 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911329
法国快递、速递、小包裹市场:份额分析、行业趋势、统计数据和成长预测(2026-2031 年)France Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
2025 年法国快递、速递和小包裹(CEP) 市值为 187.2 亿美元,预计到 2031 年将达到 228.3 亿美元,高于 2026 年的 193.5 亿美元。
预计在预测期(2026-2031 年)内,复合年增长率将达到 3.36%。
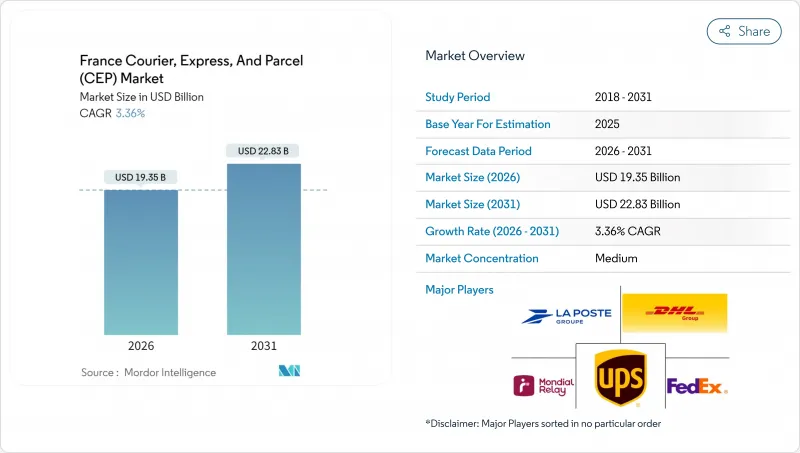
这一成长轨迹受到电子商务扩张、亚洲跨境物流以及促进低排放量营运的监管变化的影响。随着线上消费超过小包裹零售,包裹量不断成长,户外广告网路帮助业者提高配送密度并减少投递失败率。国际市场促进了小包裹的流通,增加了公路运输里程,而低申报价值则对利润率构成压力。同时,诸如法国的25个低排放区(ZFE-M)等永续性法规正在加速电动车和货运自行车在人口密集的城市中心的普及,从而永久性地改变了「最后一公里」的成本结构。为了在维持服务品质的同时达到成本和环境目标,现有企业和新参与企业竞相升级枢纽设施、数位化工具和替代燃料车辆,竞争日益激烈。
法国快递、速递、小包裹市场趋势与分析
电子商务渗透率快速成长
2024年第二季度,法国国内线上零售额年增8.4%,各大城市的小包裹量均有所成长。配送点密度的增加提高了车辆运转率,而全通路零售商则增加了宅配和线上订购线下取货服务,进一步拓展了其配送通路。巴黎的「暗店」业者正致力于提供两小时以内的配送服务,迫使承运商重新设计商店微型仓配区域的路线。法国邮政的12.8万个收发货点有助于降低配送失败的风险并缩短主干路线,从而有效控製成本。电子商务客户越来越倾向于选择永续的配送方式,而拥有碳减排认证服务的承运商在高端配送服务中获得了定价权。
来自亚洲的跨境小包裹货运量增加
预计到2024年,将有约46亿件小小包裹进入欧洲,其中91%来自中国,将重塑国内物流网络的经济格局。业者被迫处理大量低价值商品,这些商品占用空间大,但利润率低。中国电商平台与国际宅配公司(例如Temu和DHL)的合作,正将货物转运至法国机场,而这些机场目前已承担电商尖峰时段的货运量。儘管欧盟提案的低价值商品课税改革方案带来了战略上的不确定性,但取消最低价值免税额度可能会提高获利能力。国内业者正在透过以下方式应对:加快清关速度,并透过自动化海关资料收集和扩大入口网站地区的保税分类空间来降低处理成本。
价格竞争和人事费用给利润率带来压力。
2024年第四季度,道路运输公司破产数量增加了35.4%,原因是许多业者难以将不断上涨的货运和燃油成本转嫁给托运人。由于大规模电商合约的激烈竞标,高铁运价依然低迷,而大都会圈「最后一公里」的工资却在上涨,因为那里的就业机会很多。全球物流整合商正在裁员,联邦快递计画在2025年于欧洲裁员多达2,000人,以在疲软的价格环境下维持利润率。分散的独立司机分包模式进一步削弱了价格约束,许多线路的运能超过了需求。
细分市场分析
到2025年,製造业将占总收入的33.01%,主要驱动力来自汽车、航太和机械出口,这些产业需要精准的B2B交付。电子商务在2026年至2031年间将以4.24%的复合年增长率成长,这将带来大量的住宅配送,并重塑网路格局。医疗保健和金融服务由于监管和安全方面的要求,仍将保持小众但利润丰厚的态势。
多元化的需求结构将缓解某些产业疲软的影响:固定间隔的工业取货服务将提高离峰时段的车辆运转率,而隔夜住宅配送服务将提高资产利用率。能够平衡工业物流和消费物流的营运商很可能在法国宅配、速递和包裹市场占据主导地位。
预计2025年,国际快递服务成长将超过国内快递服务,并在2026年至2031年间维持4.05%的复合年增长率。然而,到2025年,国内快递仍将主导法国快递、速递、小包裹(CEP)市场65.62%的份额。来自亚洲平台的低价值进口商品推动了巴黎戴高乐机场和里昂圣埃克絮佩里机场小包裹量的增加,迫使承运商加强海关自动化流程以确保运输时间。国内快递业务受惠于密集的收件点网路和符合消费者预期的快速递送,但由于托运人会将价格与跨境服务进行比较,因此面临利润压力。
为了赢得消费者对国际运输的信任,营运商正透过免税选项和即时追踪功能来凸显自身优势。法国邮政(La Poste)2024年跨境商店件(OOH)业务量增加52%,显示灵活的取件方式可以有效降低不断上涨的「最后一公里」运输成本。那些能够熟练海关数据收集并提供端到端可视性的运输运营商,预计将在法国快递小包裹(CEP)市场不断增长的跨境领域获得更高的利润率。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 分析师支持(3个月)
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 人口统计数据
- 按经济活动分類的GDP分配
- 按经济活动分類的GDP成长
- 通货膨胀
- 经济表现和公司概况
- 电子商务产业的趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 运输和仓储业的GDP
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 物流绩效
- 基础设施
- 法律规范
- 价值炼和通路分析
- 市场驱动因素
- 电子商务渗透率快速成长
- 亚洲跨境小型货物吞吐量增加
- 更快的最后一公里配送速度和对户外广告的需求
- 推动永续性,迈向零排放车辆
- 2024年巴黎奥运物流改善措施(货运自行车区)
- Z世代(C2C)推动二手市场快速成长
- 市场限制
- 价格竞争和人事费用给利润率带来压力。
- 城市土地利用和ZFE-M法规
- 来自亚洲地区的低价值地块会降低获利能力。
- 城市週边停车场缺乏高功率电动车充电设施
- 市场创新
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 收件地址
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 配送速度
- 表达
- 非快递
- 模型
- B2B
- B2C
- C2C
- 运输重量
- 重型货物运输
- 轻型和重型货物运输
- 中型重型货物运输
- 交通工具
- 空气
- 陆上
- 其他的
- 终端用户产业
- 电子商务
- 金融服务(BFSI)
- 卫生保健
- 製造业
- 一级产业
- 批发零售(线下)
- 其他的
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 关键策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- Integer Capital Group
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- STERNE Group
- United Parcel Service(UPS)
- Walden Group
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The France courier, express, and parcel market was valued at USD 18.72 billion in 2025 and estimated to grow from USD 19.35 billion in 2026 to reach USD 22.83 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 3.36% during the forecast period (2026-2031).

E-commerce growth, cross-border flows from Asia, and regulatory changes that favor low-emission operations shape this trajectory. Parcel volumes climb as online spending grows faster than store-based retail, while out-of-home (OOH) networks help operators raise stop density and limit failed deliveries. International marketplaces drive inbound small-parcel flows that boost line-haul mileage yet compress margins because of their low declared value. Meanwhile, sustainability mandates such as France's 25 active low-emission zones (ZFE-M) accelerate fleet electrification and cargo-bike adoption in dense city cores, permanently shifting last-mile cost structures. Competitive intensity rises as incumbents and new entrants race to upgrade hubs, digital tools, and alternative-fuel fleets in order to preserve service quality while meeting cost and environmental targets.
France Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
E-Commerce Penetration Surge
National online retail sales grew 8.4% year-on-year in Q2 2024, widening the parcel pool in every major city. Higher stop density lifts vehicle utilization, while omnichannel retailers add home-delivery and click-and-collect flows that broaden shipment origin points. Dark-store operators in Paris now target sub-two-hour service windows, forcing carriers to redesign routing for micro-fulfillment zones. Pickup-point expansion underpins cost control, as La Poste operates 128,000 sites that lower failed-delivery risk and shorten trunk routes. E-commerce shoppers increasingly favor sustainable options, and carriers that certify carbon-reduced services gain pricing power within premium delivery tiers.
Rising Cross-Border Parcel Flows from Asia
About 4.6 billion small parcels entered Europe in 2024, with 91% dispatched from China, reshaping domestic network economics. Operators must process vast volumes of low-value items that occupy capacity yet generate slender margins. Partnerships between Chinese marketplaces and global express firms, such as Temu's tie-ups with DHL, channel traffic through French airports that already handle peak e-commerce flows. Proposed EU tax reforms on low-value consignments inject strategic uncertainty but could also lift yields if minimum-value exemptions disappear. Domestic players respond by automating customs data capture and expanding bonded sortation space at gateway hubs to speed clearance and cut handling costs.
Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Labor Costs
Road-transport company insolvencies rose 35.4% in Q4 2024 as operators struggled to pass wage and fuel hikes onto shippers. Fierce bidding for large e-commerce contracts keeps line-haul rates low, even as last-mile wages climb in dense cities where employment alternatives abound. Global integrators rationalize headcounts FedEx cut up to 2,000 European jobs in 2025 to protect margins in a soft-pricing environment. Fragmented owner-driver subcontracting further dampens pricing discipline because capacity outstrips demand on many lanes.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Demand for Faster Last-Mile and OOH Options
- Sustainability Push for Zero-Emission Fleets
- Urban Land-Use and ZFE-M Restrictions
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing produced 33.01% of 2025 revenue, anchored by automotive, aerospace, and machinery exports that require precise B2B deliveries. E-commerce, advancing at a 4.24% CAGR between 2026-2031, injects high-volume residential drops that reshape network design. Healthcare and financial services stay niche yet high-margin due to regulatory and security requirements.
Diversified demand shields carriers from sector-specific slowdowns. Fixed-interval industrial collections fill off-peak van capacity, while evening residential rounds improve asset utilization. Operators that balance industrial and consumer flows are positioned to outperform in the France courier, express, and parcel market.
International services grew faster than domestic in 2025 and are on course for a 4.05% CAGR between 2026-2031, even though the France courier, express, and parcel market size remains dominated by domestic deliveries at 65.62% share in 2025. Low-value imports from Asian platforms swell parcel counts at Paris-CDG and Lyon Saint-Exupery, compelling carriers to refine customs-clearance automation to protect transit times. Domestic volumes benefit from dense pickup-point networks and short lead times that align with consumer expectations, yet face yield pressure when shippers benchmark prices against cross-border offers.
Operators differentiate through duty-paid options and real-time tracking to win shopper trust on international consignments. La Poste's 52% jump in cross-border OOH traffic in 2024 demonstrates that flexible collection mitigates last-mile cost inflation. Carriers that master customs data capture and offer end-to-end visibility are expected to secure higher margins on the expanding cross-border segment of the France courier, express, and parcel market.
The France Courier, Express, and Parcel Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, Business-To-Consumer, and Consumer-To-Consumer). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- Integer Capital Group
- International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- STERNE Group
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
- Walden Group
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 E-Commerce Penetration Surge
- 4.15.2 Rising Cross-Border Parcel Flows from Asia
- 4.15.3 Demand for Faster Last-Mile and OOH Options
- 4.15.4 Sustainability Push for Zero-Emission Fleets
- 4.15.5 Paris-2024 Logistics Upgrades (Cargo-Bike Zones)
- 4.15.6 Gen-Z Second-Hand Marketplace Boom (C2C)
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Labor Costs
- 4.16.2 Urban Land-Use and ZFE-M Restrictions
- 4.16.3 Low-Value Parcels from Asian Sites Erode Yields
- 4.16.4 Sparse High-Power EV Charging at Peri-Urban Depots
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 FedEx
- 6.4.3 GEODIS
- 6.4.4 Integer Capital Group
- 6.4.5 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.6 La Poste Group
- 6.4.7 STERNE Group
- 6.4.8 United Parcel Service (UPS)
- 6.4.9 Walden Group
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment









