 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1907232
欧洲农业拖拉机机械:市场份额分析、行业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031 年)Europe Agricultural Tractor Machinery - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
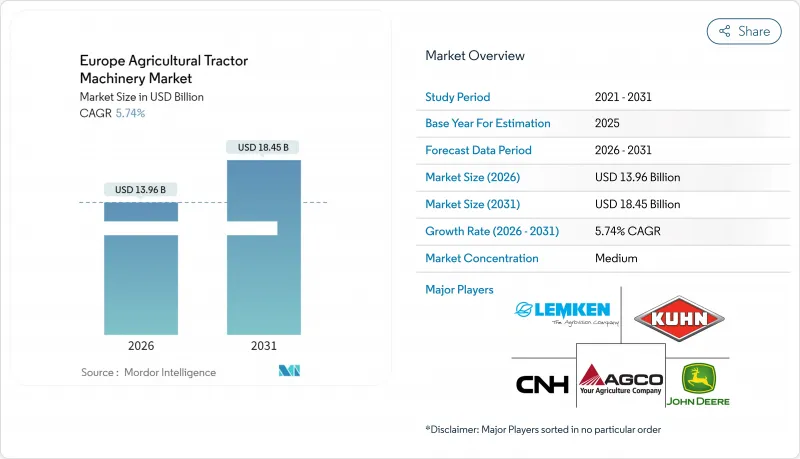
2025年欧洲农业拖拉机机械市场价值132亿美元,预计2031年将达到184.5亿美元,高于2026年的139.6亿美元。
预计在预测期(2026-2031 年)内,复合年增长率将达到 5.74%。
需求成长主要受以下因素驱动:欧盟通用农业政策的生态计画(Eco-Scheme),该计画支持精密农业设备;第五阶段排放气体法规,加速了车辆更新换代;以及持续的劳动力短缺,推动了农业自动化。供应商正积极回应,推出可透过 ISO 11783 (ISOBUS)通讯协定整合的动力化和感测器化农具。同时,电气化试点计画也催生了对与电池驱动拖拉机相容的电力消耗附件的需求。然而,经销商自 2023 年起的库存积压、大宗商品价格波动以及混合车队互通性方面的摩擦,限制了价格敏感的中东欧地区的市场接受度。竞争依然适中,前五名供应商为专注于条耕、果园除草和温室应用等细分领域的专业厂商留出了发展空间。
欧洲农业拖拉机机械市场趋势与洞察
欧盟通用农业政策下的精密农业补贴(2025-2027财政年度)
强制性生态计画将25%的直接补贴用于已证实能提高投入效率的计划,鼓励购买变数播种机、支援ISOBUS的喷雾器和产量测绘感测器。法国、德国和波兰正在经历此类升级。更广泛的应用促进了数据共用;到2024年,Telena合作社38%的成员企业都采用了遥测技术,使设备使用寿命延长了15%。认证要求有利于符合ISO 11783标准的品牌,这使得外围供应商无法获得补贴,并将需求集中到少数大型远端资讯处理生态系统中。
劳动力短缺推动了西欧和北欧对自动化的需求。
2024年,德国全职农业从业人员数量较去年同期下降12%。荷兰园艺业也面临类似的人手不足,推动了机器人播种机和视觉引导喷药机的应用。迪尔公司报告称,2024年其「See and Spray」(即视喷)系统在欧洲的出货量成长了47%。丹麦Agro公司推出了15台可昼夜运作的自主割草和压扁机,将干草收成的人力成本降低了30%。因此,欧洲农业拖拉机市场正朝着具备自主功能的动力农具方向发展,与传统被动式农具的差距日益扩大。
从2023年起,经销商持有的过剩库存将抑制新订单,这种情况将持续到2026年。
2024年初,欧洲经销商的农机库存量达到9.2个月的供应量(正常水准为5.5个月)。由于未售出的犁地和播种设备库存高达3.4亿欧元(3.6亿美元),百威集团(Baiewa)将其2025年的采购计画削减了22%。法国经销商InVivo也同样削减了18%的新订单,并将业务重心转向二手设备的维修。儘管製造商将付款期限延长至180天并提案寄售服务,但利润率的压力使得经销商不愿增加库存,减缓了欧洲农业拖拉机市场的短期成长。
细分市场分析
2025年,犁地及耕作设备占欧洲农业拖拉机市场收入的45.30%。受固定点驾驶规则和即时变数施肥演算法广泛应用的推动,预计到2031年,播种设备将以7.66%的复合年增长率成长。法国合作社Accéreal在8.5万公顷土地上安装GPS分区控制系统后,每公顷种子成本降低了12%。
播种机械市场成长最为迅猛,主要得益于旨在减少种子浪费的环保补贴政策。莱姆肯(Lemken)的电动式计量式Azurit播种机价格高出28%,但在500公顷以上的农场,三个种植季即可收回成本。牧草和饲料机械在欧洲草原地区依然需求旺盛,但其需求依赖稳定的乳牛和肉牛数量。其他专用机械市场则较为分散。这一领域表明,补贴和数据能力正在推动欧洲农业拖拉机机械市场利润转移到动力驱动和软体定义型机械。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 欧盟通用农业政策(CAP)下的精密农业补贴(2025-2027财政年度)
- 劳动力短缺推动了西欧和北欧对自动化的需求。
- 第五阶段排放气体标准促进高效率动力输出装置农用设备的改造与升级
- 控制交通农业的普及推动了对作业宽度宽、重量轻的犁地工具的需求。
- 地中海国家葡萄园和果园的快速机械化
- 新兴的电动拖拉机生态系统需要低电力消耗、支援 ISOBUS 的农具。
- 市场限制
- 从2023年起,经销商库存过剩将抑制新订单,这种情况将持续到2026年。
- 东欧小规模分散农场购置智慧农机设备成本高昂
- 复杂的互通性标准(ISOBUS、TIM)在中型农场的应用速度缓慢。
- 商品价格波动会减少农民用于购买设备的可用资金。
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按机器类型
- 犁地机械
- 犁
- 光环
- 耕耘机
- 其他犁地和栽培机械
- 种植机械
- 播种机
- 播种机
- 撒布器
- 其他播种机
- 干草和饲料机械
- 收割者和护髮素
- 打包机
- 其他干草和饲料机械
- 喷雾器
- 其他类型
- 犁地机械
- 按国家/地区
- 德国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 英国
- 西班牙
- 荷兰
- 波兰
- 其他欧洲地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial NV
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation(Kubota Corporation)
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kuhn Group(Bucher Industries AG)
- Lemken GmbH & Co. KG
- SDF Group
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Ltd
- Amazonen-Werke H. Dreyer SE
- Pottinger Landtechnik GmbH
- Vaderstad AB
- Maschio Gaspardo SpA
- Salford Group(Linamar Corporation)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Europe agricultural tractor machinery market was valued at USD 13.2 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 13.96 billion in 2026 to reach USD 18.45 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 5.74% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

Demand gains stem from the European Union Common Agricultural Policy eco-schemes that underwrite precision-farming hardware, Stage V emissions compliance that accelerates fleet renewal, and persistent labor shortages that nudge farms toward automation. Suppliers answer with powered, sensor-rich implements that integrate through the ISO 11783 (ISOBUS) protocol, while electrification pilots create a parallel pull for low-draw attachments compatible with battery tractors. At the same time, dealer inventory overhang from 2023, volatile commodity prices, and mixed-fleet interoperability frictions temper adoption in price-sensitive pockets of Central and Eastern Europe. Competitive intensity remains moderate because the top five vendors leave room for niche specialists that address strip-till, orchard under-vine mowing, or greenhouse applications.
Europe Agricultural Tractor Machinery Market Trends and Insights
Precision-Farming Subsidies Under the EU Common Agricultural Policy (2025-2027 Tranche)
Mandatory eco-schemes now channel 25% of direct payments into proven input-efficiency projects, pushing farms to buy variable-rate planters, ISOBUS sprayers, and yield-mapping sensors. France, Germany, and Poland are moving toward such upgrades. Adoption lifts data-sharing, cooperative Terrena saw 38% of members stream implement telemetry in 2024, extending equipment life by 15%. Certification requirements favor ISO 11783-compliant brands and squeeze fringe suppliers out of subsidy eligibility, consolidating demand around a few large telematics ecosystems.
Labor Shortages Accelerating Automation Demand in Western and Northern Europe
Full-time farm employment in Germany fell 12% year on year in 2024. Horticulture in the Netherlands faces similar gaps, spurring take-up of robotic planters and vision-guided sprayers. Deere and Company reported a 47% jump in European shipments of its See and Spray system during 2024. Danish Agro deployed 15 autonomous mower-conditioner units that cut hay harvest labor costs by 30% while running day and night. The Europe agricultural tractor machinery market, therefore, tilts toward powered implements with embedded autonomy, widening the gap with legacy passive tools.
Dealer Over-Inventory Amassed Since 2023 Suppressing Fresh Orders through 2026
European dealers carried 9.2 months of implement supply at the start of 2024 versus a normal 5.5 months. BayWa posted EUR 340 million (USD 360 million) in unsold tillage and seeding stock, then cut 2025 purchase plans by 22%. French distributor InVivo similarly trimmed new orders 18% and pivoted to refurbishing used assets. Manufacturers extended payment terms to 180 days and offered consignment, but the margin squeeze still discourages dealers from stocking incremental models, slowing near-term growth in the Europe agricultural tractor machinery market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Stage V Emissions Rules Propelling Retrofit and Replacement of PTO-Efficient Implements
- Growth of Controlled-Traffic Farming Boosting Demand for Lightweight, Wide-Working-Width Tillage Tools
- High Capital Cost for Smart Implements on Fragmented Small Holdings in Eastern Europe
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Plowing and cultivating machinery tools secured 45.30% of 2025 revenue in the Europe agricultural tractor machinery market. Planting machinery, aided by controlled-traffic mandates and real-time variable-rate algorithms, will grow at a 7.66% CAGR through 2031. French cooperative Axereal documented a 12% reduction in seed cost per hectare after rolling out GPS section control across 85,000 hectares.
Planting machinery capture the fastest expansion because eco-scheme payments specifically reward reductions in seed waste. Lemken's electric-meter Azurit planter sells at a 28% premium yet pays back within three seasons on farms above 500 hectares. Haying and forage machinery continue to serve the continent's grassland but hinge on stable dairy and beef herds. Other specialty implements remain fragmented. The segment illustrates how subsidy rules and data capability shift profits toward powered, software-defined machines within the wider Europe agricultural tractor machinery market size.
The Europe Agricultural Tractor Machinery Market Report is Segmented by Machinery Type (Plowing and Cultivating Machinery, Planting Machinery, and More) and by Geography (Germany, France, Italy, and More). Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation (Kubota Corporation)
- CLAAS KGaA mbH
- Kuhn Group (Bucher Industries AG)
- Lemken GmbH & Co. KG
- SDF Group
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- Tractors and Farm Equipment Ltd
- Amazonen-Werke H. Dreyer SE
- Pottinger Landtechnik GmbH
- Vaderstad AB
- Maschio Gaspardo S.p.A.
- Salford Group (Linamar Corporation)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Precision-farming subsidies under the EU Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) (2025-2027 tranche)
- 4.2.2 Labor shortages accelerating automation demand in Western and Northern Europe
- 4.2.3 Stage V emissions rules driving retrofit and replacement of PTO-efficient implements
- 4.2.4 Growth of controlled-traffic farming boosting demand for lightweight, wide-working-width tillage tools
- 4.2.5 Surge in vineyard/orchard mechanization in Mediterranean countries
- 4.2.6 Emerging electric-tractor ecosystem requiring low-draw, ISOBUS-ready implements
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Dealer over-inventory since 2023 suppressing fresh orders through 2026
- 4.3.2 High capital cost for smart implements on fragmented small holdings in Eastern Europe
- 4.3.3 Complex interoperability standards (ISOBUS, TIM) delaying adoption among mid-size farms
- 4.3.4 Volatile commodity prices lowering farmers cash flow for discretionary equipment
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.4 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Machinery Type
- 5.1.1 Plowing and Cultivating Machinery
- 5.1.1.1 Plows
- 5.1.1.2 Harrows
- 5.1.1.3 Rotovators and Cultivators
- 5.1.1.4 Other Plowing and Cultivating Machinery
- 5.1.2 Planting Machinery
- 5.1.2.1 Seed Drills
- 5.1.2.2 Planters
- 5.1.2.3 Spreaders
- 5.1.2.4 Other Planting Machinery
- 5.1.3 Haying and Forage Machinery
- 5.1.3.1 Mowers and Conditioners
- 5.1.3.2 Balers
- 5.1.3.3 Other Haying and Forage Machinery
- 5.1.4 Sprayers
- 5.1.5 Other Types
- 5.1.1 Plowing and Cultivating Machinery
- 5.2 By Country
- 5.2.1 Germany
- 5.2.2 France
- 5.2.3 Italy
- 5.2.4 United Kingdom
- 5.2.5 Spain
- 5.2.6 Netherlands
- 5.2.7 Poland
- 5.2.8 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Deere & Company
- 6.4.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Kubota Corporation (Kubota Corporation)
- 6.4.5 CLAAS KGaA mbH
- 6.4.6 Kuhn Group (Bucher Industries AG)
- 6.4.7 Lemken GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.8 SDF Group
- 6.4.9 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd
- 6.4.10 Tractors and Farm Equipment Ltd
- 6.4.11 Amazonen-Werke H. Dreyer SE
- 6.4.12 Pottinger Landtechnik GmbH
- 6.4.13 Vaderstad AB
- 6.4.14 Maschio Gaspardo S.p.A.
- 6.4.15 Salford Group (Linamar Corporation)









