 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1921889
锂离子电池用锰铁磷酸盐(LMFP)专利模式分析(2026)LMFP for Li-ion Batteries Patent Landscape Analysis 2026 |
||||||
LMFP:下一代锂离子电池极具潜力的正极材料,专利活动快速成长且变化显着
全球对高效能环保储能解决方案的需求快速成长,这主要得益于电动车(EV)和大规模储能系统(ESS)的广泛应用,使得锂离子电池(LIB)先进正极材料的研发成为关注的焦点。橄榄石结构的磷酸铁锂(LFP)因其高安全性、稳定性、低成本和环境友善性而广受认可,但其相对较低的工作电压(通常约为3.4 V/Li/Li+)和有限的能量密度使其无法满足高性能应用日益增长的需求。为了因应这项挑战,锰铁磷酸盐锂(LMFP)应运而生,它以锰部分取代橄榄石结构中的铁,成为极具潜力的替代方案。这种复合材料继承了磷酸铁锂(LFP)的高热稳定性和成本效益,同时利用锰的高氧化还原电位,使其能量密度比LFP增加了10-20%。儘管有这些优势,锂金属磷酸铁锂(LMFP)也面临着自身的挑战。这些挑战包括电子和离子电导率低、锂离子扩散缓慢、锰的浸出以及与Mn³⁺的Jahn-Teller效应相关的容量衰减。过去十年,这促使人们开展了广泛的研究,并获得了强劲的专利活动的支持。
辨识新的智慧财产权进入者
自2023年以来,中国企业已成为LMFP专利领域的主要新进者。自2023年以来,已有超过410家新的智慧财产权公司进入LMFP专利领域,其中约80%为中国公司。超过20家新进者为非中国新创企业。中国公司主要为材料和电池製造商,其他亚洲公司则主要为研发机构和材料製造商。来自美国的新进业者既包括新创企业,也包括成熟公司。其他非亚洲公司主要由研发机构、电池製造商和材料供应商组成。
本报告中提及的公司(节录)
产业:宁德时代、LG化学/LG能源解决方案、三星、Dynanonic、比亚迪、EVE Energy、村田製作所/索尼、ATL、国轩高科动力能源/Gotion、SVOLT、丰田、太平洋水泥、东芝、住友化学/田中化学、天赐科技、远景能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC、Global能源/AESC Graphene、COSMX/COSLIGHT、住友金属矿业、Sunwoda、通用汽车、荣贝科技、魁北克水电、Reliance New Energy/Lithium Werks、Epsilon Carbon/庄信万丰等。
研发机构:SEL、九州大学、产业技术综合研究所 (AIST)、东京都立大学、中南大学、物理研究所、清华大学、北京理工大学、汉阳大学、蔚山科学技术大学 (UNIST)、韩国科学技术院 (KAIST)、俄罗斯科学技术研究院 (RIST)、化学工程研究所 (KERI)、韩国科学技术院 (KAIST)、俄罗斯科学技术研究院 (RIST)、化学工程研究所 (KERI)、法国原子能委员会 (CEA) (CNRS)、弗劳恩霍夫研究所、蒙特娄大学、芝加哥大学、密西根大学、洛克希德马丁/UT-巴特尔研究所等。
本报告对与锂锰铁磷酸盐 (LMFP) 相关的专利格局进行了全面分析,包括一个包含超过 7,800 项专利的 Excel 资料库,以及全球专利趋势和主要公司专利组合的资讯。
目录
引言
亮点
主要专利转让
专利概览
- 专利公开历史
- 专利公开趋势:依申请国划分
- 主要知识产权公司时间线
- 主要知识产权公司:依公司类型划分
- 主要知识产权公司:按类型和总部所在地划分
- 主要专利持有人排名:按类型划分
- 主要新创公司/纯知识产权公司:依原籍国划分
- 专利持有人排名
- 主要专利持有人和目前专利申请人
- 主要专利持有人拥有有效专利的国家/地区
- 2023年及以后最活跃的20家智慧财产权公司
- 专利持有人智慧财产权领导层
- 主要公司知识产权组合的地域覆盖范围
- 全球专利持有人的智慧财产权策略
- 依技术领域划分的专利活动(前驱物、正极材料、正极、电池单元、其他组件)
- 按领域划分的专利公开趋势(前驱物、正极材料、正极、电池单元、其他组件)
- 按领域划分的主要专利持有人(前驱物、正极材料、正极、电池单元、其他组件)
关于新进入智慧财产权领域的公司
- 主要进入智慧财产权领域的公司(自 2023 年以来首次公开 LMFP 相关专利的公司):按原产国和领域划分
关于技术领域
LMFP前驱
LMFP 正极材料
LMFP 电极
LMFP 电池
各细分市场简介
- 专利公开趋势
- 专利活动:依申请国家划分
- 主要知识产权公司:按类型和总部所在地划分
- 主要知识产权公司和知识产权新进入者
- 专利持有人智慧财产权领导地位
- 知识产权公司在现有技术阻断方面的潜力
- 公司可执行智慧财产权组合的实力指数
- 主要专利
- 近期专利:申请中要求保护的发明概述
关于申请国家
中国
日本
韩国
欧洲
美国
各国简介
- 专利公开趋势
- 按领域划分的专利族、待审专利和已授权专利(前驱物、正极材料、正极、电池单元、其他组件)
- 专利持有人知识产权领先地位
领先智慧财产权公司简介
各知识产权公司简介:知识产权动态和专利活动水平、地理和技术覆盖范围、知识产权优势以及提升潜力。
- 日本公司:村田製作所/索尼电池、东芝、松下/三洋、GS汤浅、日立、古河、太平洋水泥、住友化学/田中化学、住友金属矿业、旭化成、MU离子解决方案、三菱化学、电化、户田工业、Zeon、丰田、日产等。
- 韩国公司:LG化学/LG能源解决方案、三星、SK集团、L&F、浦项製铁、EcoPro、现代/起亚等。
- 欧洲公司:SAFT、Blue Solutions、I-TEN、Innolith/Alevo、巴斯夫、索尔维/Syensqo、优美科、阿科玛、戴姆勒、雷诺/安培等。
- 北美公司:Amprius/Berzelius、Ignis Lithium、Quantumscape、Global石墨烯、陶氏化学、太平洋工业发展公司 (PIDC)、Nano One、通用汽车、Rivian、魁北克水电公司等。 中国公司:宁德时代 (CATL)、比亚迪、易维能源、ATL、国轩高科动力能源、SVOLT、Envison/AESC、COSMX/COSLIGHT、Sunwoda、Cornex New Energy、中国航空锂电池 (CALB)、万向A123系统、Tafel New Energy Technology/Zenergy、JEVE (天津电动车能源)、德益能源科技、力神、Phylion、海思储能科技、赣锋锂业、蔚来汽车、广汽集团、吉利控股、天合光能、一汽集团、东风汽车、理想汽车、Battero Technology、威狮新能源科技、狮王新能源科技、创恆奈米科技等。 其他公司:庄信万丰 (Johnson Matthey)、Aleees(先进锂电化学)等。 Reliance New Energy(包括 Lithium Werks/Valence Tech.)、Ola Electric Mobility 等。
附录
KnowMade 简报
Key Features
- PDF with > 400 slides
- Excel file > 7,80 patent families
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers grouped by geographical area
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio
- Patents categorized by supply chain segments (precursors, cathode active materials, cathode, battery cells).
- For each segment: IP dynamics, ranking of main patent assignees, IP newcomers, key IP players, key patents, and recent developments
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report, including hyperlinks to an updated online database.
LMFP: A promising cathode material for next-generation Li-ion batteries witnessing a fast-growing and shifting patenting activity
The burgeoning global demand for highly efficient and environmentally friendly energy storage solutions, driven primarily by the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and large-scale energy storage systems (ESS), has made the development of advanced lithium-ion battery (LIB) cathode materials a critical focus. While the olivine-structured lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is widely valued for its high safety, stability, low cost, and environmental friendliness, its relatively low operating voltage, typically around 3.4 V (vs. Li/Li+), limits its energy density and falls short of the increasing requirements for high-performance applications. Lithium manganese iron phosphate (LMFP), developed by partially substituting iron with manganese in the olivine structure, has emerged as a promising alternative. This composition incorporates the high thermal stability and cost-effectiveness of LFP while leveraging the higher redox potential of manganese, resulting in a 10% to 20% higher energy density than LFP. Despite these advantages, LMFP faces intrinsic challenges notably poor electronic and ionic conductivity, sluggish lithium-ion diffusion kinetics, manganese dissolution issues, and capacity degradation related to the Jahn-Teller effect induced by Mn3+. Consequently, extensive research, supported by robust patent activity, has been performed for the last ten years.
In this context, the present report aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the patent landscape related to the lithium manganese iron phosphate, from materials to battery cells. Knowmade's analysts have selected and analyzed more than 7,800+ patent families (inventions) related to LMFP.
The general objectives of the present report are:
- to identify and map the key IP players in each chosen technological segment (precursors, cathode active materials, cathodes, battery cells).
- to assess the geographical distribution of patent families, current legal status of patents, helping stakeholders understand strategic positioning and navigate their competitive environment.
- to get an overview of key and recent patents across the value chain.
These strategic insights will support R&D, investment, and policy decisions in the evolving field of Li-ion battery.
Understanding the main trends, the key players' IP position and IP strategy
IP competition analysis should reflect the vision of players with a strategy to enter and develop their business in the LMFP Li-ion battery market. In this report, Knowmade's analysts provide a comprehensive overview of the competitive IP landscape and latest technological developments in this field. The report identifies the IP leaders, most active patent applicants, and new entrants in the IP landscape. It also sheds light on under-the-radar companies and new players in this field. The report covers IP dynamics and key trends in terms of patents applications, patent assignees, filing countries, and technological segment of interest (precursors, cathode active materials, cathode, battery cells, etc.). Dedicated sections of the report focus on the patent portfolios of key players from various countries.

Identify the IP newcomers
Since 2023, Chinese entities have established themselves as dominant newcomers in the LMFP patent landscape. Over 410 new IP players have entered the LMFP patent landscape since 2023, with around 80% coming from China. More than 20 newcomers are non-Chinese start-ups. The main Chinese entrants are material and battery manufacturers, while other Asian newcomers are primarily R&D institutes and material producers. American newcomers include both start-ups and established companies, whereas other non-Asian entrants consist mainly of R&D organizations, battery manufacturers, and material suppliers. Dedicated sections of the report focus on the patent portfolios of IP new entrants from various countries.
Deep dive into key and recent patents across LMFP value chain
All patents selected for this study have been categorized by supply chain segment (precursor, cathode material, cathode, battery cells).
For each supply chain segment, this report includes a time-evolution of patent applications, main and key patent assignees, and a description of key and recently patented technologies. An understanding of the current technical challenges addressed in the patents is also presented.
Useful Excel patent database
This report also includes an extensive Excel database with all patents analyzed in this study, including patent information (numbers, dates, assignees, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and supply chain segments (precursors, cathode active materials, cathodes, battery cells).
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive)
INDUSTRIALS: CATL, LG Chem/LG Energy Solutions, Samsung, Dynanonic, BYD, EVE Energy, Murata/Sony, ATL, Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy/Gotion, SVOLT, Toyota, Taiheiyo Cement, Toshiba, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Tinci Materials Technology, Envision/AESC, Global Graphene, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Sunwoda, General Motors, Rongbay Technology, HydroQuebec, Reliance New Energy/Lithium Werks, Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey and more.
R&D LABORATORIES: SEL, Kyushu University, AIST, Tokyo Metropolotan University, Central South University, Institute of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing Institute of Technology, Hanyang University, UNIST, KAIST, RIST, KERI, CEA, CNRS, Fraunhofer, Universite de Montreal, University of Chicago, University of Michigan, Lockheed Martin/UT-Battelle and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Scope of the report
- Methodology
- Essentials on Solid-state Batteries
- Essentials on Halide solid electrolytes
HIGHLIGHTS
MAIN PATENT TRANFERS
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Time evolution of patent publications by filing countries
- Timeline of main IP players
- Main IP players by typology of companies
- Main IP players by typology and headquarters countries
- Ranking of main patent assignees by typology
- Main start-ups/pure players by originating countries
- Ranking of patent assignees
- Main patent owners and current patent applicants
- Countries of active patents for main patent assignees
- Most active IP players since 2023
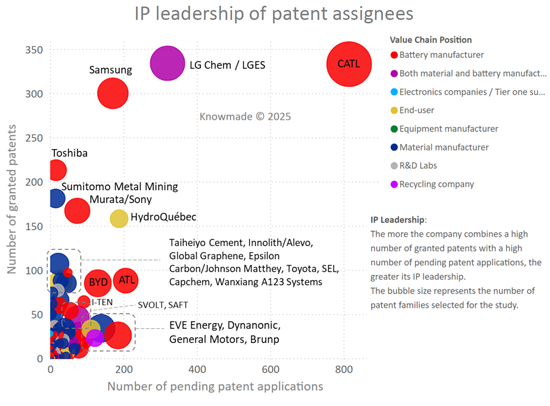
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Geographical coverage of main players' IP portfolios
- Global IP strategy of patent assignees
- Patent activities by technological segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- Time evolution of patent publications by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- Main patent assignees by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
FOCUS ON IP NEWCOMERS
- Main IP newcomers (first LMFP-related patent published in 2023 or later) by originating countries and by segments
FOCUS ON TECHNICAL SEGMENTS
LMFP precursors
LMFP cathode materials
LMFP electrode
LMFP battery cells
For each segment:
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Patent activity by filing countries
- Main IP players by typology and headquarters countries
- Key IP players and IP newcomers
- IP leadership of patent assignees
- Prior-art blocking potential of IP players
- Strength index of players' enforceable IP portfolios
- Key patents
- Overview of inventions claimed by recent patent applications
FOCUS ON FILING COUNTRIES
China
Japan
South Korea
Europe
USA
For each country:
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Patent families, pending applications and granted patents by segments (precursors, cathode materials, cathode, battery cells, and other components)
- IP leadership of patent assignees
FOCUS ON MAIN AND KEY IP PLAYERS
Fore each IP players: IP dynamics and level of patent activity, geographical & technical coverage, IP strengths, and potential for reinforcement.
- Japanese companies: Murata Manufacturing/Sony Battery, Toshiba, Panasonic/Sanyo, GS Yuasa, Hitachi, Furukawa, Taiheiyo Cement, Sumitomo Chemical/Tanaka Chemical, Sumitomo Metal Mining, Asahi Kasei, MU Ionic Solutions, Mitsubishi Chemical, Denka, Toda Kogyo, Zeon, Toyota, Nissan, and more
- South Korean companies: LG Chem/LG Energy Solution, Samsung, SK Group, L&F, Posco, EcoPro, Hyundai/kia, and more
- European companies: SAFT, Blue Solutions, I-TEN, Innolith/Alevo, BASF, Solvay/Syensqo, Umicore, Arkema, Daimler, Renault/Ampere, and more.
- North American companies: Amprius/Berzelius, Ignis Lithium, Quantumscape, Global Graphene, Dow, PIDC (Pacific Industrial Development Corporation), Nano One, General Motors, Rivian, Hydro-Quebec and more.
- Chinese companies: CATL, BYD, EVE Energy, ATL, Gotion/Guoxuan High Tech Power Energy, SVOLT, Envison/AESC, COSMX/COSLIGHT, Sunwoda, Cornex New Energy, CALB (China Aviation Lithium Battery), Wanxiang A123 Systems, Tafel New Energy Technology/Zenergy, JEVE (Tianjin EV Energy), Deyi Energy Technology, Lishen, Phylion, Hithium Energy Storage Technology, Ganfeng Lithium, NIO, GAC Group, Geely Holding, Trina Storage, FAW, Dongfeng Motor, Li-Auto, Battero Technology, WeLion New Energy Technology, Liongo New Energy Technology, Hengtron Nanotech, and more
- Other companies: Epsilon Carbon/Johnson Matthey, Aleees (Advanced Lithium Electrochemistry), Reliance New Energy (Incl. Lithium Werks/Valence Tech.), Ola Electric Mobility, and more












