 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911345
马来西亚润滑油市场:市场占有率分析、产业趋势与统计、成长预测(2026-2031)Malaysia Lubricants - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
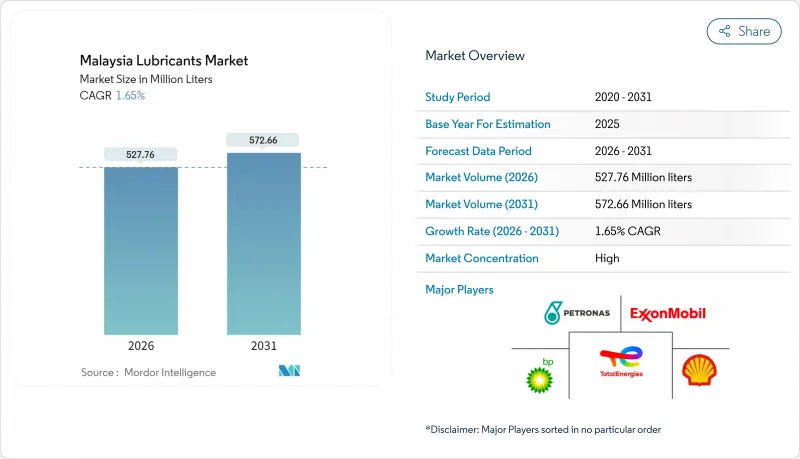
预计到 2026 年,马来西亚润滑油市场规模将达到 5.2776 亿公升,高于 2025 年的 5.1919 亿公升,预计到 2031 年将达到 5.7266 亿公升,2026 年至 2031 年的年复合成长率(CAGR)为 1.65%。
儘管由于市场成熟,成长并不十分显着,但仍保持稳定。同时,车辆保有量增加、新製造产能扩张以及基础设施投资成长对可靠润滑性能的需求等因素正在推动市场发展。乘用车在马来西亚国内汽车保有量中占据主导地位,马来西亚是东南亚国协国家中唯一一个汽车保有量超过摩托车保有量的国家,这推动了对优质引擎油的需求。政府实施的「第十二个马来西亚计画」和「2030年国家工业总体规划」(NIMP 2030)正在推动工业、建筑和高科技製造业的需求。同时,电动车的普及、更长的换油週期以及设备效率的提高限制了整体需求的成长,迫使供应商从散装矿物油转向高价值的合成油和特殊油。
马来西亚润滑油市场趋势及分析
汽车保有量和新车销售的成长将推动持续的需求。
预计到2024年,汽车总销量将达到816,747辆,年增2.1%,这将支撑润滑油需求的成长,儘管市场日益成熟。乘用车销量已超过摩托车,需求也从摩托车润滑油转向了高端汽车机油。欧盟5燃油标准的实施促使维修店和车主改用低硫全合成机油,以保护触媒后后处理系统。商用车也做出了贡献,更大的引擎油箱容量和更严格的车队维护计划抵消了乘用车销售成长放缓的影响。产业协会预测,到2030年,汽车数量将持续成长,尤其是在巴生谷、槟城和柔佛,这将为维持基础消费水准奠定基础。
第十二个马来西亚计划下的工业和基础设施扩张
马来西亚的目标是到2030年创造70万个高技能製造业就业岗位,并将高科技出口比例翻一番,达到6%。半导体、电子和石化计划需要可靠的液压油、金属加工油和加工油油,这些油品必须能够承受无尘室和高温环境的考验。预计到2023年,製造业投资将达到1,520亿马币,其中外国投资者约占化学产业资本流入的70%,这表明他们对该行业成长的持续信心。柔佛-新加坡经济特区、东海岸铁路和边佳兰综合体等基础设施计划,从建设阶段到日常工厂运营,都推动了对施工机械、大型发动机和石化设施润滑油的需求。
更长的换油週期限制了销售成长
现代合成机油的换油週期为每加註15,000至20,000公里,而传统矿物油的换油週期仅为5,000至10,000公里。即使行驶里程持续增加,这也能显着降低每辆车每年的机油消耗量。车队管理人员依赖在用油分析来延长换油週期,同时又不影响保固范围。因此,入门级矿物油销售量的下滑抵消了车队数量成长的收益,製造商正透过促销利润更高的全合成机油来弥补收入损失。为了弥补润滑油更换频率的降低,维修厂纷纷推出包含更换滤芯、四轮定位和更换空调滤芯等服务的套餐。
细分市场分析
预计到2025年,汽车机油将占马来西亚润滑油市场的50.60%。不断增长的汽车保有量支撑着基本需求,而日益严格的OEM规范正在加速从API SN等级向SP和ILSAC GF-6等级的转变,后者俱有更高的抗氧化稳定性。变速箱油是成长最快的产品,年复合成长率达2.50%,这主要得益于自排变速箱、双离合器变速箱和无段变速箱的广泛应用。混合动力汽车需要专用的电子变速箱润滑迴路,进一步推动了这项需求。马来西亚润滑油市场,包括液压油、金属加工液和加工油,也在成长,因为半导体工厂、精密加工中心和化工厂需要无污染作业和更长的润滑油使用寿命。
马来西亚润滑油市场报告按产品类型(汽车引擎油、工业引擎油、变速箱油、齿轮油、煞车油、液压油、润滑脂等)、终端用户产业(汽车、船舶、航太、重型机械、工业)和基础油类型(矿物油、合成油、半合成油、生物基油)进行细分。市场预测以公升为单位。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 市场驱动因素
- 汽车拥有量和新车销量增加
- 工业和基础设施扩张
- 过渡到合成和高性能润滑油
- 第十二个马来西亚计划下的大型政府计划
- 润滑油零售业电子商务的兴起(二线城市)
- 市场限制
- 延长换油週期,提高引擎效率
- 加速推广电动车
- 原油价格波动给利润率带来压力。
- 价值链分析
- 法律规范
- 终端用户趋势
- 汽车产业
- 製造业
- 波特五力模型
- 供应商的议价能力
- 买方的议价能力
- 新进入者的威胁
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争程度
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 依产品类型
- 汽车引擎油
- 工业机油
- 变速箱油
- 齿轮油
- 煞车油
- 油压
- 润滑脂
- 加工油(包括橡胶加工油和白油)
- 金属加工油
- 涡轮机油
- 变压器油
- 其他产品类型
- 按最终用户行业划分
- 车
- 搭乘用车
- 商用车辆
- 摩托车
- 船
- 航太
- 重型机械
- 建造
- 矿业
- 农业
- 工业的
- 发电
- 冶金/金属加工
- 纺织业
- 石油和天然气
- 其他终端用户产业
- 车
- 依基础油类型
- 矿物油性润滑剂
- 合成润滑油
- 半合成润滑油
- 生物性润滑剂
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 策略趋势
- 市占率(%)/排名分析
- 公司简介
- Advance Lube Enterprise Sdn Bhd
- BP Plc(Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Excelube Marketing Sdn Bhd
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- Liqui Moly Malaysia
- MSB Global Group Sdn. Bhd.
- Petroliam Nasional Berhad(PETRONAS)
- Petron
- Shell plc
- SINOPEC
- TotalEnergies
- UMW Lubetech Sdn Bhd
- Valvoline(Saudi Arabian Oil Co.)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
第八章:执行长面临的关键策略挑战
Malaysia Lubricants Market size in 2026 is estimated at 527.76 million liters, growing from 2025 value of 519.19 million liters with 2031 projections showing 572.66 million liters, growing at 1.65% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Growth remains steady rather than spectacular because the market is already mature, yet it benefits from a wider vehicle parc, new manufacturing capacity, and infrastructure spending that require dependable fluid performance. Passenger cars dominate the national fleet, making Malaysia the only ASEAN country where four-wheelers outnumber two-wheelers, which lifts demand for premium engine oils. Government execution of the 12th Malaysia Plan and the National Industrial Master Plan 2030 (NIMP 2030) adds incremental volume in industrial, construction, and high-tech manufacturing applications. Meanwhile, the electric-vehicle (EV) rollout, longer drain intervals, and rising equipment efficiency limit total volume growth, prompting suppliers to shift toward higher-value synthetic and specialty formulations rather than bulk mineral grades.
Malaysia Lubricants Market Trends and Insights
Rising Vehicle Parc and New-Car Sales Drive Sustained Demand
Total vehicle sales reached 816,747 units in 2024, a 2.1% gain that supports lubricant volume growth despite market maturity. Passenger cars already outnumber two-wheelers, so demand shifts toward higher-grade automotive engine oils rather than motorcycle lubricants. The implementation of Euro 5 fuel standards prompts workshops and motorists to switch to low-sulfur, full-synthetic formulations that protect catalytic after-treatment systems. Commercial vehicles also contribute because larger sump capacities and stricter fleet maintenance schedules offset slower passenger-car sales growth. Industry associations expect continuous parc expansion through 2030, particularly in the Klang Valley, Penang, and Johor, anchoring base-level consumption.
Industrial and Infrastructure Expansion Under 12th Malaysia Plan
Malaysia aims to create 700,000 high-skill manufacturing jobs by 2030 and double its high-tech export share to 6%. Semiconductor, electronics, and petrochemical projects require reliable hydraulic fluids, metalworking fluids, and process oils that withstand stringent clean-room or high-temperature environments. Manufacturing investments reached RM152 billion in 2023, with foreign investors accounting for nearly 70% of the chemical sector's capital inflows, indicating confidence in continued industrial growth. Infrastructure projects, such as the Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone, East Coast Rail Link, and Pengerang Integrated Complex, increase lubricant demand for construction machinery, heavy-duty engines, and petrochemical equipment throughout the build-out phase and in routine plant operations.
Longer Oil-Drain Intervals Constrain Volume Growth
Modern synthetics enable drain intervals of 15,000-20,000 kilometers on a single fill, compared with 5,000-10,000 kilometers for older mineral formulations. This sharply lowers annual liter consumption per vehicle, even though the number of kilometers driven continues to rise. Fleet managers rely on in-service oil analysis to extend drains without compromising warranty coverage. Consequently, volume erosion within entry-level mineral categories offsets gains from the rising car population, and producers bolster revenues by marketing higher-margin full synthetics. Workshops adapt by offering bundled services-such as filter changes, alignment, and cabin-air filtration-to compensate for reduced lubricant frequency.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Synthetic and High-Performance Lubricant Adoption Accelerates
- Government Mega-Projects Create Infrastructure Lubricant Demand
- Electric Vehicle Adoption Reshapes Long-Term Demand Patterns
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Automotive engine oil accounted for 50.60% of the Malaysia lubricants market share in 2025. A large and growing car population sustains baseline demand, while stricter OEM specifications accelerate the migration from API SN to SP and ILSAC GF-6 categories, which offer higher oxidative stability. Transmission fluids are the fastest-growing product, registering a 2.50% CAGR as automatic, dual-clutch, and continuously variable gearboxes proliferate. Hybrid vehicles further expand this need due to dedicated e-transmission lubrication circuits. The Malaysian lubricants market size, linked to hydraulic fluids, metalworking fluids, and process oils, also rises because semiconductor plants, precision machining centers, and chemical complexes require contamination-free operations and extended fluid life.
The Malaysia Lubricants Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Automotive Engine Oil, Industrial Engine Oil, Transmission Fluids, Gear Oil, Brake Fluids, Hydraulic Fluids, Greases, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive, Marine, Aerospace, Heavy Equipment, and Industrial), and Base Stock Type (Mineral Oil-Based, Synthetic, Semi-Synthetic, and Bio-Based). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Volume (Liters).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Advance Lube Enterprise Sdn Bhd
- BP Plc (Castrol)
- Chevron Corporation
- Excelube Marketing Sdn Bhd
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- FUCHS
- Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- Liqui Moly Malaysia
- MSB Global Group Sdn. Bhd.
- Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS)
- Petron
- Shell plc
- SINOPEC
- TotalEnergies
- UMW Lubetech Sdn Bhd
- Valvoline (Saudi Arabian Oil Co.)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising vehicle parc and new-car sales
- 4.2.2 Industrial and infrastructure expansion
- 4.2.3 Shift toward synthetic/high-performance lubricants
- 4.2.4 Government mega-projects under 12th Malaysia Plan
- 4.2.5 E-commerce emergence for lubricant retail (Tier-2 cities)
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Longer oil-drain intervals and engine efficiency gains
- 4.3.2 Accelerating electric-vehicle adoption
- 4.3.3 Crude-oil price volatility pressuring margins
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Framework
- 4.6 End-User Trends
- 4.6.1 Automotive Industry
- 4.6.2 Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Volume)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Automotive Engine Oil
- 5.1.2 Industrial Engine Oil
- 5.1.3 Transmission Fluids
- 5.1.4 Gear Oil
- 5.1.5 Brake Fluids
- 5.1.6 Hydraulic Fluids
- 5.1.7 Greases
- 5.1.8 Process Oil (Including Rubber Process Oil and White Oil)
- 5.1.9 Metalworking Fluids
- 5.1.10 Turbine Oil
- 5.1.11 Transformer Oil
- 5.1.12 Other Product Types
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.2.1.1 Passenger Vehicles
- 5.2.1.2 Commercial Vehicles
- 5.2.1.3 Two-Wheelers
- 5.2.2 Marine
- 5.2.3 Aerospace
- 5.2.4 Heavy Equipment
- 5.2.4.1 Construction
- 5.2.4.2 Mining
- 5.2.4.3 Agriculture
- 5.2.5 Industrial
- 5.2.5.1 Power Generation
- 5.2.5.2 Metallurgy and Metalworking
- 5.2.5.3 Textiles
- 5.2.5.4 Oil and Gas
- 5.2.5.5 Other End-Use Industries
- 5.2.1 Automotive
- 5.3 By Base Stock Type
- 5.3.1 Mineral Oil-Based Lubricants
- 5.3.2 Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.3 Semi-Synthetic Lubricants
- 5.3.4 Bio-Based Lubricants
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share (%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Advance Lube Enterprise Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.2 BP Plc (Castrol)
- 6.4.3 Chevron Corporation
- 6.4.4 Excelube Marketing Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.5 Exxon Mobil Corporation
- 6.4.6 FUCHS
- 6.4.7 Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Liqui Moly Malaysia
- 6.4.9 MSB Global Group Sdn. Bhd.
- 6.4.10 Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS)
- 6.4.11 Petron
- 6.4.12 Shell plc
- 6.4.13 SINOPEC
- 6.4.14 TotalEnergies
- 6.4.15 UMW Lubetech Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.16 Valvoline (Saudi Arabian Oil Co.)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment








