.A.B. de C.V.
- Coromandel International Ltd.
- DuPont
- Heidelberg Materials
- Holcim Ltd
- Interface Inc.
- Kingspan Group
- Owens Corning
- PPG Industries Inc
- Rockwool A/S
- Saint-Gobain
- Sika AG
- SmartLam
- Steico SE
- Weyerhaeuser Company
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Mandatory Energy-Efficiency Codes Tightening
- 4.2.2 Government Incentives and Certification Schemes
- 4.2.3 Corporate Net-Zero, Embodied-Carbon Procurement
- 4.2.4 Retrofit Wave for Ageing Building Stock
- 4.2.5 Digital Material Passports Monetising End-Of-Life Value
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Upfront Cost of Certified Materials
- 4.3.2 Certification And Performance Complexity Across Regions
- 4.3.3 Bio-Based Feedstock Supply Crunch Post-2027
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material Type
- 5.1.1 Low-carbon Concrete and Cement
- 5.1.2 Recycled Metals
- 5.1.3 Engineered / Reclaimed Wood
- 5.1.4 Mineral-wool Insulation
- 5.1.5 Cellulose and Bio-foam Insulation
- 5.1.6 Recycled-plastic Composites
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Framing
- 5.2.2 Insulation
- 5.2.3 Roofing
- 5.2.4 Exterior Siding
- 5.2.5 Interior Finishing
- 5.2.6 Other Applications
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Commercial
- 5.3.3 Industrial and Institutional
- 5.3.4 Infrastructure
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/ Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BASF
- 6.4.2 Binderholz GmbH
- 6.4.3 Cemex S.A.B. de C.V.
- 6.4.4 Coromandel International Ltd.
- 6.4.5 DuPont
- 6.4.6 Heidelberg Materials
- 6.4.7 Holcim Ltd
- 6.4.8 Interface Inc.
- 6.4.9 Kingspan Group
- 6.4.10 Owens Corning
- 6.4.11 PPG Industries Inc
- 6.4.12 Rockwool A/S
- 6.4.13 Saint-Gobain
- 6.4.14 Sika AG
- 6.4.15 SmartLam
- 6.4.16 Steico SE
- 6.4.17 Weyerhaeuser Company
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment












