 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1848062
琥珀酸:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据、成长预测(2025-2030)Succinic Acid - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
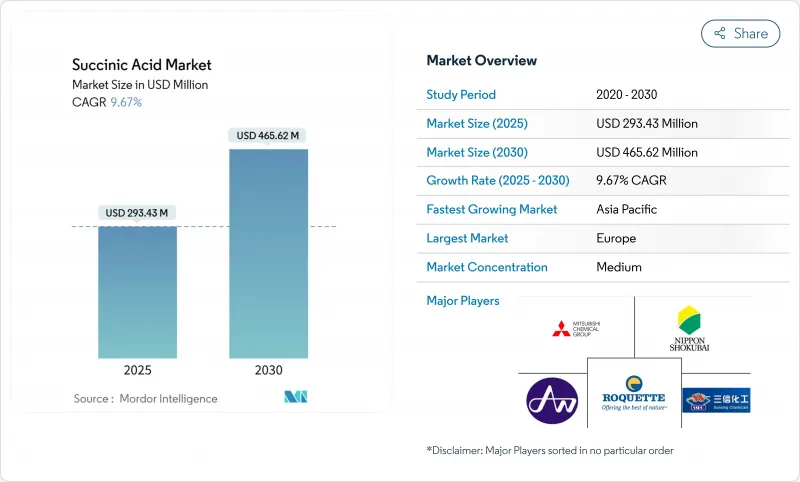
2025 年琥珀酸市场规模为 2.9343 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 4.6562 亿美元,复合年增长率为 9.67%。
市场成长的驱动因素包括:生产方式从石油基向生物基的转变、发酵成本的降低以及企业以可再生中间体为重点的永续性倡议的不断增多。市场扩张得益于对可生物降解聚合物(尤其是Polybutylene Succinate)日益增长的需求,以及其在食品和化妆品领域的广泛应用。欧洲和北美的监管支持也促进了市场发展。企业正在投资先进的发酵技术,以减少生产过程中的二氧化碳排放,从而实现净零排放目标。亚太地区也不断建立製造中心,以确保原料多样性并增强供应链稳定性。
全球琥珀酸市场趋势与见解
对可生物降解聚合物的需求不断增加
受汽车和包装行业对传统塑胶生物分解性塑胶替代品的需求推动,聚丁二酸丁二醇酯 (PBS) 的生产已成为琥珀酸需求的主要成长催化剂。慕尼黑工业大学的研究人员利用海洋细菌「盐弧菌」(Vibrio natriegens) 实现了突破性的发酵效率,将生产时间从传统的 24-48 小时週期缩短至 2-3 小时。这项技术进步解决了先前限制生物基琥珀酸竞争力的关键瓶颈——发酵可扩展性。为了符合循环经济法规,尤其是在欧洲,聚合物製造商越来越多地指定使用生物基琥珀酸进行 PBS 生产,因为欧洲的延伸生产者责任框架对不可生物降解的包装材料施加了处罚。
生物基化学品的监管支持
美国能源局2025年永续化学圆桌会议将琥珀酸确定为工业脱碳的优先平台化学品。在生物基化学品日益增长的需求的推动下,各国都在大力投资生物技术计画。根据科技部2024年的数据,印度政府启动了BioF3(生物技术促进经济、环境和就业)政策,以促进该国的高性能生物技术製造业。 FDA对食品用琥珀酸的GRAS(一般认为是安全的)核准确定了其在调味品和肉品中的最大允许含量,消除了其在食品和饮料配方中扩大使用的监管障碍。此类监管核准为生物基琥珀酸製造商提供了优先的市场进入,同时建立了有利于具有成熟生产能力的现有製造商的品质标准。
商业规模生产基础设施有限
包括BioAmber在内的几家先驱企业的破产,导致现有产能下降,同时也抑制了对製造业基础设施的新投资。开发中地区缺乏建造发酵设施所需的技术专长和资金,因此生产集中在现有的化学製造地。生物基生产的独特特性要求与传统化工厂不同的设备和工艺,这限制了现有设施的再利用,并增加了资本需求。原料供应链的发展落后于产能需求,尤其是非食品生物质原料,这些原料需要预处理基础设施投资。
細項分析
预计2025年至2030年,生物基琥珀酸的复合年增长率将达到11.38%,而油基琥珀酸在2024年将维持59.42%的市占率。生物基生产的高成长率反映了在监管要求和企业环保目标的推动下,永续生产方法的采用日益增加。向生物基生产的转变符合全球永续性倡议以及各行各业日益增强的环保意识。石油基生产凭藉其完善的基础设施和低成本,尤其是在价格敏感性高于环境问题的工业应用中,保持着市场主导。
石油基生产的成本优势源自于数十年的製程优化和现有设施的规模经济效益。生物基替代品在食品、药品和化妆品等高端领域日益受到青睐,这些领域对永续性的要求决定了更高的价格,消费者的偏好也影响购买决策。在这些高端领域,终端使用者对环保产品的需求促使他们愿意承担与生物基生产方法相关的额外成本。
区域分析
欧洲凭藉其完善的法规结构和成熟的製造基础设施,支持生物基化学品的发展,到2024年将占据32.09%的市场份额。德国和法国在产能方面领先该地区,其一体化的化工园区促进了下游加工和分销。该地区包装材料生产者责任框架的不断扩大,正在推动对由生物基琥珀酸製成的可生物降解聚合物的需求。
亚太地区是成长最快的地区,受中国、印度和东南亚快速工业化和製造能力扩张的推动,2025 年至 2030 年的复合年增长率为 10.58%。晓星在越南投资 10 亿美元用于生产生物基 1,4-丁二醇,体现了该地区在生物基化学品製造中的战略地位;该工厂的目标是到 2026 年年产能达到 50,000 公吨。中国在化学品製造业的主导地位为扩大琥珀酸生产提供了完善的基础设施,而印度日益增长的製药和个人护理行业正在创造对高等级产品日益增长的需求。该地区受益于丰富的农业废弃物原料,如稻草和玉米秸秆,为生物基生产提供了具有成本效益的原料。政府支持工业脱碳和循环经济发展的政策为全部区域采用生物基化学创造了有利条件。
儘管面临来自低成本亚洲生产的竞争压力,北美仍保持着重要的市场份额。美国农业部《2024年生物质供应链报告》指出,充足的原料供应是关键的竞争优势,这得益于完善的农业基础设施支撑可再生原料供应。美国美国能源局永续化学圆桌会议已将琥珀酸列为工业脱碳的平台化学品,并为国内生产发展提供政策支援。加拿大BioAmber商业化的失败为风险管理和市场发展策略提供了经验教训,凸显了切合实际的成本预测和市场价格假设的重要性。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- 对可生物降解聚合物的需求不断增加
- 生物基化学品的监管支持
- 扩大在食品和饮料中作为酸度调节剂和增味剂的用途
- 个人护理和化妆品需求不断增长
- 生物基生产技术的进步
- 对绿色溶剂和工业化学品的需求不断增加
- 市场限制
- 生产成本高
- 商业规模生产基础设施有限
- 能源密集型炼油损害了环境效益
- 来自替代生物基酸的竞争
- 供应链分析
- 监理展望
- 五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买家/消费者的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章市场规模及成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 石油基
- 生物基
- 按年级
- 工业/技术级
- 食品级
- 医药级
- 化妆品级
- 按用途
- 工业化学品
- 饮食
- 製药
- 个人护理和化妆品
- 其他的
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 英国
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲国家
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 其他亚太地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争态势
- 市场集中度
- 策略倡议
- 市场排名分析
- 公司简介
- Roquette Freres
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group
- Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
- Air Water Performance Chemical Inc.
- Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd
- Anhui Sunsing Chemicals
- Haihang Group
- Henan GP Chemicals Co.,Ltd
- Kunshan Odowell Co. Ltd
- Royal DSM(Reverdia)
- Wenzhou Blue Dolphin New Material Co., Ltd
- Ensince Industry Co., Ltd
- Carl Roth GmbH+Co. KG
- Axiom Chemicals Pvt. Ltd.
- LCY Biosciences Inc.
- Fengchen Group Co.,Ltd
- Shandong Biotech
- Shandong Feiyang Chemical
- Spectrum Chemical Mfg.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The succinic acid market size, valued at USD 293.43 million in 2025, is projected to reach USD 465.62 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 9.67%.

The market growth is driven by the shift from petroleum-based to bio-based production methods, reduced fermentation costs, and increased corporate sustainability initiatives focusing on renewable intermediates. The market expansion is supported by increasing demand for biodegradable polymers, specifically polybutylene succinate, along with broader adoption in food and cosmetic applications. Regulatory support in Europe and North America contributes to market development. Companies are investing in advanced fermentation technologies that reduce CO2 emissions during production, aligning with net-zero objectives. The Asia-Pacific region is establishing manufacturing centers to ensure feedstock diversity and strengthen supply chain stability.
Global Succinic Acid Market Trends and Insights
Rising demand for biodegradable polymers
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) production has emerged as the primary growth catalyst for succinic acid demand, with automotive and packaging industries mandating biodegradable alternatives to conventional plastics. Technical University of Munich researchers achieved breakthrough fermentation efficiency using the marine bacterium Vibrio natriegens, reducing production time to 2-3 hours compared to traditional 24-48 hour cycles. This technological advancement addresses the critical bottleneck of fermentation scalability that previously limited bio-based succinic acid competitiveness. Polymer manufacturers increasingly specify bio-based succinic acid for PBS production to meet circular economy regulations, particularly in Europe, where extended producer responsibility frameworks penalize non-biodegradable packaging materials.
Regulatory support for bio-based chemicals
Government policy frameworks have crystallized around bio-based chemical incentives, with the U.S. Department of Energy's 2025 sustainable chemistry roundtable identifying succinic acid as a priority platform chemical for industrial decarbonization . Owing to the rising demand for bio-based chemicals, various countries are investing heavily in biotechnology initiatives. According to the Ministry of Science and Technology data from 2024, the Government of India launched the BioF3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) policy to foster high-performance biotechnology manufacturing in the country . FDA recognition of succinic acid as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for food applications removes regulatory barriers for expanded usage in food and beverage formulations, with maximum allowable levels established for condiments and meat products. These regulatory endorsements create preferential market access for bio-based succinic acid producers while establishing quality standards that favor established manufacturers with proven production capabilities.
Limited commercial-scale production infrastructure
The collapse of several pioneering companies, including BioAmber, has reduced available production capacity while deterring new investment in manufacturing infrastructure. Developing regions lack the technical expertise and capital access required for fermentation facility construction, concentrating production in established chemical manufacturing hubs. The specialized nature of bio-based production requires different equipment and processes compared to traditional chemical plants, limiting the ability to repurpose existing facilities and increasing capital requirements. Feedstock supply chain development lags behind production capacity needs, particularly for non-food biomass sources that require preprocessing infrastructure investment.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expanding food and beverage usage as acidity regulator and flavor enhancer
- Growing demand in personal care and cosmetics
- Competition from alternative bio-based acids
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Bio-based succinic acid is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.38% during 2025-2030, while petro-based succinic acid maintains a 59.42% market share in 2024. The higher growth rate of bio-based production reflects increasing adoption of sustainable manufacturing methods, driven by regulatory requirements and corporate environmental goals. The shift toward bio-based production aligns with global sustainability initiatives and growing environmental consciousness across industries. Petro-based production retains its market leadership due to established infrastructure and lower costs, particularly in industrial applications where price sensitivity outweighs environmental concerns.
The cost advantage of petro-based production stems from decades of process optimization and economies of scale in existing facilities. Bio-based alternatives are gaining traction in premium segments such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, where sustainability requirements justify higher prices and consumer preferences influence purchasing decisions. These premium segments demonstrate increasing willingness to absorb the additional costs associated with bio-based production methods, driven by end-user demand for environmentally responsible products.
The Succinic Acid Market is Segmented Into Product Type (Petro and Bio-Based), Grade (Industrial/Technical, Food, Pharmaceuticals, and Cosmetic), Application (Industrial Chemicals, Food and Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care and Cosmetics, and Others), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Europe commands 32.09% market share in 2024, leveraging established regulatory frameworks supporting bio-based chemicals and mature manufacturing infrastructure. Germany and France lead regional production capacity with integrated chemical complexes that facilitate downstream processing and distribution. The region's extended producer responsibility frameworks for packaging materials create preferential demand for biodegradable polymers derived from bio-based succinic acid.
Asia-Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing region with 10.58% CAGR for 2025-2030, driven by rapid industrialization and expanding manufacturing capacity across China, India, and Southeast Asia. Hyosung's USD 1 billion investment in Vietnam for bio-based 1,4-butanediol production exemplifies the region's strategic positioning in bio-based chemical manufacturing, with the facility targeting 50,000 metric tons of annual capacity by 2026. China's dominance in chemical manufacturing provides established infrastructure for succinic acid production scale-up, while India's growing pharmaceutical and personal care industries create expanding demand for higher-grade products. The region benefits from abundant agricultural waste feedstocks, including rice straw and corn stalks that provide cost-effective raw materials for bio-based production. Government policies supporting industrial decarbonization and circular economy development create favorable conditions for bio-based chemical adoption across the region.
North America maintains a significant market presence despite facing competitive pressure from lower-cost Asian production. The U.S. Department of Agriculture's 2024 biomass supply chain report identifies abundant feedstock availability as a key competitive advantage, with established agricultural infrastructure supporting renewable raw material supply . The U.S. Department of Energy's sustainable chemistry roundtable prioritizes succinic acid as a platform chemical for industrial decarbonization, providing policy support for domestic production development. Canada's experience with BioAmber's failed commercialization provides lessons for risk management and market development strategies, highlighting the importance of realistic cost projections and market pricing assumptions.
- Roquette Freres
- Mitsubishi Chemical Group
- Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
- Air Water Performance Chemical Inc.
- Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd
- Anhui Sunsing Chemicals
- Haihang Group
- Henan GP Chemicals Co.,Ltd
- Kunshan Odowell Co. Ltd
- Royal DSM (Reverdia)
- Wenzhou Blue Dolphin New Material Co., Ltd
- Ensince Industry Co., Ltd
- Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG
- Axiom Chemicals Pvt. Ltd.
- LCY Biosciences Inc.
- Fengchen Group Co.,Ltd
- Shandong Biotech
- Shandong Feiyang Chemical
- Spectrum Chemical Mfg.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand for biodegradable polymers
- 4.2.2 Regulatory support for bio-based chemicals
- 4.2.3 Expanding food and beverage usage as acidity regulator and flavor enhancer
- 4.2.4 Growing demand in personal care and cosmetics
- 4.2.5 Advancements in bio-based production technologies
- 4.2.6 Rising demand for green solvents and industrial chemicals
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High production costs
- 4.3.2 Limited commercial-scale production infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Energy-intensive purification undermining eco-benefits
- 4.3.4 Competition from alternative bio-based acids
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Petro-based
- 5.1.2 Bio-based
- 5.2 By Grade
- 5.2.1 Industrial/Technical Grade
- 5.2.2 Food Grade
- 5.2.3 Pharmaceutical Grade
- 5.2.4 Cosmetic Grade
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Industrial Chemicals
- 5.3.2 Food and Beverage
- 5.3.3 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.3.4 Personal Care and Cosmetics
- 5.3.5 Others
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.2 Germany
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Russia
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Roquette Freres
- 6.4.2 Mitsubishi Chemical Group
- 6.4.3 Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.4 Air Water Performance Chemical Inc.
- 6.4.5 Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd
- 6.4.6 Anhui Sunsing Chemicals
- 6.4.7 Haihang Group
- 6.4.8 Henan GP Chemicals Co.,Ltd
- 6.4.9 Kunshan Odowell Co. Ltd
- 6.4.10 Royal DSM (Reverdia)
- 6.4.11 Wenzhou Blue Dolphin New Material Co., Ltd
- 6.4.12 Ensince Industry Co., Ltd
- 6.4.13 Carl Roth GmbH + Co. KG
- 6.4.14 Axiom Chemicals Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.15 LCY Biosciences Inc.
- 6.4.16 Fengchen Group Co.,Ltd
- 6.4.17 Shandong Biotech
- 6.4.18 Shandong Feiyang Chemical
- 6.4.19 Spectrum Chemical Mfg.
- 6.4.20 Thermo Fisher Scientific











