 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1892847
专用LTE市场机会、成长驱动因素、产业趋势分析及预测(2026-2035年)Private LTE Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2026 - 2035 |
||||||
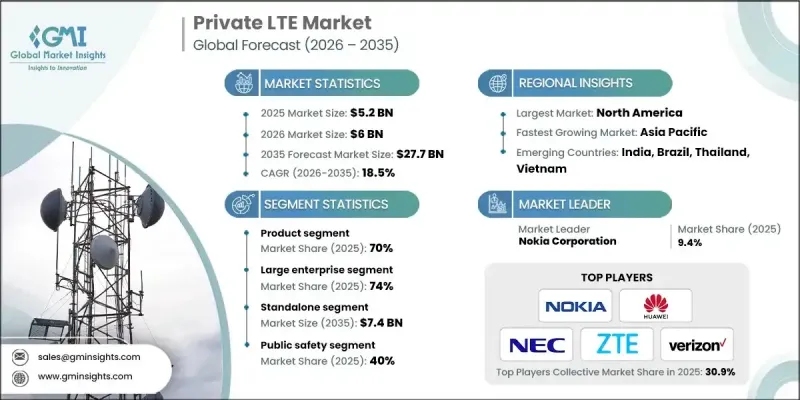
2025 年全球专用 LTE 市场价值为 52 亿美元,预计到 2035 年将以 18.5% 的复合年增长率增长至 277 亿美元。
工业自动化、机器人和即时监控的日益普及推动了这一成长,这些技术对高度可靠和确定性的无线网路提出了更高的要求。随着物联网在工厂、公用事业、能源和物流等领域的大规模部署,企业正在寻求可扩展的高效能网络,以确保服务品质 (QoS) 和无缝的行动管理。共享频谱框架和本地化授权降低了准入门槛,使中小企业 (SME) 能够部署经济高效的专用 LTE 解决方案,而无需完全依赖传统的行动网路营运商。工业 4.0 计画正在加速对连接性的投资,专用 LTE 正在成为预测性维护、员工行动办公室和边缘驱动型营运智慧的首选技术。专注于网路安全、资料主权和合规性的企业越来越依赖专用 LTE 来进行本地流量控制、存取管理和安全资料处理。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2025 |
| 预测年份 | 2026-2035 |
| 起始值 | 52亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 277亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 18.5% |
2025 年,大型企业市场占 74%,预计到 2035 年将达到 157 亿美元。大型企业凭藉其广泛的多站点营运、技术实力以及获取授权频谱和在全球范围内部署大规模网路的财力,在专用 LTE 网路部署中占据主导地位。
公共安全领域在2025年占据40%的市场份额,预计到2035年将以15.3%的复合年增长率成长。政府和紧急应变机构正在采用专用LTE网路取代过时的通讯系统,以确保关键任务连接的高可靠性和高可用性。这些网路支援即时资料传输、视讯串流和紧急应变协调,从而加快灾后復原速度并提高营运效率。
2025 年美国专用 LTE 市场价值 24 亿美元。透过 CBRS(公民宽频无线电服务)存取频谱,可以更轻鬆地部署客製化的专用 LTE 网络,扩大中小企业的采用率,并支援製造业、医疗保健、公用事业和物流行业的创新。
目录
第一章:方法论
第二章:执行概要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系分析
- 供应商格局
- 利润率分析
- 成本结构
- 每个阶段的价值增加
- 影响价值链的因素
- 中断
- 产业影响因素
- 成长驱动因素
- 不断增长的工业自动化需求
- 物联网和互联资产的扩展
- 日益增长的资料安全和主权要求
- 共享和本地化频谱的应用日益广泛
- 偏远地区对可靠连结的需求日益增长
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 初始部署和整合成本高昂
- 频谱可用性和监管复杂性
- 市场机会
- 拓展工业物联网生态系统
- 託管网路模式的成长
- 与边缘运算和人工智慧的集成
- 智慧城市和公共基础设施的采用
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管环境
- 北美洲
- 美国 - FCC 第 96 部分(CBRS 规则)
- 加拿大 - 创新、科学和经济发展部 (ISED) 在地化授权框架
- 欧洲
- 英国 - Ofcom 本地/共享许可
- 德国 - BNetzA 校园/本地许可证
- 法国 - ARCEP 本地频谱窗口
- 义大利 - 本地/校园频谱分配框架
- 西班牙 - 私人行动网路频谱供应(26 GHz / 中频段)
- 亚太地区
- 中国工信部企业专用网路授权计划
- 日本 - MIC地方5G/私人广播电台许可证
- 印度电信部/TRAI专用网路指南
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西 - ANATEL 私人网路授权
- 墨西哥 - IFT 有限用途/私有频谱特许经营权
- 阿根廷 - ENACOM 私有网路授权模式
- 中东和非洲
- 阿联酋 - TDRA 私人电信服务许可
- 南非 - ICASA 私有/本地频谱政策
- 沙乌地阿拉伯—CITC 私有网路授权选项:波特五力分析
- 北美洲
- PESTEL 分析
- 技术与创新格局
- 当前技术趋势
- 新兴技术
- 成本細項分析
- 开发成本结构
- 研发成本分析
- 行销和销售成本
- LTE 对专用无线网路的优势
- 专用LTE的工作原理/架构
- 专利分析
- 案例研究
- 永续性和环境方面
- 永续实践
- 减少废弃物策略
- 生产中的能源效率
- 环保倡议
- 未来市场展望及机会
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- MEA
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 战略展望矩阵
- 关键进展
- 併购
- 合作伙伴关係与合作
- 新产品发布
- 扩张计划和资金
第五章:市场估算与预测:依组件划分,2022-2035年
- 产品
- 基础设施
- 演进分组核心网(EPC)
- 回程
- eNodeB
- 装置
- 智慧型手机
- 手持终端
- 车辆路由
- 物联网模组
- 基础设施
- 服务
- 咨询与培训
- 整合与维护
- 託管服务
第六章:市场估算与预测:依网路模型划分,2022-2035年
- 独立版
- 杂交种
- 託管/託管式
第七章:市场估算与预测:依组织规模划分,2022-2035年
- 大型企业
- 中小企业
第八章:市场估算与预测:依应用领域划分,2022-2035年
- 公安
- 防御
- 矿业
- 运输
- 活力
- 製造业
- 其他的
第九章:市场估计与预测:依地区划分,2022-2035年
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 北欧
- 葡萄牙
- 克罗埃西亚
- 比荷卢经济联盟
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 新加坡
- 泰国
- 印尼
- 越南
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 哥伦比亚
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
- 土耳其
第十章:公司简介
- 全球参与者
- Nokia Corporation
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- ZTE Corporation
- Verizon Business
- AT&T Business
- NEC Corporation
- HPE (Aruba Networks)
- Motorola Solutions
- Siemens
- 区域玩家
- Boingo Wireless
- BT Group
- Telefonica
- Orange Business Services
- Vodafone Business
- Deutsche Telekom / T-Systems
- Rakuten Symphony
- KT Corporation
- Reliance Jio
- Emerging / Disruptor Players
- Mavenir Systems, Inc.
- Celona
- JMA Wireless
- Baicells Technologies
- Airspan Networks
- Federated Wireless
- Radisys
- Druid Software
The Global Private LTE Market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2025 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 18.5% to reach USD 27.7 billion by 2035.

The surge is driven by increasing adoption of industrial automation, robotics, and real-time monitoring, which demand highly reliable and deterministic wireless networks. With massive growth in IoT deployments across factories, utilities, energy, and logistics, enterprises are seeking scalable, high-performance networks that ensure quality of service (QoS) and seamless mobility management. Shared spectrum frameworks and localized licensing are reducing barriers to entry, allowing small and midsize enterprises (SMEs) to deploy cost-effective private LTE solutions without relying solely on traditional mobile network operators. Industry 4.0 initiatives are accelerating investment in connectivity, with private LTE emerging as the preferred technology for predictive maintenance, workforce mobility, and edge-driven operational intelligence. Enterprises concerned with cybersecurity, data sovereignty, and regulatory compliance increasingly rely on private LTE for on-premises traffic control, access management, and secure data processing.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Year | 2026-2035 |
| Start Value | $5.2 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $27.7 Billion |
| CAGR | 18.5% |
The large enterprise segment accounted for a 74% share in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 15.7 billion by 2035. Large organizations dominate private LTE rollouts due to their extensive multi-site operations, technological sophistication, and financial capacity to acquire licensed spectrum and deploy large-scale networks globally.
The public safety segment held a 40% share in 2025 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 15.3% through 2035. Government and emergency response agencies are adopting private LTE to replace outdated communication systems, ensuring mission-critical connectivity with high reliability and availability. These networks support real-time data transfer, video streaming, and coordinated responses to emergencies, enabling faster disaster recovery and operational efficiency.
U.S. Private LTE Market was valued at USD 2.4 billion in 2025. Access to spectrum via CBRS (Citizens Broadband Radio Service) is facilitating easier deployment of customized private LTE networks, expanding adoption among SMEs, and supporting innovation in manufacturing, healthcare, utilities, and logistics sectors.
Key players in the Global Private LTE Market include Affirmed Networks, Boingo, Cisco Systems, Inc., Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Mavenir Systems, Inc., NEC Corporation, Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Verizon, and ZTE Corporation. Companies in the Global Private LTE Market are strengthening their position by investing heavily in next-generation LTE and 5G technologies to enhance network performance and reliability. Strategic partnerships with industrial, manufacturing, and government sectors enable wider adoption and integration into critical infrastructure. Expanding presence in emerging regions, developing scalable and cost-effective deployment models, and offering end-to-end solutions with robust security features enhance market reach.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis, 2022 - 2035
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Component
- 2.2.3 Network model
- 2.2.4 Organization size
- 2.2.5 Application
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2026-2035
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook & strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin analysis
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.2 Growing industrial automation demand
- 3.2.1.3 Expansion of IoT and connected assets
- 3.2.1.4 Increasing data security and sovereignty requirements
- 3.2.1.5 Growing adoption of shared and localized spectrum
- 3.2.1.6 Rising need for reliable connectivity in remote sites
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High initial deployment and integration costs
- 3.2.2.2 Spectrum availability and regulatory complexity
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Expansion across industrial IoT ecosystems
- 3.2.3.2 Growth of managed and hosted network models
- 3.2.3.3 Integration with edge computing and AI
- 3.2.3.4 Adoption in smart cities and public infrastructure
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.1.1 U.S. - FCC Part 96 (CBRS Rules)
- 3.4.1.2 Canada - ISED Localized Licensing Framework
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.2.1 UK - Ofcom Local/Shared Licensing
- 3.4.2.2 Germany - BNetzA Campus/Local Licences
- 3.4.2.3 France - ARCEP Local Spectrum Window
- 3.4.2.4 Italy - Local/Campus Spectrum Allocation Framework
- 3.4.2.5 Spain - Private Mobile Network Spectrum Provision (26 GHz / Mid-Band)
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.3.1 China - MIIT Enterprise Private Network Licensing Programs
- 3.4.3.2 Japan - MIC Local 5G / Private Radio Station Licences
- 3.4.3.3 India - DoT/TRAI Captive Private Network Guidelines
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.4.1 Brazil - ANATEL Private Network Authorizations
- 3.4.4.2 Mexico - IFT Limited-Use / Private Spectrum Concessions
- 3.4.4.3 Argentina - ENACOM Private Network Licensing Model
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.4.5.1 UAE - TDRA Private Telecom Services Licensing
- 3.4.5.2 South Africa - ICASA Private/Local Spectrum Policies
- 3.4.5.3 Saudi Arabia - CITC Private Network Licensing OptionsPorter's analysis
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.5 PESTEL analysis
- 3.6 Technology and innovation landscape
- 3.6.1 Current technological trends
- 3.6.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.7 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.7.1 Development cost structure
- 3.7.2 R&D cost analysis
- 3.7.3 Marketing & sales costs
- 3.8 Advantages of LTE for private wireless networks
- 3.9 Working/Architecture of Private LTE
- 3.10 Patent analysis
- 3.11 Case study
- 3.12 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.12.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.12.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.12.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.12.4 Eco-friendly Initiatives
- 3.13 Future market outlook & opportunities
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2025
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LATAM
- 4.2.5 MEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New Product Launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion Plans and funding
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Component, 2022 - 2035 (USD Mn, Number of Nodes)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Product
- 5.2.1 Infrastructure
- 5.2.1.1 Evolved Packet Core (EPC)
- 5.2.1.2 Backhaul
- 5.2.1.3 eNodeB
- 5.2.2 Device
- 5.2.2.1 Smartphones
- 5.2.2.2 Handheld Terminals
- 5.2.2.3 Vehicular Routers
- 5.2.2.4 IoT Modules
- 5.2.1 Infrastructure
- 5.3 Service
- 5.3.1 Consulting & Training
- 5.3.2 Integration & Maintenance
- 5.3.3 Managed Service
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Network Model, 2022 - 2035 (USD Mn)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Standalone
- 6.3 Hybrid
- 6.4 Managed/Hosted
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Organization Size, 2022 - 2035 (USD Mn)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Large Enterprises
- 7.3 SMEs
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Application, 2022 - 2035 (USD Mn)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Public safety
- 8.3 Defense
- 8.4 Mining
- 8.5 Transportation
- 8.6 Energy
- 8.7 Manufacturing
- 8.8 Others
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2022 - 2035 (USD Mn, Number of Nodes)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 US
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Italy
- 9.3.5 Spain
- 9.3.6 Russia
- 9.3.7 Nordics
- 9.3.8 Portugal
- 9.3.9 Croatia
- 9.3.10 Benelux
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 Australia
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.4.6 Singapore
- 9.4.7 Thailand
- 9.4.8 Indonesia
- 9.4.9 Vietnam
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.5.4 Colombia
- 9.6 MEA
- 9.6.1 South Africa
- 9.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.3 UAE
- 9.6.4 Turkey
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Global Players
- 10.1.1 Nokia Corporation
- 10.1.2 Ericsson
- 10.1.3 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- 10.1.4 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 10.1.5 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- 10.1.6 ZTE Corporation
- 10.1.7 Verizon Business
- 10.1.8 AT&T Business
- 10.1.9 NEC Corporation
- 10.1.10 HPE (Aruba Networks)
- 10.1.11 Motorola Solutions
- 10.1.12 Siemens
- 10.2 Regional Players
- 10.2.1 Boingo Wireless
- 10.2.2 BT Group
- 10.2.3 Telefonica
- 10.2.4 Orange Business Services
- 10.2.5 Vodafone Business
- 10.2.6 Deutsche Telekom / T-Systems
- 10.2.7 Rakuten Symphony
- 10.2.8 KT Corporation
- 10.2.9 Reliance Jio
- 10.3 Emerging / Disruptor Players
- 10.3.1 Mavenir Systems, Inc.
- 10.3.2 Celona
- 10.3.3 JMA Wireless
- 10.3.4 Baicells Technologies
- 10.3.5 Airspan Networks
- 10.3.6 Federated Wireless
- 10.3.7 Radisys
- 10.3.8 Druid Software










