 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1683907
中欧和东欧快递、快递和包裹 (CEP):市场占有率分析、行业趋势和统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
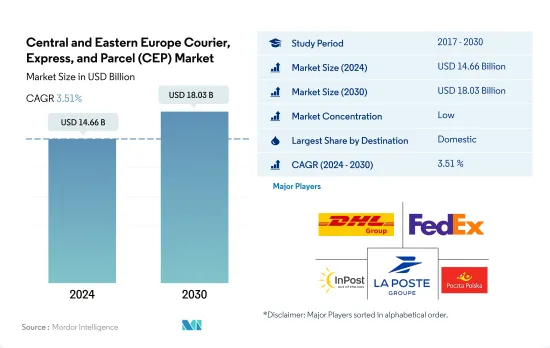
中欧和东欧快递包裹 (CEP) 市场规模预计在 2024 年将达到 146.6 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 180.3 亿美元,在预测期内(2024-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 3.51%。
由于服务范围扩大、价格降低以及电子商务使用量成长,该地区的 CEP 产业正在蓬勃发展
- 2022年,匈牙利CEP业者已开始发展该领域。例如,匈牙利营运商Magyar Posta将于2022年安装新的Leonardo分类系统,以增强其物流能力。 Leonardo 是小包裹和小包裹自动化解决方案的领先提供者。该系统将于 2023 年交付,用于处理国内和国际小包裹,每年最多可处理 1 亿件小包裹。 FoxPost 总部同样位于匈牙利,为匈牙利 20,000 家企业提供服务,在全国拥有 2,500 个小包裹储物柜。
- 欧洲领先的线上时尚和生活方式平台 Zalando 于 2021 年与捷克物流和技术公司 Zasilkovna 合作。此举是为了回应捷克客户不断变化的偏好,四分之一的捷克人选择取货点,对小包裹储物柜的偏好在三年内从 0% 增加到 6%。该合作将允许 Zalando 客户使用 1,500 个 Zasilkovna 储物柜和 4,700 个提货点,并选择货到付款作为付款方式。目的是迎合捷克顾客的偏好,为捷克顾客提供便利。此外,由于战争导致在波兰的乌克兰人数量增加,乌克兰最大的邮政业者新邮政(Nova Poshta)已将2022年向波兰寄送个人物品的关税降低2.5倍。
- 电子商务是该地区 CEP 需求的主要驱动力。例如,斯洛伐克 85.07% 的线上消费者最有可能在 2022 年进行线上购物。罗马尼亚和保加利亚的网路使用者份额在 2022 年分别达到 51.46% 和 48.78%。由于到 2027 年斯洛伐克的电子商务用户普及率将达到 318 万,该地区对 CEP 的需求预计也将增加。
中东欧地区的电子商务市场规模预计将在2022年达到346.3亿美元,进而产生对CEP运输的需求。
- 中东欧地区的电子商务市场预计将在 2022 年达到 346.3 亿美元,其中时尚和电子产业的收益占有率分别占 31.68% 和 28.10%。 2022 年,波兰(278 亿美元)将占据该地区电子商务份额最高,其次是捷克共和国(130 亿美元)。 2022 年,斯洛伐克居民(85%)是所有中东欧国家中最有可能进行网路购物的国家。 2022 年,斯洛伐克人在线上购物的比例比欧盟平均高出 10%。捷克共和国、匈牙利和爱沙尼亚在欧盟 27 国中电子商务使用率评级高于平均值。
- 波兰是该地区另一个提供国内和国际快递服务的国家。国家邮政服务 Poczta Polska 透过其快捷邮件邮政服务 (EMS) 提供这些服务。 Poczta Polska 透过 EMS 向 170 多个国家提供国际门到门快递服务。国内和国际货件的最大重量为 20 公斤。由于捷克共和国和斯洛伐克两国距离较近,国家邮政服务对寄往捷克共和国和斯洛伐克的 EMS 货件提供特别折扣。
- 由于需求不断增加,罗马尼亚是该地区提供国内和国际快递服务的国家之一。罗马尼亚国家邮政服务罗马尼亚邮政透过 EMS 提供此项服务。国内快递的重量限制为普通小包裹15 公斤,隐形物品 20 公斤。国际特快专递提供从罗马尼亚到大约 105 个国家的国际快递服务。从罗马尼亚可以透过国际宅配至大约 105 个国家,最大运送重量为 31.5 公斤。
中欧和东欧快递包裹 (CEP) 市场趋势
阿尔巴尼亚在全球挑战中面临成长放缓,而保加利亚、捷克共和国和波兰则加强了高影响力的基础设施投资
- 世界银行预测,2023年阿尔巴尼亚经济仅成长2.2%。受乌克兰战争和能源危机加剧影响,2024年阿尔巴尼亚经济成长可能进一步减弱,可能引发欧元区景气衰退并推高运输成本。不过,保加利亚已为这三个计划投资了 11 亿美元和 4.31 亿美元的国家资金,此外还为保加利亚復苏和復原计画 (RRP) 拨款 15 亿美元。其中包括在鲁塞郊区建造一个跨区域枢纽,预计于 2026 年完工。
- 2023年,捷克计画新开通118公里公路,其中包括100多公里的高速公路,并建设计画18公里的一级公路。该战略可望缓解交通拥堵、缩短旅行时间并提高道路安全。此外,高速公路和道路建设计划可以带来巨大的经济效益,创造新的就业机会并促进一个国家的经济成长。改善的交通基础设施还可以提高可及性和连接性,使企业更容易在全国范围内运输货物和服务。
- 波兰政府计划投资175亿美元用于铁路基础设施,投资366亿美元用于公路基础设施。道路和高速公路总局(GDDKiA)、波兰铁路 PKP SA、波兰铁路网(PKP-PLK)、经济发展和技术部以及基础设施部等主要机构负责涵盖全国或特定地区的计划。
保加利亚公共产业监管机构核准天然气价格降价30.7%(不含税)
- 匈牙利实施价格管制措施,维持能源价格低廉,使其天然气和电费成为欧洲最便宜的之一。匈牙利的天然气购买折扣单价约为 0.25 欧元(0.26 美元),每年最多可购买 1,729 立方公尺。同时,欧元区通膨率最高的爱沙尼亚正努力应对能源成本上涨,政府计划透过冻结电力和燃料消费税至2024年4月并考虑降低燃料税等其他措施来减轻对家庭的影响。
- 2021年天然气价格较2020年上涨49.41%。受俄乌战争影响,天然气价格上涨约七倍,煤炭价格上涨约四倍,导致能源局势不稳定,尤其导致爱沙尼亚、立陶宛、拉脱维亚三国居民消费价格上涨。 2023年6月,爱沙尼亚汽油价格在中东欧国家最高,每公升1.84美元,其次是阿尔巴尼亚,每公升1.79美元。
- 针对2023年,保加利亚公共产业监管局于2月核准将受监管的天然气价格降低30.7%,新价格为每兆瓦时124.34保加利亚列弗(67.8美元)(不含运输费、消费税和增值税)。降价是由于欧洲天气变暖和天然气蕴藏量充足导致国际天然气市场价格下跌。预计此次降价将使许多消费者受益,监管机构决定在冬季供暖季的剩余时间内保持中央暖气供应价格不变。
中东欧快递包裹 (CEP) 产业概览
中东欧快递包裹(CEP)市场较为分散,前五大公司占31.80%的市占率。市场的主要企业是:DHL集团、联邦快递、InPost、法国邮政集团和波兰邮政公司(按字母顺序排列)。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章执行摘要和主要发现
第二章 报告要约
第 3 章 简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
- 调查方法
第四章 产业主要趋势
- 人口统计
- 按经济活动分類的 GDP 分布
- 经济活动带来的 GDP 成长
- 通货膨胀率
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 交通运输仓储业生产毛额
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 物流绩效
- 基础设施
- 法律规范
- 中欧和东欧 (CEE)
- 价值链与通路分析
第五章 市场区隔
- 目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 送货速度
- 表达
- 非快递
- 模型
- 企业对企业 (B2B)
- 企业对消费者 (B2C)
- 消费者对消费者(C2C)
- 运输重量
- 重型货物
- 轻型货物
- 中等重量货物
- 运输方式
- 航空邮件
- 路
- 其他的
- 最终用户
- 电子商务
- 金融服务(BFSI)
- 卫生保健
- 製造业
- 一级产业
- 批发零售(线下)
- 其他的
- 国家名称
- 阿尔巴尼亚
- 保加利亚
- 克罗埃西亚
- 捷克共和国
- 爱沙尼亚
- 匈牙利
- 拉脱维亚
- 立陶宛
- 波兰
- 罗马尼亚
- 日本与斯洛伐克关係
- 斯洛维尼亚
- 其他中东欧
第六章 竞争格局
- 重大策略倡议
- 市场占有率分析
- 业务状况
- 公司简介
- CARGUS SRL
- DHL Group
- Fan Courier
- FedEx
- InPost
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Poczta Polska SA
- Posta Romana SA
第七章:执行长的关键策略问题
第 8 章 附录
- 世界概况
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球价值链分析
- 市场动态(DRO)
- 技术进步
- 资讯来源和进一步阅读
- 图表清单
- 关键见解
- 资料包
- 词彙表
简介目录
Product Code: 50001575
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 14.66 billion USD in 2024, and is expected to reach 18.03 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.51% during the forecast period (2024-2030).

Developing CEP segment in the region owing to services expansion, reducing tariffs, and growing e-commerce usage
- In 2022, CEP players in Hungary have taken the initiative to develop the segment. For instance, Hungarian operator Magyar Posta increased its distribution capacity with Leonardo's new sorting system in 2022. Leonardo is a major provider of automated solutions for small packets and parcels. The system, which would be supplied during 2023, is designed to process domestic and international parcels, wherein it could potentially process up to 100 million parcels a year. Also, Hungary-based FoxPost serves 20,000 businesses in Hungary, with 2,500 parcel lockers in Hungary.
- Zalando, Europe's leading online fashion and lifestyle platform, partnered with local logistics and technology Czech company Zasilkovna in 2021. The move responds to the shift in preferences of Czech customers wherein 1 in 4 Czechs chose pick-up points, and the preference for pick-up via parcel lockers rose from 0% to 6% in 3 years. Through the partnership, Zalando customers can use 1,500 Zasilkovna lockers and 4,700 pick-up points, with cash on delivery as one of the payment options. The aim is to cater to local customer preferences and provide convenience to Czech customers. Also, Nova Poshta, a major Ukrainian postal carrier, made a 2.5-fold reduction in tariffs for sending personal items to Poland in 2022, and this was done owing to the rise in the number of Ukrainians in Poland due to the war.
- E-commerce is a major driver for CEP demand in the region. For instance, 85.07% of online consumers in Slovakia were most likely to make purchases online in 2022. Share of internet users in Romania and Bulgaria stood at 51.46% and 48.78%, respectively, in 2022. With e-commerce user penetration to touch 3.18 million by 2027 in Slovakia, the demand for CEP is also projected to rise in the region.
E-commerce market in the CEE region hit USD 34.63 billion in 2022 generating the demand for CEP deliveries
- The e-commerce market in the CEE region reached a value of USD 34.63 billion in 2022, with the fashion and electronics segments leading the revenue shares with 31.68% and 28.10%, respectively. In 2022, Poland (USD 27.80 billion) had the highest e-commerce share in the region, followed by Czechia (USD 13 billion). In 2022, residents of Slovakia (85%) were the most likely to shop online in CEE countries. The percentage of people in Slovakia shopping online was 10% higher compared to the EU average in 2022. Czechia, Hungary, and Estonia were rated above average for using e-commerce among the 27 EU countries.
- Poland is another country in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. Poczta Polska, the national postal service, provides these services via express mail service (EMS). Poczta Polska facilitates door-to-door international express deliveries via EMS to over 170 countries. The maximum weight of shipments of domestic and international goods is 20 kg. The national postal service has special lowered rates for EMS shipments being delivered to the Czech Republic and Slovakia due to their proximity.
- Due to increased demand, Romania is one of the countries in the region providing domestic and international express delivery services. The Romanian Post, the national postal service, provides this service via its EMS. The domestic delivery weight limit is 15 kg for ordinary parcels and 20 kg for invisible contents. The express delivery service can cater to international deliveries to about 105 countries from Romania. The maximum weight of parcels for these shipments at the time of posting and delivery should be 31.5 kg.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
Albania faces slower growth amid global challenges, while Bulgaria, Czech Republic, and Poland ramp up high-impact infrastructure investments
- The World Bank predicts that Albania's economy will grow by only 2.2% in 2023. Albania's economic growth may be even weaker in 2024 due to the war in Ukraine and the energy crisis deepening and causing an economic downturn in the eurozone, which may increase transportation costs. However, Bulgaria invested in three projects with USD 1.5 billion allocated to Bulgaria's Recovery and Resilience Plan (RRP), along with USD 1.1 billion and USD 431 million from National Funding. This includes the construction of an intermodular regional hub outside of Rousse, which is expected to be finished by 2026.
- In 2023, the Czech Republic was expected to open up to 118 km of new highway stretches, including a plan to build over 100 km of highway and 18 km of Class I road. This strategy is expected to reduce traffic congestion, reduce travel time, and improve road safety. The highway and road construction projects may also have a significant economic impact, creating new jobs and boosting the country's economic growth. Improved transportation infrastructure may also enhance accessibility and connectivity, making it easier for businesses to move goods and services across the country.
- The Polish government plans to invest USD 17.5 billion in railway infrastructure and USD 36.6 billion in road infrastructure. The key organizations, such as the General Directorate of National Roads and Motorways (GDDKiA), Polish Railway PKP SA, Polish Railway Networks (PKP-PLK), and the Ministry of Economic Development and Technology and the Ministry of Infrastructure, are taking charge of projects spanning across the nation or specific regions.
Post approval from Bulgaria's utilities regulator, gas prices reduced by 30.7%, excluding taxes
- Hungary has implemented price regulation measures to keep energy prices low, resulting in one of the lowest gas and electricity prices in Europe. Gas prices in Hungary are available at a reduced unit price of approximately EUR 0.25 (USD 0.26) for up to 1,729 cubic meters per year. On the other hand, Estonia, which has the highest inflation rate in the Eurozone, struggles with rising energy costs, and the government plans to alleviate the impact on households by freezing excise duty on electricity and fuel until April 2024 and considering other measures, such as reducing taxes on fuels.
- In 2021, the price of natural gas increased by 49.41%, up from 2020. The price of natural gas increased by almost seven times, and coal prices quadrupled due to the Russian-Ukraine War, leading to an unstable energy situation and increased consumer price inflation, particularly in the Baltic countries of Estonia, Lithuania, and Latvia. In June 2023, Estonia recorded the highest gasoline prices among Central and Eastern European countries, at 1.84 USD per liter, followed by Albania at 1.79 USD/liter.
- In 2023, Bulgaria's utilities regulator gave its approval for a reduction of 30.7% in the regulated gas price for February, resulting in a new price of BGN 124.34 (USD 67.8) per MWh (excluding transportation costs, excise, and value-added tax). The price reduction is attributed to the lower prices in international gas markets, owing to warm weather and sufficient gas storage in Europe. This price reduction is expected to benefit significant consumers, and the regulator has decided to maintain central heating prices for the rest of the winter heating season.
Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The Central and Eastern Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fragmented, with the top five companies occupying 31.80%. The major players in this market are DHL Group, FedEx, InPost, La Poste Group and Poczta Polska SA (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Country
- 5.7.1 Albania
- 5.7.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.3 Croatia
- 5.7.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.5 Estonia
- 5.7.6 Hungary
- 5.7.7 Latvia
- 5.7.8 Lithuania
- 5.7.9 Poland
- 5.7.10 Romania
- 5.7.11 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.12 Slovenia
- 5.7.13 Rest of CEE
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 CARGUS SRL
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 Fan Courier
- 6.4.4 FedEx
- 6.4.5 InPost
- 6.4.6 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.7 La Poste Group
- 6.4.8 Poczta Polska SA
- 6.4.9 Posta Romana SA
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219






