 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911316
欧洲厢型车市场-份额分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Europe Van - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
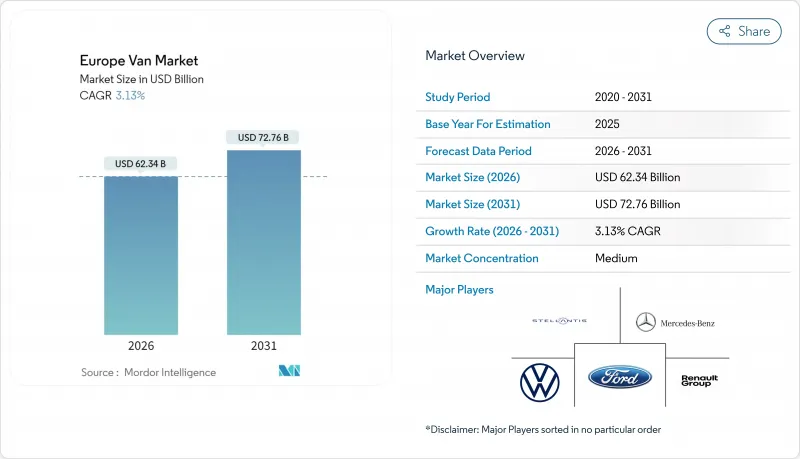
预计到 2026 年,欧洲厢型车市场规模将达到 623.4 亿美元,高于 2025 年的 604.5 亿美元。预计到 2031 年,该市场规模将达到 727.6 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 3.13%。
这一增长势头得益于欧盟日益严格的排放法规、电子商务物流的快速发展以及电池价格的快速下降。同时,柴油动力系统仍是长途运输能力的基础。德国车队营运商继续引领市场,他们将大规模批量采购与自有充电基础设施的投资相结合。此外,Stellantis 和梅赛德斯-奔驰的平台策略,以及比亚迪和上汽大通等注重价格的新兴参与企业的崛起,正在重塑竞争格局,因为整合充电服务、软体和融资已成为交易的标配。儘管半导体短缺和缺乏场内快速充电基础设施限制了短期生产,但总拥有成本 (TCO) 的平衡以及替代燃料法规的趋同正在推动欧洲厢式货车市场向电动化车队不可逆转地转变。
欧洲厢型车市场趋势与洞察
电动货车销量上升
在欧盟27个市场中的21个市场,电动货车的总拥有成本已经超过了柴油车,因此,电动货车的采购决策正从政策合规转向成本主导。 DHL订购2400辆福特E-Transit的合约表明,批量订单和工资扣除可以如何加速规模化发展。 B类驾照的适用范围扩大到4.25吨,取消了驾照限制。预测显示,到2026年,轻型商用电池式电动车(BEV)的价格将与柴油车持平,从而锁定长期需求。车队管理人员也重视电动货车更安静的驾驶体验和即时扭力反应,这些优势可以提高都市区生产力,即使在充电网路不发达的地区,电动货车的普及也推动了其市场成长。
电子商务最后一公里需求快速成长
快速成长的电子商务推动了配送车辆密度的增加和配送路线的缩短,从而优化了都市区配送中心对静音、零排放纯电动车(BEV)的需求。巴塞隆纳的微型配送中心计画减少了30%的配送车辆里程,并采用了紧凑型纯电动车(具有瞬时扭力和低噪音特性),这些车辆不会限制都市区的通行。暗店和定时配送模式将需求分散到季节性高峰之外,确保全年运转率。路线优化软体与交通系统协同工作,在提高配送效率的同时降低能耗。这些营运优势,加上不受限制的都市区通行,使得电动货车成为西欧各地最后一公里配送的首选车辆。
电池高成本,车辆资本投资较高
儘管营运成本有所降低,电动货车的初始价格仍比柴油车高出40%至60%,而且在大型场所建造充电设施需要超过100万欧元(约117万美元)的投资,这给中小运输业者带来了沉重的融资压力。租赁公司缺乏残值数据加剧了资金筹措障碍,投资回收期往往超出正常的预算週期。利率上升进一步加重了资本负担,而各国公共补贴差异巨大,降低了规划的确定性。这些成本障碍减缓了区域营运商和中小企业采用电动货车的步伐,他们通常会推迟电动化进程,直到二手纯电动车的供应改善或出现能够承担初始成本的「卡车即服务」承包解决方案。
细分市场分析
预计到2025年,N1类I型厢型车将占欧洲厢型车市场的48.76%,并在2031年之前以3.52%的复合年增长率成长。这反映了零排放车辆驾驶执照要求的放宽,B类驾照的适用范围已扩大至4.25吨。 N1类I型厢型车尺寸紧凑,非常适合低排放区、狭窄的装卸货平台和快速路边配送,而其在实际驾驶中250-300公里的续航里程足以满足整个都市区工作週期,无需在工作途中充电。
二类和三类轻型商用车对于冷藏食品运输、施工机械和区域配送仍然至关重要,但它们仍需等待高密度充电器和续航里程达400公里的电池(例如福特新款89kWh E-Transit所搭载的电池)的到来。车队管理人员正在密切关注每千瓦时有效载荷效率(kg/kWh),以确保增加的电池重量不会影响生产效率。随着新一代磷酸锂铁锂电池组在重量和成本方面的进步,较重的车型有望加入早期采用浪潮,从而巩固轻型商用车作为电气化桥头堡的地位。
到2025年,容积超过5立方公尺的车型将占欧洲厢型车市场62.78%的份额,这主要得益于经销商为实现高有效载荷率而最大化每公里收入。汽车製造商正透过模组化平台来满足这一核心市场的需求,这些平台结合了高车顶、多种轴距和2吨的有效载荷限制,例如雷诺Master的11-22立方公尺配置。
然而,容积小于5立方公尺的车型正在崛起,年复合成长率达4.67%。这主要得益于生鲜和药品配送公司对车辆在街道上的操控性、便利停车以及低容量电池的需求,这些因素都有助于降低成本。紧凑型纯电动车由于配备了容量小于50千瓦时的电池组,降低了购置成本和充电时间,因此能够更快地实现总拥有成本(TCO)的损益平衡。这种两极化的市场格局迫使汽车製造商(OEM)采取两种不同的蓝图:一种是针对托盘货物运输优化的高负载容量车型,另一种是专为密集都市区环线配送而设计的小型、软体驱动型微型货车。后者在等待时间和通行费会削弱柴油车经济性的环境中更具优势。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 分析师支持(3个月)
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 电动货车销量成长
- 电子商务最后一公里配送快速成长
- 欧盟低排放区法规
- 都市区微型仓配中心的采用
- OEM滑板电动车平台
- 电池即服务 (BaaS) 车队模式
- 市场限制
- 电池和车辆资本投资高成本
- 半导体供应受限
- 仓库内缺乏快速充电设施
- 驾驶人及驾照发放规定
- 价值/供应链分析
- 监管环境
- 技术展望
- 波特五力模型
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模及成长预测(价值(美元)及销售量(单位))
- 按车辆总重量
- N1 一级(总重量低于 2 吨)
- N1 II 类(总重量 2-2.5 吨)
- N1 III级(总重量2.5-3.5吨)
- 透过货舱
- 5立方米或以下
- 5立方米或以上
- 最终用户
- 商用车辆车队
- 对于政府和地方政府
- 租赁公司
- 按驱动类型
- 内燃机 - 汽油
- 内燃机 - 柴油
- 电池电动车
- 油电混合车
- 燃料电池电动车
- 替代燃料(压缩天然气/液化石油气)
- 按销售管道
- 厂商直销车队
- 授权经销商
- 线上/数位平台
- 按国家/地区
- 德国
- 英国
- 法国
- 义大利
- 西班牙
- 荷兰
- 瑞典
- 挪威
- 其他欧洲地区
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Stellantis NV
- Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- Volkswagen AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Renault Group
- Iveco Group NV
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- BYD Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Company
- SAIC Maxus Automotive
- MAN Truck & Bus SE
- Opel Automobile GmbH
- London Electric Vehicle Company(LEVC)
- B-ON GmbH(StreetScooter GmbH)
- Rivian Automotive LLC
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The European van market market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 62.34 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 60.45 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 72.76 billion, growing at 3.13% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Momentum stems from tightening EU emission limits, the boom in e-commerce logistics, and fast-falling battery prices, while diesel powertrains still underpin long-haul capacity. Market leadership continues to rest with German fleets that have the scale to combine large procurement orders and in-house charging investments. At the same time, platform strategies from Stellantis and Mercedes-Benz, along with price-focused entrants BYD and SAIC Maxus, are redefining competitive dynamics as integrated charging, software, and financing services become part of every deal. Although semiconductor bottlenecks and depot fast-charging gaps curb near-term output, the convergence of total cost of ownership (TCO) parity and alternative-fuels rules indicates the European van market is approaching an irreversible switch toward electrified fleets.
Europe Van Market Trends and Insights
Rise in Sales of Electric Vans
Electric-van purchases are moving from policy compliance to cost-driven decisions as the total cost of ownership now beats diesel in 21 of 27 EU markets. DHL's 2,400-unit Ford E-Transit deal shows how bulk orders and salary-sacrifice programs accelerate scale, while B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t erase licensing limits. Projections indicate price parity for light commercial BEVs by 2026, locking in long-term demand. Fleet managers also value silent operation and instant torque that improve urban productivity, reinforcing momentum even where charging networks remain incomplete.
E-commerce Last-Mile Boom
Rapid e-commerce growth drives higher van density and shorter delivery routes, making quiet, zero-emission BEVs ideal for city nodes. Barcelona's micro-hub program trimmed van miles 30%, favoring compact BEVs with instant torque and low noise that face no urban access bans . Dark stores and subscription delivery models spread demand beyond seasonal peaks, ensuring year-round utilization. Route-optimization software integrates with traffic systems, boosting drop rates while lowering energy use. These operational gains combine with unrestricted urban access to make electric vans the preferred workhorse for last-mile fleets across Western Europe.
High Battery and Vehicle CAPEX
Up-front prices for electric vans remain 40-60% above diesel, while depot chargers can push investment above EUR 1 million (~USD 1.17 million) for large sites, straining the cash flow of small haulers despite lower running costs . Financing hurdles grow as leasing firms lack residual-value data, lengthening payback periods beyond typical budget cycles. Rising interest rates add to capital pressure, and public subsidies vary widely by country, creating planning uncertainty. These cost barriers slow adoption among regional operators and SMEs, who often defer electrification until second-hand BEV supply improves or turnkey Truck-as-a-Service packages absorb initial outlays.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- EU Low-Emission-Zone Mandates
- Urban Micro-fulfilment Hub Adoption
- Semiconductor Supply Constraints
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
N1 Class I vans claimed 48.76% of the European van market share in 2025 and will expand at a 3.52% CAGR through 2031, reflecting how B-permit extensions up to 4.25 t remove driver-license barriers for zero-emission vehicles. Their compact footprints suit low-emission zones, narrow loading bays, and quick curbside drop-offs, while real-world battery ranges of 250-300 km now cover full urban duty cycles without mid-shift charging.
Class II and III models remain indispensable for refrigerated food, construction tools, and regional parcel runs but await denser chargers and 400 km batteries such as Ford's 89 kWh E-Transit update. Fleet managers compare kilograms delivered per kilowatt-hour payload efficiency to ensure that added battery mass never dilutes productivity. As next-generation lithium-iron-phosphate packs cut weight and cost, heavier classes are positioned to join the early adoption curve, reinforcing the light-duty segment's role as an electrification beachhead.
Vans above 5 m3 dominated the European van market, with 62.78% of the share in 2025, powered by wholesale distributors that maximize revenue kilometers via higher cube utilization. OEMs serve this core with modular platforms such as the Renault Master's 11-22 m3 configurations, which blend tall roofs, multiple wheelbases, and two-tonne payload ceilings.
Yet, less than/equal to 5 m3 models are rising at a 4.67% CAGR, underpinned by grocery quick-commerce and pharmacy delivery firms that prize alley maneuverability, easy parking, and lower battery capacities that keep sticker prices in check. Compact BEVs reach total cost-of-ownership breakeven faster because sub-50 kWh packs trim purchase costs and charge times. The bifurcation pushes OEMs toward dual roadmaps: high-cube variants optimized for palletized freight and smaller, software-enabled micro-vans engineered for dense urban loops where idle time and access fees erode diesel economics.
The Europe Van Market Report is Segmented by Gross Vehicle Weight (N1 Class I, N1 Class II, and N1 Class III), Cargo Space (Less Than/Equals 5 M3 and Above 5 M3), End User (Commercial Fleets, Government and Municipal, and More), Drive Type (IC Engine - Petrol, IC Engine - Diesel, and More), Sales Channel (Direct OEM Fleet Sales, and More), and Country. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Stellantis N.V.
- Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- Volkswagen AG
- Ford Motor Company
- Renault Group
- Iveco Group N.V.
- Toyota Motor Corporation
- Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- BYD Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Motor Company
- SAIC Maxus Automotive
- MAN Truck & Bus SE
- Opel Automobile GmbH
- London Electric Vehicle Company (LEVC)
- B-ON GmbH (StreetScooter GmbH)
- Rivian Automotive LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise in Sales of Electric Vans
- 4.2.2 E-commerce Last-Mile Boom
- 4.2.3 EU Low-Emission-Zone Mandates
- 4.2.4 Urban Micro-fulfilment Hub Adoption
- 4.2.5 OEM Skateboard EV Platforms
- 4.2.6 Battery-as-a-Service Fleet Models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Battery and Vehicle CAPEX
- 4.3.2 Semiconductor Supply Constraints
- 4.3.3 Limited Depot Fast-Charging Sites
- 4.3.4 Driver Shortage and License Rules
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Gross Vehicle Weight
- 5.1.1 N1 Class I (Less than/Equals 2 t GVW)
- 5.1.2 N1 Class II (2-2.5 t GVW)
- 5.1.3 N1 Class III (2.5-3.5 t GVW)
- 5.2 By Cargo Space
- 5.2.1 Less than/Equals 5 m3
- 5.2.2 Above 5 m3
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Commercial Fleets
- 5.3.2 Government and Municipal
- 5.3.3 Rental and Leasing Operators
- 5.4 By Drive Type
- 5.4.1 IC Engine - Petrol
- 5.4.2 IC Engine - Diesel
- 5.4.3 Battery Electric
- 5.4.4 Hybrid Electric
- 5.4.5 Fuel-Cell Electric
- 5.4.6 Alternative Fuel (CNG/LPG)
- 5.5 By Sales Channel
- 5.5.1 Direct OEM Fleet Sales
- 5.5.2 Authorised Dealerships
- 5.5.3 Online / Digital Platforms
- 5.6 By Country
- 5.6.1 Germany
- 5.6.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3 France
- 5.6.4 Italy
- 5.6.5 Spain
- 5.6.6 Netherlands
- 5.6.7 Sweden
- 5.6.8 Norway
- 5.6.9 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Stellantis N.V.
- 6.4.2 Mercedes-Benz Group AG
- 6.4.3 Volkswagen AG
- 6.4.4 Ford Motor Company
- 6.4.5 Renault Group
- 6.4.6 Iveco Group N.V.
- 6.4.7 Toyota Motor Corporation
- 6.4.8 Nissan Motor Co. Ltd
- 6.4.9 BYD Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Hyundai Motor Company
- 6.4.11 SAIC Maxus Automotive
- 6.4.12 MAN Truck & Bus SE
- 6.4.13 Opel Automobile GmbH
- 6.4.14 London Electric Vehicle Company (LEVC)
- 6.4.15 B-ON GmbH (StreetScooter GmbH)
- 6.4.16 Rivian Automotive LLC
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment









