 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911741
印度钢铁:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)India Steel - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
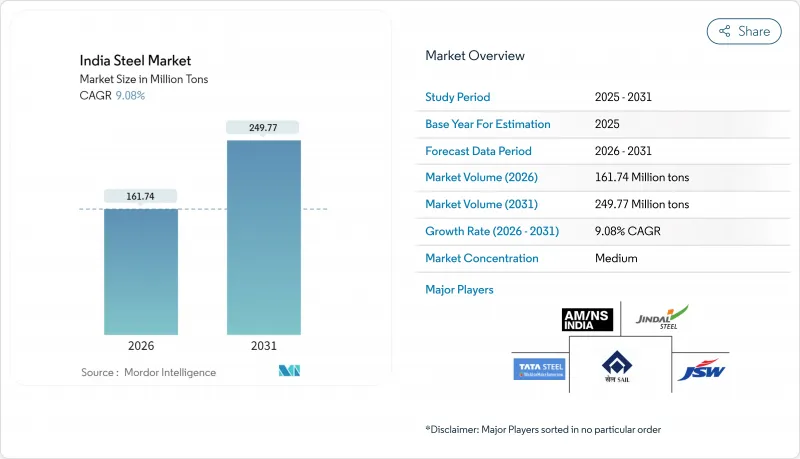
预计到 2026 年,印度钢铁市场规模将达到 1.6174 亿吨,高于 2025 年的 1.4828 亿吨。
预计到 2031 年产量将达到 2.4977 亿吨,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 9.08%。
2030年产能扩张至3亿吨的目标、加速的基础设施投资以及政策奖励,正支撑印度钢铁业的成长轨迹,并使其成为世界第二大钢铁生产国。大型政府主导计划(例如,34,800公里长的「印度公路网」(Bharatmala)、「总理住宅计画」(PM-AWAS)和「智慧城市2.0」计画)正在创造持续的国内需求,而新兴的绿色钢铁政策体係正在刺激对低碳技术的投资。主要生产商竞相确保现有和新增产能,对冲进口激增的风险,并遵守欧盟碳边境调节机制(CBAM)等出口相关环境法规,因此竞争依然激烈。同时,各邦在原材料供应和物流网络方面的优势正在推动生产向东部转移,从而促进区域经济发展并优化供应链成本。儘管印度钢铁业增加了脱碳支出、提高了资本效率并采取了增值产品策略,但这些措施在原材料价格波动的情况下仍有助于保护营运利润率,从而增强了印度钢铁业的整体韧性。
印度钢铁市场趋势与洞察
强而有力的政策支持
国家钢铁政策设定的3亿吨产能目标、特种钢生产关联激励计画(PLI)以及国内钢铁强制生产规定,共同建构了一个全面的框架,为整个印度钢铁业的需求确定性提供了保障。生产连结奖励计画(总额达2,710.6亿卢比)已在特种钢领域创造了790万吨产能,并创造了约1.5万个就业机会。政府采购中15%至50%的增值优惠标准为国内供应商提供了支持,而透过钢铁进口监控系统进行的即时进口监控则有助于完善贸易救济措施。透过总理成长能力计画(PM-Gati Shakti)实现的基础设施整合,可将物流成本降低高达15%,进而提升矿产资源丰富地区生产商的竞争力。最后,印度标准局(BIS)执行的严格品质标准确保新增产能能够生产符合国际标准的优质产品,以满足出口市场需求。
国内外对棕地和待开发区设施的资本投资迅速增加
印度钢铁业的投资週期正在加速,公私合营投资总额已超过250亿美元。产业主要企业纷纷进入该领域,现有企业也不断扩张。安赛乐米塔尔日本钢铁公司在安得拉邦投资15兆卢比的钢铁厂,正是以技术转移主导的先进高强度钢现代化改造的典范。印度钢铁管理局(SAIL)计划透过2025财年分阶段的资本支出预算拨款,到2031年将其产能从2000万吨扩大到3565万吨,这表明公共部门与国家目标保持一致。战略性外国直接投资(FDI)的流入正在引入低碳技术专长,而矿产资源丰富的东部丛集正在缩短原材料供应线,并实现规模经济。就业乘数效应,加上邦政府的支持,正在印度钢铁业形成技能发展和产业成长的良性循环。
人均钢铁消费量仍低于世界平均水平
预计到2023年,印度人均钢铁消费量将达到93.44公斤,远低于230公斤的全球平均水准。这不仅显示印度钢铁业潜力尚未充分发挥,也凸显了结构性瓶颈。由于基础设施覆盖率低和收入限制,占印度人口65%的农村市场需求仍显着偏低。消费量差异使得生产力计画决策更加复杂,因为生产者必须在扩大供应的同时兼顾实际的区域需求曲线。这些趋势表明,为了充分发挥印度钢铁业的潜力,必须同步投资农村基础建设。
细分市场分析
截至2025年,高炉-氧气转炉(BF-BOF)製程将占印度钢铁业46.12%的份额,证实了一体化工厂的坚实基础,此类工厂在大批量生产方面仍具有成本优势。随着生产商制定脱碳蓝图并优化现有设施,预计印度BF-BOF市场规模将以8.77%的复合年增长率成长。透过部分氢气注入实现效率的逐步提高和单位排放的降低,显示转型步伐切实可行。电弧炉在废钢丰富的都市区越来越受欢迎,这预示着未来产能将重新配置到低碳地区。新兴的氢气直接还原铁(DRI)先导工厂提供了第三种选择,但其商业化取决于绿色氢气的成本竞争力,预计要到2030年或更晚才能实现。
中期来看,高炉-氧气转炉联合炼钢厂将透过改进热风炉、上压回收涡轮机和炉渣造粒设备来提升能源回收和产品品质。技术合作将加速製程控制的数位化,从而扩大最佳实践工厂与普通工厂之间的产量差距。同时,二次炼钢企业将利用电弧炉的柔软性,灵活应对特殊钢材供应和不断变化的建筑标准。多种炼钢路径并存反映了印度钢铁市场的规模和废钢供应的区域差异,显示技术重组将是一个渐进的过程,而不是突飞猛进。
粗钢是整体基础钢种,预计将以7.73%的复合年增长率增长,这反映了上游综合钢厂和二级钢厂产能的扩张。约80%的高产运转率表明,在需要大规模新建设之前,产能潜力巨大。奥里萨邦、恰蒂斯加尔邦和卡纳塔克邦的铁矿石自给自足,使粗钢生产商相对于东南亚依赖进口的同行拥有持续的原材料优势,从而巩固了印度钢铁业的区域地位。
印度钢铁市场产量成长得益于一系列扶持政策,例如矿场自用配额和快速审批扩建计划环境影响评估。同时,废钢回收政策将废钢利用率从25%提高到70%,提升了生产效率。钢铁生产商正在加速采用预测性维护分析和製程优化软体,以缩小与行业领先水平的差距并降低能源消耗强度。这些共同努力巩固了钢铁业作为印度钢铁产业核心组成部分的地位。
印度钢铁市场报告按技术(高炉/碱性氧气转炉、电弧炉、其他技术)、基本形态(粗钢)、最终形态(成品钢)和终端用户行业(汽车及运输设备、建筑施工、工具及机械、消费品、能源、其他终端用户行业)进行细分。市场预测以百万吨为单位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 强而有力的政策支持
- 国内外棕地及待开发区设施资本支出(CAPEX)快速成长
- 大型基础建设项目(Bharatmala计划、PM-AWAS计划、智慧城市2.0)
- 汽车原始设备製造商转向高强度先进高强度钢和电动汽车用钢
- 氢基直接还原铁试验计画及废钢替代推广
- 市场限制
- 人均钢铁消费量仍低于全球平均水平
- 原料和能源成本波动
- 与环境、社会及公司治理(ESG)挂钩的出口碳关税(例如欧盟碳排放交易体系)
- 价值链分析
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代产品和服务的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 透过技术
- 高炉-转炉(BF-BOF)
- 电弧炉(EAF)
- 其他技术
- 按基本形式
- 粗钢
- 最终形式
- 成品钢材
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 汽车/运输设备
- 建筑/施工
- 工具/机器
- 消费品
- 活力
- 其他终端用户产业
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势(併购、合资、资本支出、绿色钢铁交易)
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- AM/NS India
- Godawari Power and Ispat
- Jindal Steel & Power Limited
- JSW Steel Limited
- Kalyani Steels
- Mukand Ltd.
- NMDC Steel Limited
- Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited
- Steel Authority of India Limited(SAIL)
- Tata Steel
- Vedanta Limited
- VISA STEEL
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
India Steel Market size in 2026 is estimated at 161.74 million tons, growing from 2025 value of 148.28 million tons with 2031 projections showing 249.77 million tons, growing at 9.08% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Expanding capacity targets of 300 million tons by 2030, accelerating infrastructure spending, and policy incentives together anchor this trajectory, positioning the India steel industry as the world's second-largest producer cohort. Government-backed megaprojects such as Bharatmala's 34,800 km highway build-out, PM-AWAS's large-scale housing programs, and Smart Cities 2.0 create durable domestic offtake, while an emerging green-steel policy ecosystem channels investment toward low-carbon technologies. Competitive intensity remains high, as leading producers race to secure brown- and green-field capacity, hedge against import surges, and comply with export-linked environmental mandates, such as the EU's CBAM. Simultaneously, state-level advantages in raw material availability and logistics connectivity spur an eastward production shift, supporting regional economic development and optimizing supply chain costs. Despite rising decarbonization outlays, capital efficiency gains, and value-added product strategies, these help shield operating margins amid volatile raw-material prices, thereby strengthening the overall resilience of the India steel industry.
India Steel Market Trends and Insights
Strong Policy Support
A comprehensive framework, combining the National Steel Policy's 300 million ton capacity target, the PLI scheme for specialty steel, and the mandate for domestically manufactured iron and steel products, underpins demand certainty across the India steel industry. Production-linked incentives worth INR 27,106 crore have already unlocked 7.9 million tons of specialty capacity and nearly 15,000 jobs. Preferential procurement thresholds of 15-50% value-added bolster domestic suppliers in government tenders, while real-time import monitoring via the Steel Import Monitoring System refines trade remedy decisions. Infrastructure integration through PM-Gati Shakti lowers logistics costs by up to 15%, sharpening competitiveness for producers in mineral-rich regions. Finally, the Bureau of Indian Standards enforces quality compliance, ensuring that new capacity delivers globally acceptable product grades that align with export market requirements.
Surge in Domestic and Foreign CAPEX for Brown-/Green-field Capacity
Private and public commitments exceeding USD 25 billion have amplified the India Steel investment cycle, drawing marquee entrants and expanding incumbents. ArcelorMittal Nippon Steel's INR 1.5 lakh crore Andhra Pradesh complex exemplifies technology-transfer driven upgrades in advanced high-strength grades. SAIL's trajectory from 20 million tons to 35.65 million tons capacity by 2031, supported by incremental FY25 capex allocations, highlights public-sector alignment with national targets. Strategic FDI flows embed knowledge of low-carbon technologies, while mineral-rich eastern clusters shorten raw material supply lines and enable economies of scale. Employment multipliers reinforce state support, creating virtuous cycles of skill development and industrial growth across the India Steel industry.
Per-Capita Steel Consumption Still Below Global Average
At 93.44 kg in 2023, India's per-capita steel usage remains far below the 230 kg global mean, signaling untapped potential but also revealing structural bottlenecks. Rural markets, which account for 65% of the population, have disproportionately low demand due to limited infrastructure penetration and income constraints. Consumption disparities complicate capacity-planning decisions, as producers must balance supply expansion with realistic regional demand curves. These patterns underline the need for parallel investments in rural infrastructure to unlock the full potential of the India Steel industry.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Large Infrastructure Pipeline (Bharatmala, PM-AWAS, Smart Cities 2.0)
- Hydrogen-Based DRI Pilots and Scrap Substitution Push
- ESG-Linked Export Carbon Tariffs (EU CBAM)
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The BF-BOF route held 46.12% India Steel industry share in 2025, a level underscoring the entrenched integrated-plant footprint that still delivers cost advantages on large volumes. The India steel market size for BF-BOF output is forecast to compound at an 8.77% CAGR as producers sweat existing assets even while charting decarbonization roadmaps. Declining unit emissions through incremental efficiency gains and partial hydrogen injection illustrate pragmatic transition pacing. Electric-arc furnaces are gaining traction in scrap-rich urban clusters, signaling a future redistribution of capacity toward low-carbon hubs. Emerging hydrogen DRI pilot plants introduce a third vector, although commercial uptake hinges on green-hydrogen cost parity, which is expected only beyond 2030.
In the medium term, BF-BOF complexes evolve through the use of hot-blast stoves, top-pressure recovery turbines, and slag granulation upgrades, thereby enhancing energy recovery and product quality. Technology partnerships accelerate process-control digitalization, widening yield spreads between best- and average-practice plants. Meanwhile, secondary producers leverage EAF flexibility to nimbly supply specialty grades and meet evolving construction standards. The coexistence of multiple routes reflects the India Steel market size and varied regional scrap-availability profiles, suggesting a gradual rather than abrupt technology realignment.
Crude steel constitutes the entire basic-form segment and is forecast to climb at a 7.73% CAGR, mirroring upstream capacity additions across integrated and secondary mills. High utilization rates of roughly 80% underscore latent headroom before extensive green-field builds are required. Iron-ore self-sufficiency across Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Karnataka grants crude-steel producers a sustained raw-material edge compared with import-dependent peers in Southeast Asia, strengthening the india steel industry position in the region.
Enabling policies, such as captive mine allocations and express environmental clearances for expansion projects, expedite throughput gains in the India steel market. Simultaneously, the Steel Scrap Recycling Policy aims to lift scrap use from 25% to 70%, driving process efficiency. Crude steel players are increasingly integrating predictive maintenance analytics and process optimization software, narrowing the gap to best performance and trimming energy intensity. These moves collectively solidify the segment's centrality within the India steel industry.
The India Steel Report is Segmented by Technology (Blast Furnace-Basic Oxygen Furnace, Electric Arc Furnace, and Other Technologies), Basic Form (Crude Steel), Final Form (Finished Steel), and End-User Industry (Automotive and Transportation, Building and Construction, Tools and Machinery, Consumer Goods, Energy, and Other End-User Industries). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Million Tons).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- AM/NS India
- Godawari Power and Ispat
- Jindal Steel & Power Limited
- JSW Steel Limited
- Kalyani Steels
- Mukand Ltd.
- NMDC Steel Limited
- Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited
- Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL)
- Tata Steel
- Vedanta Limited
- VISA STEEL
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Strong Policy Support
- 4.2.2 Surge in Domestic and Foreign CAPEX for Brown-/Green-Field Capacity
- 4.2.3 Large Infrastructure Pipeline (Bharatmala, PM-AWAS, Smart Cities 2.0)
- 4.2.4 Auto OEM Pivot to High-Strength AHSS and EV-Grade Steels (Under-Reported)
- 4.2.5 Hydrogen-Based DRI Pilots and Scrap Substitution Push (Under-Reported)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Per-Capita Steel Consumption Still Below Global Average.
- 4.3.2 Volatile Raw-Material and Energy Costs
- 4.3.3 ESG-Linked Export Carbon Tariffs (E.G., EU CBAM) (Under-Reported)
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Blast Furnace-Basic Oxygen Furnace (BF-BOF)
- 5.1.2 Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
- 5.1.3 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Basic Form
- 5.2.1 Crude Steel
- 5.3 By Final Form
- 5.3.1 Finished Steel
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.4.2 Building and Construction
- 5.4.3 Tools and Machinery
- 5.4.4 Consumer Goods
- 5.4.5 Energy
- 5.4.6 Other End-User Industries
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves (MandA, JVs, CAPEX, Green-steel deals)
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level overview, Market-level overview, Core segments, Financials, Strategic information, Market rank/share, Products and Services, Recent developments)
- 6.4.1 AM/NS India
- 6.4.2 Godawari Power and Ispat
- 6.4.3 Jindal Steel & Power Limited
- 6.4.4 JSW Steel Limited
- 6.4.5 Kalyani Steels
- 6.4.6 Mukand Ltd.
- 6.4.7 NMDC Steel Limited
- 6.4.8 Rashtriya Ispat Nigam Limited
- 6.4.9 Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL)
- 6.4.10 Tata Steel
- 6.4.11 Vedanta Limited
- 6.4.12 VISA STEEL
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment
- 7.2 Circular Economy and Scrap Processing Hubs
- 7.3 Green-steel Premiums and Export Windows








