 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1690075
MaaS(出行即服务)-市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Mobility as a Service - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
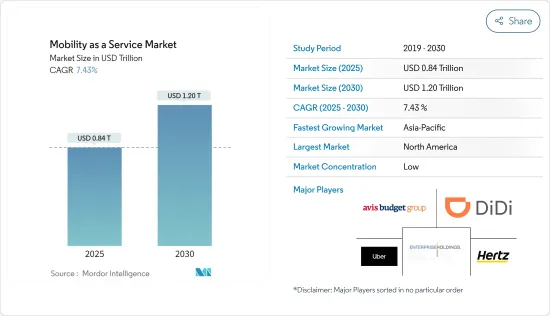
2025 年出行即服务 (MaaS) 市场规模估计为 8,400 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 1.2 兆美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 7.43%。
新冠疫情严重打击了旅游即服务 (MaaS) 市场。全球实施的封锁和社交距离规范减少了除紧急情况外的旅行需求。随着民众流动逐渐结束,市场关键业务领域受到重创,经济急剧下滑。新冠疫情为市场带来了挑战,但也带来了创新和适应的机会,例如部署用于非接触式付款和接触者追踪的MaaS解决方案。
从中期来看,出行即服务 (MaaS) 是一个不断发展的行业,旨在为个人和企业提供整合的、按需的交通解决方案。这标誌着传统交通方式的模式转移,消费者可以透过单一平台使用各种交通方式。由于都市化加快、交通拥堵加剧以及对更永续的交通替代方案的需求,预计未来几年市场将迅速扩张。
预计全国乘客使用计程车和共乘服务的偏好将会增加。因此,主要企业可能会透过增加行动应用程式提供的选项来扩展业务,以在竞争激烈的市场中保持各自的市场占有率。
日益重视减少碳排放和减缓气候变迁是 MaaS 产业发展的主要驱动力之一。 MaaS 平台可以透过提供更多永续的旅行选择来帮助减少交通对环境的影响。
推动市场发展的另一个关键方面是消费者偏好的变化,尤其是年轻一代,他们在出行选择上更注重便利性、灵活性和成本效益。
除了传统的运输公司和科技新兴企业之外,汽车製造商和公共运输等其他参与企业也正在进入 MaaS 领域,以保持竞争力并满足不断变化的客户期望。
政府措施和立法,例如对电动车的补贴以及鼓励使用共乘和公共运输,也在影响 MaaS 市场。行动应用程式、物联网 (IoT) 设备和资料分析工具是推动 MaaS 领域发展的一些关键技术。这些技术使得运输服务更有效率和个人化。
MaaS(出游即服务)市场趋势
交通壅塞加剧推动市场需求
除了缓解交通拥堵,MaaS 还可以帮助改善空气品质、减少碳排放并促进永续交通。透过提供多种交通选择,MaaS 可以鼓励个人选择更环保的交通方式,例如骑自行车或使用公共运输。
此外,MaaS 正在为公共和商业部门相关人员开闢新的经营模式和机会,从而重塑交通运输行业。随着各国政府探索将 MaaS 纳入交通网络的方法,私人公司正在增加对 MaaS 平台和服务的投资。
整体而言,全球各大城市交通拥堵带来的挑战正在促进 MaaS 领域的扩张。随着人们寻求更有效率、更环保的交通解决方案,MaaS 将在未来的城市交通中发挥越来越重要的作用。
近年来,全球许多城市都在引进MaaS(出行即服务)来解决交通拥堵和其他交通问题。例如
- 2023 年 1 月,坦帕市交通部门与该市新的交通合作伙伴 Moovit 启动了交通即服务 (MaaS) 试验计划。 Moovit 在坦帕首次亮相,是一款城市交通软体,可协助规划多模态出行,包括步行、骑自行车、滑板车、驾驶、路面电车和巴士。 Movit 不仅提供准确可靠的城市旅行信息,还提供公共运输的移动票、实时到达信息,并且与 Google Maps 或 Ways 不同,显示停车和停车换乘位置。
- 2022年10月,上海绿色出行行动平台上线,标誌着上海出行即服务(MaaS)体系建置迈出重要一步。随身行是全球首个由政府打造的城市出行即服务平台,目前已完成公共运输、叫车、智慧停车等基础功能。乘客可以透过公共运输服务获得包含所有公共运输代码的 Swipe for All 通行证。註册MaaS并开通付款功能后,即可在上海市1560条公车线路、17条渡轮线路、11条地铁线路上使用。
- 2022年9月,布拉格市实施了一项测试计划,将所有付款方式和交通服务整合到一个地方。该系统将集中管理自行车和汽车共享、计程车、停车和公共运输等行动服务的註册和付款,并将透过 Ltaka 应用程式进行开发、测试和运营,由布拉格市公司 Operator ICT 实施。
这些案例表明,在致力于缓解交通拥堵和改善交通便利性的城市中,MaaS 越来越受欢迎。随着MaaS业务在全球范围内的扩展,预计会有更多城市使用MaaS解决方案来解决其交通问题。
亚太地区是一个快速成长的市场
都市化、人口成长以及对便利永续交通的需求不断增长可能会长期推动中国出行即服务 (MaaS) 市场的发展。近年来,共享单车、共享汽车等新型出行方式为市民日常出行带来了极大便利。满足大规模出行需求也为城市管理带来了压力和挑战。此外,它对现有的公共交通系统和传统交通服务产生了重大影响。
近年来,中国致力于测试和开发MaaS计划。国务院、运输部、北京、上海、江苏、广东等省市政府等多个政府部门,在其「十四五」规划(2021-2025年)和2035年远景规划中,均提出了MaaS战略和探索性发展。
印度是世界第二人口大国,大多数人属于中产阶级,依靠计程车和自动人力车(当地三轮计程车)进行近距离通勤。印度的公共交通系统不是很发达,主要有巴士、当地火车(仅在孟买)和地铁(在某些城市)。因此,员工主要使用自己的汽车上下班。
虽然 MaaS 在印度仍相对较新,但联邦、州和地方政府的讨论和政策倡议凸显了其巨大的潜力。透过将交通方式整合为单一服务,MaaS 为印度各地的消费者提供了以灵活和个性化的方式轻鬆规划行程的能力。此外,印度正在利用其技术力和综合行动服务解决方案,使其成为一个已经很大的产业。
由于印度市场机会旺盛,许多知名公司也采取强硬倡议,加强在玛氏市场的地位。例如
- 2023年1月,叫车公司Uber表示,计画未来三年透过其平台在印度推出25,000辆电动车。与塔塔汽车签署的谅解备忘录预计将从本月开始分阶段交付25,000 辆塔塔汽车电动车 Xpres-T EV。这些电动车将部署在德里、孟买、加尔各答、清奈、海得拉巴、班加罗尔和艾哈默德巴德。
- 2022年11月,上海绿色出行一体化行动平台上线,标誌着上海出行即服务(MaaS)体系迈出重要一步。
- 2021年10月,本田推出了穿戴式装置Ashirase,可透过振动和语音引导帮助视觉障碍者导航。该设备是本田努力将行动服务扩展到传统汽车之外的一部分。
上述发展显示该地区的 MaaS 市场正在快速成长,多家参与企业进入市场并扩展其服务。预计这些发展将促进未来几年 MaaS 的发展。
MaaS(出游即服务)产业概览
行动即服务 (MaaS) 市场呈现细分化趋势,有多家参与企业占据主导地位。旅游即服务 (MaaS) 市场的知名公司包括 Uber、滴滴、Beeline Mobility 和 Moovit。企业正大力投资研发,开发尖端的新产品。
- 2022 年 12 月,SafeUP 宣布与 Moobit 合作,SafeUP 是新兴企业,开发了唯一一款社区安全应用程序,使妇女和女孩能够众包安全并即时相互保护。这项合作是为了纪念国际消除对妇女的暴力行为日,它将使 SafeUP 会员更容易规划行程和乘坐公共运输。
- 2022年8月,电动车公司Lime和旅游应用Whim将合作扩展到更多国家。 2022 年 6 月,继比利时安特卫普和布鲁塞尔之后,Whim 在芬兰赫尔辛基推出了电动Scooter。 Whim 可以使用苏黎世、温特图尔和巴塞尔的所有 Lime 电动Scooter。 Whim 与其他两家电动Scooter供应商一起在 10 多个城市开展业务,让使用者可以规划、预订和付款多种交通方式的行程。
- 2022年5月,FOD Mobility Group将为Mobileo客户推出客製化的行销支援服务。 FOD Mobility Group 现在不仅透过其市场领先的行动平台提供 MaaS(行动即服务)技术,还为没有必要行销经验或内部资源的客户提供全面的客製化行销支援服务。市场研究、策略和规划、应用程式商店设定和管理、线上/线下广告、公关、活动管理、电子邮件宣传活动、社群媒体管理、内容创作、平面设计、网站设计、搜寻引擎优化、与当地企业和旅游局联络只是所提供的部分服务。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 调查前提条件
- 研究范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场动态
- 市场驱动因素
- 市场限制
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 买家/消费者的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章市场区隔
- 按服务类型
- 车
- 公车
- 自行车
- 按运输类型
- 公共
- 私人的
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 其他欧洲国家
- 亚太地区
- 印度
- 中国
- 日本
- 韩国
- 其他亚太地区
- 其他的
- 南美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 北美洲
第六章竞争格局
- 供应商市场占有率
- 公司简介
- Whim(Maas Global)
- Uber Technologies Inc.
- Didi Chuxing
- Citymapper
- Moovel
- Beeline Mobility
- Ubigo(via-id)
- Moovit Inc.
- Bridj Technology Pty Ltd.
- Mobileo
- The Hertz Corporation
- Avis Budget Group
- Enterprise Holdings Inc.
第七章 市场机会与未来趋势
The Mobility as a Service Market size is estimated at USD 0.84 trillion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.20 trillion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.43% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The COVID-19 pandemic hurt mobility as a Service Market. With the lockdown and social distancing norms implemented worldwide, the need for mobility was reduced except for emergency purposes. With almost zero public movements, the major business area of the market was severely hit, and the economy took a nosedive. Although the COVID-19 pandemic has caused problems for the market, it has also given rise to chances for innovation and adaptation, such as the deployment of MaaS solutions for contactless payments and contact tracking.
Over the medium term, Mobility as a Service (MaaS) is a growing industry that intends to provide individuals and businesses with integrated, on-demand transportation solutions. It represents a paradigm shift from traditional modes of transportation, in which consumers can access a variety of mobility alternatives through a single platform, frequently via a subscription-based approach. The market is predicted to expand rapidly in the next years, owing to rising urbanization, increased traffic congestion, and a need for more sustainable transportation alternatives.
Passengers' preferences for utilizing taxi services and ride-sharing services across the country are expected to increase. Hence, this is likely to lead the companies to enhance the options and expand their operations to be provided in mobile applications, to retain their respective market shares in a highly competitive market.
The growing emphasis on lowering carbon emissions and mitigating climate change is one of the primary drivers of the MaaS sector. MaaS platforms may help lessen the environmental effect of transportation by providing more sustainable mobility options.
Another important aspect driving the market is changing consumer tastes, particularly among younger generations that prioritize convenience, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in their mobility options.
Other players, such as automakers and public transportation agencies, are entering the MaaS sector to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations, in addition to traditional transportation corporations and tech startups.
Government initiatives and legislation, such as subsidies for electric vehicles and encouragement for carpooling and public transit use, are also shaping the MaaS market. Mobile apps, Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets, and data analytics tools are a few of the primary technologies powering the MaaS sector. These technologies enable more effective and individualized transportation services.
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) Market Trends
Increasing Traffic Congestion Drive the Demand in the Market
MaaS can assist in improving air quality, lower carbon emissions, and encouraging sustainable transportation in addition to easing congestion. MaaS can encourage individuals to select more environmentally friendly forms of transportation, like biking or taking public transportation, by providing a variety of mobility options.
In addition, MaaS is reshaping the transportation sector by giving actors in the public and commercial sectors new business models and opportunities. While governments look for ways to incorporate MaaS into their transportation networks, private companies are increasing their investments in MaaS platforms and services.
Overall, the difficulties caused by traffic congestion in major cities throughout the world are a contributing factor in the expansion of the MaaS sector. MaaS is positioned to play an increasingly significant role in the future of urban mobility as people look for more effective and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
In recent years, many cities around the world have been adopting mobility as a service (MaaS) as a solution to the growing traffic congestion and transportation challenges. For instance,
- In January 2023, The Mobility Department of the City of Tampa launched a Mobility as a Service (MaaS) trial project with the City's new mobility partner, Moovit. Moovit debuted in Tampa as an urban mobility software that assists users in planning multimodal trips, whether they want to walk, bike, scoot, drive, ride the streetcar, or take the bus. In addition to delivering precise and reliable urban mobility information, Moovit offers mobile ticketing for public transportation, real-time arrival information, and displays parking lots and park-and-ride locations, unlike Google Maps or Waze.
- In October 2022, Shanghai inaugurated an all-in-one mobile platform for green commuting, marking an important step forward in the development of the city's Mobility as a Service (MaaS) system. The Suishenxing app, the world's first metropolitan MaaS platform established by a government, has completed its fundamental features, which include public transportation, taxi hailing, and smart parking. Users can get a swipe-for-all pass that contains all public transportation codes through its public transportation service. After registering and activating the payment feature on MaaS, it can now be used on Shanghai's 1,560 bus routes, 17 ferry lines, and 11 Metro lines.
- In September 2022, the City of Prague tested a pilot program to consolidate all payment methods and transit services in one location. A system for unified registration and payment for mobility services, such as bike and carsharing, taxis, parking, and public transportation, will be developed, tested, and operated via the Ltaka app, which is being implemented by Prague's municipal firm Operator ICT.
These instances show how MaaS is becoming more and more popular among cities as they work to ease traffic congestion and increase accessibility to transportation. It is anticipated that more cities using MaaS solutions to solve their transportation problems as the MaaS business expands globally.
Asia-Pacific is the Fastest Growing Market
Urbanization, population growth, and increasing demand for convenient and sustainable modes of transportation are likely to enable the mobility-as-a-service market in China over the long run. In recent years, new mobility represented by emerging bike-sharing and car-hailing/sharing has provided great convenience for citizens' daily transport. By meeting large mobility demands, they also brought pressures and challenges to city management. In addition, they had a big impact on existing public transport systems and traditional transport services.
China has focused on testing and developing MaaS projects in recent years. Many government departments, such as the State Council, Ministry of Transport, and province and city governments (Beijing, Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Guangdong), have highlighted to develop of a MaaS strategy or pilot in their 14th-Five-Year Plan between (2021-2025) or even in their long-term plan for 2035.
India is the second-most populous country in the world, and most people fall into the middle-class category who utilize cabs and auto-rickshaws (local three-wheeler taxis) for commuting short distances. India's public transportation system is not that well developed and is mainly characterized by buses, local trains (only in Mumbai), and metros (in select cities). Thus, employees majorly use their personal vehicle as the main mode of transportation to work.
MaaS is still relatively new in India, but discussions and policy initiatives by the federal, state, and local governments have highlighted its enormous potential. MaaS would offer consumers across India the ability to effortlessly organize trips in a flexible and personalized way by integrating transportation into a single service. Further, India is utilizing its technology prowess and integrated mobility services solutions, and it is already growing into a sizable sector.
Due to the outpouring opportunities in the Indian market, many prominent companies have also taken severe initiatives to strengthen their position in the Maas market. For instance,
- In January 2023, ride-hailing company Uber plans to introduce 25,000 electric cars in India over the next three years through its platform. A memorandum of understanding signed with Tata Motors envisages the phased delivery of 25,000 units of Tata's Xpres-T EV electric car from this month. Electric vehicles will be deployed in Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bengaluru, and Ahmedabad.
- In November 2022, an all-in-one mobile platform for green commuting in Shanghai was launched, marking an essential step forward for Shanghai's Mobility as a Service (MaaS) system.
- In October 2021, Honda launched Ashirase, a wearable device that helps visually impaired individuals navigate their surroundings using vibrations and audio guidance. The device is part of Honda's efforts to expand mobility services beyond traditional vehicles.
The above developments indicate that the MaaS market in the region is growing rapidly, with several players entering the market and expanding their services. These developments are expected to contribute to MaaS growth in the coming years.
Mobility as a Service (MaaS) Industry Overview
The mobility as a service market is fragmented, with several players accounting for significant shares in the market. Some prominent companies in the mobility as a service market are Uber, Didi, Beeline Mobility, Moovit, and others. Companies are investing heavily in R&D for the innovation of new and advanced products.
- In December 2022, SafeUP, the new startup behind the only community safety app that allows women and girls to crowdsource their safety and protect one another in real time, announced a collaboration with Moovit. SafeUP members will be able to easily plan their journeys and navigate public transportation thanks to this alliance in honor of International Day for the Elimination of Violence Against Women.
- In August 2022, Lime, an electric vehicle company, and Whim, a mobility app, expanded their collaboration to another country. In June 2022, Whim launched e-scooters in Antwerp and Brussels, Belgium, followed by Helsinki, Finland. Whim has access to all Lime e-scooters in Zurich, Winterthur, and Basel. Whim, in addition to two other e-scooter providers in more than ten cities, allows users to plan, book, and pay for trips using multiple modes of transportation.
- In May 2022, FOD Mobility Group introduces customized marketing support services for Mobilleo customers. FOD Mobility Group now offers a comprehensive range of tailored marketing support services for clients who may not have the necessary marketing experience or resources in-house, in addition to providing the Mobility as a Service (MaaS) technology itself via their market-leading Mobile platform. Market research, strategy and planning, app store setup and management, online/offline advertising, PR, event management, email campaigns, social media management, content creation, graphic design, website design, SEO, and engagement with local businesses and tourist boards are just a few of the services offered.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Drivers
- 4.2 Market Restraints
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.3.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.3.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (Market Size in Value - (USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Service Type
- 5.1.1 Car
- 5.1.2 Bus
- 5.1.3 Bike
- 5.2 By Transportation Type
- 5.2.1 Public
- 5.2.2 Private
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.1.1 United States
- 5.3.1.2 Canada
- 5.3.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.2.1 Germany
- 5.3.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.2.3 France
- 5.3.2.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.3.1 India
- 5.3.3.2 China
- 5.3.3.3 Japan
- 5.3.3.4 South Korea
- 5.3.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 Rest of the World
- 5.3.4.1 South America
- 5.3.4.2 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Vendor Market Share
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Whim (Maas Global)
- 6.2.2 Uber Technologies Inc.
- 6.2.3 Didi Chuxing
- 6.2.4 Citymapper
- 6.2.5 Moovel
- 6.2.6 Beeline Mobility
- 6.2.7 Ubigo (via-id)
- 6.2.8 Moovit Inc.
- 6.2.9 Bridj Technology Pty Ltd.
- 6.2.10 Mobileo
- 6.2.11 The Hertz Corporation
- 6.2.12 Avis Budget Group
- 6.2.13 Enterprise Holdings Inc.











