 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1687205
作物保护 -市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Agrochemicals - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
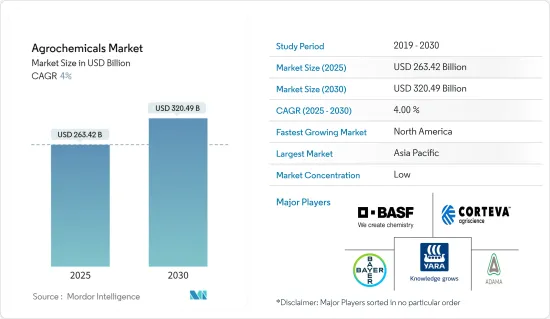
预计 2025 年农业化学品市场规模为 2,634.2 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 3,204.9 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 4%。
世界各地人口不断成长,富裕程度不断提高,消费模式也正在改变。我们不仅需要增加产量来满足需求,还需要确保满足日益富裕的人口的营养需求。此外,对更健康饮食的需求正在推动全球谷物、水果和蔬菜消费量的增加。因此,农民、联邦政府和工业界齐心协力提高作物产量,以满足世界粮食供应的需求。在这样做的同时,我们会格外小心,避免对人类安全或生态平衡造成任何不利影响。
例如,根据国际货币基金组织的数据,2021年印度总人口估计约为13.9亿人。根据联合国粮农组织预测,2021年全球将有11.7%的人口面临严重的粮食不安全状况。耕地面积减少、病虫害造成的作物损失造成浪费,对保障粮食及营养安全构成严峻挑战。根据美国农业部统计,自2000年以来,美国农地总面积逐年减少。预计到2021年,美国农地总面积将减少近5,000万英亩,至8.953亿英亩。这些因素都在增加对农药的需求,并促进农业生产。
农药的使用主要是由于大豆、玉米和棉花等基因改造作物的广泛应用。农药使用量的增加促使世界需要取得和生产更多的惰性成分。
此外,昆虫害虫、植物寄生线虫和真菌疾病不断进化并侵袭植物,导致产量下降。此外,最近的趋势是出现了对现有农药产生抗药性的害虫和昆虫,这导致了含有新活性成分的农药的开发,从而增加了疾病的发生。例如,根肿病是十字花科植物(如油菜)的一种严重的土壤传播疾病。对于油菜籽来说,根部会形成肿胀和碎石,最终导致植物过早死亡。今年,亚伯达发现了约 300 个新的根肿病田地,加拿大最大的油菜种植省曼尼托巴省和萨斯喀彻尔也开始出现病例。加拿大约有 3,000 块田地感染了根肿病,可能会对该国的菜籽产业造成毁灭性的影响。然而,此病害对作物造成的损害十分广泛,对重要的经济作物造成了巨大的损失。这使得开发新的杀菌剂成为必要,并迫使农民增加杀菌剂和杀虫剂等农药的使用。
然而,监管限制和环境问题是限制农业化学成分使用的主要因素。政府对某些成分使用的规定或限制可能会限製作物保护中成分的可用性和使用。例如,2021年12月,墨西哥政府通过法令,逐步淘汰国内使用Glyphosate类农药产品。随着消费者对农药对人类和环境健康影响的认识不断提高,预计未来几年将有更多的农药被淘汰。
农业化学品市场趋势
肥料是成长最快的产品类型
全球粮食消费率的成长速度几乎是国内生产力的10倍。儘管大宗商品价格下跌导致经济成长放缓,但大多数国家的食品需求仍在成长。预计到 2050 年,全球粮食需求将增加一倍以上,这主要受到人口增长、收入增加、都市化加快以及区域饮食结构向高价值生鲜食品和加工食品消费转变的影响。这将为农民创造新的机会,并促进农业肥料的成长。
根据粮农组织预测,到 2050 年,世界人口将达到 90 亿。人口成长带来了巨大的粮食需求,而农业用地减少则带来了重大挑战。例如,2021年,英国约有1723万公顷土地被归类为农业用地,低于2020年的1727万公顷。随着农业用地面积的减少,预计可用土地上将需要生产更多的农产品。
然而,随着人口增长对粮食安全的需求不断增长,以及中产阶级不断壮大对食物多样性的需求不断增长,农作物产量必然增加,这又推动了农民对肥料的需求。
此外,肥料对于提高田地生产力和获得产量至关重要。肥料对于作物的生长至关重要,可以提高作物的性能并产生显着的效果。充足的植物营养供应对于植物的健康生长和生产至关重要。营养需求因作物和土壤而异。这些营养需求可以透过使用化学肥料来有效满足。例如,尿素为土壤提供46%的氮,而印楝饼等有机肥料仅提供2-5%的氮,而氮是植物生长发育所必需的元素。因此,有效利用投入对于提高有限土地的生产力至关重要,而肥料是作物生产的关键投入,从而推动肥料市场的发展。
据粮农组织称,2019-2020年农业对氮磷钾肥料的使用量增加了3.02%。 2019年使用最多的肥料是氮肥,用量为41.7万吨。氮肥是非洲消耗量最大的肥料。根据国际肥料协会的数据,2019年NPK总消费量为660.5万吨。然而,使用量仍远低于全球平均水平,儘管近期使用量和产量都有所增加,但仍远低于区域政府和政府间组织设定的目标。例如,根据非洲肥料组织的报告,2020年,地图上共有14家肥料生产厂。截至2020年,非洲共有151家肥料厂,除了87家加工厂、15家有机工厂和製造工厂外,还有35家新建工厂。马拉威只有两家化肥加工厂,尚比亚有四家,而莫三比克有五家,其中一家是在2020年这个历史性时期建立的。因此,随着作物产量的增加,化肥市场也在成长,而且随着有机肥料越来越受到永续发展的青睐,预计化肥市场将进一步成长。
此外,加拿大供应了全球超过 11% 的化肥。近年来,加拿大政府也采取了多项措施,推动该国永续化肥生产。目前,加拿大的目标是改善其化肥生产和消费状况,同时保持与环境的和谐。例如,2022年7月,加拿大农业和农业食品部长宣布向位于亚伯达卡加利的Sulvaris公司投资1,685,858加元,进一步开发Sulvaris的碳控制技术,该技术利用有机碳生产高效肥料。
亚太地区是最大的市场领域
中国占全球农药市场的最大份额。由于耕地面积减少,中国有机氮、磷、钾肥的消费量正在下降。例如,根据中国绿色食品发展中心的数据,2021年中国约有984万公顷农地获得有机认证,低于2019年的1,390万公顷。水果和蔬菜的种植面积正在增加,而谷物的种植面积正在减少。
此外,澳洲统计局报告称,农民每年花费 1.8 亿美元用于农场病虫害防治,以提高产量并促进该国农业部门的成长。此外,根据《安全有效农药应用》(SEPA)的数据,澳洲正式註册的农药超过8,000种,其中约75%用于农业。澳洲政府投入巨资进行研发,以提高农业生产效率和病虫害管理。例如,2020年,澳洲政府向澳洲植物健康组织提供了60万美元,以解决在全国研讨会上发现的国内研发的关键差距。
同样,印度大米和小麦等谷物作物的大量产量是支持市场成长的主要因素。印度的杀虫剂使用量一直在稳定增加。截至 2022 年 6 月,几家主要农业化学品和作物保护公司的收益清楚地表明了该国和该地区农业化学品市场的成长。
印度政府一直采取有利措施来增加印度农药的供应和利用率。根据粮农组织预测,到2022年,印度将占全球农药消费量的15.3%(氮)、19%(磷)和14.4%(钾)。印度虽然是世界第二大氮肥生产国、第三大磷肥生产国,但其化肥供需缺口持续扩大。这导致对进口肥料的依赖增加。
此外,UPL 是印度领先的农业化学品和作物保护公司,截至 2022 年 6 月,其营业额超过 1,640 亿印度卢比(19.8 亿美元)。位居第二的是BASF印度公司,销售额约 1,300 亿印度卢比(15.7 亿美元)。资料显示,光是八个邦的农药消费量就占印度农药消费量的 70.0% 以上。随着对环境和永续性的日益重视,该地区各国政府正在实施清洁生产和生态友善农业措施,这可能会减少该国合成农药的使用。然而,各国政府正在鼓励使用微生物农药,预计未来几年其使用量将迅速成长。
农化业概况
全球作物保护化学品市场细分,主要参与企业包括拜耳作物科学股份公司、安道麦农业解决方案公司、雅苒国际公司、BASF公司、科迪华农业科学公司、纽发姆公司等。新产品发布、併购和合作是这些主要企业采用的主要策略。市场参与企业正专注于投资创新、合作和扩张以增加市场占有率。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 人口成长导致粮食需求增加
- 采用永续的农业方法
- 需要提高土地生产力
- 市场限制
- 环境和监管限制
- 成本上升及产品开发困难
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买家的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章市场区隔
- 产品类型
- 肥料
- 农药
- 佐剂
- 植物生长调节剂
- 应用
- 以作物为基础
- 粮食
- 豆类和油籽
- 水果和蔬菜
- 非作物
- 草坪和观赏草
- 其他非农作物
- 以作物为基础
- 地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 西班牙
- 英国
- 法国
- 德国
- 俄罗斯
- 义大利
- 其他欧洲国家
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 其他亚太地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 其他非洲国家
- 北美洲
第六章竞争格局
- 最受欢迎的策略
- 市场占有率分析
- 公司简介
- Bayer Crop Science AG
- BASF SE
- Corteva Agriscience AG
- Archer-Daniels-Midland(ADM)
- FMC Corporation
- Adama Agricultural Solutions
- Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan
- Nufarm Ltd
- Nutrien Ltd
- Yara International ASA
第七章 市场机会与未来趋势
The Agrochemicals Market size is estimated at USD 263.42 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 320.49 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The rising population across the world, accompanied by rising affluence, is shifting consumption patterns. There is a need not just to increase production to meet demand but also to ensure that the nutritional needs of an increasingly affluent population are met. Moreover, the demand for healthy diets has increased the consumption of cereals, fruits, and vegetables across the world. This has resulted in integration among growers, federal governments, and industries to improve crop yield to meet global food supply requirements. While all this is done, proper care is applied so as not to cause any adverse effects on human safety and ecological balance.
For instance, according to the IMF, in 2021, the estimated total population in India amounted to approximately 1.39 billion people. According to the FAO, in 2021, 11.7% of the global population experienced severe food insecurity. Shrinking arable land and loss of crops due to pest attacks lead to wastage, posing a critical challenge to ensuring food and nutritional security. According to the US Department of Agriculture, from 2000 onwards, the total land area in the US farms has decreased annually. The total farmland area has decreased by almost 50 million acres, reaching 895.3 million acres as of 2021. Such factors are raising the demand for agrochemicals, which boosts agricultural output.
Agrochemical usage is mainly driven by the growing application of genetically modified crops, such as soybean, maize, and cotton. The increasing application of agrochemicals has increased the need for the availability and production of more inert ingredients in the world.
Moreover, insect pests, plant parasitic nematodes, and fungal diseases continuously evolve and attack plants, leading to decreased yields. Furthermore, the incidence of resistant pests and insects against the existing crop protection chemicals in recent years is leading to the development of new active ingredient agrochemicals, increasing disease incidences. For instance, clubroot is a serious soil-borne disease of cruciferous plants, such as canola. In canola, swellings or galls form on the roots, which can ultimately cause premature death of the plant. About 300 new fields a year in Alberta have been found to have clubroot, and cases have started to spring up in Manitoba and Saskatchewan, Canada's largest canola growers. There are about 3,000 fields infected with clubroot in Canada, which could devastate the Canadian canola industry. However, there is rampant crop damage due to disease incidence, causing enormous losses to economically important crops. This created the need to develop new fungicides and compelled farmers to adopt an intensified application of agrochemicals such as fungicides and insecticides.
However, regulatory restrictions and environmental concerns are the major factors that can restrain the use of raw materials in agrochemicals. Government regulations and restrictions on using certain raw materials can limit their availability and use in crop protection. For instance, in December 2021, the Government of Mexico passed a decree to eliminate the use of glyphosate-based pesticide products in the country. More pesticides are projected to be eliminated in the coming years amid rising consumer awareness about the impact of pesticides on human and environmental health.
Agrochemicals Market Trends
Fertilizer is the Largest Growing Product Type
The global food consumption rate rises almost ten times faster than local production. The demand for food is growing in most countries despite the slowdown induced by the decline in commodity prices. The global demand for food is projected to more than double by 2050, driven by population growth, rising incomes, rapid urbanization, and changes in regional diets toward greater consumption of higher-value fresh and processed foods. That, in turn, creates new opportunities for farmers and propels the growth of fertilizers in agriculture.
According to FAO, the world population is projected to reach 9 billion by 2050. The increasing population creates a huge demand for food products to feed the population, which is turning into a major challenge with the decreasing farmland. For instance, in 2021, approximately 17.23 million hectares of land in the United Kingdom was classified as the utilized agricultural area, which decreased from 17.27 million hectares in 2020. The shrinking area under agriculture is anticipated to demand more produce from the available land.
However, the increasing need for food security within an expanding population and greater demand from a rising middle class for food variety necessitate the need to boost crop yields, thus driving the demand for fertilizers among farmers.
Additionally, fertilizers are essential in obtaining high yields as these are necessary to increase productivity in the field. Fertilizers are vital to crop growth, showing improved performance and noticeable results. Supplying adequate plant nutrients is essential for healthy growth as well as the production capacity of plants. The nutrient demand varies with crops and soil. These nutrient demands can be effectively fulfilled through the use of chemicals. For instance, urea provides 46% nitrogen to the soil, whereas organic fertilizers like neem cake could provide only 2-5% nitrogen, an essential element for plant growth and development. Thus, to increase productivity from the limited land, the efficient use of inputs is mandatory, driving the fertilizers market as fertilizers are an important input in crop production.
According to the FAO, the NPK fertilizer agricultural use increased by 3.02% in 2019-2020. Nitrogen was the most used fertilizer in 2019, accounting for 417 thousand metric tons. Nitrogen fertilizers are the most consumed fertilizer in Africa. According to the International Fertilizers Association, the total NPK consumption in 2019 accounted for 6,605 thousand metric tons. However, usage remains well below the global average and significantly beneath the targets set by regional governments and intergovernmental organizations despite recent growth in both sales and production. For instance, according to the Africa Fertilizers Organization report, 14 fertilizer manufacturing plants were mapped in 2020. There were 151 fertilizer plants in Africa in 2020, including 87 processing plants, 15 organic plants, and 35 new facilities apart from the manufacturing plants. Malawi accounts for only two fertilizer processing plants, and Zambia has four, whereas Mozambique has five processing plants, one of which was established during the historic period in 2020. Thus, with the increased crop production, the fertilizer market has grown and is anticipated to grow further, with a preference for organic fertilizers for sustainable development.
Furthermore, more than 11% of the world's fertilizers are supplied by Canada. In the past few years, the Canadian government has also taken several steps to promote sustainable fertilizer production in the country. Under current circumstances, Canada aims to improve fertilizer production and consumption scenario while maintaining environmental harmony. For instance, in July 2022, Canada's Minister of Agriculture and Agri-Food announced a CAD 1,685,858 investment in Sulvaris in Calgary, Alberta, for the further development of Sulvaris' carbon control technology, which produces high-efficiency fertilizers made with organic carbon.
Asia-Pacific is the Largest Segment in the Market
China accounts for the largest share of the agrochemicals market globally. Due to the decreasing cropland area, Chinese consumption of organic N, P, and K fertilizers is decreasing. For instance, according to the China Green Food Development Center, in 2021, approximately 9.84 million hectares of farmland had been certified as organic farmland in China, which has decreased from 13.9 million hectares in 2019. The cropland area under fruits and vegetables is increasing, while the area under cereals is decreasing.
Furthermore, according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, farmers reportedly spend USD 180 million each year controlling pest infestation in their farms to produce more and enhance the country's sector growth. Also, according to Safe and Effective Pesticide Applications (SEPA), more than 8000 pesticide products are formally registered for use in Australia, and around 75% of these are used for agricultural purposes. The Australian government heavily invests in research and development to increase crop production efficiency and pest management. For instance, the Australian government provided Plant Health Australia with USD 600,000 in 2020 to address critical gaps in national research and development identified in a national workshop.
Similarly, the large production of cereal crops, like rice and wheat, in India is the major factor supporting the market's growth. The use of pesticides is rising steadily in India. Revenues of a few leading pesticides and agrochemical companies as of June 2022 were a clear indication of the growth of the agrochemical market in the country and the region.
The government of India has been constantly adopting practices that have been advantageous in augmenting the accessibility and utilization of agrochemicals in India. According to FAO, in 2022. India accounts for 15.3% of the World's consumption of (N), 19 % (P), and 14.4% (K), owing to the large production of cereal crops, like rice and wheat in India. In spite of ranking as the second-largest nitrogenous fertilizer producer and third-largest phosphatic fertilizer producer in the world, the demand-supply gap of fertilizers in India is increasing continuously. It is leading to increased dependency on fertilizer imports.
In addition, UPL is the leading pesticides and agrochemical company in India based on net sales worth over INR 164 billion (USD 1.98 billion) as of June 2022. The company was followed by BASF India, which ranked in second place with net sales of roughly INR 130 billion (USD 1.57 billion). Data reveals that only eight states account for more than 70.0% of the total pesticide consumption in India. With a growing emphasis on the environment and sustainability, various governments in the region are enforcing clean production and environment-friendly agriculture policies, which may lead to a decline in synthetic pesticide usage in the country. However, the government has encouraged the use of microbial pesticides, which are projected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
Agrochemicals Industry Overview
The global agrochemicals market is fragmented, with major players including Bayer Crop Science AG, Adama Agricultural Solutions, Yara International ASA, BASF SE, Corteva Agriscience, and Nufarm. New product launches, mergers and acquisitions, and partnerships are the major strategies adopted by these leading companies in the market. Market players are focusing on investments in innovation, collaborations, and expansions to increase their market share.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing Demand for Food Due to High Population Growth
- 4.2.2 Adoption of Sustainable Farming Practices
- 4.2.3 Need for Increased Land Productivity
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Environmental and Regulatory Constraints
- 4.3.2 Increased Cost and Difficulty with Product Development
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Product Type
- 5.1.1 Fertilizers
- 5.1.2 Pesticides
- 5.1.3 Adjuvants
- 5.1.4 Plant Growth Regulators
- 5.2 Application
- 5.2.1 Crop-based
- 5.2.1.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.2.1.2 Pulses and Oilseeds
- 5.2.1.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.2.2 Non-crop-based
- 5.2.2.1 Turf and Ornamental Grass
- 5.2.2.2 Other Non-crop-based
- 5.2.1 Crop-based
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Mexico
- 5.3.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Spain
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Germany
- 5.3.2.5 Russia
- 5.3.2.6 Italy
- 5.3.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 China
- 5.3.3.2 India
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 Australia
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Africa
- 5.3.5.1 South Africa
- 5.3.5.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Most Adopted Strategies
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Bayer Crop Science AG
- 6.3.2 BASF SE
- 6.3.3 Corteva Agriscience AG
- 6.3.4 Archer-Daniels-Midland (ADM)
- 6.3.5 FMC Corporation
- 6.3.6 Adama Agricultural Solutions
- 6.3.7 Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan
- 6.3.8 Nufarm Ltd
- 6.3.9 Nutrien Ltd
- 6.3.10 Yara International ASA











