 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1797753
卫星地球观测市场机会、成长动力、产业趋势分析及 2025 - 2034 年预测Satellite-Based Earth Observation Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
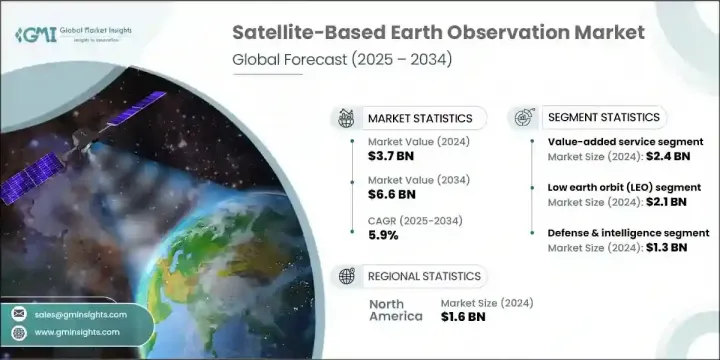
2024 年全球卫星对地观测市场价值为 37 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 5.9% 的复合年增长率增长至 66 亿美元。气候监测、国家安全和环境应用对地理空间情报的日益依赖推动了持续的需求。卫星小型化的进步和部署成本的降低极大地促进了小型卫星的部署。这些紧凑型平台可为农业、国防和灾难应变等多个领域提供经济高效的高解析度资料。人工智慧和云端运算在将原始卫星图像转换为可操作资料方面发挥关键作用,从而增强了产业和政府的决策能力。由于全球致力于监测气候模式、优化城市发展和提高抵御自然灾害的能力,需求也在上升。
更高的精度、更短的资料传输週期以及更方便的复杂分析平台,持续推动市场的发展,使人们能够近乎即时地洞察地表状况。这些改进大幅缩短了资料收集与可操作决策之间的时间间隔,使农业、环境保护、城市规划和紧急管理等领域的利害关係人能够更有效地应对挑战。卫星资料与人工智慧和机器学习的结合,进一步增强了探测细微环境变化、监测基础设施、评估作物健康状况以及以前所未有的精度追踪森林砍伐或污染的能力。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 37亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 66亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 5.9% |
加值服务领域在2024年创造了24亿美元的收入。这一增长源于对基于卫星资料的客製化分析日益增长的需求。这些洞察支持基础设施、能源、智慧城市和农业等关键领域的更智慧的规划和营运。人工智慧平台的整合以及与分析提供者的合作,能够在环境追踪和城市发展等领域提供更具体的解决方案。透过统一平台简化分析访问,可以提高采用率,尤其是在寻求快速、直观和可靠资讯传递系统的用户中。
2024年,低地球轨道(LEO)市值达21亿美元。小型卫星和紧凑型立方体卫星的兴起促进了这一增长,因为这些平台能够提供高解析度影像和快速重访间隔。高频成像支援土地利用测绘、作物健康追踪和紧急应变等应用。发射供应商与卫星公司之间的合作改善了获取途径,并降低了营运成本。这些优势加速了商业和公众对详细、持续的地球观测的兴趣,尤其是在国防、永续发展和环境监测等领域。
2024年,美国卫星对地观测市场产值达13.8亿美元。这一领先地位源自于对卫星创新和国家安全技术的大规模投资。企业必须使其产品与灾害应变、气候资料收集和策略监视方面不断变化的需求保持一致。重视整合人工智慧驱动的资料分析、基于云端的交付模式和安全通讯系统,将进一步提升供应商在未来政府合约和商业合作中保持竞争力的优势。
全球卫星对地观测市场的主要参与者包括 Planet Labs PBC、MinoSpace、GeoOptics Inc.、ICEYE Oy、Capella Space Inc.、OroraTech GmbH、空中巴士防务与航太、Spire Global, Inc.、ImageSat International NV、Maxar Technologies Inc.、BlackSky Technology Inc.、LiveSky Technology Inc. Ltd.。为了加强在卫星对地观测市场的地位,各公司正专注于整合人工智慧和机器学习演算法,以实现更智慧的资料解读。许多公司正在与分析公司建立合作伙伴关係,共同开发针对国防、农业和环境监测等特定行业的客製化服务。扩大小型卫星星座可以实现更广泛的覆盖范围和更频繁的资料收集。
目录
第一章:方法论与范围
第二章:执行摘要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系统分析
- 供应商格局
- 利润率
- 成本结构
- 每个阶段的增值
- 影响价值链的因素
- 中断
- 产业生态系统分析
- 产业衝击力
- 成长动力
- 地理空间资料的需求不断增加
- 气候变迁监测
- 政府和国防应用
- 云端运算和人工智慧分析的普及
- 卫星小型化进展
- 陷阱与挑战
- 高昂的初始投资和启动成本
- 轨道碎片和空间拥堵
- 成长动力
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管格局
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL分析
- 科技与创新格局
- 当前的技术趋势
- 新兴技术
- 新兴商业模式
- 合规性要求
- 国防预算分析
- 全球国防开支趋势
- 区域国防预算分配
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 中东和非洲
- 拉丁美洲
- 重点国防现代化项目
- 预算预测(2025-2034)
- 对产业成长的影响
- 各国国防预算
- 供应链弹性
- 地缘政治分析
- 劳动力分析
- 数位转型
- 合併、收购和策略伙伴关係格局
- 风险评估与管理
- 主要合约授予(2021-2024)
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 中东和非洲
- 市场集中度分析
- 按地区
- 关键参与者的竞争基准
- 财务绩效比较
- 收入
- 利润率
- 研发
- 产品组合比较
- 产品范围广度
- 科技
- 创新
- 地理位置比较
- 全球足迹分析
- 服务网路覆盖
- 各区域市场渗透率
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 领导者
- 挑战者
- 追踪者
- 利基市场参与者
- 战略展望矩阵
- 财务绩效比较
- 2021-2024 年关键发展
- 併购
- 伙伴关係和合作
- 技术进步
- 扩张和投资策略
- 永续发展倡议
- 数位转型倡议
- 新兴/新创企业竞争对手格局
第五章:市场估计与预测:依产品类型,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- EO数据
- 光学成像资料
- 雷达图像资料
- 高光谱影像资料
- 热红外线成像资料
- 其他的
- 加值服务
- 分析与洞察服务
- 地理空间情报平台
- 其他的
第六章:市场估计与预测:按卫星轨道,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 低地球轨道(LEO)
- 中地球轨道(MEO)
- 地球静止轨道(GEO)
第七章:市场估计与预测:按技术,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 光学(电光)
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR)
- 高光谱和多光谱
- 热红外线感测器
- LiDAR 系统
- 其他的
第八章:市场估计与预测:按应用,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 农业和林业
- 国防与情报
- 环境与气候监测
- 都市与基础建设规划
- 能源、采矿和自然资源
- 海运与运输
- 其他的
第九章:市场估计与预测:依最终用途,2021 - 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 政府和国防
- 军事和情报机构
- 民政和公共安全部门
- 商业的
- 农业综合企业及林业公司
- 环境服务提供者
- 建筑和城市规划公司
- 能源和矿业公司
- 海上物流营运商
- 其他的
- 研究与学术
- 其他的
第 10 章:市场估计与预测:按地区,2021 年至 2034 年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 西班牙
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- 中东和非洲
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 南非
- 阿联酋
第 11 章:公司简介
- Global Key Players
- Regional Key Players
- 颠覆者/利基市场参与者
- 卡佩拉太空公司
- Pixel公司
- 奥罗拉技术有限公司
- UrtheCast 公司
- GeoOptics公司
The Global Satellite-Based Earth Observation Market was valued at USD 3.7 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 5.9% to reach USD 6.6 billion by 2034. Increasing reliance on geospatial intelligence for climate surveillance, national security, and environmental applications is driving consistent demand. Advancements in satellite miniaturization and lower deployment costs have significantly boosted the deployment of smaller satellites. These compact platforms deliver cost-effective, high-resolution data across several sectors, including agriculture, defense, and disaster response. Artificial intelligence and cloud computing play a pivotal role in transforming raw satellite imagery into actionable data, thereby enhancing decision-making for industries and governments alike. Demand is also rising due to global efforts aimed at monitoring climate patterns, optimizing urban growth, and improving resilience to natural disasters.

Enhanced accuracy, shorter data delivery cycles, and easy access to sophisticated analytics platforms continue to push the market forward, enabling near real-time insights into Earth's surface conditions. These improvements are drastically reducing the time between data collection and actionable decision-making, allowing stakeholders in sectors such as agriculture, environmental conservation, urban planning, and emergency management to respond more effectively. The integration of satellite data with AI and machine learning has further amplified the ability to detect subtle environmental changes, monitor infrastructure, assess crop health, and track deforestation or pollution with unprecedented precision.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $3.7 billion |
| Forecast Value | $6.6 billion |
| CAGR | 5.9% |
The value-added services segment generated USD 2.4 billion in 2024. This growth is tied to the increasing requirement for customized analysis derived from satellite data. These insights support smarter planning and operations in key sectors such as infrastructure, energy, smart cities, and agriculture. Integration of AI-powered platforms and partnerships with analytics providers allows for more specific solutions in areas like environmental tracking and city development. Simplified access to analytics through unified platforms increases adoption, especially among users seeking fast, intuitive, and reliable information delivery systems.
The low Earth orbit (LEO) segment was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2024. The rise of small satellites and compact CubeSats contributes to this growth, as these platforms deliver high-resolution visuals and rapid revisit intervals. Frequent imaging supports applications such as land use mapping, crop health tracking, and emergency response. Collaboration between launch providers and satellite firms has improved access and reduced operational costs. These advantages have accelerated the expansion of commercial and public interest in detailed, constant Earth observation, especially across defense, sustainability, and environmental monitoring initiatives.
United States Satellite-Based Earth Observation Market generated USD 1.38 billion in 2024. This leadership stems from large-scale investment in satellite innovation and national security technologies. Companies must align their product offerings with evolving needs in disaster readiness, climate data gathering, and strategic surveillance. Emphasis on integrating AI-driven data analysis, cloud-based delivery models, and secure communications systems will further enhance the positioning of vendors seeking to remain competitive in future government contracts and commercial engagements.
Key participants in the Global Satellite-Based Earth Observation Market include Planet Labs PBC, MinoSpace, GeoOptics Inc., ICEYE Oy, Capella Space Inc., OroraTech GmbH, Airbus Defence and Space, Spire Global, Inc., ImageSat International N.V., Maxar Technologies Inc., BlackSky Technology Inc., LiveEO GmbH, L3Harris Technologies Inc., China Siwei Surveying and Mapping Technology Co., Ltd., and MDA Space Ltd. To strengthen their presence in the satellite-based Earth observation market, companies are focusing on integrating AI and machine learning algorithms for more intelligent data interpretation. Many are forming partnerships with analytics firms to co-develop customized services tailored to specific industries like defense, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Expanding constellations of smaller satellites enables broader coverage and more frequent data collection.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology and scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Product type trends
- 2.2.2 Satellite orbit trends
- 2.2.3 Technology trends
- 2.2.4 Application trends
- 2.2.5 End use trends
- 2.2.6 Regional trends
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034 (USD Billion)
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.3 Industry impact forces
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3.1.1 Increasing demand for geospatial data
- 3.3.1.2 Climate change monitoring
- 3.3.1.3 Government and defense applications
- 3.3.1.4 Proliferation of cloud computing and AI analytics
- 3.3.1.5 Advancements in satellite miniaturization
- 3.3.2 Pitfalls and challenges
- 3.3.2.1 High Initial Investment and Launch Costs
- 3.3.2.2 Orbital Debris and Space Congestion
- 3.3.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4 Growth potential analysis
- 3.5 Regulatory landscape
- 3.5.1 North America
- 3.5.2 Europe
- 3.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.5.4 Latin America
- 3.5.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
- 3.8 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.8.1 Current technological trends
- 3.8.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.9 Emerging business models
- 3.10 Compliance requirements
- 3.11 Defense budget analysis
- 3.12 Global defense spending trends
- 3.13 Regional defense budget allocation
- 3.13.1 North America
- 3.13.2 Europe
- 3.13.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.13.4 Middle East and Africa
- 3.13.5 Latin America
- 3.14 Key defense modernization programs
- 3.15 Budget forecast (2025-2034)
- 3.15.1 Impact on industry growth
- 3.15.2 Defense budgets by country
- 3.16 Supply chain resilience
- 3.17 Geopolitical analysis
- 3.18 Workforce analysis
- 3.19 Digital transformation
- 3.20 Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships landscape
- 3.21 Risk assessment and management
- 3.22 Major contract awards (2021-2024)
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.2.1.1 North America
- 4.2.1.2 Europe
- 4.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.1.4 Latin America
- 4.2.1.5 Middle East & Africa
- 4.2.2 Market Concentration Analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.3 Competitive benchmarking of key players
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.3.1.1 Revenue
- 4.3.1.2 Profit margin
- 4.3.1.3 R&D
- 4.3.2 Product portfolio comparison
- 4.3.2.1 Product range breadth
- 4.3.2.2 Technology
- 4.3.2.3 Innovation
- 4.3.3 Geographic presence comparison
- 4.3.3.1 Global footprint analysis
- 4.3.3.2 Service network coverage
- 4.3.3.3 Market penetration by region
- 4.3.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.3.4.1 Leaders
- 4.3.4.2 Challengers
- 4.3.4.3 Followers
- 4.3.4.4 Niche players
- 4.3.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.3.1 Financial performance comparison
- 4.4 Key developments, 2021-2024
- 4.4.1 Mergers and acquisitions
- 4.4.2 Partnerships and collaborations
- 4.4.3 Technological advancements
- 4.4.4 Expansion and investment strategies
- 4.4.5 Sustainability initiatives
- 4.4.6 Digital transformation initiatives
- 4.5 Emerging/ startup competitors landscape
Chapter 5 Market estimates and forecast, By Product Type, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 EO Data
- 5.2.1 Optical imaging data
- 5.2.2 Radar imaging data
- 5.2.3 Hyperspectral imaging data
- 5.2.4 Thermal infrared imaging data
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 Value-added services
- 5.3.1 Analytics & Insight Services
- 5.3.2 Geospatial Intelligence Platforms
- 5.3.3 Others
Chapter 6 Market estimates and forecast, By Satellite Orbit, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Low earth orbit (LEO)
- 6.3 Medium earth orbit (MEO)
- 6.4 Geostationary orbit (GEO)
Chapter 7 Market estimates and forecast, By Technology, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Optical (electro-optical)
- 7.3 Synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
- 7.4 Hyperspectral & multispectral
- 7.5 Thermal infrared sensors
- 7.6 LiDAR systems
- 7.7 Others
Chapter 8 Market estimates and forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Agriculture & forestry
- 8.3 Defense & intelligence
- 8.4 Environmental & climate monitoring
- 8.5 Urban & infrastructure planning
- 8.6 Energy, mining & natural resources
- 8.7 Maritime & transportation
- 8.8 Others
Chapter 9 Market estimates and forecast, By End Use, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Government & defense
- 9.2.1 Military & intelligence agencies
- 9.2.2 Civil government & public safety departments
- 9.3 Commercial
- 9.3.1 Agribusiness & forestry companies
- 9.3.2 Environmental service providers
- 9.3.3 Construction & urban planning firms
- 9.3.4 Energy & mining companies
- 9.3.5 Maritime logistics operators
- 9.3.6 Others
- 9.4 Research & academia
- 9.5 Others
Chapter 10 Market estimates and forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Million)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 North America
- 10.2.1 U.S.
- 10.2.2 Canada
- 10.3 Europe
- 10.3.1 Germany
- 10.3.2 UK
- 10.3.3 France
- 10.3.4 Spain
- 10.3.5 Italy
- 10.3.6 Netherlands
- 10.4 Asia Pacific
- 10.4.1 China
- 10.4.2 India
- 10.4.3 Japan
- 10.4.4 Australia
- 10.4.5 South Korea
- 10.5 Latin America
- 10.5.1 Brazil
- 10.5.2 Mexico
- 10.5.3 Argentina
- 10.6 Middle East and Africa
- 10.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 10.6.2 South Africa
- 10.6.3 UAE
Chapter 11 Company profiles
- 11.1 Global Key Players
- 11.1.1 Maxar Technologies Inc.
- 11.1.2 Airbus Defence and Space
- 11.1.3 Planet Labs PBC
- 11.1.4 ImageSat International N.V.
- 11.1.5 Spire Global Inc
- 11.2 Regional Key Players
- 11.2.1 North America
- 11.2.1.1 BlackSky Technology Inc.
- 11.2.1.2 L3Harris Technologies Inc
- 11.2.1.3 MDA Space Ltd.
- 11.2.2 Europe
- 11.2.2.1 LiveEO GmbH
- 11.2.2.2 Satellite Vu Ltd.
- 11.2.2.3 ICEYE Oy
- 11.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 11.2.3.1 SpaceWill Information Co., Ltd.
- 11.2.3.2 MinoSpace
- 11.2.3.3 XRTech Group
- 11.2.3.4 China Siwei Surveying and Mapping Technology Co., Ltd.
- 11.2.1 North America
- 11.3 Disruptors / Niche Players
- 11.3.1 Capella Space Inc.
- 11.3.2 Pixxel Inc
- 11.3.3 OroraTech GmbH
- 11.3.4 UrtheCast Corp.
- 11.3.5 GeoOptics Inc.












