 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1848065
印尼化肥:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)Indonesia Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
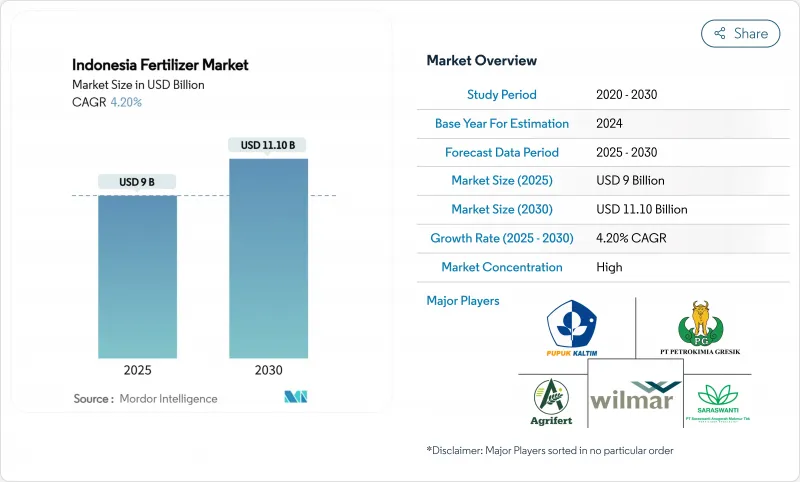
预计印尼化肥市场将以 4.2% 的复合年增长率成长,到 2025 年达到 90 亿美元,到 2030 年达到 111 亿美元。
政府对老旧油棕种植园的更新换代给予了大力补贴,这构成了印尼化肥市场整体需求的支柱。在最高零售价制度下,政府提供了950万吨的补贴,即使天然气价格高企挤压了生产商的利润空间,化肥消费量仍保持稳定。价值超过10亿美元的新型NPK复合肥掺混计划正在提升国内化肥的附加价值,并使印尼化肥市场能够更好地满足区域出口需求。
竞争动态反映出极高的市场集中度,前五大公司,包括PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)、PT Petrokimia Gresik、Wilmar International Limited、PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk和Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd(一体化的棕榈油业务占据了重要地位。这种集中度既造成了营运效率低下,也带来了战略上的脆弱性,因为主要生产商的供应中断可能会对国家的粮食安全产生重大影响。
印尼化肥市场趋势及洞察
扩大政府化肥补贴(HET)
根据印尼农业部的数据,2025年的预算累计950万吨补贴化肥(460万吨尿素、420万吨复合肥和50万吨有机肥),尿素价格为每公斤2250印尼币(约合0.14美元),复合肥价格为每公斤2300印尼币(约合0.15美元)。这些价格远低于市场价格。这项有保障的供应支撑了印尼的化肥市场,同时政府支出也达到了约33亿美元,约占GDP的2.8%。透过将化肥供应与农民资料库「e-RDKK」连接起来,政府最大限度地减少了诈欺行为,并确保了重点作物所需的养分供应。供应商还可以追踪季度需求,从而改善生产计画和营运资金规划。
稻米和玉米自给自足计划
普拉博沃总统提出的2026年实现水稻自给自足、三年内实现玉米自给自足的目标,正推动苏拉威西岛和加里曼丹岛等新兴种植区广泛采用均衡型氮磷钾复合肥,而非单一营养素肥料。高种植密度和计画中的双季种植将增加每公顷的养分需求,抵消精密农业未来带来的效率提升。根据「卡蒂尼·塔尼」(Kartini Tani)计画发放的种子包中包含推荐肥料,鼓励农民进行综合土壤肥力管理。据私人经销商称,自2024年中期以来,东部岛屿对富锌氮磷钾复合肥的需求增加了两倍。
天然气价格波动推高了尿素成本。
目前,再气化液化天然气的交易价格为每百万英热单位16.77美元,而先前补贴政策下的价格仅为每百万英热单位6美元,这使得每吨尿素的成本增加了50至70美元,挤压了国内生产商的净利率。生产商正在寻求与布兰特原油价格挂钩的长期天然气合同,以稳定投入成本。一些工厂正在评估与碳捕获相关的蓝氨生产方案,以获得优惠资金筹措并对石化燃料波动风险。
细分市场分析
2024年,尿素将占印尼化肥市场氮肥份额的60%,这得益于政府对高产量水稻种植技术(HET)的支持,预计2025年尿素产量将达460万吨。同时,普通肥料将占据主导地位,市场份额为54%。丰富的本地氨原料供应使得尿素成本保持在较低水平,而广泛的经销商网络则将产品分销到偏远的水稻和玉米种植区,这些地区消耗了“Swasembada Pangan”计划下大部分的氮肥投入。硝酸铵钙和硫酸铵则满足了特定土壤的需求,而国内氨的合成基本上满足了国内需求,进一步巩固了氮肥在印尼化肥市场规模中的领先地位。
微量元素肥料将实现最快成长,到2030年复合年增长率将达到8.1%,这得益于精密农业从爪哇岛扩展到苏门答腊岛,并支持出口导向园艺业的发展。复合肥料(NPK)的销售量也将强劲增长,新增的200万吨复合肥产能将使国内名目产量增至1400万吨,从而降低对进口的依赖,并根据不同微区的需求定制微量元素包衣。磷酸盐和钾肥的价格仍受运费波动的影响,因为印尼大部分磷酸二铵(DAP)、磷酸一铵(MAP)和氯化钾(MOP)依赖进口。同时,次要营养元素在加里曼丹岛和苏门答腊岛的酸性土壤中越来越受欢迎,这限制了人工林的长期产量。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 扩大政府化肥补贴(HET)
- 稻米和玉米自给自足计划
- Pupuk 印尼的新 NPK 混合工厂
- 棕榈油人工林再种植週期
- 种植需要特殊营养的出口园艺作物
- 爪哇岛早期采用无人机精准施肥技术
- 市场限制
- 补贴预算削减导致的供应缺口
- 天然气价格波动导致尿素成本上涨
- 假化肥料透过非官方管道广泛流通。
- 泥炭地养分径流面临的环境压力
- 监管状态
- 技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争强度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 复合肥
- 纯肥料
- 氮肥
- 尿素
- 硝酸铵钙(CAN)
- 氨
- 硝酸铵
- 硫酸铵
- 其他氮肥
- 磷肥
- 磷酸一铵(MAP)
- 磷酸二铵(DAP)
- 三重过磷酸钙(TSP)
- 其他磷肥
- 钾肥
- 钾肥(MOP)
- 其他钾肥
- 次要营养元素肥料
- 微量营养素
- 按作物类型
- 谷物和谷类
- 豆类和油籽
- 经济作物
- 水果和蔬菜
- 草坪和观赏作物
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur(PKT)
- PT Petrokimia Gresik
- Wilmar International Limited
- Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd(Kuok Group)
- PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk
- Yara International ASA
- EuroChem Group AG
- ICL Group Ltd.
- OCI Global NV
- PT Meroke Tetap Jaya
- PT Jadi Mas
- PT Dupan Anugerah Lestari
- PT Pupuk Sriwidjaya Palembang
- PT Pupuk Kujang Cikampek
- PT Pupuk Iskandar Muda
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Indonesia fertilizer market size stands at USD 9 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 11.1 billion by 2030, expanding at a 4.2% CAGR.

Strong public funding for input subsidies and the replanting of aging oil-palm estates forms the backbone of demand across the Indonesia fertilizer market. A government allocation of 9.5 million metric tons of subsidized product under the Highest Retail Price scheme stabilizes consumption even when natural-gas prices spike, compressing producer margins. New NPK blending projects worth more than USD 1 billion enhance domestic value addition and keep the Indonesia fertilizer market on track to serve regional export demand.
Competitive dynamics reflect extreme market concentration, with the top 5 companies, including PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT), PT Petrokimia Gresik, Wilmar International Limited, PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk, and Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group), maintaining significant positions through integrated palm oil operations. This concentration creates both operational efficiency and strategic vulnerability, as supply disruptions from major producers can significantly impact national food security.
Indonesia Fertilizer Market Trends and Insights
Government Fertilizer Subsidy (HET) Expansion
As per the Indonesian ministry, the 2025 budget earmarked 9.5 million metric tons of subsidized fertilizer, 4.6 million metric tons of urea, 4.2 million metric tons of NPK, and 500,000 metric tons of organic keeping prices at IDR 2,250/kg (USD 0.14) for urea and IDR 2,300/kg (USD 0.15) for NPK, levels far below commercial quotations This guaranteed volume underpins the Indonesia fertilizer market even as fiscal outlays approach USD 3.3 billion, roughly 2.8% of GDP. By linking deliveries to the e-RDKK farmer database, authorities minimize leakages and channel nutrients to priority crops. Suppliers also gain visibility on quarterly offtake, allowing smoother production scheduling and working-capital planning.
Rice And Corn Self-Sufficiency Programs
President Prabowo targets rice self-sufficiency by 2026 and corn self-sufficiency within three years, spurring wider adoption of balanced NPK over single-nutrient products across new cultivation zones in Sulawesi and Kalimantan. Higher planting density and double-cropping schedules lift per-hectare nutrient requirements, offsetting future efficiency gains from precision farming. Seed packages issued under the Kartini Tani program include fertilizer recommendations, nudging farmers toward integrated soil fertility management. Private distributors report that demand for zinc-enriched NPK has tripled in the eastern islands since mid-2024.
Natural-Gas Price Volatility Raising Urea Costs
Regasified LNG now trades at USD 16.77 per MMBtu versus USD 6 under the previous subsidy, adding USD 50-70 to the cost of every metric ton of urea and squeezing margins for domestic manufacturers. Producers seek long-term gas contracts indexed to Brent-minus formulas to stabilize input costs. Several plants are evaluating carbon-capture linked blue ammonia pathways to unlock concessional finance and hedge against fossil fuel volatility.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- New NPK Blending Plants Under Pupuk Indonesia
- Palm-Oil Plantation Replanting Cycle
- Environmental Pressure on Peatland Nutrient Runoff
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Straight fertilizers led with 54% of the Indonesia fertilizer market share in 2024, a position anchored by urea's 60% slice of nitrogen volume and by the government's HET-backed allocation of 4.6 million metric tons for the 2025 season. Abundant local ammonia feedstock keeps urea costs low, while wide dealer networks push product into remote rice and corn belts that consume the bulk of nitrogen inputs under the swasembada pangan plan. Calcium ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate fill soil-specific niches, and in-country ammonia synthesis largely feeds domestic demand, reinforcing leadership for nitrogenous grades within the Indonesia fertilizer market size.
Micronutrient fertilizers post the quickest climb, advancing at an 8.1% CAGR to 2030 as precision farming spreads from Java to Sumatra and supports export-oriented horticulture. Complex NPK sales also rise steadily because 2 million metric tons of new blending capacity lifts national nameplate output to 14 million metric tons, curbing reliance on imports and tailoring micronutrient coatings by micro-region. Phosphatic and potash grades remain exposed to freight swings because Indonesia imports almost all DAP, MAP, and MOP, while secondary nutrients gain traction in acidic soils across Kalimantan and Sumatra that limit long-term plantation yields.
The Indonesia Fertilizer Market Report is Segmented by Type (Complex Fertilizers and Straight Fertilizers {Nitrogenous Fertilizers, Phosphatic Fertilizers, Potash Fertilizers, and More}), and by Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, Commercial Crops, Fruits and Vegetables, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- PT Petrokimia Gresik
- Wilmar International Limited
- Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group)
- PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk
- Yara International ASA
- EuroChem Group AG
- ICL Group Ltd.
- OCI Global N.V.
- PT Meroke Tetap Jaya
- PT Jadi Mas
- PT Dupan Anugerah Lestari
- PT Pupuk Sriwidjaya Palembang
- PT Pupuk Kujang Cikampek
- PT Pupuk Iskandar Muda
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government fertilizer subsidy (HET) expansion
- 4.2.2 Rice and corn self-sufficiency programs
- 4.2.3 New NPK blending plants under Pupuk Indonesia
- 4.2.4 Palm-oil plantation replanting cycle
- 4.2.5 Growth in export-oriented horticulture needing specialty nutrients
- 4.2.6 Early adoption of drone-based precision fertilization in Java
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Subsidy budget cuts creating supply gaps
- 4.3.2 Natural-gas price volatility raising urea costs
- 4.3.3 Proliferation of counterfeit fertilizers in informal channels
- 4.3.4 Environmental pressure on peatland nutrient runoff
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Complex Fertilizers
- 5.1.2 Straight Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.1 Nitrogenous Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.1.1 Urea
- 5.1.2.1.2 Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN)
- 5.1.2.1.3 Ammonia
- 5.1.2.1.4 Ammonium Nitrate
- 5.1.2.1.5 Ammonium Sulfate
- 5.1.2.1.6 Other Nitrogenous Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.2 Phosphatic Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.2.1 Mono-ammonium Phosphate (MAP)
- 5.1.2.2.2 Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP)
- 5.1.2.2.3 Triple Super-phosphate (TSP)
- 5.1.2.2.4 Other Phosphatic Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.3 Potash Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.3.1 Muriate of Potash (MOP)
- 5.1.2.3.2 Other Potash Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.4 Secondary Nutrient Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.5 Micronutrients
- 5.2 By Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.2.2 Pulses and Oil Seeds
- 5.2.3 Commercial Crops
- 5.2.4 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.2.5 Turf and Ornamental Crops
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- 6.4.2 PT Petrokimia Gresik
- 6.4.3 Wilmar International Limited
- 6.4.4 Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group)
- 6.4.5 PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk
- 6.4.6 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.7 EuroChem Group AG
- 6.4.8 ICL Group Ltd.
- 6.4.9 OCI Global N.V.
- 6.4.10 PT Meroke Tetap Jaya
- 6.4.11 PT Jadi Mas
- 6.4.12 PT Dupan Anugerah Lestari
- 6.4.13 PT Pupuk Sriwidjaya Palembang
- 6.4.14 PT Pupuk Kujang Cikampek
- 6.4.15 PT Pupuk Iskandar Muda







