 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1852016
印度农业机械:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)India Agricultural Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
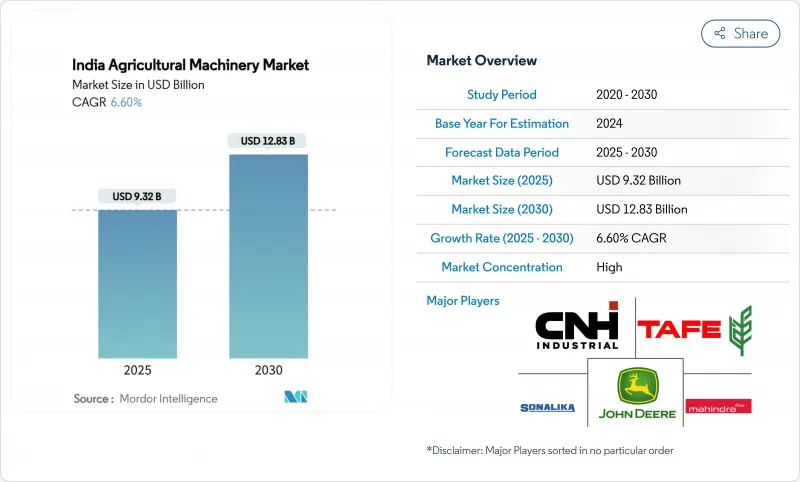
据估计,到 2025 年,印度农业机械市场规模将达到 181.5 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 272.9 亿美元,预测期内复合年增长率为 8.5%。
强有力的公共部门奖励、持续的农村劳动力短缺以及快速的数位化正在推动全国范围内的农机设备普及。农业机械化方案(SMAM)提供的补贴降低了拖拉机、灌溉系统和精准农机设备的初始成本,而客製化的就业中心则扩大了小农户的就业管道。随着都市区化进程的加速和农业劳动力的减少,生产者正转向能够确保及时播种和收穫的机械化解决方案。同时,数位农业计画正在建立农民登记系统和带有地理标籤的作物资料库,以支援精准农机设备的部署和数据主导贷款。排放气体法规和针对低排放气体的新激励措施正在刺激对更清洁动力传动系统的投资,使电动和混合模式成为新兴但具有战略意义的成长点。竞争对手之间的竞争日益激烈,前五名供应商占据了81.5%的市场份额,这促使他们推出新产品并扩大中功率拖拉机和智慧农具的产能。
印度农业机械市场趋势与洞察
鼓励引入机械化的政府体系
SMAM的政策干预措施为个人机械购置提供40%至50%的补贴,为客製化租赁中心提供高达80%的补贴。光是在北方邦,SMAM在2014年至2024年间就发放了656.6亿印度卢比(约7.9亿美元),分发了17.6万台机械,并建立了1,0769个客製化租赁中心。诸如农民无人机补贴和国家粮食安全任务特定作物支援等配套倡议进一步扩大了对精准设备的需求。这些项目不仅最大限度地降低了前期成本,还加强了售后服务网络,促进了不同农业气候区的可持续机械化。
由于人口持续向都市区迁移,农村地区出现劳动力短缺。
根据家庭调查数据,仅有9%的主要收入来源者从事农业,远低于历史上超过50%的水准。季节性迁徙高峰出现在播种和收穫季节,加剧了劳动力短缺,但机械化可以透过及时耕作、播种和收割来弥补这一缺口。联合收割机可减少高达30%的劳动力,并将收穫后损失降低2-4个百分点。透过客製化中心共用机械设备,可以进一步利用稀缺机械,从而在劳动力短缺地区维持作物集约化生产。
设备成本高且信贷管道有限
儘管政府提供了丰厚的补贴,但一台中型拖拉机的售价仍超过60万印度卢比(约7,200美元),这对许多小农户来说遥不可及。正规贷款机构通常要求提供抵押品,且利率比优惠贷款高出200-300个基点,这抑制了大规模投资。虽然客製化的租赁中心可以降低成本,但其分布极不均衡:印度东部每个地区不到12个租赁中心,而北部地区则超过45个,进一步加剧了区域间的差距。
细分市场分析
2024年,拖拉机将维持40.5%的收入份额,凸显其在各种种植系统中耕作和运输的关键作用。在灌溉机械领域,微灌泵和滴灌系统是成长最快的细分市场,年复合成长率达10.5%,这主要得益于电费上涨,从而支持了抗旱计画和精准灌溉。犁、耙和旋耕机等农机具将受益于小农户机械化程度的提高,因为这些农具提供了入门级的机械化解决方案,且资本投入低于拖拉机。随着旺季劳动力短缺加剧,收割机械将保持稳定成长,联合收割机和青贮收割机对于商业性农业生产及时收割作物至关重要。
将全球导航卫星系统与传统农具结合的适配器,正在将传统拖拉机转变为智慧机器,能够以±2.5厘米的精度进行直线犁地和播种,从而减少6%至8%的投入浪费。电动旋耕机和电池驱动的果园喷雾器在果农中越来越受欢迎,他们优先考虑低噪音和零排放。印度的农业机械市场持续多元化发展,打包机、割草机和碎草机在旨在遏制露天焚烧的残茬管理方案中发挥越来越重要的作用。市场领导正在透过模组化附件生态系统来应对这一需求,使单一拖拉机底盘能够支援20多种针对不同任务的农具,从而将拥有成本分摊到多个收入来源。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 政府计划促进机械化应用
- 由于人口持续向都市区迁移,农村地区出现劳动力短缺。
- 农民生产组织和合约农业集群
- 提供贷款服务的数位信贷平台
- 奖励可加速电气设备普及
- 气候保险有利于机械化农业
- 市场限制
- 高昂的资本成本和有限的信贷管道
- 所拥有土地分散限制了规模效益。
- 各州的排放法规各不相同。
- 熟练的远端资讯处理技术人员短缺
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按类型
- 联结机
- 小于50马力
- 50~75 HP
- 76~100 HP
- 101~150 HP
- 150马力或以上
- 装置
- 耕耘机
- 光环
- 旋耕机和耕耘机
- 播种施肥机
- 其他设备(挖坑机、电动除草机等)
- 灌溉机械
- 喷水灌溉
- 滴灌
- 其他灌溉设备(中心支轴式喷灌系统、微型喷灌等)
- 收割机
- 联合收割机
- 青贮收割机
- 其他收割机械(甘蔗收割机、马铃薯收割机等)
- 干草和饲料机械
- 割草机和压扁机
- 打包机
- 其他干草饲料机械(翻晒机、耙草机等)
- 联结机
- 按最终用户农场规模划分
- 小型农场(小于5公顷)
- 中型农场(5-20公顷)
- 大型农场(超过20公顷)
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- International Tractors Limited(Sonalika)
- Escorts Kubota Limited
- VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group SpA
- Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- Kirloskar Group
- Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The India Agricultural Machinery Market size is estimated at USD 18.15 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 27.29 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.

Robust public-sector incentives, persistent rural labor shortages, and rapid digitalization are converging to accelerate equipment adoption nationwide. Subsidies under the Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) lower the upfront cost of tractors, irrigation systems, and precision implements, while custom-hiring centers extend access to smallholder farmers. Rising urban migration reduces available farm labor, pushing growers toward mechanized solutions that can sustain timely planting and harvesting operations. In parallel, the Digital Agriculture Mission is creating a farmer registry and geotagged crop database that will underpin precision equipment deployment and data-driven financing. Emission regulations plus emerging incentives for low-emission tractors spur investment in cleaner powertrains, positioning electric and hybrid models as a nascent but strategic growth pocket. Competitive rivalry intensifies as the top five vendors command an 81.5% share, prompting new product launches and capacity expansions geared toward mid-power tractors and smart implements.
India Agricultural Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Government schemes boosting mechanization adoption
Policy interventions under SMAM provide 40%-50% subsidies on individual machinery purchases and up to 80% on custom-hiring centers. In Uttar Pradesh alone, SMAM disbursed INR 65.66 billion (USD 790 million) between 2014 and 2024, distributing 176,000 machines and establishing 10,769 custom-hiring centers, which collectively expand access to high-capacity equipment across smallholder communities. Complementary initiatives such as the Kisan Drone subsidy and crop-specific support under the National Food Security Mission channel further demand high-precision implements. These programs not only minimize upfront costs but also strengthen after-sales networks, thereby fostering sustained mechanization across diverse agro-climatic zones.
Rural labor shortage caused by sustained migration to urban centers
Household survey data indicate that only 9% of main income earners remain in farming, down from historic norms above 50%. Seasonal out-migration peaks during planting and harvesting, intensifying labor deficits that mechanization can bridge through timely tillage, sowing, and harvesting. Combine harvesters cut labor requirements by up to 30% and reduce post-harvest losses by 2-4 percentage points, making them indispensable in rice-wheat rotations. Equipment sharing through custom-hiring centers further leverages scarce machinery to maintain cropping intensities in labor-scarce districts.
High equipment cost and limited credit access
Despite generous subsidies, a mid-horsepower tractor still requires an outlay exceeding INR 600,000 (USD 7,200), a sum beyond the reach of many marginal growers. Formal lenders often demand collateral, and interest spreads remain 200-300 basis points above prime lending, deterring big-ticket investments. Custom-hiring centers cushion the cost hurdle but are unevenly distributed, eastern India hosts fewer than 12 centers per district versus 45-plus in parts of the north, perpetuating regional disparities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- FPOs and contract farming aggregation
- Digital credit platforms enabling financing
- Fragmented landholdings limit scale efficiency
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tractors retained a 40.5% revenue share in 2024, underscoring their foundational role in tillage and haulage across diverse cropping systems. Irrigation Machinery is the fastest growing segment with micro-irrigation pumps and drip systems advancing at a 10.5% CAGR, propelled by drought-mitigation programs and rising electricity tariffs that favor precision watering. Equipment segments, including plows, harrows, and rotovators, benefit from the mechanization push in smallholder farming, where these implements provide entry-level mechanization solutions that require lower capital investment than tractors. Harvesting machinery experiences steady growth as labor shortages intensify during peak seasons, with combine harvesters and forage harvesters becoming essential for timely crop collection in commercial farming operations.
Adapters that merge global navigation satellite systems with traditional implements are converting conventional tractors into smart machines that execute straight-line plowing and seed placement within +-2.5 cm precision, reducing input waste by 6%-8%. Electric-assist rotovators and battery-powered orchard sprayers are gaining traction among fruit growers, where low noise and zero emissions are prized. The India agricultural machinery market continues to diversify as balers, mowers, and mulchers gain relevance in residue-management schemes aimed at curbing open-field burning. Market leaders respond with modular attachment ecosystems, allowing a single tractor chassis to support over 20 task-oriented implements, thereby spreading ownership cost over multiple revenue streams.
The India Agricultural Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Type (Tractors, Equipment, Irrigation Machinery, Harvesting Machinery, and More) and by End-User Farm Size (Smallholdings, Medium Farms, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- Escorts Kubota Limited
- VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- AGCO Corporation
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- SDF Group S.p.A.
- Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- Kirloskar Group
- Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government Schemes Boosting Mechanization Adoption
- 4.2.2 Rural labor shortage caused by sustained migration to urban centers
- 4.2.3 FPOs and Contract Farming Aggregation
- 4.2.4 Digital Credit Platforms Enabling Financing
- 4.2.5 Electric Equipment Incentives Accelerating Adoption
- 4.2.6 Climate Insurance Favoring Mechanized Cultivation
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Equipment Cost and Limited Credit Access
- 4.3.2 Fragmented Landholdings Limit Scale Efficiency
- 4.3.3 Emission Norms Vary Across States
- 4.3.4 Lack of Skilled Telematics Technicians
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.1.1.1 Less than 50 HP
- 5.1.1.2 50 to 75 HP
- 5.1.1.3 76 to 100 HP
- 5.1.1.4 101 to 150 HP
- 5.1.1.5 Greater than 150 HP
- 5.1.2 Equipment
- 5.1.2.1 Plows
- 5.1.2.2 Harrows
- 5.1.2.3 Rotovators and Cultivators
- 5.1.2.4 Seed and Fertilizer Drills
- 5.1.2.5 Other Equipment (Post-Hole Diggers, Power Weeders, etc.)
- 5.1.3 Irrigation Machinery
- 5.1.3.1 Sprinkler Irrigation
- 5.1.3.2 Drip Irrigation
- 5.1.3.3 Other Irrigation Machinery (Center-Pivot Systems, Micro-Sprinklers, etc.)
- 5.1.4 Harvesting Machinery
- 5.1.4.1 Combine Harvesters
- 5.1.4.2 Forage Harvesters
- 5.1.4.3 Other Harvesting Machinery (Sugarcane Harvesters, Potato Harvesters, etc.)
- 5.1.5 Haying and Forage Machinery
- 5.1.5.1 Mowers and Conditioners
- 5.1.5.2 Balers
- 5.1.5.3 Other Haying and Forage Machinery (Tedders, Rakes, etc.)
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.2 By End-User Farm Size
- 5.2.1 Smallholdings (Less than 5 ha)
- 5.2.2 Medium Farms (5 to 20 ha)
- 5.2.3 Large Farms (Greater than 20 ha)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- 6.4.2 TAFE Motors and Tractors Limited
- 6.4.3 Deere & Company
- 6.4.4 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.5 International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- 6.4.6 Escorts Kubota Limited
- 6.4.7 VST Tillers Tractors Ltd.
- 6.4.8 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.9 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.4.10 Yanmar Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.11 SDF Group S.p.A.
- 6.4.12 Tirth Agro Technology Private Limited
- 6.4.13 Kirloskar Group
- 6.4.14 Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd.








