 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1911804
欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP) 市场:市场份额分析、行业趋势和统计数据、成长预测 (2026-2031)Europe Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
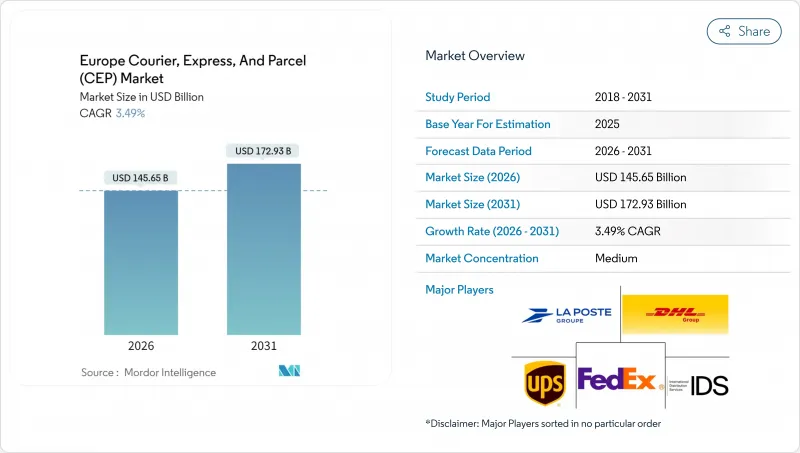
预计到 2026 年,欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP) 市场规模将达到 1,456.5 亿美元。
这意味着从 2025 年的 1,407.4 亿美元成长到 2031 年的 1,729.3 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 3.49%。
这种温和的成长轨迹掩盖了更深层的结构性变化,电子商务的扩张、监管的协调以及技术的应用正在重塑整个欧洲大陆的「最后一公里」配送网路。零售商正优先考虑差异化的配送体验。由于81%的欧洲消费者如果无法选择自己偏好的配送方式就会放弃购买,竞争的焦点正从价格转向服务品质。欧盟层级的增值税改革-数位时代增值税改革(ViDA)将于2035年前分阶段实施,届时将规范跨境资料流,并有利于拥有先进合规系统的大型营运商。同时,超过50万的司机缺口正在加速自动化投资,导致营运商面临劳动力短缺的问题。日益严格的永续性要求以及在市中心(尤其是在荷兰)引入零排放区,正在推动扩大电动车队和宅配柜密度,并促进有能力投资绿色资产的运输业者之间的整合。
欧洲宅配、速递与小包裹(CEP) 市场趋势与洞察
爆炸性成长的电子商务和全通路零售的快速发展
社交电商的兴起正推动小包裹配送摆脱传统的季节性模式,转向难以预测、受趋势主导的高峰模式,这使得欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP) 市场亟需灵活的运力规划。预计到 2025 年,德国电商包装材料支出将达到 39.9 亿美元,并在 2034 年前保持 14.03% 的年复合成长率(CAGR),凸显了包装材料对这一增长的重要性。由于 79% 的买家表示,如果退货流程繁琐,他们会取消订单,因此,先进的逆向物流正从附加服务转变为核心竞争力。医疗保健领域的小包裹递送也正乘着这股全通路浪潮的东风。 DHL 斥资 20 亿欧元(约 22 亿美元)的医疗保健物流业务正在资助专业的低温运输服务,以满足日益增长的网路药局需求。网红推广活动带来的包裹量集中化,迫使物流公司设计动态路线演算法来应对流量激增,同时维持服务水准。
欧盟内部跨境贸易自由化与增值税改革
ViDA电子帐单令将于2030年7月生效,届时欧盟内部所有形式的B2B贸易将统一采用EN16931标准,从而减少人工文书工作并加快清关速度。一站式服务中心将于2028年7月扩展,届时成员国之间将可使用单一增值税号,这对每天处理数百万个跨境小包裹的欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)市场而言是一项重大利好。强制性的10天课税期要求企业对IT系统维修,这将使已拥有整合资料湖的营运商获得优势。同时,进口管制系统2(ICS2)要求在欧盟边境通行前提交详细的进口总表,这将加强安全性,并为拥有详细产品级资料管道的承运商提供竞争优势。这些措施将降低扩张壁垒,同时提高数位化合规标准,并促进向国际一体化的长期转型。
价格竞争和体积重量系统带来的利润率压力
疫情后产能过剩导致业者重新推出折扣以捍卫市场份额,儘管货运量有所增长,但欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP) 市场的盈利却在下降。按体积计费的运费本应反映实际消耗量,但营运商通常会为策略客户免除此项费用,这比提高成本效益更快地挤压了利润空间。 Impost 收购 YoDell Inc. 和 Sending Inc. 凸显了营运商转向透过非内生性扩张来降低固定成本的趋势。承运商增加了尖峰时段费用和燃油额外费用,而托运人则利用多承运商软体来提高价格边际收益,以此进行反击。这种拉锯战限制了短期内的价格復苏,同时也进一步推动了产业的整合。
细分市场分析
到 2025 年,电子商务领域的份额将保持在 34.45%,其中医疗小包裹预计将以 3.79% 的复合年增长率在 2026 年至 2031 年间实现最快增长。人口老化和网路药局的兴起使得温控最后一公里配送成为优先事项。
DHL 的 20 亿欧元(22 亿美元)计画旨在推动对符合 GDP 标准的设施、冷链包装和专用控制塔的投资。製造商需要专用的零件运输路线,而金融服务文件则催生了一个对安全快递服务的特定市场。在零售淡季,货运公司会交叉销售当日送达的生物医学产品运输服务,以弥补车队运转率的下降。
2025年,国际小包裹配送将占欧洲宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)市场收入的34.28%,国内服务则占据剩余的市场份额。预计2026年至2031年间,国际货运的复合年增长率将达到3.73%,超过国内货运的成长速度,主要得益于简化的增值税支付方式和经销商履约。
随着配送时间与国内标准接轨,欧洲消费者越来越多地从邻国购买商品。 InPost 的网路于 2024 年 11 月在欧盟八个国家推出,采用自助取件柜配送模式,避免了人工分类和海关延误。 ICS2 资料要求初期会延长跨境货物的前置作业时间,但会减少欧盟内部运输的摩擦点。服务可预测性的提高吸引了更多中小型出口商,促使现有邮政业者改善追踪系统并扩大高端跨境服务。
其他福利
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 人口统计数据
- 按经济活动分類的GDP分配
- 按经济活动分類的GDP成长
- 通货膨胀
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业的趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 运输和仓储业的GDP
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 物流绩效
- 基础设施
- 法律规范
- 中欧和东欧
- 法国
- 德国
- 义大利
- 荷兰
- 北欧国家
- 俄罗斯
- 西班牙
- 瑞士
- 英国
- 价值炼和通路分析
- 市场驱动因素
- 爆炸性成长的电子商务和全通路零售的快速发展
- 欧盟内部跨境贸易自由化与增值税改革
- 扩大宅配柜和PUDO网络
- 透过自动化和人工智慧提高营运效率
- 透过碳成本内部化实现绿色CEP车队优势
- 多承运商小包裹管理平台的兴起
- 市场限制
- 价格竞争和按尺寸收费系统对利润率造成压力。
- 司机和仓库工人严重短缺
- 宅配工人国家最低工资法
- 网路安全和资料主权合规成本不断上升
- 市场创新
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 运输速度
- 表达
- 非快递
- 模型
- B2B
- 企业对消费者 (B2C)
- 消费者对消费者 (C2C)
- 运输重量
- 重型货物
- 轻型货物
- 中等重量货物
- 交通工具
- 航空
- 路
- 其他的
- 终端用户产业
- 电子商务
- 金融服务(BFSI)
- 卫生保健
- 製造业
- 一级产业
- 批发零售(线下)
- 其他的
- 国家
- 阿尔巴尼亚
- 保加利亚
- 克罗埃西亚
- 捷克共和国
- 丹麦
- 爱沙尼亚
- 芬兰
- 法国
- 德国
- 匈牙利
- 冰岛
- 义大利
- 拉脱维亚
- 立陶宛
- 荷兰
- 挪威
- 波兰
- 罗马尼亚
- 俄罗斯
- 斯洛伐克共和国
- 斯洛维尼亚
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 瑞士
- 英国
- 其他欧洲
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 关键策略措施 竞争格局:市场集中度/关键策略趋势/市场占有率分析/公司简介/DHL集团/
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- International Distributions Services(including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Logista
- Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- Post NL
- Poste Italiane
- Sterne Group
- United Parcel Service(UPS)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 145.65 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 140.74 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 172.93 billion, growing at 3.49% CAGR over 2026-2031.

This moderate trajectory masks deeper structural shifts as e-commerce expansion, regulatory harmonization, and technology adoption reshape last-mile networks across the continent. Retailers are prioritizing delivery-experience differentiation because 81% of European shoppers abandon baskets when preferred options are unavailable, tilting competitive focus from price to service quality. EU-level VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) reforms, phased through 2035, are standardizing cross-border data flows, favoring scale players with advanced compliance systems. Meanwhile, a driver shortfall exceeding 500,000 openings has accelerated automation investment as operators grapple with labor scarcity. Heightened sustainability mandates and city-center zero-emission zones, notably in the Netherlands, add urgency for electric fleets and parcel-locker density, reinforcing consolidation among carriers that can fund green assets.
Europe Courier, Express, And Parcel (CEP) Market Trends and Insights
Explosive E-Commerce and Omnichannel Retail Boom
Social-commerce momentum is steering parcel flows toward unpredictable, trend-driven peaks rather than traditional seasonality, requiring flexible capacity planning across the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market. German e-commerce packaging spend reached USD 3.99 billion in 2025, reflecting 14.03% CAGR (2025-2030) expectations through 2034, underlining the packaging intensity of this growth. Reverse-logistics sophistication is turning from add-on to core capability, as 79% of shoppers cancel purchases when returns appear difficult. Healthcare parcels are piggybacking on this omnichannel wave; DHL's EUR 2 billion (USD 2.20 billion) health-logistics rollout funds specialized cold-chain services aligned with rising e-pharmacy penetration. Volume concentration around influencer promotions compels carriers to design dynamic routing algorithms to absorb traffic surges without impairing service-level compliance.
Liberalized Intra-EU Cross-Border Trade and VAT Reforms
ViDA's e-invoicing mandate arriving in July 2030 will standardize EN16931 formats for all intra-EU B2B trades, shrinking manual paperwork and accelerating customs clearances. The July 2028 expansion of the One-Stop Shop lets merchants maintain a single VAT ID across member states, a boon for the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market handling millions of cross-border parcels daily. Advanced IT retrofits are required because declarations must be filed within 10 days of chargeable events, favoring operators that already run integrated data lakes. Concurrently, Import Control System 2 obliges detailed entry summaries before crossing EU borders, tightening security and tilting the playing field to carriers with rich product-level data pipelines. Together, these measures reduce friction in sales expansion while raising digital-compliance thresholds, shaping a long-run shift toward international consolidation.
Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Dimension-Based Tariffs
Post-pandemic overcapacity has resurrected discounting as operators defend share, eroding yields despite volume growth in the Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market. Dimensional-weight pricing, meant to reflect cubic consumption, often gets waived for strategic accounts, compressing margins faster than cost-line efficiencies. InPost's acquisitions of Yodel and Sending highlight the pivot toward inorganic density to dilute fixed overhead. Carriers add peak or fuel surcharges but shippers push back, leveraging multicarrier software to arbitrage rates. The tug-of-war limits near-term price recovery while stoking further consolidation.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Expansion of Parcel Lockers and PUDO Networks
- Automation and AI-Driven Operational Efficiency
- Acute Driver and Warehouse-Labor Shortages
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
E-commerce retained a 34.45% share in 2025, yet healthcare parcels are set to rise fastest at 3.79% CAGR between 2026-2031. Aging populations and e-pharmacy expansion make temperature-controlled last-mile a priority.
DHL's EUR 2 billion (USD 2.20 billion) program funds GDP-compliant facilities, cool-chain packaging, and dedicated control towers. Manufacturers require part-express lanes, and financial-services documents sustain secure-courier niches. Carriers cross-sell same-day biomedical pickup to monetize vehicle downtime during retail off-peak cycles.
Cross-border parcel flows accounted for 34.28% of revenues in 2025 as domestic services retained the remainder of Europe courier, express, and parcel (CEP) market share. International consignments are forecast to climb at a 3.73% CAGR between 2026-2031, outpacing domestic growth as ViDA simplifies VAT settlement and merchants centralize fulfillment.
European shoppers increasingly purchase from neighboring states once delivery times align with domestic benchmarks. InPost's November 2024 network activation across eight EU countries uses a locker-to-locker model that bypasses manual sorting and customs delays. ICS2 data prerequisites initially elongate lead-times for goods sourced outside the bloc, but EU-internal routes face fewer friction points. Improved service predictability attracts SME exporters, prompting postal incumbents to upgrade track-and-trace and push into premium cross-border offerings.
The Europe Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (E-Commerce and More), Destination (Domestic and International), Speed of Delivery (Express and Non-Express), Shipment Weight (Heavy Weight Shipments, and More), Mode of Transport (Air, Road, and Others), and Model (Business-To-Business, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- GEODIS
- International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- La Poste Group
- Logista
- Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- Post NL
- Poste Italiane
- Sterne Group
- United Parcel Service (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Logistics Performance
- 4.12 Infrastructure
- 4.13 Regulatory Framework
- 4.13.1 Central and Eastern Europe (CEE)
- 4.13.2 France
- 4.13.3 Germany
- 4.13.4 Italy
- 4.13.5 Netherlands
- 4.13.6 Nordics
- 4.13.7 Russia
- 4.13.8 Spain
- 4.13.9 Switzerland
- 4.13.10 United Kingdom
- 4.14 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.15 Market Drivers
- 4.15.1 Explosive E-Commerce and Omnichannel Retail Boom
- 4.15.2 Liberalized Intra-EU Cross-Border Trade and VAT Reforms
- 4.15.3 Expansion of Parcel Lockers and PUDO Networks
- 4.15.4 Automation and AI-Driven Operational Efficiency
- 4.15.5 Carbon-Cost Internalization Favouring Green CEP Fleets
- 4.15.6 Rise of Multicarrier Parcel-Management Platforms
- 4.16 Market Restraints
- 4.16.1 Margin Squeeze from Price Wars and Dimension-Based Tariffs
- 4.16.2 Acute Driver and Warehouse-Labor Shortages
- 4.16.3 Country-Level Courier Wage-Floor Legislation
- 4.16.4 Rising Cyber-Security and Data-Sovereignty Compliance Costs
- 4.17 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.18 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.18.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.18.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.18.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.18.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.18.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
- 5.7 Country
- 5.7.1 Albania
- 5.7.2 Bulgaria
- 5.7.3 Croatia
- 5.7.4 Czech Republic
- 5.7.5 Denmark
- 5.7.6 Estonia
- 5.7.7 Finland
- 5.7.8 France
- 5.7.9 Germany
- 5.7.10 Hungary
- 5.7.11 Iceland
- 5.7.12 Italy
- 5.7.13 Latvia
- 5.7.14 Lithuania
- 5.7.15 Netherlands
- 5.7.16 Norway
- 5.7.17 Poland
- 5.7.18 Romania
- 5.7.19 Russia
- 5.7.20 Slovak Republic
- 5.7.21 Slovenia
- 5.7.22 Spain
- 5.7.23 Sweden
- 5.7.24 Switzerland
- 5.7.25 United Kingdom
- 5.7.26 Rest of Europe
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DHL Group
- 6.4.2 FedEx
- 6.4.3 GEODIS
- 6.4.4 International Distributions Services (including GLS)
- 6.4.5 La Poste Group
- 6.4.6 Logista
- 6.4.7 Otto GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.8 Post NL
- 6.4.9 Poste Italiane
- 6.4.10 Sterne Group
- 6.4.11 United Parcel Service (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment









