 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851256
汽车机器人:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Automotive Robotics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
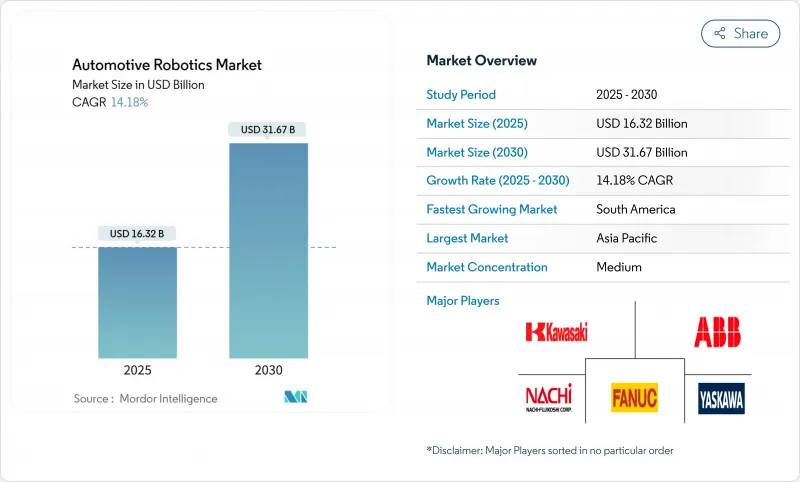
预计到 2025 年,汽车机器人市场规模将达到 163.2 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到约 316.7 亿美元,复合年增长率为 14.18%。
快速的电气化、日益扩大的劳动力缺口以及不断提高的品质要求正迫使汽车製造商用智慧联锁和协调的单元取代人工操作工位。电动车电池组整合、电动动力传动系统组装以及整车品质检验对操作精度的要求越来越高,而人工操作已无法满足此要求,尤其是在整车製造商要求100%检验的情况下。
全球汽车机器人市场趋势与洞察
自动化提高了产量和质量
65.3% 的製造商认为自动化是消除生产瓶颈的最快路径,并计划投资新的机器人以提高生产线产量。国际机器人联合会 (IFR) 的数据显示,到 2024 年,工业机器人的运作将增加 14%,这是自 2018 年以来最快的年增长率。先进的检测单元的零件检测速度比座标测量机快 10 倍,无需延长生产週期即可达到 100% 检测。人工智慧视觉技术能够检测出小于 0.05 毫米的缺陷,为白车身焊接和最终修整制定了新的品质标准。硬体价格的下降使得许多工厂能够在 1 到 3 年内收回资本支出,从而增强了扩大机器人数量的商业理由。
电动车电池和电动动力传动系统製造需求
电动车组装引入了更重、更少的次组件,这需要独特的搬运、密封和焊接方法。 ABB 估计,即使规划建造 80 座超级工厂,电池供应仍无法满足需求,凸显了高产能机器人生产的必要性。将电池生产线与组装线集中布局有助于提高永续性并减少物流,但这只有在机器人能够在电池和车身拆解之间灵活切换的情况下才能实现。专用铝焊接单元和报废车身拆解机器人(例如 Thoth 公司的 DisMantleBot)体现了向电动车转型过程中涌现的新兴领域。
高昂的资本投资和安装成本
儘管价格下降,但规模较小的供应商仍然认为价值六位数的机器人单元风险很高。像Rapid Robotics这样的FANUC即服务(RaaS)供应商透过捆绑硬体、服务和软体的月度合同,降低了高额的资本支出。整合通常会使初始成本翻倍,因为它需要对生产线进行改造,以配备防护装置、视觉校准和操作员培训。 Fanuc斥资1.1亿美元扩建位于奥本山的园区,显示要实现承包部署,需要进行大量的生态系统投资。总拥有成本还取决于维护、软体更新和网路安全补丁,而这些成本在商业案例中往往被低估。
细分市场分析
到2024年,汽车製造商将占据汽车机器人市场61.18%的份额,这反映出它们有能力承担资本成本,并将焊接、喷漆和密封等机器人整合到所有主要生产线中。目前,该领域优先考虑将人工智慧视觉技术应用于内装和最终检验,并寻求协作机器人来完成以往由人工完成的人体工学任务。服务中心是成长最快的细分市场,年复合成长率高达14.31%,这得益于电动车诊断和ADAS校准技术推动了售后维修车间机械化流程的发展。
技能提升依然至关重要。像梅赛德斯-奔驰这样的汽车製造商正在引入人形机器人,以使员工摆脱重复性的取货工作;而独立维修厂则在投资机器人四轮定位系统,以缩短预约时间。复杂维修业务持续从经销商转移到多品牌服务中心,这很可能在未来十年推动汽车机器人市场的发展。
到2024年,机械臂将占总收入的36.54%,但价值正迅速转移到分析、视觉和网路安全控制器。软体和服务正以14.64%的复合年增长率成长,使其成为策略竞争的焦点。云端託管的仪錶板可以追踪使用率、提供预测性警报,并将一次性资本支出转化为持续的收益。
车队级编配平台将数百个单元整合到一个虚拟实体中,使生产计划人员能够在几分钟内而非几天内重新分配任务。随着硬体净利率的下降,供应商透过持续的软体更新和应用商店生态系统来实现差异化竞争,这进一步推动了汽车机器人市场转向基于结果的合约模式。
区域分析
到2024年,亚太地区将占据全球汽车机器人市场46.55%的份额,其中中国以42.95万台的产量和每万人470台机器人的密度领先。像新松和易斯顿这样的国内厂商受益于政府激励政策,从而降低了采购成本;而日本整合商则持续改进用于多品种组装的精益机器人单元。东南亚各国政府正在扩大与生产挂钩的奖励,以鼓励整车製造商实现电动车生产线的本地化,并配备全自动电池组生产站。
南美洲的复合年增长率最高,达到14.94%,这主要得益于跨国公司大量涌入:Stellantis公司累计56亿欧元用于建设灵活的电动汽车生产能力,通用汽车则在巴西投资14亿美元兴建了一座机器人车身工厂。这些交易均包含技术转移条款,允许当地整合商获得先进焊接软体的许可,加速提升本土技术水准。不断上涨的薪资通膨正在加速向机器人转型,尤其是在巴西的底盘和动力传动系统工厂。
北美正积极推动製造业回流,以降低地缘政治风险。美墨加协定(USMCA)的原产地规则鼓励供应商自动化,以在劳动力短缺的情况下保持成本竞争力。联邦政府对电池生产的补贴政策刺激了新的超级工厂计划,这些项目将整合用于电池堆迭和模组组装的重型机器人。欧洲市场依然强劲,但高功能安全合规要求促使高端机器人解决方案更受青睐。德国仍然是领先的研发中心,但利润压力正迫使汽车製造商将大规模生产转移到成本更低的地区。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 自动化提高了产量和质量
- 电动车电池和电动动力传动系统製造需求
- 汽车产业中心劳动力短缺与薪资上涨
- 原始设备製造商越来越重视品质一致性
- 协作机器人能够实现灵活的混合型生产线
- 新兴市场的生产连结奖励计画
- 市场限制
- 高昂的资本投资和安装成本
- 熟练机器人程式设计师短缺
- 互联小区内的网路安全风险
- 伺服马达/晶片供电波动
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按最终用户类型
- 汽车製造商(OEM)
- 零件製造商(一级和二级供应商)
- 售后市场及服务中心
- 依组件类型
- 控制器
- 机械臂
- 末端执行器
- 驱动器和感测器
- 软体和服务
- 依产品类型
- 笛卡儿机器人
- SCARA机器人
- 关节机器人
- 协作机器人(cobots)
- 其他类型(平行型、圆柱型)
- 依功能类型
- 焊接机器人
- 绘画机器人
- 组装和拆卸机器人
- 切割和铣削机器人
- 物料输送机器人
- 检测和品质测试机器人
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 韩国
- 东南亚
- 亚太其他地区
- 中东和非洲
- 土耳其
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 南非
- 其他中东和非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- ABB Ltd
- FANUC Corporation
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries(Robotics)
- Omron Adept Technologies
- Honda Motor Co(Robotics)
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp
- Harmonic Drive Systems
- RobCo SWAT Ltd
- Denso Wave Inc
- Comau SpA
- Staubli Robotics
- Universal Robots A/S
- Hyundai Robotics
- Epson Robots
- OTC Daihen
- Siasun Robot & Automation
- Estun Automation
- Techman Robot
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The automotive robotics market stood at USD 16.32 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach about USD 31.67 billion by 2030, advancing at a 14.18% CAGR.

Rapid electrification, widening labor gaps, and mounting quality expectations are prompting vehicle makers to replace manual stations with intelligent articulated and collaborative cells. Electric-vehicle battery pack integration, e-powertrain assembly, and full-body quality verification increasingly require motion precision that manual processes cannot match, especially as OEMs press for 100% inspection.
Global Automotive Robotics Market Trends and Insights
Automation to Boost Throughput & Quality
Manufacturers cite automation as the quickest route to alleviate production bottlenecks; 65.3% plan new robot investments to raise line throughput. The International Federation of Robotics logged a 14% rise in operational industrial robots during 2024, marking the steepest annual jump since 2018. Advanced inspection cells now test parts 10 times faster than coordinate-measuring machines, opening the door to 100% inspection without extending cycle time. AI-enabled vision detects defects smaller than 0.05 mm, creating a new quality baseline for body-in-white welding and final trim. As hardware prices drop, many plants recover capital outlays in one to three years, reinforcing the business case for expanded fleets.
EV-Battery & E-Powertrain Manufacturing Needs
Electric-vehicle assembly introduces heavier yet fewer sub-assemblies that require distinct handling, sealing, and welding methods. ABB estimates that 80 planned gigafactories will still leave battery supply short of demand, underscoring the need for high-throughput robotic production . Co-locating battery lines with final assembly promotes sustainability and reduces logistics, but only if robots can alternate between battery and body tasks. Specialized aluminum welding cells and end-of-life disassembly robots such as Thoth's DisMantleBot illustrate new niches emerging from the EV shift.
High Capex & Installation Costs
Small and medium suppliers still view six-figure robot cells as risky despite falling price points. Robotics-as-a-service vendors such as Rapid Robotics offset sticker shock through monthly contracts that bundle hardware, service, and software. Integration often doubles upfront spend because lines must be re-rigged for guarding, vision calibration, and operator training. FANUC's USD 110 million Auburn Hills campus expansion shows the ecosystem investment needed to make turnkey deployment viable. Total cost of ownership also hinges on maintenance, software refreshes, and cyber-patching, often underestimated in business cases.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Labor Shortages & Wage Inflation in Auto Hubs
- Tighter OEM Quality-Consistency Mandates
- Scarcity of Skilled Robot Programmers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Vehicle makers held 61.18% of the automotive robotics market in 2024, reflecting their ability to absorb capital costs and embed articulated welders, painters, and sealers across every major line. This cohort now prioritizes AI vision for trim-and-final inspection and seeks cobots that can tackle ergonomic tasks once left to humans. Service centers form the fastest-growing slice, riding a 14.31% CAGR as EV diagnostics and ADAS calibration push mechanized processes into aftermarket bays.
Upskilling remains critical. OEMs such as Mercedes-Benz integrate humanoid robots to relieve staff from repetitive fetching tasks, while independent garages invest in robotic wheel alignment systems to shorten appointment times. Continued migration of complex repairs from dealerships to multi-brand centers will buoy the automotive robotics market into the next decade.
Robotic arms represented 36.54% of revenue in 2024, yet value is quickly shifting toward analytics, vision, and cyber-secure controllers. Software and services are advancing at a 14.64% CAGR, making this the prime strategic battleground. Cloud-hosted dashboards track utilization and issue predictive alerts, converting one-time capex into annuity streams.
Fleet-level orchestration platforms unify hundreds of cells into one virtual entity, enabling production planners to redeploy tasks in minutes rather than days. As hardware margins compress, vendors differentiate through continuous software updates and app-store ecosystems, reinforcing the automotive robotics market's move toward outcome-based contracting.
The Automotive Robotics Market Report is Segmented by End-User Type (Vehicle Manufacturers (OEMs), Component Manufacturers (Tier-1 and 2), and More), Component Type (Controllers, Robotic Arms, and More), Product Type (Cartesian Robots, SCARA Robots, and More), Function Type (Painting Robots, Welding Robots, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retained 46.55% of the automotive robotics market in 2024, anchored by China's 429,500 unit output and a robot density of 470 per 10,000 workers. Domestic vendors such as Siasun and Estun benefit from state incentives that keep acquisition costs low, while Japanese integrators continue to refine lean robotic cells for high-mix assembly. Southeast Asian governments extend production-linked incentives, inviting OEMs to localize EV lines with fully automated battery pack stations.
South America logs the highest 14.94% CAGR as multinationals commit fresh capital: Stellantis has earmarked EUR 5.6 billion for flexible EV capacity, and General Motors is spending USD 1.4 billion on robotic body shops in Brazil. Technology-transfer clauses in these deals allow local integrators to license advanced welding software, accelerating domestic expertise. Rising wage inflation reinforces the shift to robotics, particularly in Brazil's chassis and powertrain plants.
North America pursues reshoring to mitigate geopolitical risk. USMCA rules of origin encourage suppliers to automate to maintain cost competitiveness despite labor shortages. Federal credits targeting battery production spark new gigafactory projects that integrate high-payload robots for cell stacking and module assembly. Europe holds steady yet demands high functional-safety compliance that favors premium robotic solutions. Germany continues to act as an R&D hub, even as margin pressure spurs automakers to transfer volume production to lower-cost regions.
- ABB Ltd
- FANUC Corporation
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Robotics)
- Omron Adept Technologies
- Honda Motor Co (Robotics)
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp
- Harmonic Drive Systems
- RobCo SWAT Ltd
- Denso Wave Inc
- Comau SpA
- Staubli Robotics
- Universal Robots A/S
- Hyundai Robotics
- Epson Robots
- OTC Daihen
- Siasun Robot & Automation
- Estun Automation
- Techman Robot
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Automation to boost throughput and quality
- 4.2.2 EV-battery and e-powertrain manufacturing needs
- 4.2.3 Labor shortages and wage inflation in auto hubs
- 4.2.4 Tighter OEM quality-consistency mandates
- 4.2.5 Cobots enabling flexible mixed-model lines
- 4.2.6 Emerging-market production-linked incentives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capex and installation costs
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of skilled robot programmers
- 4.3.3 Cyber-security risks in connected cells
- 4.3.4 Servo-motor / chip supply volatility
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD))
- 5.1 By End-User Type
- 5.1.1 Vehicle Manufacturers (OEMs)
- 5.1.2 Component Manufacturers (Tier-1 and 2)
- 5.1.3 After-market and Service Centers
- 5.2 By Component Type
- 5.2.1 Controllers
- 5.2.2 Robotic Arms
- 5.2.3 End Effectors
- 5.2.4 Drives and Sensors
- 5.2.5 Software and Services
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Cartesian Robots
- 5.3.2 SCARA Robots
- 5.3.3 Articulated Robots
- 5.3.4 Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
- 5.3.5 Other Types (Parallel, Cylindrical)
- 5.4 By Function Type
- 5.4.1 Welding Robots
- 5.4.2 Painting Robots
- 5.4.3 Assembly and Disassembly Robots
- 5.4.4 Cutting and Milling Robots
- 5.4.5 Material-Handling Robots
- 5.4.6 Inspection and Quality-Testing Robots
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 South-East Asia
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Turkey
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd
- 6.4.2 FANUC Corporation
- 6.4.3 KUKA AG
- 6.4.4 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.5 Kawasaki Heavy Industries (Robotics)
- 6.4.6 Omron Adept Technologies
- 6.4.7 Honda Motor Co (Robotics)
- 6.4.8 Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp
- 6.4.9 Harmonic Drive Systems
- 6.4.10 RobCo SWAT Ltd
- 6.4.11 Denso Wave Inc
- 6.4.12 Comau SpA
- 6.4.13 Staubli Robotics
- 6.4.14 Universal Robots A/S
- 6.4.15 Hyundai Robotics
- 6.4.16 Epson Robots
- 6.4.17 OTC Daihen
- 6.4.18 Siasun Robot & Automation
- 6.4.19 Estun Automation
- 6.4.20 Techman Robot
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment











