 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906877
马来西亚货运与物流:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据与成长预测(2026-2031)Malaysia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
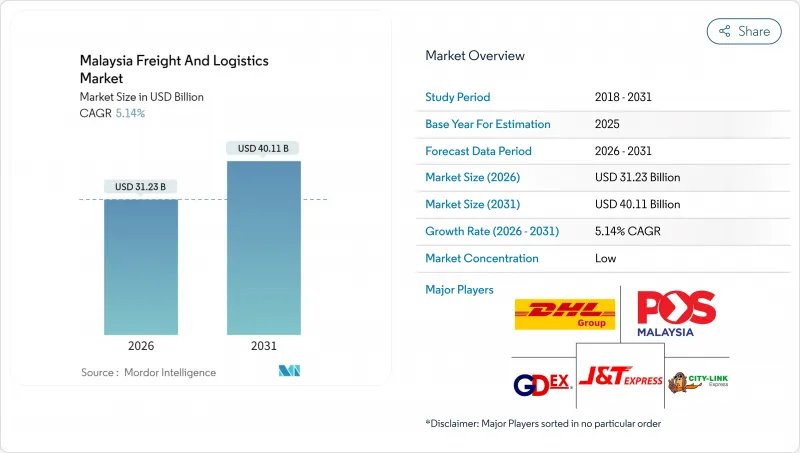
马来西亚货运和物流市场预计将从 2025 年的 297 亿美元成长到 2026 年的 312.3 亿美元,到 2031 年达到 401.1 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 5.14%。
巴生港作为世界第十大货柜港口的崛起、政府对铁路和公路计划的大规模投资以及电子商务的持续增长势头,正推动马来西亚整个货运和物流市场重组供应链网络、优先发展仓储自动化并重新评估与承运人的合作关係。预计到2024年,外国直接投资将达到3,785亿马币(823亿美元),创造20.7万个就业岗位,并带动跨境货运、增值配送和专业製造物流的需求。消费者对当日配送的偏好正在加速末端物流网络的完善,而诸如定向柴油补贴和简化海关手续等监管倡议则缓解了成本压力和边境摩擦。全球承运商正在加强与本地企业的合作,以确保空运量、海运配额和温控运输能力,从而巩固马来西亚作为东盟乃至整个亚太贸易网络枢纽的地位。
马来西亚货运及物流市场趋势及展望
B2C电子商务的爆炸性成长推动了最后一公里配送创新
当日配送已成为普遍预期,各大平台上95%的订单都能在24小时内发出。 64.8%的网路用户更倾向于免费送货,这推动了马来西亚货运物流市场采用自动化分类系统、微型仓配中心和数据驱动的路线规划。像MR DIY这样的零售商在实施机器人系统后效率提升了200%,显示自动化是竞争优势的基础。 UPS与Ninja Van的伙伴关係将全球快递服务扩展到52家零售店,为出口商提供了更广泛的货舱空间和数位追踪服务。同时,中小企业在区域贸易的参与度也不断提高。这些累积效应增强了运力弹性和服务多样性,从而支撑了马来西亚货运物流市场近期的成长动能。
外商直接投资主导的製造业生产激增改变了工业物流
2024年核准的马币(约823亿美元)投资额创历史新高,这些资金正涌入半导体製造厂、先进汽车零件和可再生能源设备领域。半导体投资带动了对防静电包装、安全机器人和保税仓库通道的需求。像MKS Instruments这样的精密设备製造商正在建造“购物中心”,这需要同步的原材料进口和高频次的运输。柔佛-新加坡经济特区内的跨境税收优惠预计将创造100个计划和2万个技术岗位,为马来西亚货运和物流市场的新走廊奠定基础。日益严格的ESG(环境、社会和治理)标准也在推动货物运输的长期多元化,投资者优先考虑靠近铁路支线的可再生能源和多式联运枢纽。
儘管进行了基础设施投资,港口拥挤仍限制了其吞吐能力。
巴生港船舶平均等待时间为1.3至1.46天,堆场运转率超过90%,严重影响了船期可靠性。儘管马来西亚海事单一窗口系统于2025年2月推出,已将文件处理週期从五天缩短至数小时,但码头扩建规模不太可能跟上近期货柜吞吐量的成长。西港控股公司(Westport Holdings)的数十年扩张计划旨在将总吞吐量大幅提升至远超目前的水平,但经红海绕行的航线增加已加剧了到港拥堵和堆场产能过剩。随着全球航运公司重新分配货柜,马来西亚的货运和物流市场正面临短期租船费率飙升和库存失衡的局面,这可能会侵蚀吞吐量成长带来的利润。
细分市场分析
截至2025年,製造业将占马来西亚货运和物流市场的38.98%,主要得益于槟城4,310亿马币(937亿美元)的出口引擎和雪兰莪的电子产业丛集。跨国公司正在寻求保税运输路线、符合静电放电防护(ESD)标准的仓库以及货物护送服务,从而推动服务差异化。电动车零件和可再生能源设备的成长将进一步扩大马来西亚的货运和物流市场,对超大型货柜装卸和专业吊装的需求也将随之成长。儘管批发和零售贸易的绝对规模小规模,但在2026年至2031年期间,受可支配收入成长和数位支付普及的推动,预计其复合年增长率将达到5.46%。像99 Speedmart这样的超级市场计划将其门市数量翻一番,这就需要配备多温区转运中心和位于消费中心附近的微型仓配中心。
在农业、渔业和林业领域,获得清真认证的低温运输对于开拓中东市场至关重要,这提升了演算法驱动的温度追踪平台的商业性价值。建筑物流与RTS Link和槟城机场扩建等重大计划直接相关,需要重型起重机、夜间车队运输和准时製材料供应协调。儘管石油、天然气和采矿业仍具有週期性,但在大宗商品价格波动的情况下,对ISO槽式货柜、船舶清洁服务和管道维护零件的稳定需求仍然是马来西亚货运和物流业的支柱。
到2025年,货运将占马来西亚货运和物流市场收入的55.62%,反映了製造业出口和区域分销的强劲趋势。受电商企业将当日达服务外包给多模态承运商的推动,马来西亚宅配、速递和小包裹解决方案的货运和物流市场规模预计将在2026年至2031年间以5.86%的复合年增长率快速增长。 UPS和Ninja Van等公司在巴生谷地区的扩张,使得自动化枢纽能够利用位址验证软体和物联网标籤来降低投递负载容量,企业正在仓库安装倾斜式分类机,并部署电动货车以避开吉隆坡週边的拥挤路段。此外,16项贸易协定降低了跨境关税并统一了标籤标准,使中小企业更容易接触到海外买家。小包裹密度的持续增加将增强与飞机货舱供应商的议价能力,但如果柴油补贴的取消速度超过生产力提高的速度,利润率仍有可能下降。
在小包裹递送 (CEP) 领域之外,仓储和货运代理业者正在引入付费使用制,使微企业能够按货柜而非托盘租用空间。温控运输符合马来西亚的清真认证标准,并为水产品、糖果甜点和生物製药等高附加价值货物开闢了优质运输路线。预计到 2031 年,随着小包裹和合约物流活动吸收大量资金,货运代理在马来西亚货运和物流市场的份额将略有下降。然而,大型计划货物(例如太阳能电池板、涡轮机和炼油厂储槽)的专用卡车运输将继续支撑基准货运量。技术成熟度、监管透明度和劳动力供应将在很大程度上决定现有企业或新进入者能够获得增量价值。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 人口统计数据
- 按经济活动分類的GDP分配
- 按经济活动分類的GDP成长
- 通货膨胀
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业的趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 运输和仓储业GDP
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 卡车运输营运成本
- 卡车运输车队规模(按类型)
- 主要卡车供应商
- 物流绩效
- 透过交通方式分享
- 海运船队运力
- 班轮运输连接
- 停靠港口和演出
- 货运费率趋势
- 货物运输量趋势
- 基础设施
- 法规结构(公路和铁路)
- 法规结构(海事和航空)
- 价值炼和通路分析
- 市场驱动因素
- B2C电子商务交易量爆炸性成长
- 外国直接投资主导製造业产出激增
- 大型政府主导计划(东海岸铁路、泛婆罗洲高速公路)
- 透过RCEP进行的跨境贸易流动
- 对清真认证物流的需求不断增长
- 疫苗和生物製药低温运输发展
- 市场限制
- 港口和最后一公里拥堵
- 长期卡车驾驶人短缺
- 由于国内沿海运输政策,沿海运输受到限制
- 更严格的排放法规(相当于欧盟6标准)抑制了资本投资
- 市场创新
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 终端用户产业
- 农业、渔业、林业
- 建设业
- 製造业
- 石油天然气、采矿和采石
- 批发和零售
- 其他的
- 物流职能
- 宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)
- 按目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 按目的地
- 货运代理
- 透过交通工具
- 航空
- 海路和内河航道
- 其他的
- 透过交通工具
- 货物运输
- 透过交通工具
- 航空
- 管道
- 铁路
- 路
- 海路和内河航道
- 透过交通工具
- 仓库/存储
- 透过温度控制
- 非温控型
- 温度控制
- 透过温度控制
- 其他服务
- 宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 重大策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- MMC Corporation Bhd
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- Transocean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
The Malaysia freight and logistics market is expected to grow from USD 29.70 billion in 2025 to USD 31.23 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 40.11 billion by 2031 at 5.14% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Port Klang's rise to the world's 10th-busiest container port, extensive government funding for rail and highway projects, and sustained e-commerce momentum are reshaping supply-chain networks, warehouse automation priorities, and carrier partnerships across the Malaysia freight and logistics market. Foreign direct investment reached MYR 378.5 billion (USD 82.3 billion) in 2024, creating 207,000 jobs and expanding demand for cross-border forwarding, value-added distribution, and specialized manufacturing logistics. Consumers' preference for same-day delivery is accelerating last-mile network densification, while regulatory moves such as targeted diesel subsidies and simplified customs windows are easing cost pressures and border friction. Global carriers are deepening local ties to secure air-cargo uplift, sea-freight allocations, and temperature-controlled capacity, reinforcing Malaysia's hub role within ASEAN and the broader Asia-Pacific trade lattice.
Malaysia Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
Explosive B2C E-commerce Volumes Drive Last-Mile Innovation
Same-day fulfillment has become a standard expectation, with leading platforms shipping 95% of orders within 24 hours. Free-delivery preferences among 64.8% of internet users are forcing providers in the Malaysia freight and logistics market to adopt automated sortation, micro-fulfillment centers, and data-driven route planning. Retailers such as MR DIY achieved 200% efficiency gains after installing robotic systems, proving that automation now underpins competitive advantage. Partnerships like UPS-Ninja Van extend global express products to 52 retail outlets, offering exporters wider belly-hold access and digital tracking that aligns with rising SME participation in regional trade. The cumulative impact adds capacity resilience and service diversity, supporting the near-term growth trajectory of the Malaysia freight and logistics market.
Surge in FDI-Led Manufacturing Output Transforms Industrial Logistics
Record MYR 378.5 billion (USD 82.3 billion) investment approvals in 2024 are channeling funds toward semiconductor fabs, advanced automotive components, and renewable-energy assemblies. Semiconductor investments are triggering demand for electrostatic-discharge-compliant packaging, secure robotics, and bonded-warehouse clearance lanes. Precision-engineering firms such as MKS Instruments are building "super centers" that require synchronized inbound raw-material flows and high-frequency outbound shipments. Cross-border tax incentives inside the Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone are expected to add 100 projects and 20,000 skilled jobs, anchoring new corridors for the Malaysia freight and logistics market. As ESG criteria tighten, investors also prioritize multimodal nodes near renewable energy and rail spurs, reinforcing long-term freight diversification.
Port Congestion Constrains Capacity Despite Infrastructure Investment
Average vessel waiting times of 1.3-1.46 days at Port Klang, alongside yard utilization above 90%, undermine schedule dependability. The Malaysia Maritime Single Window, launched in February 2025, has trimmed documentation cycles from five days to mere hours, but physical quay expansions will still lag near-term TEU growth. Westports Holdings' multi-decade expansion blueprint aims to propel total capacity far beyond present limits, yet Red Sea rerouting has already intensified arrival bunching and yard overflow. As global carriers reallocate boxes, the Malaysia freight and logistics market faces short-term charter premium spikes and inventory imbalances that erode margin gains from higher throughput.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Mega-Projects Unlock Regional Connectivity
- RCEP Integration Accelerates Intra-ASEAN Trade Flows
- Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage Threatens Operational Scalability
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing held 38.98% of Malaysia freight and logistics market share in 2025, supported by Penang's MY 431 billion (USD 93.7 billion) export engine and Selangor's electronics clusters. Multinationals require bonded trucking corridors, ESD-safe warehouses, and secure-freight escorts, driving service differentiation. Growth in electric vehicle components and renewable energy equipment further expands the Malaysia freight and logistics market size for oversized container handling and specialized rigging. Wholesale and retail trade, although smaller in absolute dollars, is on pace for a 5.46% CAGR between 2026-2031 as disposable incomes rise and digital payment adoption widens. Supermarket chains like 99 Speed Mart plan to double store counts, demanding multi-temperature cross-docks and micro-fulfillment centers proximate to consumption hotspots.
Agriculture, fishing, and forestry depend on certified halal cold chains to penetrate Middle-East demand pools, giving algorithm-driven temperature traceability platforms greater commercial pull. Construction logistics ties directly to mega-projects such as the RTS Link and Penang Airport expansion, requiring heavy-lift cranes, night-time convoy escorts, and synchronized just-in-time material sequencing. Oil, gas, and mining remain cyclical but sustain steady demand for ISO tank containers, hull-cleaning services, and pipeline maintenance parts, anchoring a baseline for the Malaysia freight and logistics industry amid commodity swings.
Freight transport generated 55.62% of Malaysia freight and logistics market revenue in 2025, reflecting entrenched manufacturing exports and regional distribution flows. The Malaysia freight and logistics market size linked to courier, express, and parcel solutions is growing faster at a 5.86% CAGR (2026-2031) as e-retailers outsource same-day coverage to multi-modal carriers. Automated hubs, such as UPS-Ninja Van's expanded Klang Valley outlets, harness address-verification software and IoT tags to trim failed-delivery rates. As online orders fill truck bays, operators retrofit depots with tilt-tray sorters and deploy electric vans to navigate congestion nodes near Kuala Lumpur. The segment also benefits from 16 trade pacts that suppress cross-border clearance fees and harmonize labeling, easing SME access to overseas buyers. Continuous parcel-density escalation strengthens bargaining power with airline belly-hold providers, but margin compression remains a risk if diesel subsidies phase down faster than productivity gains materialize.
Beyond CEP, warehousing and forwarding units explore pay-as-you-use charging, allowing micro-enterprises to lease bins rather than full pallet slots. Temperature-controlled shipping aligns with Malaysia's halal-certification standards, opening premium lanes for value-added consolidation of seafood, confectionery, and biologics. The freight transport share of the Malaysia freight and logistics market is expected to decline marginally by 2031 as parcel and contract-logistics activities absorb disproportionate capital. Yet specialized trucking for oversized project cargo-solar panels, turbines, refinery vats-continues to anchor baseline volumes. Technology readiness, regulatory clarity, and workforce availability will largely determine whether incumbents or new entrants capture the incremental value.
The Malaysia Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- MMC Corporation Bhd
- NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express (KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- Transocean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 Explosive B2C E-Commerce Volumes
- 4.25.2 Surge in FDI-led Manufacturing Output
- 4.25.3 Government Mega-Projects (ECRL, Pan-Borneo Highway)
- 4.25.4 RCEP-Driven Cross-Border Trade Flows
- 4.25.5 Rising Demand for Certified Halal Logistics
- 4.25.6 Cold-Chain Build-Out for Vaccines and Biologics
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Port and Last-Mile Congestion
- 4.26.2 Chronic Truck-Driver Shortage
- 4.26.3 Domestic Cabotage Policy Limits Coastal Shipping
- 4.26.4 Tightening Euro-VI - Like Emission Rules, Capex Squeeze
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 City-Link Express
- 6.4.2 CJ Logistics Corporation
- 6.4.3 DHL Group
- 6.4.4 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.5 FedEx
- 6.4.6 FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.7 GDEX Group
- 6.4.8 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.9 Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- 6.4.10 J&T Express
- 6.4.11 Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- 6.4.12 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.13 MMC Corporation Bhd
- 6.4.14 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.15 POS Malaysia Bhd
- 6.4.16 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.17 SkyNet Worldwide Express, Inc.
- 6.4.18 Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.19 Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.20 Transocean Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.21 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.22 Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment





