|
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1690899
东南亚废弃物发电:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测( 垃圾焚化发电)Southeast Asia Waste-to-Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
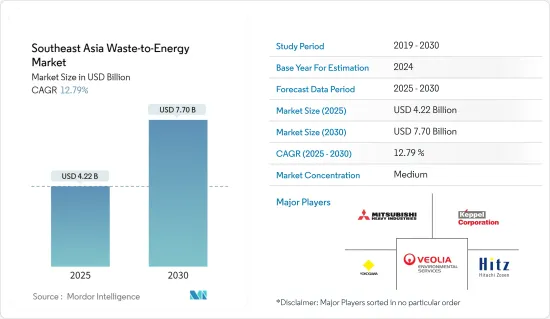
东南亚垃圾焚化发电市场规模预计在 2025 年为 42.2 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 77 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 12.79%。
主要亮点
- 从长远来看,废弃物产生量的增加、对废弃物管理的日益关注以满足永续城市生活的需求以及对非石化燃料能源来源的日益关注,正在推动东南亚废弃物转化能源市场的需求。
- 相反,预计高资本成本将在研究期间阻碍市场成长。
- 然而,树枝状液体能源(DLE)等新兴的 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)技术预计将在未来几年为市场相关人员提供庞大的商机。 DLE 的发电效率提高了四倍,同时还具有消除工厂内排放和废水问题的额外好处。
- 马来西亚是东南亚地区发展最快的国家之一。该国正在加强改善废弃物管理,其中 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)发挥关键作用。
东南亚垃圾焚化发电市场趋势
对热能废弃物转换的需求不断增长
- 热基废弃物转换是利用热能将废弃物转化为可用能源,例如电能、热能或燃料。这种方法涉及应用各种利用热量作为催化剂将废弃物转化为能源的技术。
- 人口快速成长和都市化导致废弃物产生量大幅增加,对废弃物管理带来挑战。废弃物热能转换可以有效管理并减少需要掩埋或焚烧的废弃物量。
- 2023 年 1 月,总部位于荷兰的 Harvest Waste(前身为阿姆斯特丹废弃物环境咨询与技术 BV)开始对越南湄公河三角洲地区朔庄省的废弃物转化能源计画进行初步研究。计划总营运成本预计约为1亿美元。
- 人们对可靠、永续能源来源的需求日益增长。基于热的 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)技术可以将废弃物转化为可用能源,例如电能或热能。它有助于能源产出,也有助于实现能源结构多样化,从而减少对石化燃料的依赖。
- 东南亚是世界上城市人口成长最快的地区之一。城市人口的快速成长导致全部区域城市人口产生的废弃物量激增。除新加坡外,大部分废弃物都是有机废弃物(约 50% 或更多)。
- 由于人口不断增长,该地区对电力的需求近年来大幅增加。以泰国为例,2021年至2022年,电力消耗量预计将增加3%以上。
- 因此,鑑于上述情况,预计预测期内对基于热的 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)系统的需求将会增加。
马来西亚:预计将显着成长
- 马来西亚政府正在积极推动永续废弃物管理实践和可再生能源发展。为支持垃圾焚化发电产业,已推出了各种措施和政策,包括上网电价、税收优惠和法规结构。这些措施为该行业的投资和发展创造了有利的环境。
- 与许多其他国家一样,马来西亚由于人口增长、都市化和工业化而产生越来越多的废弃物。这迫切需要有效的废弃物管理解决方案。 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)计划提供了一种永续的方式来解决日益增长的废弃物量,同时产生可再生能源。
- 2023 年 5 月,马六甲州政府下令在 Sungai Udang 卫生固态废弃物处置场快速建造废弃物能源 (WTE) 工厂或焚化炉。他们的目标是让该设施明年投入运作,比原定的 2026 年更早。
- 此外,马来西亚有大量有机废弃物适合废弃物转化为能源的过程。废弃物、农业废弃物等有机废弃物可以有效利用,进行厌氧消化和堆肥,从而生产出沼气和肥料。丰富的有机废弃物资源为垃圾焚化发电计划提供了有利条件。
- 此外,马来西亚政府也设定了可再生能源目标,以增加可再生能源在该国能源结构中的份额。 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)技术透过利用废弃物资源产生可再生能源有助于实现这些目标。 WtE(垃圾焚化发电)技术与国家永续性目标一致,并支持向低碳经济的转型。
- 根据国际可再生能源机构的预测,2022年可再生能源装置容量将达到9,044兆瓦,2018年至2022年间的成长率将超过20%。
- 因此,鑑于上述情况,预计马来西亚将在预测期内在市场研究中发挥关键作用。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章 简介
- 研究范围
- 市场定义
- 调查前提
第 2 章执行摘要
第三章调查方法
第四章 市场概况
- 介绍
- 2028 年市场规模(MW)及需求预测
- 最新趋势和发展
- 政府法规和政策
- 市场动态
- 驱动程式
- 废弃物产生量增加
- 环境议题与永续性目标
- 限制因素
- 垃圾焚化发电成本高
- 驱动程式
- 供应链分析
- 产业吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁产品/服务
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场区隔
- 科技
- 身体的
- 热
- 焚化
- 协同处理
- 热解/气化
- 生物
- 厌氧消化
- 区域市场分析 {市场规模和需求预测到 2028 年(仅按地区)}:马来西亚
- 马来西亚
- 印尼
- 泰国
- 新加坡
- 越南
- 其他东南亚地区
第六章 竞争格局
- 併购、合资、合作、协议
- 主要企业策略
- 公司简介
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- Keppel Corporation
- PT Yokogawa Indonesia
- Veolia Environment SA
- Hitachi Zosen Corp
- MVV Energie AG
- Martin GmbH
- Babcock & Wilcox Volund AS
第七章 市场机会与未来趋势
- 国际合作与投资
简介目录
Product Code: 72358
The Southeast Asia Waste-to-Energy Market size is estimated at USD 4.22 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 7.70 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 12.79% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- Over the long term, the increasing amount of waste generation, growing concern for waste management to meet the need for sustainable urban living, and increasing focus on non-fossil fuel sources of energy are driving the demand for the Southeast Asia Waste-to-Energy Market.
- Conversely, the high capital costs are expected to hinder market growth during the study period.
- Nevertheless, emerging waste-to-energy technologies, such as Dendro Liquid Energy (DLE), are expected to create significant opportunities for market players over the coming years. It is four times more efficient in terms of electricity generation, with the additional benefits of no emission discharge and effluence problems at plant sites,
- Malaysia is one of the fastest-growing countries in the Southeast Asian region. The country ramped up its efforts in improving waste management, in which waste-to-energy plays a key role.
Southeast Asia Waste-to-Energy Market Trends
Growing Demand for Thermal-Based Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- Thermal-based waste-to-energy conversion refers to utilizing thermal energy to convert waste materials into usable forms of energy, such as electricity, heat, or fuel. This approach involves the application of various technologies that use heat as a catalyst for converting waste into energy.
- Rapid population growth and urbanization led to a significant increase in waste generation, posing challenges for waste management. Thermal-based waste-to-energy conversion effectively manages and reduces the waste volume that must be landfilled or incinerated.
- In January 2023, Harvest Waste, a company based in the Netherlands (formerly Amsterdam Waste Environmental Consultancy and Technology), commenced initial studies for a thermal waste-to-energy venture in the Mekong Delta province of Soc Trang in Vietnam. The project is estimated to cost around USD 100 million.
- There is a growing need for reliable and sustainable energy sources. Thermal-based waste-to-energy technologies allow waste conversion into usable energy forms, such as electricity and heat. It contributes to energy generation and helps diversify the energy mix, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Southeast Asia includes one of the fastest-growing urban populations globally. The rapid growth in the urban population led to explosive growth in the amount of waste generated by the urban population across the region. Most of this waste is organic (about or more than 50%) except in Singapore.
- With the growing population, the region's electricity demand increased significantly in recent years. For instance, in Thailand, electricity consumption increased by more than 3% between 2021 and 2022.
- Therefore, as per the above points, the demand for thermal-based waste-to-energy systems is expected to increase during the forecasted period.
Malaysia Expected to Witness Significant Growth
- The Malaysian government actively promoted sustainable waste management practices and renewable energy development. They implemented various initiatives and policies to support the waste-to-energy sector, including feed-in tariffs, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks. These measures create a conducive environment for investment and growth in the industry.
- Like many other countries, Malaysia is experiencing a rise in waste generation due to population growth, urbanization, and industrialization. It creates a pressing need for efficient waste management solutions. Waste-to-energy projects offer a sustainable method to tackle the growing waste volume while generating renewable energy.
- In May 2023, the Melaka state government ordered the expedited construction of the Waste to Energy (WTE) plant or incinerator at the Sungai Udang Sanitary Solid Waste Disposal Site. They aim to include the facility operational next year, earlier than the original target of 2026.
- Furthermore, Malaysia includes a significant proportion of organic waste, which is well-suited for waste-to-energy conversion processes. Organic waste, such as food waste and agricultural residues, can be efficiently utilized for anaerobic digestion or composting, leading to biogas or fertilizer production. The abundance of organic waste resources presents favorable conditions for waste-to-energy projects.
- Additionally, the Malaysian government set renewable energy targets to increase the share of renewable energy in the country's energy mix. Waste-to-energy technologies contribute to fulfilling these targets by generating renewable energy from waste resources. It aligns with the country's sustainability goals and supports the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- According to International Renewable Energy Agency, the total renewable energy installed capacity in 2022 was 9044 MW registering a growth rate of more than 20% between 2018 and 2022.
- Therefore, according to the above points, Malaysia is expected to play a key role in the market studies during the forecasted period.
Southeast Asia Waste-to-Energy Industry Overview
The Southeast Asia waste-to-energy market is moderately consolidated. The key players in the market (in no particular order) include Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd, Keppel Corporation, PT Yokogawa Indonesia, Veolia Environment SA, and Hitachi Zosen Corp, among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in MW, till 2028
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.1.1 Increasing Waste Generation
- 4.5.1.2 Environmental Concerns and Sustainability Goals
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.5.2.1 High Capital Costs Involved in Waste-to-Energy Infrastructure
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Technology
- 5.1.1 Physical
- 5.1.2 Thermal
- 5.1.2.1 Incineration
- 5.1.2.2 Co-processing
- 5.1.2.3 Pyrolysis/gasification
- 5.1.3 Biological
- 5.1.3.1 Anaerobic Digestion
- 5.2 Geography Regional Market Analysis {Market Size and Demand Forecast till 2028 (for regions only)}
- 5.2.1 Malaysia
- 5.2.2 Indonesia
- 5.2.3 Thailand
- 5.2.4 Singapore
- 5.2.5 Vietnam
- 5.2.6 Rest of Southeast Asia
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd
- 6.3.2 Keppel Corporation
- 6.3.3 PT Yokogawa Indonesia
- 6.3.4 Veolia Environment SA
- 6.3.5 Hitachi Zosen Corp
- 6.3.6 MVV Energie AG
- 6.3.7 Martin GmbH
- 6.3.8 Babcock & Wilcox Volund AS
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 International Collaborations and Investments
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219