 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1849989
农业酵素:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据、成长预测(2025-2030)Agricultural Enzymes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
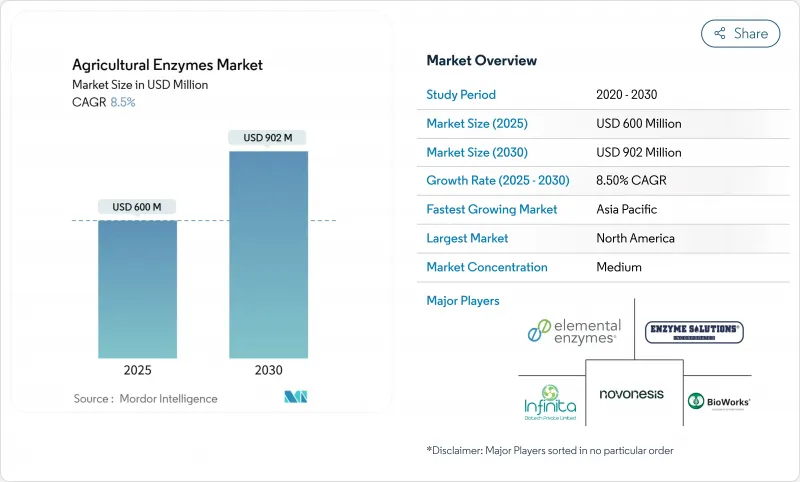
预计到 2025 年,农业酵素市场规模将达到 6 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 9.02 亿美元,预测期内复合年增长率为 8.5%。
这一增长反映了对合成化学品监管的日益严格、消费者对无残留食品需求的不断增长,以及酶製剂和递送技术的稳步进步。成熟市场的商业生产商正在用酵素生物製药取代一些传统投入品,而亚太地区的小农户在专案补贴计画的支持下,正逐步转向使用产量生物製药。精准发酵和人工智慧主导的蛋白质设计技术的同步发展正在缩短产品开发週期,而长期碳信用计画则为采用再生酶解决方案的农民提供了新的收入来源。随着大型农化公司透过合作和收购加强其生物製剂产品组合,以及专业生物技术公司竞相将下一代多酶混合物商业化,竞争日益激烈。
全球农业酵素市场趋势与洞察
有机和无残留食品的需求
随着零售商收紧农药残留基准值,以及欧盟「从农场到餐桌」战略要求到2030年将化学农药的使用量减少50%,全球有机农产品的支出正在增长。农民在有机认证管道可获得20%至30%的溢价,足以抵销采用酵素製剂来促进无化学残留养分转换所带来的转型成本。添加酵素製剂的种植方案有助于缩小有机系统中的产量差距,其原理是透过提高磷氮肥的有效性、增强植物的防御机制以及改善土壤微生物群的平衡。西班牙的商业果园主报告称,2024年从磷肥改用颗粒状磷酸酶-尿素酶混合物后,产量提高了9%,这充分证明了其经济效益。类似的成果目前正在推动加拿大温室蔬菜种植业的推广,液态纤维素酶混合物透过改善作物轮作间的生物质分解,缩短了作物的生长週期。
生物投入物的引入迅速增加
巴西目前已在其超过60%的耕地上应用生物作物保护方案,比例远超过欧盟和美国。作物对合成除草剂和杀菌剂的抗药性日益增强,加速了人们寻找新的作用机制,使农业酵素成为生物防治微生物的协同增效剂。在马托格罗索州,农民在2024/25年度种植玉米时,使用含有脂肪酶和甘露聚醣酶的种子处理剂,使玉米产量提高了4.6%。类似的成长动能在印度也十分明显,该国政府提供的补贴可涵盖高达30%的酵素製剂投入成本,从而推动了小农户的采用,并促进了两位数的市场成长。
零散的监管核准
生物製药开发商仍面临核准时间长短不一的问题,例如在欧盟,根据产品分类的不同,可能需要提交多份申请。虽然美国新推出的统一生物技术监管网站提高了国内的透明度,但全球协调统一仍遥遥无期。审批延误会使平均商业化週期延长18至24个月,增加合规成本,并促使一些公司优先考虑少数但价值较高的市场。规模较小的创新企业面临的困境尤其严重,因为它们通常需要与大型农化公司合作以获得监管支持,这限制了它们自身的市场进入策略。
细分市场分析
磷酸酶能够降解土壤中固定的磷,而土壤中固定的磷占化肥施用量的80%之多。预计到2024年,磷酸酶将占据农业酵素市场37%的份额。由于化肥价格波动,谷物和油籽作物对磷固定解决方案的需求仍然强劲。因此,预计到2030年,磷酸酶在农业酵素市场规模中将继续保持其主导地位。纤维素酶在CelOCE及其相关创新技术的推动下,以13.8%的复合年增长率引领成长。这些酵素能够分解作物残茬,释放醣类,从而为有益微生物提供养分并改善土壤结构。尿素酶、解离酶和蛋白酶构成了纤维素酶产品组合,越来越多的混合酶产品将多种酶的互补活性结合起来,以适应复杂的田间条件。
在高端园艺领域,多酵素混合物的应用趋势尤其明显。种植者希望透过单一处理实现精准的养分调动或增强作物的抗逆性。新兴企业公司正在开发农场发酵套件,使种植者能够酿造新鲜的富含纤维素酶的混合物,从而避免保质期问题并降低成本。领导者正在整合磷酸酶和尿素酶的协同作用,以提高水稻田的氮肥利用效率并减少挥发,这反映出农业酵素市场解决方案的日益丰富。
到2024年,液态产品仍将占据农业酵素市场46.2%的份额,这主要得益于其与现有喷洒设备的兼容性以及高效的叶面吸收。然而,物流成本和对低温运输的依赖正促使产品经理转向耐温性更强的技术。颗粒状产品正以12.4%的复合年增长率快速发展,目前已采用「颗粒剂内生物反应器」结构,可将酵素的稳定性提高至24个月,并在接触土壤后达到定时释放。
粉剂配方经济实惠,但需要专门的混合设备。水溶性混合颗粒模糊了这个界限,兼具液体的便利性和颗粒的耐用性。配方的多样性将是企业脱颖而出的关键,尤其对于那些希望在亚太和非洲等热带地区实现成长、但这些地区低温运输缺口依然存在的公司而言更是如此。
区域分析
北美地区预计到2024年将占农业酵素市场的约35%,这得益于其完善的分销体系和生物投入品快速的监管审批流程。上个种植季,加拿大种植者种植了1,180万公顷基改作物,为配套的酵素製剂计画创造了有利环境。美国的生物刺激剂市场同样蓬勃发展,富含酵素的叶面喷布在杏仁和番茄种植者中越来越受欢迎。
亚太地区是成长最快的地区,预计到2030年将达到10%的复合年增长率。印度的生物农业产业预计到2023年将达到124亿美元,政府补贴可涵盖高达30%的酵素製剂成本,加速小农户对酵素製剂的采用。低温运输缺口仍然是一个重大障碍,印度的酪农产业仍缺乏80%的所需产能,导致製造商专注于颗粒状产品。中国的土地改革鼓励发展更大规模的农场,从而改善了可大规模应用的酵素製剂技术的商业前景。
得益于「绿色新政」下严格的农药减量目标,欧洲在生物防治领域中保持着稳固的地位。预计生物防治活性物质的种类将从2011年的120种增加到2022年的近220种,同期销售额将翻倍,达到15.49亿欧元。南美洲市场在巴西的推动下(巴西的生物製药采用率高达60%)正经历着成熟且不断扩张的市场,尤其是在大豆和玉米的酵素强化种子处理方面。中东和非洲展现出新的潜力,但这取决于监管的清晰度和低温运输投资,其中南非和海湾国家作为早期采用者处于领先地位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 有机和无残留食品的需求
- 生物投入物的快速采用
- 加强研发和产品创新
- 种子披衣衣微剂量递送
- 再生农业碳信用计划
- 农场内酵素发酵装置
- 市场限制
- 监管核准分散
- 土壤和气候造成的性能差异
- 热带地区低温运输缺口
- 化学品的隐性短期投资报酬率
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依酶类型
- 磷酸酶
- 脱氢酶
- 尿素酶
- 蛋白酶
- 解离酶
- 纤维素酶
- 其他酵素类型
- 按剂型
- 液体
- 粉末
- 颗粒状
- 透过使用
- 作物保护
- 生育能力提高
- 植物生长调节
- 透过应用模式
- 种子处理
- 叶面喷布
- 土壤处理
- 按作物类型
- 粮食
- 油籽和豆类
- 水果和蔬菜
- 草坪和观赏植物
- 其他作物
- 按地区
- 北美洲
- 美国
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地区
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 其他欧洲地区
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 日本
- 印度
- 澳洲
- 亚太其他地区
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中东
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公国
- 土耳其
- 其他中东地区
- 非洲
- 南非
- 肯亚
- 其他非洲地区
- 北美洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Novonesis
- Elemental Enzymes
- Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- Bioworks Inc.
- Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- Biocatalysts Ltd
- Enzyme Development Corporation
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Agricultural Enzymes Market size is estimated at USD 600 million in 2025, and is anticipated to reach USD 902 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period.

This growth reflects the tightening of regulations on synthetic chemicals, a greater consumer appetite for residue-free food, and steady advances in enzyme formulation and delivery technologies. Commercial growers in mature markets are replacing a share of conventional inputs with enzyme-based biologicals, while smallholders in Asia-Pacific are moving toward yield-boosting biologicals supported by targeted subsidy programs. Parallel advances in precision fermentation and AI-driven protein design are reducing product-development cycles, while long-term carbon-credit programs are generating new revenue streams for farmers who deploy regenerative enzyme solutions. Competitive intensity is rising as agrochemical majors strengthen biological portfolios through partnerships and acquisitions, and specialized biotechnology firms race to commercialize next-generation multi-enzyme cocktails.
Global Agricultural Enzymes Market Trends and Insights
Organic and Residue-free Food Demand
Global spending on organic produce is climbing as retailers tighten residue thresholds, and the EU Farm to Fork Strategy mandates a 50% cut in chemical pesticide use by 2030. Farmers gain 20-30% price premiums in certified organic channels, offsetting the transition costs of adopting enzymes that mobilize nutrients without chemical residues. Enzyme-embedded programs help close yield gaps in organic systems by enhancing phosphorus and nitrogen availability, fortifying plant defense pathways, and improving soil microbiome balance. Commercial orchard operators in Spain reported a 9% yield uplift after switching from phosphate fertilizers to a blended phosphatase-urease granule in 2024, demonstrating clear economic returns. Similar outcomes are now driving uptake in greenhouse vegetables across Canada, where liquid cellulase blends shorten crop cycles by improving biomass breakdown between rotations.
Biological Input Adoption Surge
Brazil now applies biological crop-protection solutions on more than 60% of cultivated land, significantly ahead of adoption rates in the EU and USA. Mounting resistance to synthetic herbicides and fungicides is accelerating the search for new modes of action, positioning agricultural enzymes as synergistic companions to biocontrol microbes. Row-crop growers in Mato Grosso logged a 4.6% corn-on-corn yield gain in the 2024/25 season after integrating a seed-treatment cocktail containing lipase and mannanase enzymes. Similar momentum is unfolding in India, where state-level subsidy programs cover up to 30% of enzyme input costs, catalyzing smallholder adoption and fueling double-digit market growth.
Fragmented Regulatory Approvals
Biological input developers still navigate divergent approval timelines, with the EU requiring multiple dossiers depending on product classification. The new US Unified Website for Biotechnology Regulation improves domestic transparency, yet global harmonization remains distant.Delays add 18-24 months to average commercialization cycles, inflating compliance costs and prompting some firms to prioritize fewer, high-value markets. Smaller innovators struggle most, often partnering with larger agrochemical companies for regulatory support, which can limit independent go-to-market strategies.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Intensified Research and Development, and Product Innovation
- Seed-coating Micro-dose Delivery
- Cold-chain Gaps in Tropical Regions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Phosphatases captured 37% of the agricultural enzymes market in 2024 by unlocking immobilized soil phosphorus that otherwise reaches 80% of applied fertilizer. As fertilizer prices remain volatile, demand for phosphorus-mobilizing solutions stays strong across cereals and oilseeds. The agricultural enzymes market size for phosphatases is, therefore, set to maintain a dominant revenue position through 2030. Cellulases, propelled by CelOCE and related innovations, top the growth chart at a 13.8% CAGR. These enzymes deconstruct crop residues, releasing sugars that fuel beneficial microbes and improve soil structure. Ureases, lyases, and proteases round out the portfolio, with cocktail products increasingly combining complementary activities to match complex field conditions.
The shift toward multi-enzyme blends is pronounced in high-value horticulture, where growers demand precise nutrient mobilization and stress-response enhancement in one pass. Start-ups are developing on-farm fermentation kits that allow growers to brew fresh cellulase-rich mixes, avoiding shelf-life concerns and reducing costs. Larger players integrate phosphatase-urease synergies to improve nitrogen use efficiency and mitigate volatilization in paddy fields, reflecting a broadening solution set within the agricultural enzymes market.
Liquid products retained 46.2% of the agricultural enzymes market size in 2024, primarily due to their compatibility with existing spraying equipment and efficient foliar absorption. Yet logistics costs and cold-chain dependency are steering product managers toward more temperature-tolerant technologies. Granular products, advancing at 12.4% CAGR, now embed "bioreactor-in-a-granule" architectures that stabilize enzymes for up to 24 months while enabling timed release after soil contact.
Powder formulations occupy a cost-efficient middle ground, but require dedicated mixing equipment. Hybrid water-dispersible granules blur these lines, providing liquid-like convenience with granular durability. Expect competitive differentiation to hinge on formulation versatility, particularly for companies pursuing growth in the Asia-Pacific and African tropics where cold-chain gaps persist.
The Agricultural Enzymes Market is Segmented by Enzyme Type (Phosphatases and More), by Formulation (Liquid and More), by Application (Crop Protection and More), by Mode of Application (Seed Treatment and More), by Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oil Seeds and Pulses, and More), and by Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Middle East, and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America, holding about 35% of the agricultural enzymes market in 2024, benefits from robust distribution infrastructure and rapid regulatory clearance for biological inputs. Canadian growers planted 11.8 million hectare of genetically engineered crops last season, creating a receptive environment for complementary enzyme programs. The US biostimulant segment is equally vibrant, with enzyme-infused foliar sprays gaining traction among almond and tomato producers.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, on track for a 10% CAGR through 2030. India's BioAgri segment reached USD 12.4 billion in 2023, and state subsidies now cover up to 30% of enzyme costs, accelerating adoption among smallholders. Cold-chain gaps remain a material hurdle; 80% of the required capacity is still absent across India's dairy sector, prompting manufacturers to emphasize granular products. China's land-transfer reforms encourage larger farm units, improving the business case for enzyme technologies that can be applied at scale.
Europe retains a strong foothold thanks to stringent pesticide-reduction goals under the Green Deal. Biocontrol active substances climbed from 120 in 2011 to almost 220 in 2022, doubling revenue to EUR 1.549 billion in that period. South America, led by Brazil's trail-blazing 60% biological adoption, remains a mature yet expanding arena, particularly for enzyme-enhanced seed treatments in soy and corn. The Middle East and Africa show emerging promise, though growth hinges on regulatory clarity and cold-chain investment, with South Africa and the Gulf states spearheading early adoption.
- Novonesis
- Elemental Enzymes
- Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- Bioworks Inc.
- Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- Biocatalysts Ltd
- Enzyme Development Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Organic and Residue-free Food Demand
- 4.2.2 Biological Input Adoption Surge
- 4.2.3 Intensified Research and Development, and Product Innovation
- 4.2.4 Seed-coating Micro-dose Delivery
- 4.2.5 Regenerative-Ag Carbon-Credit Programs
- 4.2.6 On-farm Enzyme Fermentation Units
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented Regulatory Approvals
- 4.3.2 Soil and Climate based Performance Variability
- 4.3.3 Cold-chain Gaps in Tropical Regions
- 4.3.4 Invisible Short-term ROI vs Chemicals
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porters Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Enzyme Type
- 5.1.1 Phosphatases
- 5.1.2 Dehydrogenases
- 5.1.3 Ureases
- 5.1.4 Proteases
- 5.1.5 Lyases
- 5.1.6 Cellulases
- 5.1.7 Other Enzyme Types
- 5.2 By Formulation
- 5.2.1 Liquid
- 5.2.2 Powder
- 5.2.3 Granular
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Crop Protection
- 5.3.2 Fertility Enhancement
- 5.3.3 Plant Growth Regulation
- 5.4 By Mode of Application
- 5.4.1 Seed Treatment
- 5.4.2 Foliar Spray
- 5.4.3 Soil Treatment
- 5.5 By Crop Type
- 5.5.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.5.2 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.5.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.5.4 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.5.5 Other Crops
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Russia
- 5.6.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Kenya
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Novonesis
- 6.4.2 Elemental Enzymes
- 6.4.3 Enzyme Solutions Inc.
- 6.4.4 Bioworks Inc.
- 6.4.5 Infinita Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Biocatalysts Ltd
- 6.4.7 Enzyme Development Corporation











