 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1527363
TrendForce (2024年):近眼显示的市场趋势技术分析TrendForce 2024 Near-Eye Display Market Trend and Technology Analysis |
||||||
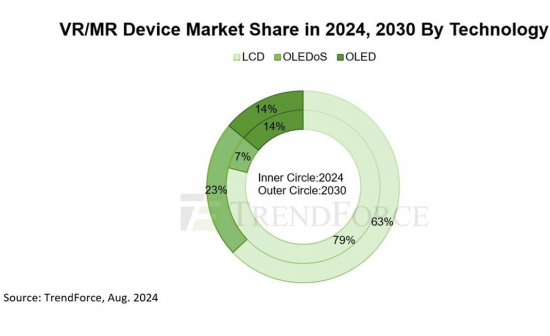
TrendForce:2030年VR/MR设备出货量将达3,700万台,OLEDoS和LCD占据高阶和主流市场
根据TrendForce最新报告,随着库存清理,近眼显示器(NED)出货量预计在未来几年将增加。在高阶VR/MR市场,OLEDoS的技术占有率预计到2030年将上升至23%,而在主流市场,LCD将继续占据近眼显示器63%的占有率。
TrendForce 将 VR/MR 装置定义为近眼显示器,即透过单一显示器提供沉浸式体验的装置。强调透明性、将虚拟和现实使用区域融为一体的设备被归类为AR设备。
TrendForce指出,VR/MR已经在娱乐和游戏领域奠定了坚实的基础。此外,Apple Vision Pro 将于 2024 年推出,预计将为 VR/MR 应用开闢新途径。目前存在的高定价和有限服务内容的问题预计会随着时间的推移而改善。因此,TrendForce预测,到2030年,VR/MR设备出货量将达到3,730万台,2023年至2030年复合年增长率为23%。
厂商策略将推动OLEDoS在VR/MR市场的普及
Sony和苹果在 Apple Vision Pro 上的合作确立了 OLEDoS 在高阶 VR/MR 市场的主导地位。此次合作凸显了业界对高解析度 VR/MR 设备的追求,并提升了 OLEDoS 的知名度。
OLEDoS采用CMOS和高亮度OLED元件,实现高发光效率,使OLEDoS产品的基本解析度达到3,000 PPI以上。 TrendForce 指出,CMOS 製造的复杂性和低产量使得 OLEDoS 显示器的製造成本更高,限制了采用的成长。
TrendForce也指出,除了国外企业积极投资OLEDoS领域外,SeeYa、京东方等中国厂商也紧跟在后。这有望促进该技术未来在VR/MR设备市场的扩展,并有助于降低CMOS技术的成本和提高良率。 OLEDoS在高阶市场仍有潜力,TrendForce预计其市占率将从2024年的7%成长到2030年的23%。开发资源投资与迭代显示规格增强 LCD 竞争力
在主流近眼显示器市场,由于Meta对成本效益的重视,LCD技术仍占主导地位。然而,随着更高清晰度和影像品质的进步,1,200 PPI LCD 产品将面临其他技术的竞争。 TrendForce预计2024年LCD近眼显示器产品出货量为680万片,较2023年减少5.6%。
TrendForce指出,LCD的复杂元件仍有最佳化的空间。例如,改进液晶材料以减少眩晕,更新背板技术将解析度提高到 1,500 PPI 以上。京东方在LCD在近眼显示器的应用上投入了大量资金,在VR/MR设备中LCD显示规格不断更新和迭代,确保该技术在中低价市场保持强劲竞争力。 TrendForce预测,到2030年,LCD技术将占据63%的市占率。
OLED的市占率维持在13-15%。
发光材料沉积后无法完全覆盖萤幕,这会在使用VR/MR设备时恶化纱门效果。 TrendForce表示,OLED在高阶市场的竞争力不如OLEDoS,性价比也不如LCD产品。此外,OLED在VR/MR市场的应用高度依赖特定製造商,从长远来看限制了其渗透率。 TrendForce预计,2024年至2030年OLED在VR/MR市场的市占率将维持在13-15%。
目录
第1章 近眼显示开发概要
- AR/VR/MR 的诞生
- 从现实到虚拟:虚拟和真实影像的连续光谱
- MR在行销中的两个主要意义
- 用于创建 XR 体验的技术架构
- 圣杯:MR 的“鲸鱼时刻”
- AR/VR/MR规格分析
- AR/VR/MR显示技术路线图
- AR/VR/MR 市场挑战:高水准的 PPI
- 眼睛的最高解析度仅限于中心:从视网膜到中央凹
- 注视点显示:有效地重新分配像素
- AR/VR/MR 显示器面临的挑战:聚散调节衝突 (VAC)
- VR/MR设备显示解决方案开发
- VR/MR 的关键指标: "失控" 的解析度要求
- VR/MR 困境:PPD/厚度与功耗权衡
- VR/MR光学技术重要指标:厚度
- VR/MR光学技术主要指标:FOV
- VR/MR困境:降低MPRT以降低显示电阻
- 薄饼光学元件对于 VR/MR 技术至关重要
- Pancake 2.0:光学技术亮点
- Pancake 2.0:更薄
- Pancake 2.0:更有效率
- VR/MR光学系统现状
- VR/MR显示器:LCD和OLED
- PPD 围绕 VR/MR 的竞争:从显示器扩展到系统
- VST 显示延迟问题
- 使显示规格符合 VR/MR 要求
- AR 市场挑战:永远不会太小
- AR 市场挑战:永不光明
- 光学系统的趋势
- 光引擎与光学系统
- 光学分析状况
- 显示规格与 AR 需求保持一致
- AR(扩增实境)显示技术矩阵
第2章 近眼显示市场趋势分析
- NED 市场规模分析(2024-2028 年)
- VR/MR 市场规模分析(2024-2028 年)
- AR市场规模分析(2024-2028)
- VR/MR 市场规模分析:LCD/OLEDoS(2024-2028 年)
- AR市场规模分析:OLEDoS/LEDoS(2024-2028)
第3章 近眼显示技术概要
3.1 OLEDoS
- OLEDoS的基本流程
- OLEDoS技术现状
- OLEDoS:PPI 和亮度进一步提升
- OLEDoS 分析:Sony/eMagin/Kopin/RAONTECH
- 铝阳极製程作为高解析度 OLEDoS 的替代品
- 铝阳极的采用可能会改变OLEDoS产业的分工
- 透明 OLEDOS:SOI 上的 OLED
- OLEDoS:2024 年从 AR 过渡到 VR/MR
3.2 LEDoS
- 扩增实境 (AR):LEDoS 製造流程
- LEDoS 技术组合路线图
- 更新 LEDoS 设备和製造工艺
- 外延:基板材质与尺寸选项
- 晶片:2D/3D结构分析
- 晶片製造及后端晶片製造工艺
- ALD 钝化
- 连接:温度、压力和精度非常重要的技术要素
- 接头:CTE 不匹配
- 加入:尺寸不符问题
- 非常规键结:LED+单基板工艺
- LED 光源的内在限制:光集中的挑战
- 片上光学:微光学是新焦点
- 全彩微显示技术
- InGaN红光技术
- 红光困境:InGaN 还是 AlInGaP? ALD钝化
- InGaN红色LED:仍在开发中
- 全彩显示:QD颜色转换优缺点分析
- 全彩:QDCC透过NRET机制进一步发展
- QDCC 能够实现高达 3,000 PPI 的高解析度
- 全彩显示:RGB垂直堆迭
- 垂直堆迭 LEDoS 技术
- 垂直堆迭LEDoS技术面临的挑战
- 垂直堆迭LEDoS技术的优势
- 垂直堆迭 LED PKG:显示器的商业应用
- LEDoS 小型化的下一个 "战场" :QDCC 与垂直堆迭
- 全彩化:多色/单色可调 LED
- 线/棒 LEDoS:进阶 PPI 应用的效率优势
- NED 的 LEDoS 技术评估
- 线材/棒材 LEDoS:优点与缺点
- LEDoS微显示器主要技术分析
3.3液晶萤幕
- 主要 LCD 技术:色序
- LCD关键技术:Mini LED背光
- LCD(玻璃上)PPI 突破
- LCD(玻璃上)高帧率
- LCD背光革命:雷射
- LCD背光革命:雷射+HOE
- LCD技术发展综述:充分释放LCD潜力
- LCD与VR/MR保持竞争力: "武器库" 丰富
3.4 硅基液晶
- LCOS:光引擎的小型化
- LCOS:显示模组尺寸缩小至0.47cc
3.5 DLP
- DLP 的进一步发展:TRP(倾斜和滚动像素)技术
3.6 磅
- LBS:光引擎的生态系与小型化
- 雷射光束扫描 (LBS):尺寸/分辨率
3.7 OLED
- OLED 与其他技术之间的良性循环
- 垂直堆迭OLED驱动电路:OLED-on-OS-on-Si
第四章产业布局及企业趋势:最新情况
- XR 公司针对 LEDoS 的併购 (M&A) 策略概述
- Google 的併购策略(JDC/Raxium)
- Meta 的併购策略(InfiniLED/MLED)
- Apple 的併购策略(Luxvue/Tesoro)
- Porotech
- JBD
- 史丹
- 瑞索维
- Saphlux
- Mojo 愿景
- 奥斯坦多
- LG OLEDoS 的历史(2021-2024 年)
- Att合作,为企业进军高阶MR市场
- Apple Vision Pro 显示器与光学元件
- Apple Vision Pro 外溢效应
- Apple Vision Pro 作为消费市场的生产力工具
- LCD 与 OLED 微显示器之战:Quest 3 与 Vision Pro
TrendForce: VR/MR Device Shipments to Reach 37 Million Units by 2030, with OLEDoS and LCD Dominating High-End and Mainstream Markets
TrendForce's latest report reveals that shipments of near-eye displays are expected to increase year-by-year over the next few years following inventory clearance. It is anticipated that OLEDoS will dominate the high-end VR/MR market, with its technological share rising to 23% by 2030, while LCD will continue to occupy the mainstream market, holding a 63% share in near-eye displays.
TrendForce defines VR/MR devices as near-eye displays that achieve an immersive experience through a single display. Devices emphasizing transparency and the integration of virtual and real-world applications are classified as AR devices.
TrendForce notes that VR/MR has already established a solid foundation in the entertainment and gaming sectors. Furthermore, the introduction of Apple Vision Pro in 2024 is expected to open new avenues for VR/MR applications. Current issues of high pricing and limited service content are expected to improve over time. Therefore, TrendForce predicts that VR/MR device shipments could reach 37.3 million units by 2030, with a CAGR of 23% from 2023 to 2030.

Manufacturers' strategies drive OLEDoS penetration in the VR/MR market
The collaboration between Sony and Apple on the Apple Vision Pro has established OLEDoS as dominant in the high-end VR/MR market. This partnership highlights the industry's pursuit of high-resolution VR/MR devices and has increased attention on OLEDoS.
OLEDoS employs CMOS and top-emitting OLED components to achieve higher luminous efficiency, pushing the basic resolution of OLEDoS products to over 3,000 PPI. TrendForce notes that the complexity of CMOS manufacturing and its lower yield rates result in high production costs for OLEDoS displays, which limit its penetration growth.
TrendForce also indicates that, in addition to international companies actively investing in the OLEDoS field, Chinese manufacturers such as SeeYa and BOE are also following suit. This is expected to drive the future expansion of this technology in the VR/MR device market, helping to reduce costs and improve yield for CMOS technology. OLEDoS still has potential in the high-end market, with TrendForce estimating its market share will increase from 7% in 2024 to 23% in 2030.
Investment in development resources and iteration of display specifications strengthen LCD competitiveness
In the mainstream near-eye display market, LCD technology remains dominant due to Meta's focus on cost-effectiveness. However, as these devices continue to pursue higher resolution and image quality, LCD products-with their 1,200 PPI-will face competition from other technologies. TrendForce estimates that in 2024, the shipment volume of LCD near-eye display products will be 6.8 million units, a 5.6% decrease compared to 2023.
TrendForce points out that there is still room for optimization in the complex components of LCD. For example, improving liquid crystal materials to reduce dizziness and upgrading backplane technology to boost resolution beyond 1,500 PPI. BOE has invested heavily in the application of LCD in near-eye displays, with continuous updates and iterations of LCD display specifications in VR/MR devices, ensuring this technology maintains strong competitiveness in the mid-to-low-end market. TrendForce forecasts that LCD technology will hold a 63% market share by 2030.
OLED market share to remain between 13% and 15%
Emission material cannot fully cover the screen after deposition, which exacerbates the screen door effect when using VR/MR devices. TrendForce indicates that OLED is less competitive than OLEDoS in the high-end market and cannot match the cost-effectiveness of LCD products. Additionally, the application of OLED in the VR/MR market relies heavily on specific manufacturers, limiting its long-term penetration rate. TrendForce estimates that from 2024 to 2030, the market share of OLED in the VR/MR market will remain between 13% and 15%.
Table of Contents
Chapter I. Near-Eye Display Development Overview
- The Birth of AR / VR / MR
- From Reality to Virtuality: The Continuous Spectrum of Virtual and Real Images
- Two Major Meanings of MR in Marketing
- Technical Architecture for Creating XR Experiences
- Holy Grail: "The Whale Moment" of MR
- AR / VR / MR Specification Analysis
- AR / VR / MR Display Technology Roadmap
- AR / VR / MR Market Challenges: High PPI
- Highest Resolution for Eyes is Limited to the Central Area:From the Retina to Fovea
- Foveated Display: Efficient Redistribution of Pixels
- AR / VR / MR Display Challenges: Vergence Accommodation Conflict (VAC)
- Development of VR / MR Device Display Solutions
- Key Indicators for VR / MR : The "Out of Control" Requirements of Resolution
- VR / MR Dilemma: Trade Off between PPD/Thickness and Power Consumption
- Key Indicators for VR / MR Optical Technology: Thickness
- Key Indicators for VR / MR Optical Technology: FOV
- VR / MR Dilemma: Reduced MPRT to Suppress Display Drag
- Pancake Optics Becomes a Must for VR / MR Technology
- Pancake 2.0: Highlights of the Optical Technology
- Pancake 2.0: Thickness Is Further Decreased
- Pancake 2.0: Efficiency Is Further Increased
- VR / MR Optic System Landscape
- VR / MR Displays: LCD vs. OLED
- PPD Competitions for VR / MR Extend from Displays to Systems
- Latency Issues of VST Displays
- Aligning Display Specifications with VR / MR Requirements
- AR Market Challenges- Never Too Small
- AR Market Challenges- Never Too Bright
- Optical System Trend
- Light Engine vs. Optical System
- Optical Analysis Landscape
- Aligning Display Specifications with AR Requirements
- Augmented Reality Display Technology Matrix
Chapter II. Near-Eye Display Market Trend Analysis
- 2024-2028 NED Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 VR / MR Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 AR Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 VR / MR Market Size Analysis :LCD/OLEDoS
- 2024-2028 AR Market Size Analysis :OLEDoS/LEDoS
Chapter III. Near-Eye Display Technology Overview
3.1 OLEDoS
- OLEDoS Basic Process
- OLEDoS Technology Landscape
- OLEDoS: Further Increases in PPI and Brightness
- OLEDoS Analysis: Sony / eMagin / Kopin / RAONTECH
- Al Anode Process as an Alternative to High-Resolution OLEDoS
- Adopting Al Anode May Change Division of Labor in OLEDoS Industry
- Transparent OLEDoS: OLED-on-SOI
- OLEDoS Shifts from AR to VR / MR in 2024
3.2 LEDoS
- Augmented Reality: LEDoS Manufacturing Process
- LEDoS Technology Portfolio Roadmap
- LEDoS Equipment and Manufacturing Process Upgrades
- Epitaxy: Substrate Materials and Size Options
- Chip: 2D / 3D Structural Analysis
- Chipmaking and Back-end Chipmaking Processes
- ALD Passivation
- Bonding: Temperature, Stress, and Precision are Key Technical Factors
- Bonding: CTE Mismatch
- Bonding: Size Mismatch Problem
- Non-conventional Bonding: LED + Single-substrate Process
- Intrinsic Limitations of LED Light Sources: Light Concentration Challenge
- On-chip Optics: Micro-optics is a New Focus
- Full Color Microdisplay Technologies
- InGaN Red Light Technology
- Red Light Dilemma: InGaN or AlInGaP?ALD Passivation
- InGaN Red LEDoS Are Still Under Development
- Full Color Display: QD Color Conversion Pros and Cons Analysis
- Full-colorization: QDCC To Be Further Advanced by NRET Mechanism
- QDCC Capable of High Resolution Up to 3,000 PPI
- Full Color Display: RGB Vertical Stacking
- Vertical Stacking LEDoS Technology
- Vertical Stacking LEDoS Technology Challenges
- Advantages of Vertical-stacking LEDoS Technology
- Vertically Stacked LED PKG: Commercial Application Aiming at Displays
- Next "Battlefield" for LEDoS Miniaturization: QDCC vs. Vertical Stacking
- Full-colorization: Multiple or One Color Tunable LED
- Wire/Rod LEDoS: An Edge in Efficiency for High PPI Applications
- LEDoS Technology Evaluation for NED
- Wire/Rod LEDoS: Pros and Cons
- LEDoS Microdisplay Key Technology Analysis
3.3 LCD
- Key LCD Technology: Color Sequential
- LCD Key Technology: Mini LED Backlight
- LCD (on Glass) PPI Breakthrough
- LCD (on Glass) High Frame Rate
- LCD Backlight Revolution: Laser
- LCD Backlight Revolution: Laser + HOE
- LCD Technological Development Summary: LCD Potential Fully Release
- LCD Maintain Competitiveness in VR / MR: The Abundant "Arsenal"
3.4 LCoS
- LCOS: Light Engine Miniaturization
- LCOS: Display Module Size Shrinks to 0.47cc
3.5 DLP
- DLP Further Advancement: Tilt-and-Roll Pixel (TRP) Technology
3.6 LBS
- LBS: Ecosystem and Light Engine Miniaturization
- Laser Beam Scanning: Size / Resolution
3.7 OLED
- Positive Cycle Between OLED and Other Technologies
- Vertical Stacking of OLED Driver Circuits: OLED-on-OS-on-Si
Chapter IV. Industry Layout and Player Dynamic Updates
- XR Companies M&A Strategies Overview for LEDoS
- Google M&A Strategies (JDC/Raxium)
- Meta M&A Strategies (InfiniLED/MLED)
- Apple M&A Strategies (Luxvue/Tesoro)
- Porotech
- JBD
- Sitan
- Raysolve
- Saphlux
- Mojo Vision
- Ostendo
- LG OLEDoS Advancement History (2021-2024)
- Collaborate to Enter the High-end MR Competition in Businesses
- Apple Vision Pro Display and Optic
- Apple Vision Pro Spillover Effect
- Apple Vision Pro as a Productivity Tool for Consumer Market
- Microdisplay Battle between LCD and OLED: Quest 3 vs. Vision Pro










