 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911473
印尼汽车租赁市场:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Indonesia Car Rental - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
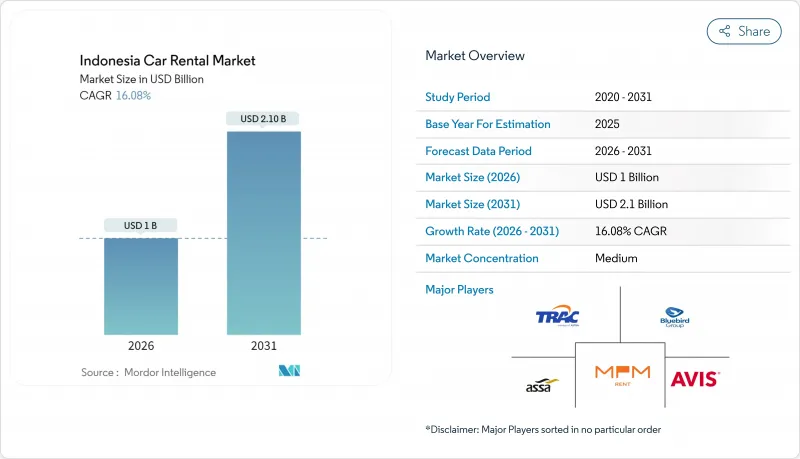
预计到2026年,印尼汽车租赁市场规模将达到10亿美元,高于2025年的8.6亿美元。预计到2031年,该市场规模将达到21亿美元,2026年至2031年的复合年增长率为16.08%。
可支配收入的成长、中产阶级旅行预算的扩大以及智慧型手机的普及,预计将为未来五年印尼旅游业持续两位数成长创造有利条件。政府设定的2025年接待外国游客1460万至1600万人次的目标(高于2024年的1390万人次)表明,即使商务旅行在印尼2024年GDP增长5.05%的推动下復苏,旅游需求依然强劲。线上平台正在重新定义消费者对透明度、按需服务和数位支付的期望。同时,针对电池式电动车(BEV)的新激励措施正将电气化定位为未来的收入来源。随着基于应用程式的出行生态系统模糊了叫车和日常租赁之间的界限,竞争压力日益加剧,迫使传统营运商加快车队现代化和数据驱动定价策略的实施。
印尼汽车租赁市场趋势与洞察
国际和国内游客数量不断增加
2024年,印尼接待了约1,390万国际观光和超过10亿人次的国内旅行,显示随着边境限制的放宽,旅游业迅速復苏。旅游部预测,在落地签计画的扩大和「峇里岛十大新目的地」推广的推动下,2025年游客人数将增加至1,460万至1,600万。对科莫多和龙目岛等区域机场的大规模资本投资增加了座位容量,使旅客来源不再局限于爪哇岛。世界旅游及旅行理事会(WTTC)预测,2025年旅游业将占印尼国内生产毛额(GDP)的4.6%。不断扩大的游客群体直接推动了对租车和专车服务的需求,尤其是在公共交通不便的岛屿上。
数位优先预订平台的激增
预计到2024年,印尼数位经济规模将达到900亿美元,并在电子商务交易激增的推动下持续成长。到2024年,线上预订将占总交易额的很大一部分,并且随着消费者涌向提供即时比价、无现金支付和会员奖励的超级应用程序,线上预订量将逐年显着增长。像Bluebird Taxi与Gojek这样的合作模式,让现有车辆业者能够触及全国的基本客群,同时降低获客成本。聚合平台正在利用其丰富的数据来优化动态定价、提高车辆运转率,并即时追加销售提升销售和辅助服务。
叫车超级应用正在蚕食短期租赁市场。
2024年,Grab和Gojek占据了印尼绝大多数的随选旅游市场。提案的Grab-GoTo合作预计将透过将配送、支付和共乘整合到一个钱包中,进一步深化网路效应。都市区消费者更倾向于选择上门接送服务而非自驾租车,以避免拥堵费和停车位短缺的问题。商务旅客也透过费用管理平台预订共乘服务,以避免前往传统的机场接送柜檯。为了保持竞争力,租车公司正在探索按小时计费的套餐、与航空公司建立忠诚度合作关係,以及为那些不太容易被应用程式商业化所影响的小众市场推出高端SUV车型。
细分市场分析
至2025年,线上通路将占印尼汽车租赁市场收入的68.84%,年复合成长率达16.85%。这一主导地位反映了智慧型手机的高普及率、无现金支付的快速增长以及消费者对整合行程规划、地图和电子钱包等功能的超级应用程式的亲和性。印尼的线下汽车租赁市场仍将以线下旅行社门市为主导,到2025年仍将保持可观的收入,但随着小规模业者越来越多地将车辆上线聚合平台以吸引价格敏感型游客,其市场份额将会下降。
超级应用生态系统整合了叫车、外送和数位银行服务,以促进日常租赁套餐的交叉销售。现有品牌正在引入基于云端的预订引擎、推播通知折扣和人工智慧客服聊天机器人,以提供与科技平台媲美的用户体验。线上收集的数据可以根据国籍、旅行目的和消费金额进行细分,使营运商能够进行里程限制的A/B测试或捆绑销售Wi-Fi路由器以提高收入。
预计到2025年,短期租赁(1-30天)将占印尼汽车租赁市场57.88%的份额,主要受季节性旅游高峰的推动。长期租赁合约预计也将在2025年成为该市场的主要收入来源,年复合成长率将达到17.12%。各公司正采用经营性租赁的方式来节省资金,并将维护责任转移给服务供应商。
长期租赁方案通常包含驾驶人薪资、定期检查和全额保险,从而保障客户免受残值波动的影响。车队管理人员正在应用远端资讯处理技术来监控消费量和预防性维护,从而减少运作。这一趋势也催生了二手车处置渠道,车龄超过三到五年的车辆会被竞标或出售给网约车司机,相比点对点转售,这种方式能更快地收回成本。
构成比到2025年,旅游业将占印尼总收入的63.74%,而商务出行将成为下一个成长引擎,年复合成长率将达到17.62%。印尼的投资合格评级和快速的许可证审批流程正鼓励国际公司迁址,增加了对高阶主管接送、计划现场接送以及外籍员工家属交通的需求。此外,工厂工人的通勤套餐和业务流程外包(BPO)员工的共乘麵包车也扩大了潜在需求。
旅游预订主要集中在峇里岛、日惹和龙目岛,自驾游套装行程包含精心设计的行程和多语言GPS导航。印尼的群岛地形和缺乏城际列车网络,使得租车公司能够充分利用这一优势,提供机场接送服务、优先SIM卡套餐安排和24小时道路救援系统等客製化服务。同时,企业合约也日益多元化,有助于缓解季节性波动,并确保车辆运转率的可预测性。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 国际和国内游客数量不断增加
- 数位优先预订平台的激增
- 企业对长期营业性租赁的需求日益增长
- 政府电动车蓝图加速车队电气化进程
- 清真旅游套餐推动了小众租赁需求。
- 区域机场连通性扩展方面取得快速进展
- 市场限制
- 共享旅游超级应用程式正在蚕食短期租赁市场。
- 现有业者之间日益激烈的价格竞争
- 都市区的交通拥挤和停车位不足会抑制私家车的使用。
- 区域许可製度分散以及税收合规负担
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方和消费者的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 按预订类型
- 在线的
- 离线
- 按租赁期限
- 短期(少于30天/30天内)
- 中期(1个月至12个月)
- 长期(12个月或以上)
- 透过使用
- 旅游休閒
- 日常通勤
- 企业车队/商务旅游
- 机场接送
- 按车辆类型
- 经济型/掀背车
- 多用途汽车(MPV)
- 运动型多用途车(SUV)
- 豪华/行政
- 按燃料类型
- 内燃机(ICE)-汽油车
- 内燃机(ICE)- 柴油
- 油电混合车
- 电池式电动车(BEV)
- 最终用户
- 对于企业
- 个人
- 透过租赁管道
- 聚合平台
- 直接面向消费者(汽车租赁公司)
- 超应用程式捆绑包
- 按地区
- Java
- 雅加达都会区 (Jabodetabek)
- 西爪哇(不包括雅加达)
- 中爪哇和东爪哇
- 峇里岛和努沙登加拉
- 苏门答腊
- 加里曼丹
- 苏拉威西
- 巴布亚马鲁古群岛
- Java
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Blue Bird Group
- TRAC Astra Rent A Car
- Adi Sarana Armada(ASSA Rent)
- Mitra Pinasthika Mustika Rent
- The Hertz Corporation
- Avis Budget Group
- Europcar Indonesia
- Indorent(PT Indomobil Multi Jasa)
- Globe Rent a Car
- Otomo
- Grab Rentals
- GoCar Rental(Gojek)
- DOcar
- Movic
- Easyrent
- Tiket.com Car Rental
- Traveloka Car Rental
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Indonesian car rental market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 1.0 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 0.86 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 2.1 billion, growing at 16.08% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Over the next five years, rising disposable incomes, expanding middle-class travel budgets, and widespread smartphone adoption set a favorable backdrop for sustained double-digit growth. The government's target of welcoming between 14.6 and 16 million foreign visitors in 2025, up from 13.9 million in 2024, signals resilient tourism demand even as business travel rebounds on the back of Indonesia's 5.05% GDP growth in 2024. Online platforms are redefining customer expectations around transparency, on-demand availability, and digital payments, while new incentives for battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) position electrification as a future profit pool. Competitive pressure intensifies as app-based mobility ecosystems blur the line between ride-hailing and daily rentals, prompting traditional operators to accelerate fleet modernization and data-driven pricing strategies.
Indonesia Car Rental Market Trends and Insights
Rising International and Domestic Tourist Arrivals
In 2024, Indonesia welcomed around 13.9 million international visitors and recorded over 1 billion domestic journeys, marking a swift rebound in its tourism sector following the easing of border restrictions. The Ministry of Tourism projects inbound visitors will rise to between 14.6 and 16 million in 2025, supported by visa-on-arrival expansion and marketing of the "10 New Balis" destinations. Significant capital investment in Komodo, Lombok, and other regional airports increases seat capacity and disperses travel flows beyond Java. The World Travel & Tourism Council projects the sector will contribute 4.6% to GDP in 2025. A larger tourist base directly lifts self-drive rentals and chauffeured packages, particularly in islands where public transport is limited.
Surge in Digital-First Booking Platforms
In 2024, Indonesia's digital economy hit the USD 90 billion mark, buoyed by a surge in e-commerce transactions, with projections indicating further growth. Online rental bookings accounted for a substantial share of the overall transactions in 2024 and are growing significantly annually as consumers gravitate to super-apps offering instant price comparison, cashless payments, and loyalty rewards. Partnerships like Blue Bird taxis integrating with Gojek allow legacy fleets to unlock a nationwide customer base while cutting acquisition costs. Aggregators use rich data to fine-tune dynamic pricing, optimize fleet utilization, and upsell insurance or ancillary services in real time.
Ride-Hailing Super-Apps Cannibalizing Short-Term Rentals
Grab and Gojek processed a significant number of on-demand rides in Indonesia during 2024. A proposed Grab-GoTo tie-up could deepen network effects, bundling deliveries, payments, and ride-sharing into a single wallet. Urban consumers prefer door-to-door rides over self-drive rentals to avoid congestion fees and parking scarcity. Corporate travelers also book ride-hailing through expense-management dashboards, bypassing traditional airport pickup counters. To stay relevant, rental firms are exploring hourly packages, loyalty linkage with airlines, and premium SUVs to serve niches less exposed to app-based commoditization.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Corporate Demand for Long-Term Operational Leasing
- Government EV Roadmap Accelerating Fleet Electrification
- Intensifying Price-Led Competition Among Incumbents
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Online channels generated 68.84% of the Indonesian car rental market revenue in 2025, climbing at a 16.85% CAGR. The dominance reflects deep smartphone penetration, a cashless payment boom, and consumer comfort with super-apps integrating trip planning, mapping, and digital wallets. Indonesia's car rental market size, attributed to offline travel-agency counters, remained at significant revenue in 2025 but is losing share as small operators list fleets on aggregator portals to reach price-sensitive tourists.
Super-app ecosystems combine ride-hailing, food delivery, and digital banking, encouraging cross-selling day-long rental packages. Legacy brands adopt cloud-based reservation engines, push-notification discounts, and AI-enabled customer-service chatbots to match the user experience of tech platforms. Data captured online allows segmentation by nationality, trip purpose, and spend, enabling operators to A/B test mileage caps or bundle Wi-Fi routers for incremental revenue.
Short-term bookings, defined as rentals lasting 1-30 days, held a 57.88% share in the Indonesian car rental market in 2025 due to seasonal tourism peaks. Long-term contracts surpassed the noteworthy revenue i the Indonesian car rental market in 2025 and are projected to expand at a 17.12% CAGR. Corporations adopt operating leases to preserve capital and shift maintenance responsibilities to service providers.
Long-term packages typically include driver salaries, periodic servicing, and full insurance, insulating clients from residual-value swings. Fleet managers deploy telematics to monitor fuel consumption and preventive maintenance, reducing downtime. The trend also anchors used-vehicle disposal channels, where cars aged three to five years are auctioned or sold to ride-hailing drivers, recouping capital faster than private resales.
Tourism accounted for 63.74% of revenue in 2025; however, business mobility is on course to become the next growth engine, expanding at an 17.62% CAGR. Indonesia's investment-grade rating and quick licensing approvals spur multinational relocations, raising demand for executive transfers, project-site shuttles, and expatriate family transport. Daily commuting packages for factory staff and shared vans for BPO workers also widen addressable volumes.
Tourism bookings concentrate in Bali, Yogyakarta, and Lombok, where self-drive packages include itinerary curation and GPS navigation in multiple languages. Car rental firms tailor airport meet-and-greet services, fast-track SIM card kits, and 24/7 roadside assistance, leveraging Indonesia's archipelagic geography and limited inter-city rail. In parallel, corporate contracts diversify income, cushioning seasonality and yielding predictable fleet-utilization ratios.
The Indonesia Car Rental Market Report is Segmented by Booking Type (Online and Offline), Rental Duration (Short-Term, Medium-Term and Long-Term), Application (Tourism and Leisure, Daily Commuting, and More), Vehicle Type (Economy/Hatchback and More), Fuel Type (ICE-Petrol, ICE-Diesel, and More), End-User (Corporate and Individual), Rental Channel, and Region. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Blue Bird Group
- TRAC Astra Rent A Car
- Adi Sarana Armada (ASSA Rent)
- Mitra Pinasthika Mustika Rent
- The Hertz Corporation
- Avis Budget Group
- Europcar Indonesia
- Indorent (PT Indomobil Multi Jasa)
- Globe Rent a Car
- Otomo
- Grab Rentals
- GoCar Rental (Gojek)
- DOcar
- Movic
- Easyrent
- Tiket.com Car Rental
- Traveloka Car Rental
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising International and Domestic Tourist Arrivals
- 4.2.2 Surge in Digital-First Booking Platforms
- 4.2.3 Growing Corporate Demand for Long-Term Operational Leasing
- 4.2.4 Government EV Roadmap Accelerating Fleet Electrification
- 4.2.5 Halal-Friendly Tourism Packages Boosting Niche Rentals
- 4.2.6 Rapid Expansion of Secondary-Airport Connectivity
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Ride-Hailing Super-Apps Cannibalizing Short-Term Rentals
- 4.3.2 Intensifying Price-Led Competition Among Incumbents
- 4.3.3 Urban Congestion and Parking Scarcity Deterring Self-Drive
- 4.3.4 Fragmented Regional Licensing and Tax Compliance Burden
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Booking Type
- 5.1.1 Online
- 5.1.2 Offline
- 5.2 By Rental Duration
- 5.2.1 Short-term (Less than/Equals 30 days)
- 5.2.2 Medium-term (1 to 12 months)
- 5.2.3 Long-term (Above 12 months)
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Tourism and Leisure
- 5.3.2 Daily Commuting
- 5.3.3 Corporate Fleet / Business Mobility
- 5.3.4 Airport Transfer
- 5.4 By Vehicle Type
- 5.4.1 Economy / Hatchback
- 5.4.2 Multi-Purpose Vehicle (MPV)
- 5.4.3 Sports Utility Vehicle (SUV)
- 5.4.4 Luxury / Executive
- 5.5 By Fuel Type
- 5.5.1 ICE - Petrol
- 5.5.2 ICE - Diesel
- 5.5.3 Hybrid-Electric
- 5.5.4 Battery-Electric (BEV)
- 5.6 By End-user
- 5.6.1 Corporate
- 5.6.2 Individual
- 5.7 By Rental Channel
- 5.7.1 Aggregator Platforms
- 5.7.2 Direct-to-Consumer (Rental Co.)
- 5.7.3 Super-App-Based Bundles
- 5.8 By Region
- 5.8.1 Java
- 5.8.1.1 Greater Jakarta (Jabodetabek)
- 5.8.1.2 West Java (ex-Jakarta)
- 5.8.1.3 Central and East Java
- 5.8.2 Bali and Nusa Tenggara
- 5.8.3 Sumatra
- 5.8.4 Kalimantan
- 5.8.5 Sulawesi
- 5.8.6 Papua and Maluku
- 5.8.1 Java
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Blue Bird Group
- 6.4.2 TRAC Astra Rent A Car
- 6.4.3 Adi Sarana Armada (ASSA Rent)
- 6.4.4 Mitra Pinasthika Mustika Rent
- 6.4.5 The Hertz Corporation
- 6.4.6 Avis Budget Group
- 6.4.7 Europcar Indonesia
- 6.4.8 Indorent (PT Indomobil Multi Jasa)
- 6.4.9 Globe Rent a Car
- 6.4.10 Otomo
- 6.4.11 Grab Rentals
- 6.4.12 GoCar Rental (Gojek)
- 6.4.13 DOcar
- 6.4.14 Movic
- 6.4.15 Easyrent
- 6.4.16 Tiket.com Car Rental
- 6.4.17 Traveloka Car Rental
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment









