 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1851452
美国工厂自动化和工业控制:市场份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2025-2030 年)United States Factory Automation And Industrial Controls - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
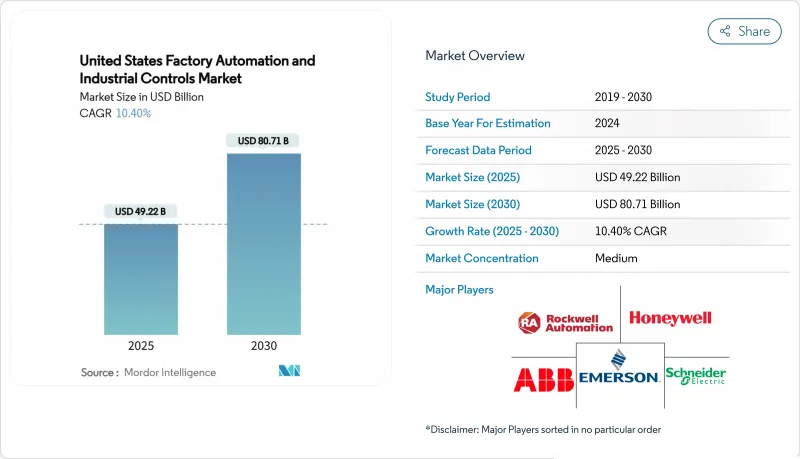
美国工厂自动化和工业控制市场预计到 2025 年将达到 492.2 亿美元,到 2030 年将达到 807.1 亿美元,年复合成长率为 10.40%。
这项成长预测反映了製造业向智慧生产线的转型,这种转型旨在弥补劳动力短缺,遵守更严格的安全奖励,并利用《晶片製造和生产创新法案》(CHIPS Act)和《通货膨胀削减法案》(Inflation Reduction Act)提供的回流激励措施。半导体製造厂、电池工厂和清洁能源组件製造商引领新的资本投资,而棕地也在竞相进行改造,配备可程式逻辑控制器(PLC)、机器视觉系统和工业IoT感测器,以实现即时维修。儘管硬体支出仍然占据主导地位,但随着製造商寻求基于结果的合同,包含网路安全、预测性维护和性能保证等服务的合同正日益受到青睐。虽然网路风险上升和关税不确定性仍然是挑战,但州和联邦政府的政策协调一致,鼓励国内数位化製造业的发展,从而增强了整体投资前景。
美国工厂自动化与工业控制市场趋势与洞察
回流工厂奖励和《晶片製造和生产法案》(CHIPS Act)加速了半导体工厂的自动化进程。
《晶片与科学法案》引发了美国史上规模最大的物料输送浪潮,亚利桑那州、德克萨斯和俄亥俄州数十亿美元的工厂纷纷采用超洁净机器人、奈米级精度运动系统以及可最大限度减少颗粒污染的自动化物料搬运系统。每增加10亿美元的晶片製造投资,通常都会带动对高速晶圆搬运机器人、机器学习驱动的製程控制系统以及安全整合PLC平台的需求,从而推动2亿至3亿美元的自动化支出。各州的税收抵免政策进一步促使大型计划向南部和西部山区转移,这些地区新建的待开发区工厂可以从第一天起就采用全数数位化、无人值守的製造单位。随着工厂业主寻求能够缩短认证週期并保护机密性的承包解决方案,提供硬体、MES软体和全生命週期服务的供应商正在获得竞争优势。
劳动力短缺推动协作机器人的应用
目前製造业面临75万个工作机会的缺口,到2030年,这数字可能高达210万。为了应对这一局面,经营团队正越来越多地部署协作机器人(cobot)来处理单调重复性的工作,同时提升员工在品质、维护、数据分析等方面的技能。调查显示,57%的工厂认为机器人将增强而非取代人类的工作,即使在工会化的工厂中,机器人的应用也不断增长。汽车组装引领着这一潮流,但随着即插即用的协作机器人价格更加亲民,并配备了无需代码的编程接口,中小规模的工厂也纷纷效仿。联邦和州政府的培训津贴正在推动这一趋势,用于支付机器人操作和安全认证计画的学费,加速劳动力与技术的融合。
美国各类棕地设施中传统OT互通性所面临的挑战
历经数次工业革命而建成的工厂运作着各种专有通讯协定,导致资料流难以无缝衔接。系统整合商经常会遇到千禧年之前安装的PLC,这些PLC缺乏原生乙太网路接口,迫使他们使用客製化驱动程序,从而增加计划成本和风险。诸如基于TSN的OPC UA之类的开放架构旨在实现连接标准化,但由于停机时间窗口仍然狭窄且资本预算仍然不足,进展速度低于软体供应商的预期。自动化巨头和组件供应商之间的合作项目已经开始发布预认证的互通性软体包,但许多规模较小的公司仍在推迟计划,直到投资的商业价值明确为止。
细分市场分析
到2024年,硬体支出将占总支出的72%,製造商将采购机器人、驱动器、感测器和人机介面(HMI)来实现生产线的数位化。儘管美国工厂自动化和工业控制硬体市场的规模预计将以中位数个位数的速度成长,但服务领域的扩张速度将更快,这预示着市场将转向基于订阅的支援、远端状态监控和效能保证。领先的供应商正在将软体许可、网路安全管理和人员培训捆绑到多年期合约中,从而稳定收入并将奖励与客户产量挂钩。软体平台将车间数据与製造执行系统(MES)和云端分析连接起来,实现闭合迴路优化,从而减少废料和能源消耗。虽然硬体层仍然至关重要,但价值获取正在转移到整合商和原始设备製造商(OEM)身上,他们将设备、数据和专业知识与可衡量的成果联繫起来。
服务板块12.8%的复合年增长率反映了製造商更倾向于可预测的营运支出而非前期投资。领先的汽车製造商和消费品公司青睐「即服务」型机器人焊接单元、「视觉即服务」检测和「安全即服务」解决方案,以规避技术过时的风险。拥有远端营运中心的供应商提供全天候支援和即时洞察,在不增加人员配置的情况下缩短平均维修时间,并推动持续改进。此类模式创造了新的利润空间,并在竞争激烈的硬体市场中使供应商脱颖而出。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 回流激励措施和《晶片製造和生产法案》(CHIPS Act)加速了美国半导体工厂的自动化进程
- 劳动力短缺推动美国製造业采用协作机器人。
- 《通膨抑制法案》促进清洁能源製造业发展,推动先进自动化投资
- 美国职业安全与健康管理局 (OSHA) 加强机械安全合规性,推动了对安全整合控制系统的需求。
- 美国OEM供应商网路中用于即时OEE优化的棕地工业物联网改装
- 扩大电动车产能需要灵活、高速的组装组装线
- 市场限制
- 美国各类棕地设施中传统OT互通性所面临的挑战
- 儘管有税额扣抵,但高昂的初始资本支出限制了美国中型製造商的采用。
- 互联控制系统中的网路安全风险阻碍了其广泛应用。
- 贸易政策波动影响关键自动化组件的供应
- 价值/供应链分析
- 行业法规和政策
- 监管/技术展望
- 波特五力分析
- 供应商的议价能力
- 消费者议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
- 投资分析
- 关键案例研究和部署场景
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按组件
- 硬体
- 软体
- 服务
- 按类型
- 工业控制系统
- 分散式控制系统(DCS)
- 可程式逻辑控制器(PLC)
- 监控与数据采集(SCADA)
- 产品生命週期管理(PLM)
- 製造执行系统(MES)
- 人机介面(HMI)
- 其他工业控制系统
- 现场设备
- 机器视觉
- 工业机器人
- 马达和驱动器
- 安全系统
- 感测器和发射器
- 其他现场设备
- 工业控制系统
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 石油和天然气
- 化工/石油化工
- 电力/公共产业
- 饮食
- 汽车与运输
- 製药
- 半导体和电子学
- 金属和采矿
- 纸浆和造纸
- 其他终端用户产业
- 按地区(美国)
- 美国东北部
- 美国中西部
- 美国南部
- 美国西部
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Emerson Electric Co.
- ABB Ltd
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Omron Corporation
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Fanuc Corporation
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- KUKA AG
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Beckhoff Automation GmbH and Co. KG
- GE Vernova(GE Automation and Controls)
- Keyence Corporation
- Danfoss Drives A/S
- Parker Hannifin Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Advantech Co.
- Cognex Corporation
- Delta Electronics
- Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems Co.
- BandR Industrial Automation GmbH
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The United States factory automation and industrial controls market reached USD 49.22 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 80.71 billion by 2030, advancing at a 10.40% CAGR.

The projected growth reflects a manufacturing pivot toward smart production lines that offset labor shortages, comply with stricter safety rules, and capture reshoring incentives delivered through the CHIPS Act and Inflation Reduction Act. Semiconductor fabs, battery plants, and clean-energy component makers lead new capital expenditure, while brownfield sites race to retrofit programmable logic controllers (PLCs), machine-vision systems, and industrial IoT sensors for real-time optimization. Hardware continues to dominate spending, yet service-led contracts that bundle cybersecurity, predictive maintenance, and performance guarantees are gaining momentum as manufacturers pursue outcome-based agreements. Heightened cyber-risk and tariff uncertainty remain hurdles, but the overall investment thesis is reinforced by state and federal policy alignment that rewards domestic, digitally enabled production.
United States Factory Automation And Industrial Controls Market Trends and Insights
Reshoring incentives & CHIPS Act accelerate semiconductor factory automation
The CHIPS and Science Act has triggered the largest wave of domestic semiconductor investment on record, with multibillion-dollar fabs in Arizona, Texas, and Ohio specifying ultra-clean robotics, nanometer-precision motion systems, and automated material handling that minimize particle contamination. Every USD 1 billion allocated to chip fabrication typically pulls USD 200-300 million of automation spend, magnifying demand for high-speed wafer transfer robots, machine-learning-driven process control, and safety-integrated PLC platforms. State-level abatements further shift large projects toward the South and Mountain West, where purpose-built greenfield sites can adopt fully digital, lights-out manufacturing cells from day one. Suppliers that bundle hardware, MES software, and lifecycle services gain a competitive edge as fab owners seek turnkey solutions that shorten qualification cycles and protect sensitive.
Labor shortage drives collaborative robotics adoption
Manufacturing payrolls face a 750,000-person gap today and risk 2.1 million unfilled roles by 2030, pressing management teams to deploy collaborative robots (cobots) that assume monotonous, high-repetition tasks while up-skilling employees into quality, maintenance, and data-analytics positions. Surveys show 57% of plants report that robots augment rather than eliminate human jobs, reinforcing adoption even in unionized facilities. Automotive assemblers are first movers, but small and midsize job shops follow suit as plug-and-play cobots drop in price and gain no-code programming interfaces. Federal and state training grants amplify the trend by covering tuition for certificate programs in robot operation and safety, accelerating labor-technology convergence.
Legacy OT interoperability challenges in diverse U.S. brownfield facilities
Plants built across several industrial revolutions run a patchwork of proprietary protocols, making seamless data flow difficult. Integrators often confront PLCs installed before Y2K with no native Ethernet interface, forcing custom drivers that inflate project cost and risk. Open-architecture movements such as OPC UA over TSN aim to standardize connectivity, but progress is slower than software vendors predict because downtime windows remain narrow and capital budgets are stretched. Collaborative initiatives involving automation majors and component suppliers have begun to release pre-certified interoperability bundles, yet many small firms still delay projects until clearer return on investment emerges
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Clean-energy manufacturing boost from Inflation Reduction Act
- OSHA-enforced machine-safety compliance raises demand for safety-integrated control systems
- Cyber-security risks in connected control systems hinder deployment
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hardware accounted for 72% spending in 2024 as manufacturers purchased robots, drives, sensors, and HMIs to digitalize production lines. The United States factory automation and industrial controls market size for hardware is projected to post mid-single-digit growth while services expand faster, signaling a transition toward subscription-based support, remote condition monitoring, and performance guarantees. Leading suppliers bundle software licenses, cybersecurity management, and workforce training into multi-year agreements that stabilize revenue and align incentives with customer output. Software platforms bridge field data to MES and cloud analytics, enabling closed-loop optimization that lowers scrap and energy intensity. The hardware layer thus remains indispensable, yet value capture is migrating to integrators and OEMs that orchestrate devices, data, and domain expertise into measurable outcomes.
The services segment's 12.8% CAGR reflects manufacturer preference for predictable operating expenditure over upfront capital outlay. As-a-service robotic welding cells, vision-as-a-service inspection, and security-as-a-service packages resonate with tier-one automotive and consumer packaged goods firms seeking to hedge technology obsolescence. Vendors that co-locate remote operations centers provide 24/7 support and real-time insight, shortening mean time to repair and driving continuous improvement cycles without inflating headcount. Such models unlock new margin pools and differentiate suppliers in a crowded hardware market.
United States Factory Automation and Industrial Controls Market Report is Segmented by Component (Hardware, Software, and More), Type (Industrial Control Systems and Field Devices), and End-User Industry (Oil and Gas, Metals and Mining, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Emerson Electric Co.
- ABB Ltd
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Omron Corporation
- Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- Fanuc Corporation
- Bosch Rexroth AG
- KUKA AG
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Beckhoff Automation GmbH and Co. KG
- GE Vernova (GE Automation and Controls)
- Keyence Corporation
- Danfoss Drives A/S
- Parker Hannifin Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Banner Engineering Corp.
- Advantech Co.
- Cognex Corporation
- Delta Electronics
- Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems Co.
- BandR Industrial Automation GmbH
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Reshoring Incentives and CHIPS Act Accelerating Semiconductor Factory Automation in the U.S.
- 4.2.2 Labor Shortage Driving Collaborative Robotics Adoption Across U.S. Manufacturing
- 4.2.3 Clean-Energy Manufacturing Boost from Inflation Reduction Act Stimulating Advanced Automation Investments
- 4.2.4 OSHA-Enforced Machine-Safety Compliance Elevating Demand for Safety-Integrated Control Systems
- 4.2.5 Brownfield IIoT Retrofits for Real-Time OEE Optimization Among U.S. OEM Supplier Network
- 4.2.6 EV Production Expansion Necessitating Flexible High-Speed Assembly Automation Lines
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Legacy OT Interoperability Challenges in Diverse U.S. Brownfield Facilities
- 4.3.2 High Initial CapEx Limiting Adoption by Mid-Sized U.S. Manufacturers Despite Tax Credits
- 4.3.3 Cyber-Security Risks in Connected Control Systems Hindering Deployment
- 4.3.4 Trade Policy Volatility Impacting Supply of Critical Automation Components
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Industry Policies and Regulations
- 4.6 Regulatory or Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
- 4.9 Key Case Studies and Implementation Scenarios
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Component
- 5.1.1 Hardware
- 5.1.2 Software
- 5.1.3 Services
- 5.2 By Type
- 5.2.1 Industrial Control Systems
- 5.2.1.1 Distributed Control System (DCS)
- 5.2.1.2 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
- 5.2.1.3 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
- 5.2.1.4 Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- 5.2.1.5 Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
- 5.2.1.6 Human Machine Interface (HMI)
- 5.2.1.7 Other Industrial Control Systems
- 5.2.2 Field Devices
- 5.2.2.1 Machine Vision
- 5.2.2.2 Industrial Robotics
- 5.2.2.3 Motors and Drives
- 5.2.2.4 Safety Systems
- 5.2.2.5 Sensors and Transmitters
- 5.2.2.6 Other Field Devices
- 5.2.1 Industrial Control Systems
- 5.3 By End-user Industry
- 5.3.1 Oil and Gas
- 5.3.2 Chemical and Petrochemical
- 5.3.3 Power and Utilities
- 5.3.4 Food and Beverage
- 5.3.5 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.3.6 Pharmaceutical
- 5.3.7 Semiconductor and Electronics
- 5.3.8 Metals and Mining
- 5.3.9 Pulp and Paper
- 5.3.10 Other End-user Industries
- 5.4 By Region (United States)
- 5.4.1 Northeast U.S.
- 5.4.2 Midwest U.S.
- 5.4.3 South U.S.
- 5.4.4 West U.S.
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.2 Siemens AG
- 6.4.3 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.4 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.5 ABB Ltd
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.7 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.8 Omron Corporation
- 6.4.9 Yokogawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.10 Fanuc Corporation
- 6.4.11 Bosch Rexroth AG
- 6.4.12 KUKA AG
- 6.4.13 Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Beckhoff Automation GmbH and Co. KG
- 6.4.15 GE Vernova (GE Automation and Controls)
- 6.4.16 Keyence Corporation
- 6.4.17 Danfoss Drives A/S
- 6.4.18 Parker Hannifin Corporation
- 6.4.19 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.20 Banner Engineering Corp.
- 6.4.21 Advantech Co.
- 6.4.22 Cognex Corporation
- 6.4.23 Delta Electronics
- 6.4.24 Hitachi Industrial Equipment Systems Co.
- 6.4.25 BandR Industrial Automation GmbH
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment






