|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1891233
软体定义车辆 (SDV) 普及率:2026 年Software-defined Vehicles Adoption Report 2026 |
|||||||
范例预览
汽车产业正从以硬体为中心的设计转向以软体为先的方法,从根本上改变车辆架构和开发方式。 流程和驾驶员体验。向软体定义车辆 (SDV) 的转变实现了持续的功能更新、集中式运算以及透过订阅服务实现的新型获利模式。然而,这也带来了一些挑战,例如复杂的组织结构、网路安全风险以及多系统软体堆迭的整合。
本报告全面分析了 SDV 的现状,并详细介绍了主要 OEM 和一级供应商的采用策略。报告从多个技术和战略角度审视了市场,包括电气/电子 (E/E) 架构的演进、八层软体栈的组成、人工智慧在开发中的作用以及车辆安全监管框架。
本报告的研究结果是基于 2025 年初对 86 位来自 OEM 和供应商的汽车行业高管进行的调查,以及对 20 多位专家的深度访谈。 它也融合了来自上海车展 (AutoShanghai 2025) 和法兰克福国际车展 (IAA Mobility 2025) 等重要产业活动的洞见。
范例预览


报告概述
- 140 页报告:详细介绍了定义 SDV 市场的采用趋势、技术和策略。
- 市场优先级资料:45% 的 OEM 将 SDV 列为首要策略重点,超过了自动驾驶和电气化。
- 财务分析:领先的 OEM 将 21% 的 SDV 相关支出分配给软体,并将类似比例分配给电子电气 (E/E) 架构。
- 按区域划分的架构详情分析:许多 OEM 正在采用分区式 E/E 架构,以简化布线并集中运算资源。
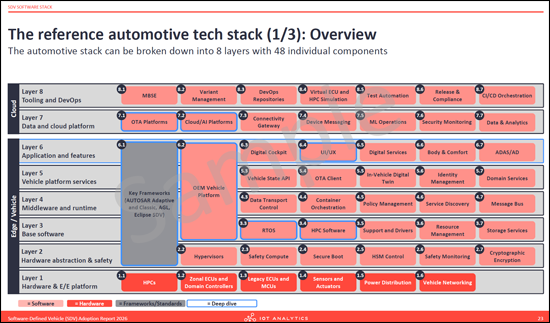
- 软体堆迭结构分析:组织了从硬体抽象层到云端平台的 8 层 48 个元件的结构。
- 供应商与OEM趋势: 分析主要厂商的策略,包括特斯拉、宝马、宾士、蔚来、日产、AWS、微软和恩智浦。
范例预览

关键分析领域
- SDV概述: 将SDV定义为采用软体优先方法建构的车辆,涵盖四个维度:车辆架构、云端整合、软体驱动工程和生命週期管理。概述了从分散式ECU到集中式计算的过渡。
- 车辆架构: 详细阐述从基于域的电子电气架构向基于区域的电子电气架构的过渡。分析区域设计的优势,例如减轻重量和简化布线,同时也探讨了技能差距和高昂的初始成本等障碍。
- SDV 软体堆迭: 将参考汽车技术堆迭分解为八层,包括硬体和电子电气平台、中介软体和应用层。我们评估了关键框架,例如 AUTOSAR Adaptive 和 Eclipse SDV,并深入研究了车辆平台,例如 MB.OS 和 Tesla OS。
- 人工智慧的角色与应用: 我们分析了人工智慧在车辆模型开发过程中的价值。数据显示,绝大多数原始设备製造商 (OEM) 认为人工智慧在软体开发和验证方面最有价值。我们也讨论了生成式人工智慧在程式码产生和需求工程的应用。
- 安全与监管: 我们分析了软体定义虚拟 (SDV) 扩充功能的攻击面,并识别出五种关键攻击途径,包括 ECU 漏洞利用和 OTA 漏洞。我们概述了符合 ISO 21434 和 UN R155/R156 等标准的合规性要求。
- OEM 和供应商采用策略: 我们将特斯拉和蔚来等科技原生公司的努力与传统公司的努力进行比较。我们重点介绍了欧洲 OEM 如何比亚太地区的同行更积极地优先考虑 SDV。
- 趋势与挑战: 辨识出云端原生开发流程的采用与软体堆迭模组化等宏观趋势。同时,也探讨了消费者对订阅模式的抵制以及软体工程人才短缺等挑战。
公司列表:
|
|
|
目录
第一章:摘要整理
第二章:引言
- 引言:章节概述与要点
- 传统汽车产业面临三大压力
- 因此,OEM厂商正在投资三大关键产品策略
- IoT Analytics 的 2025 年调查显示,SDV 是首要策略问题
- 欧洲 OEM 厂商和供应商处于 SDV 革命的前沿
- SDV 的定义
- 製造商和产业协会如何定义 SDV
- SDV 有四个关键要素维度
- 这些维度在汽车开发的整体 V 模型中都扮演着独特的角色。
- 为什么软体定义车辆 (SDV) 如此重要?关键引言
- SDV 的演变
- 原始设备製造商 (OEM) 每年都在 SDV 上进行投资,其中大部分投资用于软体和电子电气 (E/E) 架构。
- 案例研究:梅赛德斯-奔驰的软体定义未来
- 专家市场共识:技术原生 OEM 在 SDV 方面拥有明显的领先优势
第三章 车辆架构
- 车辆架构:章节概要与重点
- SDV 要求将改变未来的电子电气架构
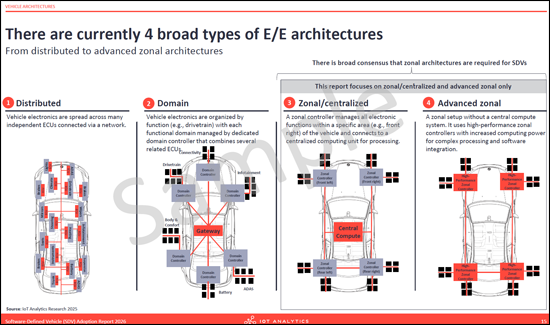
- 目前,电子电气架构种类繁多。
- 采用区域架构
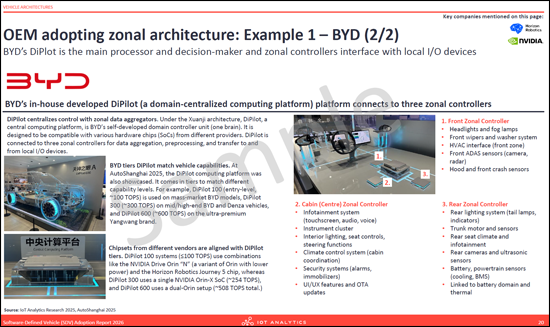
- 采用区域架构的OEM厂商:范例1 - 比亚迪
- 采用区域架构的OEM厂商:范例2 - 特斯拉
- 采用区域架构的OEM厂商:范例3 - Rivian
- 采用区域架构的供应商:范例 - NXP
- 区域架构的主要优势
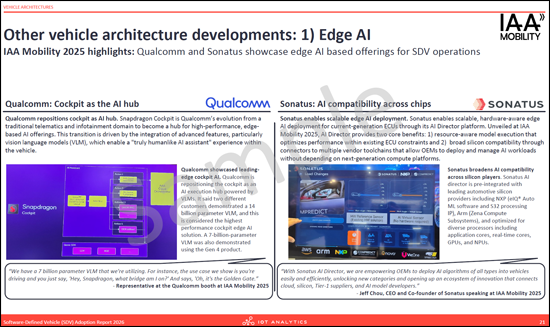
- 其他车辆架构发展:1 - 边缘AI
- 其他车辆架构发展:2 - 硬体虚拟化
第四章 SDV软体堆迭
- SDV软体堆迭:章节概述与要点
- 参考汽车技术栈
- 详细分析1:关键框架
- 详细分析2:OEM车辆平台
- 详细分析3:即时作业系统 (RTOS)
- 详细分析4:高效能运算 (HPC) 软体
- 详细分析5:OTA平台
- 详细分析 6:云端平台
- 详细分析 7:使用者介面/使用者体验
- 详细分析 8:应用与功能 - SDV 的功能
第五章:人工智慧的作用与应用
- 人工智慧的作用与应用:章节概述及要点
- 人工智慧在汽车开发中的价值创造潜力
- 详情:人工智慧在区域架构开发中的作用
- 人工智慧在车辆设计和车辆应用中的作用
- 人工智慧在建构特定车辆系统中的作用
- 关键的人工智慧赋能车辆功能
- 生成式人工智慧的作用
第六章:安全与监理的作用
- 安全与监管的功能:章节概述及要点
- SDV 中的网路安全风险
- 网路安全在…中的作用SDV V 模型
- 整体网路安全成熟度
- 关键网路安全主题的职责
- 汽车厂商安全厂商展示 1:上游
- 汽车厂商安全厂商展示 2:关键软体
- 法规
- OEM 和供应商采用策略:章节概述和要点
- OEM SDV 采用(10 个部分)
- 供应商 SDV 实施
第 7 章:趋势与挑战
- 趋势与挑战:章节概要与重点
- 趋势
- 挑战
- 其他见解:EW25 SDV 小组讨论亮点
第 8 章:研究方法
第 9 章:物联网分析
A report detailing the adoption of software-defined vehicles, incl. deep-dive on the software stack, specific OEM and supplier adoption strategies, and key trends and challenges.
Sample preview



The automotive industry is transitioning from hardware-centric engineering to a software-first approach, fundamentally altering vehicle architecture, development processes, and the driver experience. This shift to Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs) enables continuous feature updates, centralized computing, and new monetization models through subscription-based services. However, it also introduces complexities in organizational structure, cybersecurity risks, and the integration of multi-system software stacks.
The "Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV) Adoption Report 2026" provides a comprehensive analysis of the SDV landscape, detailing the adoption strategies of major OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers. It examines the market through multiple technical and strategic lenses: the evolution of electrical/electronic (E/E) architectures, the composition of the 8-layer software stack, the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in development, and the regulatory frameworks governing vehicle security.
The findings in this report rely on a survey of 86 automotive executives from OEMs and suppliers, conducted in early 2025, alongside 20+ in-depth expert interviews. The research also incorporates insights from major industry events such as AutoShanghai 2025 and IAA Mobility 2025.
Sample preview



Report at a glance
- 140-page report: Detailing the adoption trends, technologies, and strategies defining the SDV market.
- Market prioritization data: Analysis indicates that 45% of OEMs classify SDVs as their top strategic priority, surpassing autonomous driving and electrification.
- Financial insights: Data details that leading OEMs allocate 21% of their SDV expenditure to software, with a nearly equal portion dedicated to electrical/electronic architectures.
- Deep dive into Zonal Architectures: Examines the migration status, with a vast majority of OEMs currently adopting zonal E/E architectures to reduce wiring complexity and centralize compute power.
- Software stack breakdown: A structural analysis of the SDV software stack, identifying 8 layers and 48 components, from hardware abstraction to cloud platforms.
- Vendor and OEM landscape: Profiles strategies from key players including Tesla, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Nio, Nissan, AWS, Microsoft, and NXP.
Sample preview

Key areas of analysis
- Introduction to SDVs: Defines the SDV as a vehicle built with a software-first approach across four dimensions: vehicle architecture, cloud integration, software-driven engineering, and lifecycle management. It outlines the shift from distributed ECUs to centralized computing.
- Vehicle architectures: Details the transition from domain-based to zonal E/E architectures. The section analyzes the benefits of zonal designs, such as weight reduction and simplified wiring, while addressing barriers like skill gaps and high upfront costs.
- The SDV software stack: Dissects the reference automotive tech stack into 8 layers, including the hardware & E/E platform, middleware, and application layers. It evaluates key frameworks such as AUTOSAR Adaptive and Eclipse SDV, and deep-dives into vehicle platforms like MB.OS and Tesla OS.
- Role and adoption of AI: Analyzes the value of AI across the V-model development process. Data indicates that the overwhelming majority of OEMs see the greatest value for AI in software development and validation. The section also covers Generative AI applications in code generation and requirements engineering.
- Security and regulations: Examines the expanded attack surface of SDVs, identifying five primary attack vectors including ECU exploitation and OTA vulnerabilities. It outlines compliance requirements with standards such as ISO 21434 and UN R155/R156.
- OEM and supplier adoption strategies: Contrasts the approaches of tech-native players like Tesla and Nio against traditional incumbents. It highlights that European OEMs prioritize SDVs significantly more aggressively than their APAC counterparts.
- Trends and challenges: Identifies macro trends such as the adoption of cloud-native development pipelines and the modularization of software stacks. It also addresses challenges like consumer pushback on subscription models and the shortage of software engineering talent.
A data-driven foundation for key business functions
- Strategy & corporate development: Align strategic roadmaps with the shift toward zonal architectures, which a vast majority of competitors are adopting, and assess investment priorities where 45% of OEMs classify SDVs as their top strategic goal.
- Product management: Inform feature roadmaps by analyzing the adoption of specific SDV capabilities; for instance, a significant majority of new vehicles sold in 2024 possessed Software-Over-The-Air (SOTA) capabilities.
- R&D & engineering leadership: Direct resource allocation based on industry priorities, noting that software accounts for the leading share of SDV budgets. Evaluate the utility of AI, as a clear majority of peers expect it to be critical for ADAS simulation.
- Market intelligence: Assess the competitive landscape by reviewing the platform strategies of major players like BMW, Stellantis, Nissan, and BYD, and understanding the friction points between OEMs and suppliers regarding "white-box" code sharing.
Key concepts defined
- Software-Defined Vehicle (SDV): An automobile engineered with a software-first approach, where core functions (control, connectivity, user experience) and development processes are primarily defined by software rather than hardware.
- Zonal Architecture: An E/E architecture that groups Electronic Control Units (ECUs) by their physical location (zones) within the vehicle rather than by function, connecting them to central computing units to simplify wiring and processing.
- Vehicle Platform: An end-to-end software ecosystem (e.g., MB.OS, VW.OS) that manages hardware, enables real-time control, supports OTA updates, and provides a development environment for applications.
- Over-the-Air (OTA): The capability to download and install software and firmware updates remotely, managing the lifecycle of vehicle software without physical dealership visits.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Centralized computing units within the vehicle that process complex, data-intensive workloads such as AI, ADAS, and cross-domain functions.
Questions answered:
- What is a software-defined vehicle (definition), and which stakeholders treat SDV as a strategic priority?
- Which components of the automotive technology stack are foundational to SDV development and operations?
- What types of zonal architecture are emerging, and what are its benefits and adoption challenges?
- How valuable is AI expected to be across SDV lifecycle?
- What are SDV cybersecurity risks and mitigation approaches?
- What are the SDV adoption strategies of OEMs and suppliers?
- What are the key trends and challenges in SDV adoption?
Companies mentioned:
A selection of companies mentioned in the report.
|
|
|
Table of Contents
1. Executive summary
- The insights in this report are based on 4 main research sources
- Executive summary (4 parts)
- Analyst opinion: 4 things that stood out in our research
2. Introduction
- Introduction: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- The traditional automotive industry is experiencing pressure on 3 fronts
- As a result, OEMs are investing in 3 key product strategies
- IoT Analytics' 2025 survey shows SDV is the top strategic priority
- European OEMs and suppliers are at the forefront of SDV revolution
- Definition of an SDV
- How manufacturers and industry associations define SDV
- There are 4 main dimensions of an SDV
- Each of the 4 dimensions plays a separate role across the automotive development V-model
- Why are SDVs so important? Key quotes
- Evolution of SDVs
- OEMs invest into SDVs each year with most spending on software and E/E architectures
- Case in point: Mercedes-Benz's software-defined future (3 parts)
- Expert market consensus: Tech-native OEMs are clearly ahead with SDVs
3. Vehicle architectures
- Vehicle architectures: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- SDV requirements change future E/E architectures
- There are currently broad types of E/E architectures
- Zonal architecture adoption (5 parts)
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 1 - BYD (2 parts)
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 2 - Tesla
- OEM adopting zonal architecture: Example 3 - Rivian
- Supplier adopting zonal architecture: Example - NXP (2 parts)
- Key benefits of zonal architecture
- Other vehicle architecture developments: 1 - Edge AI
- Other vehicle architecture developments: 2 - Hardware virtualization
4. The SDV software stack
- SDV Software stack: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- The reference automotive tech stack (3 parts)
- Deep dive 1: Key frameworks (2 parts)
- Deep dive 2: OEM Vehicle Platform (7 parts)
- Deep dive 3: RTOS (2 parts)
- Deep dive 4: HPC software (2 parts)
- Deep dive 5: OTA platforms (2 parts)
- Deep dive 6: Cloud platforms (6 parts)
- Deep dive 7: UI/UX (2 parts)
- Deep dive 8: Applications and features - What SDV enables
5. Role and adoption of AI
- Role and adoption of AI: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- AI's value creation potential in vehicle development
- Deep-dive: Role of AI in zonal architecture development
- The role of AI for vehicle design and vehicle applications
- Role of AI when building specific vehicle systems
- Key vehicle functions that make use of AI
- The role of generative AI
6. Role of security and regulations
- Role of security and regulations: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- Cybersecurity risks in SDVs (2 parts)
- The role of cybersecurity in the SDV V-Model
- Overall cybersecurity maturity
- Responsibility for key cybersecurity topics
- Automotive cybersecurity vendor showcase 1: Upstream
- Automotive cybersecurity vendor showcase 2: Critical Software
- Regulations (2 parts)
- OEM and supplier adoption strategies: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- OEM SDV adoption (10 parts)
- Supplier SDV adoption (4 parts)
7. Trends and challenges
- Trends and challenges: Chapter overview and key takeaways
- Trend 1 (3 parts)
- Trend 2
- Trend 3
- Trend 4
- Challenge 1 (2 parts)
- Challenge 2 (2 parts)
- Challenge 3 (3 parts)
- Other insights: Highlights from the EW25 SDV panel discussion
8. Methodology
- The insights in this report are based on 4 main research sources
- Complete list of survey questions (2 parts)
- Complete list of interview questions
- Respondent sampling overview (3 parts)
9. About IoT Analytics
- About IoT Analytics
- Other publications by IoT Analytics
- Information and contact











