 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911498
印度公路货运:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)India Road Freight Transport - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
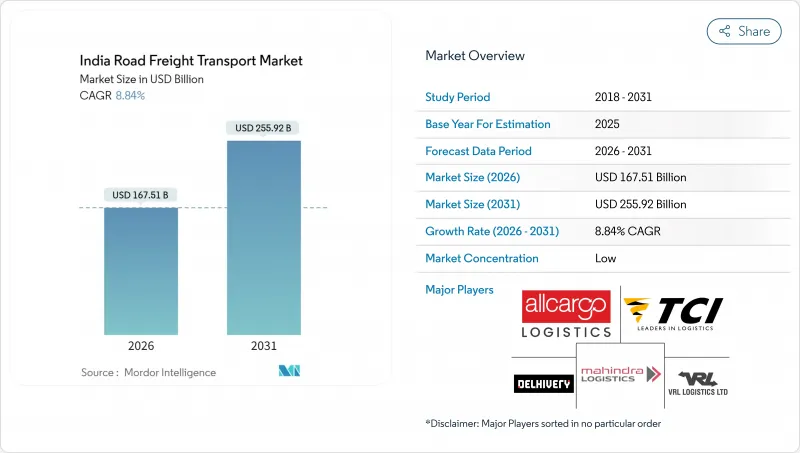
印度公路货运市场规模预计从2025年的1,539亿美元成长到2026年的1,675.1亿美元,预计到2031年将达到2,559.2亿美元,2026年至2031年的复合年增长率为8.84%。
这一令人瞩目的成长反映了印度作为全球成长最快的主要经济体的地位,其主要驱动力包括强劲的製造业復苏、蓬勃发展的电子商务以及公共部门大力推进的高速公路和多模态走廊建设。基础设施的改善,包括146,145公里长的国家高速公路网、FASTag电子收费系统的广泛应用以及专用货运走廊的早期建设,正在缩短运输时间、提高卡车运转率并缓解运力短缺问题。商品和服务税(GST)、电子运单和客户服务等级协定(SLA)的引入,正在推动正规物流服务的普及,因为托运人越来越倾向于选择合规且技术先进的供应商。同时,受数位支付和区域(三、四线)城市电子商务需求的推动,印度农村消费的成长正在重塑配送路线,并增强中短途货运的货运量前景。
印度公路货运市场趋势与洞察
履约迅速扩展到第一和第二大都市区以外。
线上零售在三、四线城市的渗透正推动印度公路货运市场稳定成长。受智慧型手机在农村地区普及和统一支付介面(UPI)支付快速发展的推动,预计2025年至2030年印度电子商务产业将以22%的复合年增长率成长。快速电商业者正在区域城市建立微型仓配中心,以实现10分钟送达,从而刺激了零担货运和越库作业的需求。 Delhivery的服务范围扩展至超过18,700个邮递区号区域,标誌着新一代物流网络的扩张。区域承运商能够协商各州的检查、轴重限制和替代性通行税,因此在获取以往仅限于非正式网路的货运方面具有优势。数位付款基础消除了货到付款的摩擦,并支援小包裹透明且可追溯的发票。
促进基础设施发展:Bharatmala Gatishakti走廊
到2024年,高速公路日均建设里程将达到40公里,凸显了「印度公路网计画」(Bharatmala Plan)的强劲势头,该计画的目标是建成34,800公里高速公路。 「加蒂·沙克蒂计画」(Gati Shakti Plan)下的综合规划已将土地征用核准时间从数年缩短至数月,并促进了公路、铁路和公共产业设施走廊的整合。港口与工厂之间连通性的提升已使艾哈默德巴德巴德-孟买和德里-坎普尔高速公路的平均卡车速度提高了15%至20%。马士基承诺在港口区域投资50亿美元,显示跨国公司对走廊性能提升充满信心。建设热潮本身也带动了对水泥、钢铁和机械的需求,从而增加了货运量,加强了基础製造业物流。
驾驶人和劳动力老化
旺季期间驾驶人导致车辆閒置,德里至孟买以及班加罗尔至清奈之间的运转率下降高达20%,从而推高了公路货运价格并延长了前置作业时间。年轻的劳工越来越倾向在电商中心从事轮班工作,而非进行多日跨州运输,导致经验丰富的长途货运人才流失。各邦的培训中心各自为政,导致技能认证等级参差不齐,安全标准也不一致。重型车辆驾驶人的薪资预计每年增长12%至15%,而这部分成本最终转嫁给了托运人。儘管安全技术援助卓有成效,但人力资本的限制仍是限製印度公路货运市场产能扩张的一大因素。
细分市场分析
国内製造业与生产挂钩激励机制的结合,吸引了对电子、汽车零件和製药业的资本投资,因而带动了出口货运量的成长。预计2026年至2031年间,製造业将以10.05%的复合年增长率成长,成为印度公路货运市场成长最快的领域。受消费主导的日常消费品(FMCG)和耐用消费品回流运输的支撑,批发和零售贸易将保持30.21%的最大份额。农业、渔业和林业将保持稳定,但由于工业货运的成长,其份额略有下降。
生产关联激励(PLI)工厂正聚集在港口周围和西部专用货运走廊(WDCC)的交汇点,从而提升了古吉拉突邦-马哈拉斯特拉邦-德里沿线的运输密度。假设政策维持稳定且外国直接投资(FDI)持续成长,预计到2031年,印度製造业货物的公路货运市场规模将超过5,42亿美元。随着低温运输缺口的缩小,农业部门的份额预计将稳定在10%左右。虽然专用货运走廊正推动铁路运输向更高价值的领域发展,但托运人对门到门柔软性的偏好仍然保护着道路运输营运商免受运输方式转变的影响。
儘管国内航运网络仍将占据主导地位,预计到2025年将占63.02%的市场份额,但未来的成长预计将转向跨境航运网络,2026年至2031年的复合年增长率将达到10.23%。近期成长要素包括印度-孟加拉国走廊的无纸化清关以及IMEC的管道计划,预计将降低西行货物的多模态成本。马士基专注于内陆港口的投资旨在到2030年将出口货柜处理能力翻一番,预计将提升国际航运在印度公路货运市场的份额。
印度海关平均停留时间为85小时,与亚洲主要枢纽相比仍存在瓶颈。预计数位化清关和基于区块链的载货证券将显着缩短这一时间,越来越多的出口商将选择结合公路和铁路的货柜运输环线。儘管随着国内消费的成长,国内运输距离仍将增加,但全球供应链的重组将使印度成为中国的替代选择,并透过新兴的陆海走廊,促进通往海湾合作委员会成员国和欧洲的双边路线。
到2025年,整车运输(FTL)在矿物、钢捲和预包装快速消费品(FMCG)领域的市占率将维持在80.12%。然而,从2026年到2031年,零担运输(LTL)的复合年增长率将达到9.89%,超过印度整体公路货运市场的成长速度。位于那格浦尔、印多尔和海得拉巴的枢纽辐射式仓库支援快速转运,使90%的城市对之间的交货时间缩短至48小时以内。透过演算法将混合货物分配到托盘集装箱,提高了装载率并降低了每公里成本。
轻资产第三方物流利用自营的微型车队进行最后一公里配送,以最小的资本投入扩大覆盖范围。货运平台提供动态仪錶板和有保障的配送时段,从而实现可预测服务的溢价定价。整车运输 (FTL) 对大宗货物仍然很重要,但随着小批量货物运输的日益普遍,其份额预计将略有下降。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 分析师支持(3个月)
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 按经济活动分類的GDP分配
- 按经济活动分類的GDP成长
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业的趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 运输和仓储业GDP
- 物流绩效
- 道路长度
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格趋势
- 卡车运输营运成本
- 按车型分類的卡车拥有数量
- 主要卡车供应商
- 公路货运量趋势
- 公路货运价格趋势
- 按交通方式分享
- 通货膨胀
- 法律规范
- 价值炼和通路分析
- 市场驱动因素
- 电子商务物流履约需求正快速扩展到主要都会区(第一线和二线城市)以外的地区。
- 促进基础设施发展(透过「印度公路网计画」和「加蒂沙克蒂走廊」)。
- 微企业越来越多地采用有组织的第三方/第四方物流模式
- 合理化替代燃料(CNG/LNG)关税
- 数位货运市场的快速扩张
- 针对时效性强、保存期限短产品的绿色通道政策
- 市场限制
- 驾驶人和劳动力老化
- 铁路车辆报废政策的延迟意味着老旧车辆继续运作,从而增加了成本。
- 儘管FASTag自动化技术普及,通行费仍上涨。
- 主要都会区以外缺乏冷藏和冷冻物流基地
- 市场创新
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 终端用户产业
- 农业、渔业、林业
- 建造
- 製造业
- 石油天然气、采矿和采石
- 批发和零售
- 其他的
- 目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 卡车装载规范
- 整车运输 (FTL)
- 低于100%的运费(零担运输)
- 货柜运输
- 货柜运输
- 非货柜运输
- 距离
- 长途
- 短程交通
- 货物类型
- 液体货物
- 固态货物
- 温度控制
- 非温控型
- 温度控制
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 关键策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- AP Moller-Maersk
- Allcargo Logistics(including Gati Express)
- CJ Darcl Logistics Limited
- Delhivery Ltd.
- DHL Group
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- GEODIS
- Mahindra Logistics
- Nippon Express Holdings
- Transport Corporation of India(TCI)
- V-Trans
- Varuna Group
- VRL Logistics Ltd.
- Safexpress
- Shree Tirupati Logistics
- Xpressbees
- Om Logistics Supply Chain
- CKB Group
- Glottis
- SAR Logistics
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
India road freight transport market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 167.51 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 153.9 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 255.92 billion, growing at 8.84% CAGR over 2026-2031.

The headline growth mirrors India's position as the world's fastest-growing major economy, with a robust manufacturing revival, a booming e-commerce sector, and a decisive public-sector push on highways and multimodal corridors. Infrastructure additions such as the 146,145 km national highway network, widespread FASTag tolling, and the early roll-out of Dedicated Freight Corridors are shrinking transit times, lifting truck utilization, and easing capacity shortages. Organized logistics penetration is rising as GST, e-way bills, and customer-side service-level agreements push shippers toward compliant, technology-equipped providers. Meanwhile, India's rural consumption story, backed by digital payments and tier-3 and tier-4 e-commerce demand, is redrawing delivery routes and fortifying volume prospects for small and mid-distance hauls.
India Road Freight Transport Market Trends and Insights
E-commerce Fulfilment Boom Beyond Tier-1 and Tier-2 Cities
Penetration of online retail into tier-3 and tier-4 catchments is propelling steady incremental volumes for the India road freight transport market. India's e-commerce sector is tracking a 22% CAGR between 2025-2030 as rural smartphone ownership and UPI payments scale rapidly. Quick-commerce players are building micro-fulfilment hubs in secondary towns to meet ten-minute delivery pledges, raising demand for LTL consolidation and cross-docking. Delhivery now covers 18,700+ pin codes, signaling the breadth of new-age distribution lanes. Regional carriers that can negotiate state-level border checks, axle-load limits, and octroi substitutes are positioned to win loads that once stayed within informal networks. The digital payment backbone removes cash-on-delivery friction and supports transparent, trackable invoicing for small consignments.
Infrastructure Push via Bharatmala and Gati Shakti Corridors
Daily highway construction hit 40 km in 2024, underscoring the momentum behind Bharatmala's 34,800 km mandate. Integrated planning under PM Gati Shakti has compressed right-of-way approvals from multiple years to months and is aligning road, rail, and utility corridors. Improved port-to-factory links are already nudging average truck speeds upward by 15-20% on the Ahmedabad-Mumbai and Delhi-Kanpur arteries. Maersk's USD 5 billion port-side investment commitment underlines multinational confidence in corridor performance gains. The construction boom itself churns freight for cement, steel, and machinery, adding volume layers that reinforce basal manufacturing flows.
Driver Shortage and Ageing Workforce
Peak-season fleet idling due to driver gaps has clipped utilization by up to 20% on Delhi-Mumbai and Bangalore-Chennai sectors, inflating line-haul rates and stretching lead times. Young workers favor predictable shifts in e-commerce hubs over week-long interstate runs, causing an experience drain in long-haul trucking. State-run training centers work in silos, leaving skills certification uneven and safety standards patchy. Wage inflation, estimated at 12-15% year-on-year for heavy-vehicle operators, compounds cost-pass-through into shipper tariffs. Safety-tech aids help, yet human capital constraints remain a drag on capacity expansion in the India road freight transport market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Adoption of Organized 3PL/4PL Models by MSMEs
- Rapid Scaling of Digital Freight Marketplaces
- Slow Adoption of Vehicle-Scrappage Policy
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Domestic manufacturing's link to Production Linked Incentive schemes is attracting electronics, auto-component, and pharmaceutical cap-ex, translating to elevated outbound tonnage. With a 10.05% CAGR between 2026-2031, manufacturing contributes the highest incremental volume to the India road freight transport market. Wholesale and Retail Trade remains the single-largest shareholder at 30.21%, powered by consumption-led FMCG and consumer durables backflows. Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry retains a steady base, though its share inches down as industrial freight climbs.
PLI-linked factories are clustering near ports and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor junctions, prompting higher load density on Gujarat-Maharashtra-Delhi stretches. The Indian road freight transport market size for manufacturing consignments is likely to exceed USD 54.2 billion by 2031, assuming stable policy continuity and sustained foreign direct investment. Agriculture's share may steady around the low-teens as cold-chain gaps narrow, all else equal. Shipper preference for door-to-door flexibility continues to shield road carriers from modal leakage, even as Dedicated Freight Corridors bring rail into higher-value brackets.
The domestic lattice dominates today with a 63.02% share in 2025, yet future growth tilts toward cross-border links, which are clocking a 10.23% CAGR between 2026-2031. Near-term catalysts include paperless customs on the India-Bangladesh corridor and IMEC's pipeline, which promises multimodal savings on westbound cargo. Maersk's hinterland-driven port investments aim to double export-bound container capacity by 2030, lifting the international slice of the India road freight transport market.
Customs dwell time, averaging 85 hours, remains a bottleneck compared with leading Asian hubs. Digital customs and blockchain-enabled bills of lading are expected to chop that figure materially, pulling more exporters toward truck-plus-rail containerized loops. Domestic mileage will still swell as rural consumption rises, but global supply-chain realignments position India as a China-plus-one alternative, spurring bilateral lanes into GCC and Europe via emerging land-sea corridors.
Full-Truck-Load kept 80.12% share in 2025, serving minerals, steel coils, and packaged FMCG. Yet LTL's 9.89% CAGR between 2026-2031 outpaces the overall India road freight transport market. Hub-and-spoke depots in Nagpur, Indore, and Hyderabad feed rapid trans-shipment, cutting delivery promises to under 48 hours for 90% of urban pairs. Algorithms allocate mixed orders into palletized pods, lifting fill factors and shrinking per-kilo costs.
Asset-light third-party logistics use owner-operator micro fleets for last-mile links, minimizing cap-ex and accelerating coverage. Freight platforms supply dynamic dashboards that guarantee slot times, unlocking premium pricing for predictable service. FTL will remain irreplaceable for bulk commodities, yet its share ratio is projected to erode marginally as parcelization broadens.
The India Road Freight Transport Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Manufacturing, and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Truckload Specification (FTL and LTL), Distance (Long Haul and Short Haul), Goods Configuration (Fluid Goods and Solid Goods), Temperature Control (Non-Temperature and Temperature Controlled), and by Containerization. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- A.P. Moller-Maersk
- Allcargo Logistics (including Gati Express)
- CJ Darcl Logistics Limited
- Delhivery Ltd.
- DHL Group
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- GEODIS
- Mahindra Logistics
- Nippon Express Holdings
- Transport Corporation of India (TCI)
- V-Trans
- Varuna Group
- VRL Logistics Ltd.
- Safexpress
- Shree Tirupati Logistics
- Xpressbees
- Om Logistics Supply Chain
- CKB Group
- Glottis
- SAR Logistics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.4 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.4.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.4.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.5 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.6 Logistics Performance
- 4.7 Length of Roads
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Pricing Trends
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Road Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.15 Road Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.16 Modal Share
- 4.17 Inflation
- 4.18 Regulatory Framework
- 4.19 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.20 Market Drivers
- 4.20.1 E-Commerce Fulfilment Boom Beyond Tier-1 and Tier-2 Cities
- 4.20.2 Infrastructure Push Via Bharatmala and Gati Shakti Corridors
- 4.20.3 Growing Adoption of Organised 3PL/4PL Models by MSMEs
- 4.20.4 Duty Rationalisation for Alternative Fuels (CNG/LNG)
- 4.20.5 Rapid Scaling of Digital Freight Marketplaces
- 4.20.6 Green-Lane Policy for Time-Critical Perishables
- 4.21 Market Restraints
- 4.21.1 Driver Shortage and Ageing Workforce
- 4.21.2 Slow Adoption of Vehicle-Scrappage Policy Keeps Ageing Fleet Operational, Raising Costs
- 4.21.3 Toll-Cost Inflation Despite FASTag Automation
- 4.21.4 Limited Cold-Chain Nodes Outside Metros
- 4.22 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.23 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.23.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.23.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.23.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.23.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.23.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Destination
- 5.2.1 Domestic
- 5.2.2 International
- 5.3 Truckload Specification
- 5.3.1 Full-Truck-Load (FTL)
- 5.3.2 Less than-Truck-Load (LTL)
- 5.4 Containerization
- 5.4.1 Containerized
- 5.4.2 Non-Containerized
- 5.5 Distance
- 5.5.1 Long Haul
- 5.5.2 Short Haul
- 5.6 Goods Configuration
- 5.6.1 Fluid Goods
- 5.6.2 Solid Goods
- 5.7 Temperature Control
- 5.7.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.7.2 Temperature Controlled
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 A.P. Moller-Maersk
- 6.4.2 Allcargo Logistics (including Gati Express)
- 6.4.3 CJ Darcl Logistics Limited
- 6.4.4 Delhivery Ltd.
- 6.4.5 DHL Group
- 6.4.6 Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- 6.4.7 GEODIS
- 6.4.8 Mahindra Logistics
- 6.4.9 Nippon Express Holdings
- 6.4.10 Transport Corporation of India (TCI)
- 6.4.11 V-Trans
- 6.4.12 Varuna Group
- 6.4.13 VRL Logistics Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Safexpress
- 6.4.15 Shree Tirupati Logistics
- 6.4.16 Xpressbees
- 6.4.17 Om Logistics Supply Chain
- 6.4.18 CKB Group
- 6.4.19 Glottis
- 6.4.20 SAR Logistics
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment









