 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1885866
超快速电动车充电(350kW+)系统市场机会、成长驱动因素、产业趋势分析及2025-2034年预测Ultra-Fast EV Charging (350kW+) Systems Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034 |
||||||
2024 年全球超快速电动车充电(350kW+)系统市值为 21.8 亿美元,预计到 2034 年将以 20.1% 的复合年增长率增长至 148.1 亿美元。
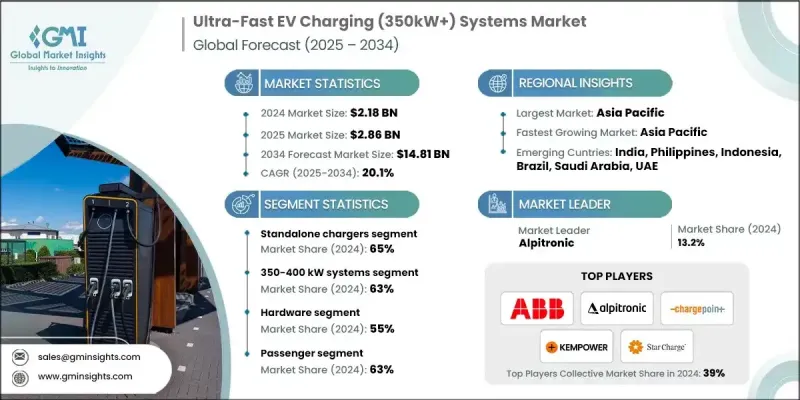
全球对超快速电动车充电器(350kW+)的需求激增,正在重塑全球电动车基础设施。这些高功率充电器可使相容车辆在20分钟内将电池电量充至80%,大幅减少停机时间,加速电动车的普及。它们对于乘用车和商用车电动车领域都至关重要,提供高压运转、可扩展的模组化设计和先进的热管理。充电器製造商、电力电子供应商和电力合作伙伴正在进行策略性投资,以简化技术整合、降低安装成本并提高系统可靠性。新冠疫情间接推动了基础设施投资,因为各国政府强调低排放出行、永续性和清洁交通,并推出激励措施以扩大高功率充电网路。电动车普及率的不断提高进一步增加了对能够高效服务于商用车和乘用车的350kW+充电系统的需求。
| 市场范围 | |
|---|---|
| 起始年份 | 2024 |
| 预测年份 | 2025-2034 |
| 起始值 | 21.8亿美元 |
| 预测值 | 148.1亿美元 |
| 复合年增长率 | 20.1% |
2024年,独立式充电桩市占率达到65%,预计到2034年将以20.5%的复合年增长率成长。独立式充电桩凭藉其部署灵活性、较低的安装复杂性以及对公共和高速公路网路的适用性,占据了市场主导地位。它们可以独立运行,安装在服务站、零售中心和休息区等场所,并提供350千瓦以上的超快速充电,满足电动车用户日益增长的快速充电需求。
2024年,350-400千瓦系统市占率达到63%,预计2025年至2034年间将以20.5%的复合年增长率成长。这些系统因其性价比高且相容于大多数800伏特电动车架构而备受青睐。它们可在20分钟内将电池容量充至70-80%,是乘用车和轻型商用车的理想选择。其广泛的电动车相容性推动了全球公共和高速公路充电网路的普及。
中国超快速电动车充电(350kW+)系统市场占40%的份额,市场规模达3.666亿美元。中国在该市场的领先地位归功于其大规模的电动车生产、政府支持的基础设施项目以及成本效益高的製造生态系统。 「新能源汽车(NEV)」政策的出台,以及超过150亿美元的充电基础设施投资,加速了超快充电桩在各大城市和高速公路的部署。
超快速电动车充电(350kW+)系统市场的主要参与者包括西门子、ABB、Alpitronic、台达、华为、ChargePoint、Heliox、Kempower、StarCharge 和 Tritium。市场参与者正大力投资研发,以提高充电器的效率、模组化程度和热管理能力,同时降低安装和维护成本。各公司正与电力公司、电动车製造商和基础设施开发商建立战略合作伙伴关係,以扩展充电网路并确保与各种电动车型号的兼容性。地理扩张,尤其是在电动车普及率高的地区,有助于巩固市场地位。併购使公司能够整合技术并提升服务能力。此外,各公司也正在整合数位平台,以实现即时监控、预测性维护和便利的支付解决方案,进而提升客户体验。
目录
第一章:方法论
- 市场范围和定义
- 研究设计
- 研究方法
- 资料收集方法
- 资料探勘来源
- 全球的
- 地区/国家
- 基准估算和计算
- 基准年计算
- 市场估算的关键趋势
- 初步研究和验证
- 原始资料
- 预测模型
- 研究假设和局限性
第二章:执行概要
第三章:行业洞察
- 产业生态系分析
- 供应商格局
- 利润率分析
- 成本结构
- 每个阶段的价值增加
- 影响价值链的因素
- 中断
- 产业影响因素
- 成长驱动因素
- 全球乘用车和商用车领域电动车普及率激增
- 政府加大资金投入和基础设施激励措施,以促进超快速充电设施的部署
- OEM与充电网路业者合作进行大规模推广活动
- 电力电子、转换器和热管理技术的进步
- 车队电气化计画的增加推动了高吞吐量充电需求。
- 产业陷阱与挑战
- 超快速充电基础设施的高昂资本支出和安装成本
- 多个地区电网容量有限,面临能源供应挑战
- 市场机会
- 提高储能和再生能源与超快速充电器的整合度
- 新兴市场和发展中市场超快速充电部署的增加
- 对专用车队和物流充电中心的需求不断增长
- 模组化、多埠和可扩展充电系统的发展突飞猛进
- 企业和政府永续发展措施的增加促进了基础设施投资。
- 成长驱动因素
- 成长潜力分析
- 监管环境
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 波特的分析
- PESTEL 分析
- 技术与创新格局
- 当前技术趋势
- 新兴技术
- 专利分析
- 价格趋势
- 按地区
- 按组件
- 成本細項分析
- 永续性和环境影响分析
- 永续实践
- 减少废弃物策略
- 生产中的能源效率
- 环保倡议
- 碳足迹考量
- 投资和融资分析
- 政府资助计划
- NEVI 公式计划(50亿美元)
- 欧盟连接欧洲设施(CEF)
- 替代燃料基础设施设施(AFIF)
- 中国新能源汽车补贴计划
- 州和省级激励措施
- 私人投资趋势
- 公私合作模式
- 绿色债券与永续金融
- 基础建设基金与房地产投资信託基金
- 政府资助计划
- 商业模式分析
- CPO自有营运模式
- OEM自有充电网络
- 公用事业公司拥有的基础设施
- 零售和商业房东
- 计费即服务 (CaaS) 模式
- 混合及新兴模型
- 安装调试过程
- 安装前规划
- 土建工程及场地准备
- 电气安装
- 调试与测试
- 按功率位准进行时间轴分析
- 安装成本明细
- 未来展望与机会
- 新兴应用
- 下一代创新
- 投资机会
- 风险评估
第四章:竞争格局
- 介绍
- 公司市占率分析
- 北美洲
- 欧洲
- 亚太地区
- 拉丁美洲
- 主要市场参与者的竞争分析
- 竞争定位矩阵
- 战略展望矩阵
- 关键进展
- 併购
- 合作伙伴关係与合作
- 新产品发布
- 扩张计划和资金
第五章:市场估算与预测:依组件划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 硬体
- 电源模组
- 电缆和连接器
- 冷却系统
- 外壳和安装支架
- 软体
- 能源管理系统
- 支付和存取控制
- 远端监控与分析
- 服务
- 安装与调试
- 维护与升级
- 网管
第六章:市场估计与预测:依安装量划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 独立式充电器
- 整合系统
第七章:市场估算与预测:依功率等级划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 350-400千瓦系统
- 400-500千瓦系统
- 500千瓦以上的系统
第八章:市场估算与预测:依配置划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 单埠系统
- 多埠系统(2-4个连接埠)
- 模组化可扩充系统
第九章:市场估计与预测:依应用领域划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 公共充电站
- 商业车队充电
- 住宅/私人充电
- 高速公路和长途充电网络
第十章:市场估价与预测:依车辆类型划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 搭乘用车
- 掀背车
- 轿车
- SUV
- 商用车辆
- 轻型商用车(LCV)
- 中型商用车(MCV)
- 重型商用车(HCV)
第十一章:市场估计与预测:按地区划分,2021-2034年
- 主要趋势
- 北美洲
- 我们
- 加拿大
- 欧洲
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 俄罗斯
- 亚太地区
- 中国
- 印度
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 韩国
- 菲律宾
- 印尼
- 拉丁美洲
- 巴西
- 墨西哥
- 阿根廷
- MEA
- 南非
- 沙乌地阿拉伯
- 阿联酋
第十二章:公司简介
- 全球参与者
- ABB
- Alpitronic
- ChargePoint
- Delta
- Enel X
- Exicom Power Solutions
- Huawei
- Kempower
- Phoenix Contact
- StarCharge
- Webasto
- 区域玩家
- BTC Power
- Circontrol
- Compleo Charging Solutions
- EVTEC
- Heliox
- Ingeteam
- Phihong
- SK Signet
- TELD (TGood Electric)
- Tritium DCFC
- 新兴参与者
- Blink Charging
- Designwerk Technologies
- Gravity
- HICI Digital Power Technology
- Nxu
- Qingdao Hardhitter Electric
- Rhombus Energy Solutions (BorgWarner)
- Shijiazhuang Tonhe Electronics
- Zerova (Noodoe EV)
The Global Ultra-Fast EV Charging (350kW+) Systems Market was valued at USD 2.18 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 20.1% to reach USD 14.81 billion by 2034.

The surge in demand for ultra-fast EV chargers (350kW+) is reshaping the electric vehicle infrastructure worldwide. These high-power chargers allow compatible vehicles to reach 80% battery capacity in under 20 minutes, significantly reducing downtime and accelerating EV adoption. They are essential for both passenger and commercial EV segments, offering high-voltage operation, scalable modular designs, and advanced thermal management. Charger manufacturers, power electronics suppliers, and utility partners are investing strategically to simplify technology integration, lower installation costs, and enhance system reliability. The COVID-19 pandemic indirectly boosted infrastructure investments, as governments emphasized low-emission mobility, sustainability, and clean transportation, introducing incentives to expand high-power charging networks. Rising EV adoption has further increased the demand for 350 kW+ charging systems capable of servicing both commercial and passenger vehicles efficiently.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $2.18 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $14.81 Billion |
| CAGR | 20.1% |
The standalone chargers segment held a 65% share in 2024 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.5% through 2034. Standalone chargers dominate the market due to their deployment flexibility, lower installation complexity, and suitability for public and highway networks. Operating independently, they can be installed across service stations, retail hubs, and rest areas while providing ultra-fast 350 kW+ charging, meeting the growing demand for rapid turnaround among EV users.
The 350-400 kW systems segment captured 63% share in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 20.5% between 2025 and 2034. These systems are favored for their cost-performance balance and compatibility with most 800 V EV architectures. They can recharge 70-80% of battery capacity in under 20 minutes, making them ideal for passenger and light commercial vehicles. Their broad EV compatibility has driven adoption across public and highway charging networks globally.
China Ultra-Fast EV Charging (350kW+) Systems Market held a 40% share, generating USD 366.6 million. The country's dominance is attributed to its large-scale EV production, government-supported infrastructure programs, and cost-effective manufacturing ecosystem. Policy initiatives under the "New Energy Vehicle (NEV)" program, coupled with investments exceeding USD 15 billion in charging infrastructure, have accelerated the deployment of ultra-fast chargers across major cities and highways.
Key players in the Ultra-Fast EV Charging (350kW+) Systems Market include Siemens, ABB, Alpitronic, Delta, Huawei, ChargePoint, Heliox, Kempower, StarCharge, and Tritium. Market players are investing heavily in R&D to improve charger efficiency, modularity, and thermal management while reducing installation and maintenance costs. Companies are forming strategic partnerships with utility providers, EV manufacturers, and infrastructure developers to expand charging networks and ensure compatibility with diverse EV models. Geographic expansion, particularly in regions with high EV adoption, strengthens market presence. Mergers and acquisitions allow firms to consolidate technology and enhance service capabilities. Companies are also integrating digital platforms for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and user-friendly payment solutions to enhance customer experience.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 360° synopsis, 2021 - 2034
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Regional
- 2.2.2 Installation
- 2.2.3 Power rating
- 2.2.4 Component
- 2.2.5 Vehicle
- 2.2.6 Application
- 2.2.7 Configuration
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2026-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future outlook and strategic recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin analysis
- 3.1.3 Cost structure
- 3.1.4 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.5 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.6 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.1.1 Surge in global EV adoption across passenger and commercial segments
- 3.2.1.2 Increase in government funding and infrastructure incentives for ultra-fast charging deployment
- 3.2.1.3 Rise in OEM and charging network collaborations for large-scale rollouts
- 3.2.1.4 Growth in advancements of power electronics, converters, and thermal management technologies
- 3.2.1.5 Increase in fleet electrification initiatives driving high-throughput charging demand
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.2.1 High capital expenditure and installation costs for ultra-fast charging infrastructure
- 3.2.2.2 Limited grid capacity and energy supply challenges in several regions
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.2.3.1 Increase in integration of energy storage and renewables with ultra-fast chargers
- 3.2.3.2 Rise in ultra-fast charging deployment across emerging and developing markets
- 3.2.3.3 Growth in demand for dedicated fleet and logistics charging hubs
- 3.2.3.4 Surge in development of modular, multi-port, and scalable charging systems
- 3.2.3.5 Increase in corporate and government sustainability initiatives boosting infrastructure investment
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 LAMEA
- 3.5 Porter's analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.7.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.8 Patent analysis
- 3.9 Price trends
- 3.9.1 By region
- 3.9.2 By component
- 3.10 Cost breakdown analysis
- 3.11 Sustainability and environmental impact analysis
- 3.11.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.11.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.11.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.11.4 Eco-friendly initiatives
- 3.12 Carbon footprint considerations
- 3.13 Investment and funding analysis
- 3.13.1 Government funding programs
- 3.13.1.1 NEVI formula program ($5 billion)
- 3.13.1.2 EU connecting Europe facility (CEF)
- 3.13.1.3 Alternative fuels infrastructure facility (AFIF)
- 3.13.1.4 China NEV subsidy programs
- 3.13.1.5 State and provincial incentives
- 3.13.2 Private investment trends
- 3.13.3 Public-private partnership models
- 3.13.4 Green bonds and sustainable finance
- 3.13.5 Infrastructure funds and REITs
- 3.13.1 Government funding programs
- 3.14 Business model analysis
- 3.14.1 CPO-owned & operated model
- 3.14.2 OEM-owned charging networks
- 3.14.3 Utility-owned infrastructure
- 3.14.4 Retail & commercial host-owned
- 3.14.5 Charging-as-a-service (CaaS) model
- 3.14.6 Hybrid & emerging models
- 3.15 Installation & commissioning process
- 3.15.1 Pre-installation planning
- 3.15.2 Civil works & site preparation
- 3.15.3 Electrical installation
- 3.15.4 Commissioning & testing
- 3.15.5 Timeline analysis by power level
- 3.15.6 Installation cost breakdown
- 3.16 Future outlook & opportunities
- 3.16.1 Emerging Applications
- 3.16.2 Next-Generation Innovations
- 3.16.3 Investment Opportunities
- 3.16.4 Risk Assessment
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 LAMEA
- 4.3 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.4 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.5 Strategic outlook matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New Product Launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion Plans and funding
Chapter 5 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Component, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Hardware
- 5.2.1 Power modules
- 5.2.2 Cables & connectors
- 5.2.3 Cooling systems
- 5.2.4 Enclosures & mounts
- 5.3 Software
- 5.3.1 Energy management systems
- 5.3.2 Payment & access control
- 5.3.3 Remote monitoring & analytics
- 5.4 Services
- 5.4.1 Installation & commissioning
- 5.4.2 Maintenance & upgrades
- 5.4.3 Network management
Chapter 6 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Installation, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Standalone chargers
- 6.3 Integrated systems
Chapter 7 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Power rating, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 350-400 kW systems
- 7.3 400-500 kW systems
- 7.4 500+ kW systems
Chapter 8 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Configuration, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Single-port systems
- 8.3 Multi-port systems (2-4 ports)
- 8.4 Modular expandable systems
Chapter 9 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Application, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 Public charging stations
- 9.3 Commercial fleet charging
- 9.4 Residential / private charging
- 9.5 Highway and long-distance charging networks
Chapter 10 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Vehicle, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 10.1 Key trends
- 10.2 Passenger vehicles
- 10.2.1 Hatchbacks
- 10.2.2 Sedans
- 10.2.3 SUV
- 10.3 Commercial vehicles
- 10.3.1 Light commercial vehicles (LCV)
- 10.3.2 Medium commercial vehicles (MCV)
- 10.3.3 Heavy commercial vehicles (HCV)
Chapter 11 Market Estimates & Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 ($Bn, Units)
- 11.1 Key trends
- 11.2 North America
- 11.2.1 US
- 11.2.2 Canada
- 11.3 Europe
- 11.3.1 Germany
- 11.3.2 UK
- 11.3.3 France
- 11.3.4 Italy
- 11.3.5 Spain
- 11.3.6 Russia
- 11.4 Asia Pacific
- 11.4.1 China
- 11.4.2 India
- 11.4.3 Japan
- 11.4.4 Australia
- 11.4.5 South Korea
- 11.4.6 Philippines
- 11.4.7 Indonesia
- 11.5 Latin America
- 11.5.1 Brazil
- 11.5.2 Mexico
- 11.5.3 Argentina
- 11.6 MEA
- 11.6.1 South Africa
- 11.6.2 Saudi Arabia
- 11.6.3 UAE
Chapter 12 Company Profiles
- 12.1 Global Players
- 12.1.1 ABB
- 12.1.2 Alpitronic
- 12.1.3 ChargePoint
- 12.1.4 Delta
- 12.1.5 Enel X
- 12.1.6 Exicom Power Solutions
- 12.1.7 Huawei
- 12.1.8 Kempower
- 12.1.9 Phoenix Contact
- 12.1.10 StarCharge
- 12.1.11 Webasto
- 12.2 Regional Players
- 12.2.1 BTC Power
- 12.2.2 Circontrol
- 12.2.3 Compleo Charging Solutions
- 12.2.4 EVTEC
- 12.2.5 Heliox
- 12.2.6 Ingeteam
- 12.2.7 Phihong
- 12.2.8 SK Signet
- 12.2.9 TELD (TGood Electric)
- 12.2.10 Tritium DCFC
- 12.3 Emerging Players
- 12.3.1 Blink Charging
- 12.3.2 Designwerk Technologies
- 12.3.3 Gravity
- 12.3.4 HICI Digital Power Technology
- 12.3.5 Nxu
- 12.3.6 Qingdao Hardhitter Electric
- 12.3.7 Rhombus Energy Solutions (BorgWarner)
- 12.3.8 Shijiazhuang Tonhe Electronics
- 12.3.9 Zerova (Noodoe EV)







