 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1844491
中东和非洲接近感测器:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Middle East And Africa Proximity Sensors - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
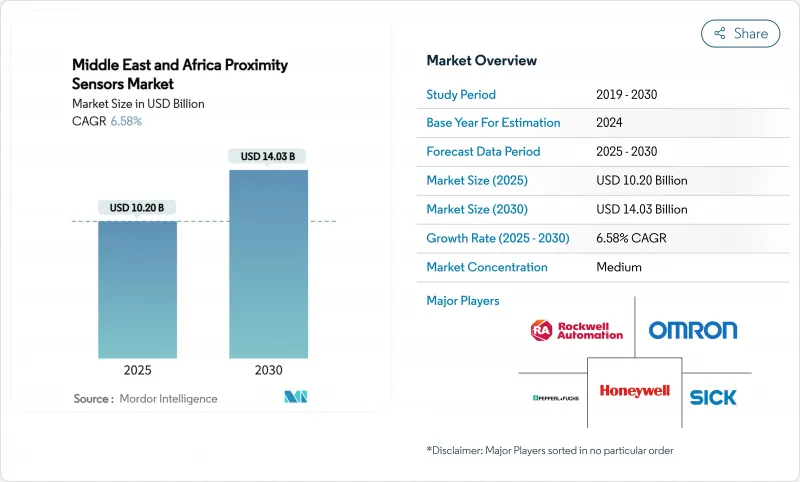
中东和非洲接近感测器市场预计到 2025 年将达到 102 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 140.3 亿美元,复合年增长率为 6.58%。
该地区的多元化发展、大规模可再生能源部署以及不断增长的汽车枢纽正在创造对非接触式感测设备的持续需求。虽然沙乌地阿拉伯、阿拉伯联合大公国 (UAE) 和南非继续集中大部分工业自动化计划,但埃及的风能走廊和摩洛哥的出口导向汽车厂正在推动最快的成长。海湾合作委员会国家的进口替代激励措施有利于能够本地化最终组装的供应商,而 IO-Link 的稳定采用正在使偏好倾向于数位输出设备。在恶劣的沙漠和采矿环境中,传统光电感测器的限制正在推动人们采用远距超音波和坚固的电感感测器。欧洲和日本供应商之间的合作标誌着策略转向共用区域生产和服务网络,以满足当地的认证需求。
中东和非洲接近感测器市场趋势和洞察
GCC离散製造业的工业自动化投资
海湾合作委员会(GCC)各国政府正根据其国家工业战略,要求提高新建工厂的自动化程度,推动工厂营运商采用能够承受高温和细尘的感测器网路。整合式 IO-Link 连接现已成为沙乌地阿拉伯和阿联酋主要待开发区计划的实际规范,可实现设备级诊断,从而减少非计划性停机时间。在海湾合作委员会自由区内完成的接近感测器次组件受本地内容规则和降低的关税约束,这鼓励全球供应商与本地分销商共同生产。这些政策与能源补贴相结合,使中东和北非地区的接近感测器市场保持稳定上升的趋势。
扩大摩洛哥和南非的汽车组装
摩洛哥预计到2024年将生产61.4万辆汽车,成为欧盟最大的外部汽车供应商。丹吉尔自由区的一级供应商正在指定使用远距雷射和超音波感测器进行电池组定位,使每条生产线的感测器数量增加高达20%。儘管南非面临整体产量下滑的局面,但为了保持全球竞争力,南非正在推进电池组装环节的自动化,这进一步刺激了中东和北非地区的接近感测器市场。
沙漠尘埃条件下光电感测器性能劣化
严重的沙尘暴会使光学感测器的可靠性降低 80% 以上,造成传送带和包装线的计划外停机,迫使操作员依赖每月的清洁週期和保护性空气吹扫系统,从而增加总体拥有成本并抑制中东和北非地区接近感测器市场对光电模型的广泛采用。
細項分析
2024年,超音波式感测器将占中东和北非地区接近感测器接近感测器的41.3%,市场规模达42亿美元。其密封设计消除了容易积聚灰尘的光学窗口,从而延长了矿山和钢厂的平均故障间隔时间。超音波感测器仅占销售额的14%,但随着风电场逐步实现远距检测的标准化,其复合年增长率可望达到9.8%。光电式感测器的采用受限于灰尘导致的误触发,而电容式感测器在食品和饮料生产线中仍占有一席之地,其非接触式液位感测技术可防止污染。磁霍尔效应感测器适用于汽车和船舶等细分应用,而新型涡流感测器则有助于航太工业的复合材料检测。原生IO-Link支援正成为所有类型感测器的关键采购标准,这进一步强化了中东和北非地区接近感测器市场的数位化主题。
第二代电感式平台整合了片上温度补偿和自癒演算法,可隔离部分线圈故障。供应商强调符合IECEx标准,以确保在石化区安装,而此监管障碍有利于老牌欧洲製造商。同时,日本和韩国供应商正在扩大其区域库存,以缩短前置作业时间,这在政府资金筹措里程碑压缩计划工期的情况下,是一个关键的差异化因素。
受装配线大规模生产和拾放机器人的推动,10 毫米以下的短距离感测器占据了 48.7% 的市场份额。然而,预计 40 毫米以上的远距感测器的复合年增长率将达到 8.9%,随着组装机和公用事业规模的太阳能发电厂对探测范围的要求越来越高,这一差距正在缩小。光是沙乌地阿拉伯 2.9 吉瓦的风发电工程就预计在 2025 年至 2027 年间就需要 5 万个远距感测器。中距离感测器(10-40 毫米)在自动化仓库和不同输送机宽度的包装系统中保持均衡的份额。
感测器製造商目前正在将微功率雷达整合到远距槽中,这增加了传统超音波线的竞争压力。在超高频探头中,高频电容式探头在半导体后端组装越来越受到关注。这类应用在该地区尚处于起步阶段,但在海湾合作委员会的技术蓝图中却是一个突出的特征。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场状况
- 市场概况
- 市场驱动因素
- GCC离散製造业的工业自动化投资
- 扩大摩洛哥和南非的汽车组装
- 阿联酋清真食品智慧包装生产线激增
- 沙乌地阿拉伯和埃及的风力发电机建设推动远距感测器的发展
- 恶劣采矿环境中的免维护电感式感测器(南非、纳米比亚)
- 市场限制
- 沙漠尘埃环境中光电感测器性能的劣化
- 撒哈拉以南地区二级汽车供应商的资本支出週期波动
- 尼日利亚和肯亚的本地附加价值低=进口关税高
- 假冒低价感测器(非官方贸易)降低品牌溢价
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监理展望(IEC Ex、SASO、GSO)
- 技术展望(IO-Link、ASIC小型化)
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章市场规模及成长预测
- 依技术
- 电感式
- 电容式
- 光电式
- 超音波
- 磁性(霍尔效应)
- 其他(涡流、光学)
- 按检测范围
- 短距离(小于10毫米)
- 中距离(10-40mm)
- 远距(40mm以上)
- 依输出类型
- 数字(NPN、PNP)
- 模拟(电流、电压)
- 按最终用户产业
- 车
- 工业製造与自动化
- 消费性电子产品
- 饮食
- 航太/国防
- 包装/物流
- 可再生能源
- 其他的
- 按国家
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 南非
- 埃及
- 奈及利亚
- 其他中东和非洲地区
第六章 竞争态势
- 市场集中度
- 策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- SICK AG
- Omron Corporation
- Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- STMicroelectronics NV
- Datalogic SpA
- IFM Electronic gmbh
- Balluff gmbh
- Keyence Corporation
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Panasonic Industry
- Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- Baumer Holding AG
- Contrinex SA
- Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- Autonics Co. Ltd.
- Riko Opto-electronics
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market stood at USD 10.2 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 14.03 billion by 2030, registering a 6.58% CAGR.

The region's diversification push, large-scale renewable-energy roll-outs and growing automotive hubs are creating sustained demand for non-contact sensing devices. Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and South Africa continue to concentrate the bulk of industrial automation projects, while Egypt's wind corridors and Morocco's export-oriented vehicle plants are driving the fastest incremental volumes. Import-substitution incentives in GCC states favour suppliers that can localise final assembly, and the steady adoption of IO-Link is tilting preference toward digital-output devices. Long-range ultrasonic and ruggedised inductive types are gaining visibility as harsh desert and mining environments expose the limits of legacy photoelectric alternatives. Cooperative ventures among European and Japanese vendors signal a strategic shift toward shared regional production and service networks that can meet local certification demands.
Middle East And Africa Proximity Sensors Market Trends and Insights
Industrial-automation investments in GCC discrete manufacturing
GCC governments are mandating higher automation ratios in new factories under national industrial strategies, pushing plant operators toward sensor networks that can withstand high ambient temperatures and fine dust. Integrated IO-Link connectivity is now a de-facto specification in major Saudi and Emirati green-field projects, enabling device-level diagnostics that cut unscheduled downtime. Local content rules grant tariff relief for proximity-sensor sub-assemblies finished within GCC free zones, steering global suppliers toward joint manufacturing with regional distributors. These policies, coupled with subsidised energy, keep the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market on a steady uptrend.
Automotive assembly expansion across Morocco and South Africa
Morocco produced 614,000 vehicles in 2024 and has become the European Union's largest external vehicle supplier, a status that necessitates near-zero defect tolerances on body-in-white lines. Tier-1 suppliers in Tangier's free zone are specifying long-range laser and ultrasonic sensors for battery-pack positioning, raising per-line sensor counts by up to 20%. South Africa, while contending with lower overall volumes, is automating battery-assembly stages to stay globally competitive, further stimulating the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Photonic-sensor performance degradation in desert dust conditions
Severe sandstorms can slash optical-sensor reliability by more than 80%, triggering unplanned stoppages on conveyor and packaging lines. Operators resort to monthly cleaning cycles and protective air-purge systems, lifting the total cost of ownership and restraining wider adoption of photoelectric models within the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in UAE smart-packaging lines for halal foods
- Wind-turbine build-out in Saudi Arabia and Egypt
- Volatile capex cycles in Sub-Saharan automotive Tier-2 suppliers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Inductive devices contributed 41.3% to the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market in 2024, valued at a Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market size of USD 4.2 billion. Their sealed construction eliminates optical windows that accumulate dust, extending mean-time-between-failure in mines and steel mills. Ultrasonic units, though only 14% of revenue, are on track for the fastest 9.8% CAGR as wind-energy operators standardise on long-range detection. Photoelectric adoption is restricted by dust-induced false triggers, while capacitive variants retain a foothold in food-and-beverage lines where non-contact level sensing prevents contamination. Magnetic Hall-effect sensors meet niche automotive and marine applications, and emerging eddy-current models serve aerospace composites inspection. Across all formats, native IO-Link support is becoming a decisive purchase criterion, reinforcing the digitalisation theme in the Middle East and Africa proximity sensors market.
Second-generation inductive platforms now bundle on-chip temperature compensation and self-healing algorithms that isolate partial coil faults. Suppliers emphasise conformity to IECEx standards to secure placement in petrochemical zones, a regulatory hurdle that favours established European manufacturers. Meanwhile, Japanese and Korean vendors are expanding regional stockholding to shorten lead times, a key differentiator where project schedules are compressed by government funding milestones.
Short-range models below 10 mm dominated at 48.7% share thanks to high unit volumes on assembly lines and pick-and-place robots. Yet long-range units above 40 mm are forecast to chart an 8.9% CAGR, closing the gap as turbine and utility-scale solar plants specify wider detection envelopes. A 2.9 GW tranche of Saudi wind projects alone will require an incremental 50,000 long-range sensors during 2025-2027. Medium-range devices (10-40 mm) keep a balanced presence in automated storage and packaging systems where conveyor widths vary.
Sensor makers now incorporate micro-power radar for long-range slots, raising competitive pressure on legacy ultrasonic lines. At the ultra-short end, high-frequency capacitive probes are gaining interest for semiconductor backend assembly, an application cluster still nascent in the region but flagged in GCC technology roadmaps.
The Middle East and Africa Proximity Sensors Market is Segmented by Technology (Inductive, Capacitive), Sensing Range (Short, Medium, Long), Output Type (Digital, Analog), End-User Industry (Automotive, Industrial Manufacturing and Automation), and Country (Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Egypt, Nigeria, and Rest of Middle East and Africa). The Market Size and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- SICK AG
- Omron Corporation
- Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Datalogic S.p.A.
- IFM Electronic gmbh
- Balluff gmbh
- Keyence Corporation
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Schneider Electric SE
- Panasonic Industry
- Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- Baumer Holding AG
- Contrinex SA
- Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- Autonics Co. Ltd.
- Riko Opto-electronics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Industrial-Automation Investments in GCC Discrete Manufacturing
- 4.2.2 Automotive Assembly Expansion across Morocco and South Africa
- 4.2.3 Surge in UAE Smart-Packaging Lines for Halal Foods
- 4.2.4 Wind-Turbine Build-Out in Saudi Arabia and Egypt Driving Long-Range Sensors
- 4.2.5 Maintenance-Free Inductive Sensors in Harsh Mining Sites (RSA, Namibia)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Photonic-Sensor Performance Degradation in Desert Dust Conditions
- 4.3.2 Volatile Capex Cycles in Sub-Saharan Automotive Tier-2 Suppliers
- 4.3.3 Low Local Value-Add = High Import Tariffs in Nigeria and Kenya
- 4.3.4 Counterfeit Low-Cost Sensors Diluting Brand Premiums (informal trade)
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook (IEC Ex, SASO, GSO)
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (IO-Link, ASIC miniaturization)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Inductive
- 5.1.2 Capacitive
- 5.1.3 Photoelectric
- 5.1.4 Ultrasonic
- 5.1.5 Magnetic (Hall-Effect)
- 5.1.6 Others (Eddy-Current, Optical)
- 5.2 By Sensing Range
- 5.2.1 Short Range (less than 10 mm)
- 5.2.2 Medium Range (10-40 mm)
- 5.2.3 Long Range (greater than 40 mm)
- 5.3 By Output Type
- 5.3.1 Digital (NPN, PNP)
- 5.3.2 Analog (Current, Voltage)
- 5.4 By End-User Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive
- 5.4.2 Industrial Manufacturing and Automation
- 5.4.3 Consumer Electronics
- 5.4.4 Food and Beverage
- 5.4.5 Aerospace and Defense
- 5.4.6 Packaging and Logistics
- 5.4.7 Renewable Energy
- 5.4.8 Others
- 5.5 By Country
- 5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.4 Egypt
- 5.5.5 Nigeria
- 5.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 SICK AG
- 6.4.2 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.3 Pepperl+Fuchs SE
- 6.4.4 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.5 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.6 STMicroelectronics N.V.
- 6.4.7 Datalogic S.p.A.
- 6.4.8 IFM Electronic gmbh
- 6.4.9 Balluff gmbh
- 6.4.10 Keyence Corporation
- 6.4.11 Delta Electronics Inc.
- 6.4.12 Banner Engineering Corp.
- 6.4.13 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.14 Panasonic Industry
- 6.4.15 Turck gmbh and Co. KG
- 6.4.16 Baumer Holding AG
- 6.4.17 Contrinex SA
- 6.4.18 Carlo Gavazzi Holding AG
- 6.4.19 Autonics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Riko Opto-electronics
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment








