 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1445640
日本第三方物流(3PL):市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2024-2029 年)Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
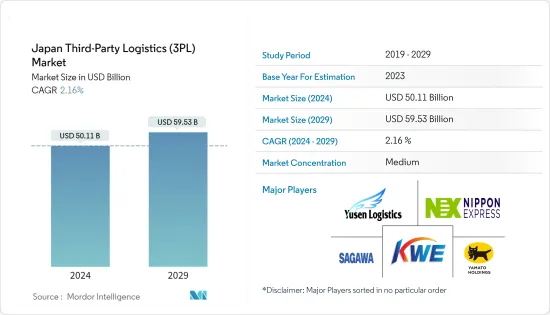
日本第三方物流(3PL)市场规模预计到 2024 年为 501.1 亿美元,预计到 2029 年将达到 595.3 亿美元,预测期间(2024-2029 年)将以 2.16% 的复合年增长率增长。
主要亮点
- COVID-19 的爆发对运输、储存和运输货物的物流公司产生了直接影响。物流公司帮助公司开展业务并将产品交付给客户。它们已成为国内外价值链的重要组成部分。因此,大流行造成的供应链中断可能会影响该行业的竞争力、经济扩张和就业创造。
- 随着时间的推移,日本在供应链领域取得了长足的进步。例如,我们利用数位科技改造传统产业。近年来,影响物流的社会经济因素发生了显着变化。这些因素包括人口减少或老化、某些地区的新想法、小件物品的更频繁的交付以及不同的客户需求。在日本,随着大公司考虑其物流网路的运作方式并将更多任务外包给 3PL 供应商以降低成本并提高效率,对 3PL 的需求正在增加。
- 3PL 公司营运供应链,向所有产业和消费者提供材料和货物。日本是东亚最大的经济体之一,其製造业严重依赖 3PL。因此,像大和控股这样的组织跻身于世界顶级物流提供者之列。群岛1.2亿人口处理了47.1亿吨国内货物,对外贸易增加了9亿吨。
- 自2000年以来,日本对大型现代化物流租赁设施的需求大幅增加。物流业务外包、企业房地产失衡以及多个旧仓库的搬迁都是导致这一增长的原因。日本的货运和物流业是经济的重要组成部分,占GDP的5%以上。
- 物流业以其激烈的成本竞争而闻名。击败竞争对手需要复杂的协调和规模经济。透过使用「第三方物流」(也称为「3PL」),物流公司开始简化业务。自动化和人工智慧 (AI) 是成本控制的进一步工具。
物流系统产业可能会发展并融入更多此类技术解决方案。自动化仓库目前已投入使用,但全自动卡车上路还需要一段时间。日本的自动化进步不会很快到来。该公司的物流部门正面临人手不足,最重要的是,人口迅速老化是驱动因素,使公平价格的服务面临风险。该倡议的两个目标是提高卡车运输业的生产力,并创造一个吸引和留住老年工人和女司机的工作环境。在进一步自动化发生之前,这种策略是否足以有效稳定市场还有待观察。
日本第三方物流(3PL)市场趋势
汽车和製造业成长推动市场
日本一直是製造机械和汽车工业的世界领导者之一。日本经济产业省 (METI) 表示,高科技製造业是日本最重要的成长部门之一。日本製造业的核心领域包括消费性电器产品、汽车製造、半导体製造、光纤、光电子、光媒体、钢铁、影印机等。
日本长期以来一直是世界主要汽车出口国之一。以高品质製造和高效物流服务而闻名。高度发展的基础设施和港口网络以及密集的航运网络支撑着该国作为出口大国的地位。
日本汽车业的一些主要公司都设有内部物流部门。 Vantec 是日本领先的汽车物流供应商,隶属于日立运输系统集团。万泰集团支援汽车零件的顺序供应,以满足汽车製造商复杂的物流需求。
日野汽车所设想的未来移动社会用「SPACE」一词来表达。 “共享(共用运动、空间、时间)”、“平台(自由兼容各种服务)”、“自主(自由驾驶)”、“互联(将移动性与人、物、城市连接起来)” “电力” (提高效率和弹性)。
低温运输物流发展
日本是继美国之后全球第二成长最快且成熟的医药市场。国际社会对日本医药市场的兴趣将为低温运输物流服务供应商创造机会。该国的公司正在透过与竞争对手和向 3PL 公司提供平台服务的公司的交易、合作伙伴关係和协议,显着改进和更新其服务。
低温运输市场也因其所需的能源量和製程中产生的排放而闻名。这些公司正在建立物流中心,并将车辆改造为环保型、最大限度地减少排放气体并运作永续能源来源。
日本政府和联合国儿童基金会 (UNICEF) 于 2022 年 2 月 20 日向卫生署和 SAMES 捐赠了三辆冷藏车。这些货车将用于运输疫苗。 Masami Kibuchi 在帝力的 SAMES 工厂发表演说。日本驻东帝汶大使和层级副代表 Ainoa Jaureguibeitia 向卫生部副部长 Bonifacio Maukoli dos Reis 赠送了车辆。
此外,还提供步入式冷却室,目前已安装在艾纳罗、包考、博博纳罗和厄库斯省的所有区域仓库中。拥有配备所有部件的冷藏车、步入式冷却器和冷冻非常重要,这样疫苗就可以安全储存并快速发送到城镇和医疗机构。
日本第三方物流(3PL)产业概况
这个市场相当小,最大的参与者是 Yusen 物流、Expeditors、DHL、Hitachi Transport System 和 Kuehne Nagel。自行处理物流的零售和製造公司也在市场中发挥重要作用。
日本的电子商务市场正以前所未有的速度成长。这体现在日本附加价值服务的快速成长,导致日本物流业的包装、标籤和分类业务大幅成长。
联合运输或联合运输是将多家公司的货物发送到一个通用的交货点,以解决该国的高需求和劳动力短缺问题,帮助运输公司找到有可用卡车空间的司机和托运人。可以采取平台应用程式等措施。 ,都市区的小型仓库作为中间配销中心,收集货物。
物流行业变革的目标,例如使用自动驾驶机器和车辆,是为了消除该行业对整个经济的碳排放。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月分析师支持
目录
第一章简介
- 研究成果
- 调查先决条件
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
- 分析调查方法
- 调查阶段
第三章执行摘要
第四章市场动态与洞察
- 目前的市场状况
- 市场动态
- 促进因素
- 抑制因素
- 机会
- 价值链/供应链分析
- 行业政策法规
- 仓储市场的整体趋势
- CEP、最后一哩配送和低温运输物流等其他细分市场的需求
- 关于电子商务业务的见解
- 技术趋势和自动化
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代产品的威胁
- 竞争公司之间的敌意强度
- 新型冠状病毒感染疾病对市场的影响
第五章市场区隔
- 按服务
- 国内运输管理
- 国际运输管理
- 付加仓储配送
- 按最终用户
- 製造业和汽车
- 石油、天然气和化学品
- 流通贸易(包括电子商务在内的批发零售贸易)
- 製药与医疗保健
- 建造
- 其他最终用户
第六章 竞争形势
- 公司简介
- Nippon Express
- Yamato Holdings
- Kintetsu World Express
- Sagawa Express
- Hitachi Transport System
- Nichirei Logistics
- Sankyu
- Kokusai Express
- Fukuyama
- Mitsui-Soko
- Alps Logistics
- Yusen Logistics
- DHL*
第七章 市场的未来
第8章附录
- 宏观经济指标(GDP分布,依活动划分,运输和仓储部门对经济的贡献)
- 对外贸易统计-分产品进出口额
- 深入了解主要出口目的地和进口国家
The Japan Third-Party Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 50.11 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 59.53 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 2.16% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

Key Highlights
- The COVID-19 epidemic had a direct effect on logistics companies, which move, store, and move goods.Logistics companies help businesses do business and get their products to customers. They became an important part of value chains both inside and outside of national borders. Hence, supply chain interruptions brought on by the pandemic could affect the sector's competitiveness, economic expansion, and job creation.
- Japan has made a lot of progress in the supply chain space over time. For example, it has embraced digital technologies to change a traditional industry. In the last few years, the social and economic factors that affect logistics have changed a lot. These factors include a shrinking or aging population, new ideas in some areas, more frequent deliveries of smaller goods, and different customer needs. In Japan, there is more demand for 3PL as large companies look at how their logistics networks work and outsource more tasks to 3PL providers to cut costs and improve efficiency.
- 3PL logistics firms are the ones who run supply chains and get materials and goods to all industries and consumers. Japan, one of the biggest economies in East Asia, relies on 3PL logistics a lot because of its manufacturing industry. As a result, organizations like Yamato Holdings are among the top logistics providers globally. 120 million people in the archipelago handled 4.71 billion tons of domestic freight, and foreign trade added 900 million tons more.
- Since 2000, there has been a big rise in the need for large, modern logistics leasing facilities in Japan. Outsourcing logistics operations, imbalances in corporate real estate, and moving out of multiple old warehouses all contributed to the rise. The freight and logistics industry in Japan is a big part of the economy, making up more than 5% of the GDP.
- The logistics business is known for its fierce cost competitiveness. To outbid rivals, sophisticated coordination and economies of scale are required. Through the use of "third-party logistics," sometimes known as "3PL," logistics firms have begun to streamline their operations. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are further tools for cost control.
It's likely that the logistics systems industry will grow to include more of these technical solutions. Although automated warehouses are now in use, it will be some time before fully autonomous trucks are allowed on the roads. Automation advancements cannot arrive soon enough for Japan. Its logistics sector is experiencing a manpower deficit, and on top of that, drivers are aging quickly, endangering the availability of services at fair prices. Two goals of this effort are to increase productivity in the trucking sector and to foster work environments that attract and retain older and female drivers. It has to be seen whether this tactic stabilizes the market effectively enough until automation advances further.
Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market Trends
Growth in automotive and manufacturing sector driving the market
Japan has always been and is one of the global leaders in the manufacturing machinery and automobile industries. The Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) says that high-tech manufacturing is one of Japan's most important growth sectors. The core areas in Japan's manufacturing sector are consumer electronics, automobile manufacturing, semiconductor manufacturing, optical fibers, optoelectronics, optical media, steel and iron, and copy machines.
Since a long time ago, Japan has been one of the top exporters of cars in the world. It is known for its high-quality manufacturing and efficient logistics services. Its highly developed infrastructure and port network support its status as an exporting giant, as do its dense concentration of shipping lines.
Some of the major players in the automotive industry in Japan also have in-house logistics arms. Vantec, a leading automotive logistics provider in Japan, operates under the HTS Group. The Vantec Group supports the sequential supply of auto parts in full alignment with the complex logistics requirements of automotive manufacturers.
As per Hino Motors, the future mobility society to be considered is represented by the word "SPACE". "Shared (sharing of movement, space, and time)" "Platform (corresponding to various services freely) and "Autonomous (free from driving)" "Connected (connecting mobility with people, things, and cities)" "Electricity" (increase efficiency and flexibility).
Development in cold chain logistics
Japan is the second-fastest-growing mature pharmaceutical market in the world, following the United States. The international interest in the Japanese pharmaceutical market will create opportunities for cold chain logistics service providers. The companies in the country are heavily improving and updating their services through deals, partnerships, and agreements with competitors and companies that provide platform services to the 3PL companies.
The cold chain market is also known for the amount of energy required in the process and the huge amount of emissions that occur. The companies are setting up logistics centers and transforming vehicles into ones that are environment-friendly, produce minimum emissions, and run on sustainable sources of energy.
The Government of Japan and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) gave three refrigerated vans to the Ministry of Health and SAMES on February 20, 2022. These vans will be used to move vaccines.At the SAMES compound in Dili, Masami Kinefuchi, the Japanese ambassador to Timor-Leste, and Ainhoa Jaureguibeitia, the deputy UNICEF representative, gave the vehicles to Sr. Bonifacio Maucoli dos Reis, the vice minister of health.
Moreover, walk-in cool rooms have been provided and are currently being installed at all regional warehouses in the municipalities of Ainaro, Baucau, Bobonaro, and the Special Administrative Area of Oecusse. It is important to have refrigerated vans, walk-in coolers, and freezer rooms with all of their parts so that vaccines can be kept safely and quickly sent to towns and medical facilities.
Japan Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Industry Overview
The market is pretty small, and its biggest players are Yusen Logistics, Expeditors, DHL, Hitachi Transport System, and Kuehne Nagel. Retail and manufacturing companies that handle their own logistics also play a big role in the market.
Japan's e-commerce market is growing at a rate that has never been seen before. This is reflected in the rapid growth of value-added services in Japan.As a result, packaging, labeling, and sorting activities have seen a large spike in the Japanese logistics industry.
To deal with the high demand and lack of workers in the country, steps can be taken like joint or shared delivery, which sends goods from multiple companies to common delivery points, platform apps, which help delivery companies find drivers with empty truck space and shippers, the use of small warehouses in cities as intermediate distribution centers, and collection logistics.
The goal of the changes in the logistics industry, like the use of self-driving machines and vehicles, is to get rid of the sector's carbon footprint on the economy as a whole.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.3 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Industry Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 General Trends in Warehousing Market
- 4.6 Demand From Other Segments, such as CEP, Last Mile Delivery, Cold Chain Logistics Etc.
- 4.7 Insights on Ecommerce Business
- 4.8 Technological Trends and Automation
- 4.9 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.9.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.9.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.9.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.9.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.9.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.10 Impact of COVID--19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Domestic Transportation Management
- 5.1.2 International Transportation Management
- 5.1.3 Value-added Warehousing and Distribution
- 5.2 By End-User
- 5.2.1 Manufacturing & Automotive
- 5.2.2 Oil & Gas and Chemicals
- 5.2.3 Distributive Trade (Wholesale and Retail trade including e-commerce)
- 5.2.4 Pharma & Healthcare
- 5.2.5 Construction
- 5.2.6 Other End-Users
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Overview (market concentration and major players)
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Nippon Express
- 6.2.2 Yamato Holdings
- 6.2.3 Kintetsu World Express
- 6.2.4 Sagawa Express
- 6.2.5 Hitachi Transport System
- 6.2.6 Nichirei Logistics
- 6.2.7 Sankyu
- 6.2.8 Kokusai Express
- 6.2.9 Fukuyama
- 6.2.10 Mitsui-Soko
- 6.2.11 Alps Logistics
- 6.2.12 Yusen Logistics
- 6.2.13 DHL*
7 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Macroeconomic Indicators (GDP Distribution, by Activity, Contribution of Transport and Storage Sector to economy)
- 8.2 External Trade Statistics - Exports and Imports, by Product
- 8.3 Insights into Key Export Destinations and Import Origin Countries









