 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1906909
义大利货运与物流:市场占有率分析、产业趋势、统计数据与成长预测(2026-2031)Italy Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031) |
||||||
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
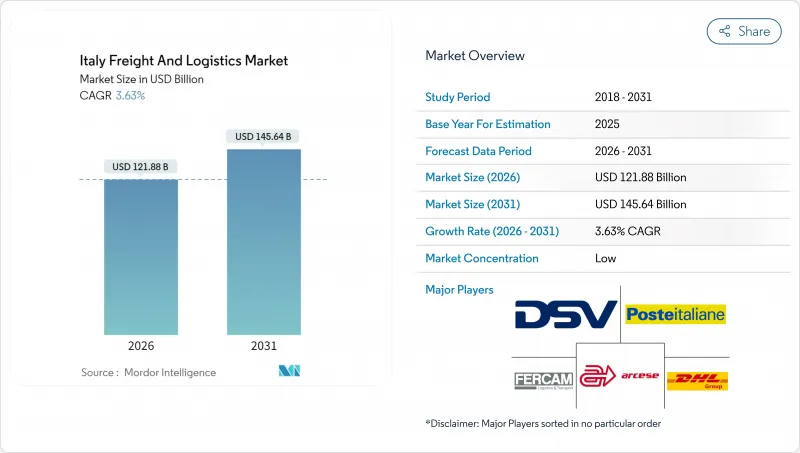
预计到 2026 年,义大利货运和物流市场规模将达到 1,218.8 亿美元,高于 2025 年的 1,176.1 亿美元。
预计到 2031 年将达到 1,456.4 亿美元,2026 年至 2031 年的复合年增长率为 3.63%。
与国家復苏与韧性计画 (NRRP) 相关的投资正在扩大港口和铁路运力,而不断增长的电子商务需求正在加速小包裹量的增加,对传统的长途运输网络构成挑战。义大利的货运和物流市场受益于其作为欧洲和地中海门户的地位,但劳动力短缺和车队老化正成为成本压力。药品和高檔食品出口对低温运输的需求不断增长,刺激了对温控仓库的需求,而工业4.0下的自动化奖励正在支持北部枢纽的现代化改造。诸如德迅收购Fercam Italia 80%股份等整合活动,凸显了市场正向能够处理复杂多模态的大型综合供应商转变。
义大利货运物流市场趋势及分析
电子商务小包裹激增和最后一公里投资
2024年,国内小包裹占义大利宅配(CEP)市场的66.54%。这反映了线上零售的快速成长,其市场规模达到588亿欧元(649亿美元),年增6%。义大利的货运和物流市场透过扩大其高密度储物柜网络来应对这一增长。 DHL和义大利邮政的合资企业计画安装1万个自动化收件点,将都市区的小包裹递送成本降低30%。亚马逊物流将当日达服务扩展到15个城市,促使传统承运商投资于微型仓配和电动车队。承运商正在重组其枢纽辐射式网络,以适应重量低于100公斤的小包裹,这些小包裹在电子商务流通中占据主导地位。促进都市区零排放车辆使用的政策与营运商的车队更新策略一致。在配送需求尖峰时段,产能短缺仍然是一个问题,因此需要与云端配送平台合作来吸收过剩的配送量。
食品和药品出口导致低温运输需求增加
2024年,药品出口占药品出口总额的80%以上,支撑了对温控运输的需求。 UPS收购了Frigo-Trans和BPL,强化了其在欧洲的GDP级低温运输网络,并将米兰的医药产业丛集定位为新兴市场货运枢纽。 2024年,温控仓库容量将占总容量的7.81%,但由于疫苗物流和生物製药生产的扩张,预计2025年至2030年将以3.53%的复合年增长率成长。米兰、罗马和波隆那机场货运区的冷藏空间正在扩建,以满足生物技术物流的需求。本地业者可以透过采用主动包装技术的端到端检验运输路线来获得附加价值。节能型可再生系统可享有NRRP(国家再生能源计画)为永续物流设施提供的补助。
驾驶人和卡车车队老化
义大利只有2.2%的职业司机年龄在25岁以下,随着资深驾驶人退休,可能会出现人员短缺的风险。重型车辆的平均车龄为19.1年,高于欧盟平均水平,这降低了车辆的可靠性并增加了维护成本。 2024年罗马爆发的抗议活动凸显了服务品质的下降,并促使人们呼吁加快外国司机的驾照发放。津贴项目涵盖每位驾驶者高达24,000欧元(26,487美元)的培训费用,但繁琐的申请流程阻碍了补贴的普及。租赁公司正在推广灵活的里程收费以加快车辆更新,但资金仍然是主导义大利货运和物流市场的小规模车队面临的一大限制因素。
细分市场分析
到2025年,製造业将占总收入的31.12%,这主要得益于遍Lombardia、Piemonte和Emilia-Romagna三大区的汽车、机械和生命科学生产基地。零件流通需要同步的准时交付,从而促进承运商和一级供应商之间的合作。批发和零售业是成长最快的产业,在2026年至2031年间,其复合年增长率将达到3.86%,这主要得益于全通路品牌对隔日达全国配送服务的需求。由于国家復苏计画(NRRP)的实施,建筑物流领域对骨材、钢材和预製模组的铁路和公路运输需求不断增长。
能源转型政策导致石油和天然气运输投资下降,承运商转向可再生能源计划货物运输。农业、渔业和林业部门加强了优质橄榄油和葡萄酒的出口,增加了对低温运输和冷藏货柜的需求。可再生能源技术组装和数位服务等新兴产业正在使义大利货运和物流市场的基本客群多元化,并降低週期性风险。
到2025年,货运代理业务将占义大利货运和物流市场的重要性。该业务涵盖了从北部工业丛集到全国各地消费市场的物流运输。随着网路购物重新定义配送频率并加速网路复杂化,2026年至2031年间,快速配送服务(CEP)的复合年增长率将达到4.17%。在仓储领域,随着工业4.0倡议的推进,北部地区的设施正在实施多层自动化,从而确保更高的产能和扩充性。货运代理业将利用义大利位于亚欧干线上的位置来协调多式联运。其他服务包括计划货物协调和危险品处理。
随着承运商将清关和库存管理纳入运输合同,综合服务正在模糊功能边界。义大利邮政的业务转型已显现多元化迹象,显示2025年服务扩张的成效显着,届时物流收入将超过邮政服务收入。交叉销售正在提高工业客户的留存率,他们寻求的是门到门的可视性和合规性。在整合数位平台上整合运输、仓储和附加价值服务的营运商将在义大利货运和物流市场中获得竞争优势。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市场预测(ME)表
- 3个月的分析师支持
目录
第一章 引言
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 调查范围
第二章调查方法
第三章执行摘要
第四章 市场情势
- 市场概览
- 人口统计数据
- 按经济活动分類的GDP分配
- 按经济活动分類的GDP成长
- 通货膨胀
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业的趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 运输和仓储业部门的GDP
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 卡车运输营运成本
- 卡车运输车队规模(按类型)
- 主要卡车供应商
- 物流绩效
- 透过交通方式分享
- 海运船队运力
- 班轮运输连接
- 停靠港口和演出
- 货运费率趋势
- 货物吨位趋势
- 基础设施
- 法规结构(公路和铁路)
- 法规结构(海事和航空)
- 价值炼和通路分析
- 市场驱动因素
- 电子商务小包裹激增和最后一公里投资
- 食品和药品出口引起的低温运输需求
- 国家復苏与再投资计画(NRRP)和泛欧交通运输网络(TEN-T)走廊的基础建设
- 工业4.0税收优惠促进智慧物流技术发展
- 储物柜网路改变了都市区自提点(取还)方式
- 由于设备升级导致铁路服务暂停,运输量转移到公路。
- 市场限制
- 驾驶人和卡车车队老化
- 北韩和南韩的营运成本存在巨大差异
- 到2025年,由于主要港口走廊的铁路建设,运输能力将出现短缺。
- 由于电池和危险材料法规,电动车物流合规成本增加。
- 市场创新
- 波特五力分析
- 新进入者的威胁
- 买方的议价能力
- 供应商的议价能力
- 替代品的威胁
- 竞争对手之间的竞争
第五章 市场规模与成长预测
- 终端用户产业
- 农业、渔业、林业
- 建设业
- 製造业
- 石油天然气、采矿和采石
- 批发和零售
- 其他的
- 物流职能
- 宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)
- 按目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 按目的地
- 货运代理
- 透过交通工具
- 航空
- 海路和内河航道
- 其他的
- 透过交通工具
- 货物运输
- 透过交通工具
- 航空
- 管道
- 铁路
- 路
- 海路和内河航道
- 透过交通工具
- 仓储
- 透过温度控制
- 非温控型
- 温度控制
- 透过温度控制
- 其他服务
- 宅配、速递和小包裹(CEP)
第六章 竞争情势
- 市场集中度
- 重大策略倡议
- 市占率分析
- 公司简介
- Amazon
- Arcese Trasporti SpA
- BRT SpA
- CMA CGM Group(Including CEVA Logistics)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- Fercam SpA
- International Distributions Services PLC(Including GLS)
- Grimaldi Group
- GRUBER Logistics SpA
- Italsempione
- Italtrans
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Mercitalia Rail
- MSC Mediterranean Shipping Company SAA
- Poste Italiane
- Savino Del Bene SpA
- Transmec Group
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
第七章 市场机会与未来展望
Italy freight and logistics market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 121.88 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 117.61 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 145.64 billion, growing at 3.63% CAGR over 2026-2031.

Investment tied to the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP) is expanding port and rail capacity, while e-commerce demand accelerates parcel volumes that challenge traditional long-haul networks. The Italy freight and logistics market benefits from the country's gateway role between Europe and the Mediterranean, yet labor shortages and an aging vehicle fleet raise cost pressures. Rising cold-chain needs from pharmaceutical and premium food exports stimulate temperature-controlled warehousing, and automation incentives under Industry 4.0 support modernization in northern hubs. Consolidation activities, such as DACHSER acquiring 80% of Fercam Italia, highlight a shift toward larger, integrated providers capable of handling complex multimodal flows.
Italy Freight And Logistics Market Trends and Insights
E-Commerce Parcel Surge and Last-Mile Investments
Domestic parcels within CEP captured a 66.54% share in 2024, reflecting surging online retail that hit EUR 58.8 billion (USD 64.9 billion) and grew 6% year over year. The Italy freight and logistics market responds by adding dense locker grids; the DHL-Poste Italiane venture targets 10,000 automated pickup points and cuts per-parcel urban delivery cost by 30%. Amazon Logistics extended same-day coverage to 15 more cities, compelling traditional carriers to invest in micro-fulfillment and electric fleets. Carriers reengineer hub-and-spoke layouts to support sub-100-kilogram shipments that dominate e-commerce flows. Urban policy incentives for zero-emission vehicles align with operator fleet renewal strategies. Capacity challenges persist on peak shopping days, driving collaboration with crowd-shipping platforms to absorb overflow volumes.
Cold-Chain Demand from Food and Pharma Exports
Medicinal drugs sustained above 80% of the pharmaceutical export value in 2024, anchoring demand for temperature-controlled distribution. UPS acquired Frigo-Trans and BPL, bolstering European GDP-grade cold-chain coverage and positioning Milan's pharma cluster as a hub for emerging-market shipments. Temperature-controlled warehousing claims only 7.81% of total capacity in 2024, yet it is expected to expand at a 3.53% CAGR (2025-2030) as vaccine logistics and biologics production widen demand. Airport cargo zones in Milan, Rome, and Bologna add cool-room space to capture biotech flows. Regional specialization enables operators to capture value via end-to-end validated lanes with active packaging. Energy-efficient refrigeration systems benefit from NRRP grants earmarked for sustainable logistics facilities.
Driver Shortages and Aging Truck Fleet
Only 2.2% of professional drivers in Italy are under 25, creating succession risk as veteran operators retire. The average heavy-duty vehicle age of 19.1 years exceeds the EU average and lowers fleet reliability, inflating maintenance costs. Protests in Rome during 2024 spotlighted declining service quality and urged fast-track license recognition for foreign drivers. Grant programs cover up to EUR 24,000 (USD 26,487) per driver for training, yet uptake lags amid cumbersome application rules. Leasing firms promote flexible pay-per-kilometer schemes to accelerate fleet renewal, but capital constraints persist among micro-fleets dominating the Italy freight and logistics market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Infrastructure Upgrades Under NRRP and TEN-T Corridors
- Industry 4.0 Tax Credits Boosting Smart-Logistics Tech
- High North-South Operating-Cost Differential
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manufacturing accounted for 31.12% of 2025 revenue, anchored in automotive, machinery, and life-science production hubs across Lombardy, Piedmont, and Emilia-Romagna. Component flows require synchronized just-in-sequence deliveries, fostering collaboration between hauliers and tier-one suppliers. Wholesale and retail trade grows fastest at 3.86% CAGR (2026-2031) as omnichannel brands demand nationwide next-day fulfillment. Construction logistics gains from NRRP works, shipping aggregates, steel, and prefabricated modules to rail and highway sites.
Energy transition policies taper investments in oil and gas haulage, nudging carriers toward renewables project cargo. Agriculture, fishing, and forestry strengthen export footprints in premium olive oil and wine, raising cold-chain and reefer container needs. Emerging sectors such as renewable technology assembly and digital services diversify the Italy freight and logistics market's customer base, cushioning cyclical risk.
Freight transport generated 62.88% of 2025 revenue, underscoring the centrality of road, rail, sea, and air moves in the Italy freight and logistics market. The segment captures flows from industrial clusters in the North to consumer markets nationwide. CEP services record a 4.17% CAGR between 2026-2031 as online shopping resets delivery frequency benchmarks and accelerates network densification. Warehousing and storage rides Industry 4.0 incentives to add multi-level automation in northern facilities, lifting throughput and assuring scalability. Freight forwarding leverages Italy's positioning on Asia-Europe lanes to orchestrate multimodal movements, while other services encompass project cargo orchestration and hazardous goods handling.
Integrated offerings now blur function lines as carriers embed customs brokerage and inventory control within transport contracts. Diversification is visible in Poste Italiane's pivot: revenue from logistics operations outpaced mail services in 2025, validating service expansion. Cross-selling boosts stickiness with industrial clients demanding door-to-door visibility and compliance. The Italy freight and logistics market rewards operators that fuse transport, warehousing, and value-added services under unified digital platforms.
The Italy Freight and Logistics Market Report is Segmented by End User Industry (Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry, Construction, Manufacturing, Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying, Wholesale and Retail Trade, and Others) and by Logistics Function (Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP), Freight Forwarding, Freight Transport, Warehousing and Storage, and Other Services). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Amazon
- Arcese Trasporti SpA
- BRT SpA
- CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- FedEx
- Fercam SpA
- International Distributions Services PLC (Including GLS)
- Grimaldi Group
- GRUBER Logistics SpA
- Italsempione
- Italtrans
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Mercitalia Rail
- MSC Mediterranean Shipping Company S.A.A
- Poste Italiane
- Savino Del Bene SpA
- Transmec Group
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Demographics
- 4.3 GDP Distribution by Economic Activity
- 4.4 GDP Growth by Economic Activity
- 4.5 Inflation
- 4.6 Economic Performance and Profile
- 4.6.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.6.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.7 Transport and Storage Sector GDP
- 4.8 Export Trends
- 4.9 Import Trends
- 4.10 Fuel Price
- 4.11 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.12 Trucking Fleet Size by Type
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Logistics Performance
- 4.15 Modal Share
- 4.16 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.17 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.18 Port Calls and Performance
- 4.19 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.20 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.21 Infrastructure
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.23 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.24 Value Chain and Distribution Channel Analysis
- 4.25 Market Drivers
- 4.25.1 E-Commerce Parcel Surge and Last-Mile Investments
- 4.25.2 Cold-Chain Demand from Food and Pharma Exports
- 4.25.3 Infrastructure Upgrades Under NRRP and TEN-T Corridors
- 4.25.4 Industry 4.0 Tax Credits Boosting Smart-Logistics Tech
- 4.25.5 Locker Networks Altering Urban PUDO Mix
- 4.25.6 Rail-Upgrade Disruptions Shifting Volumes to Road
- 4.26 Market Restraints
- 4.26.1 Driver Shortages and Ageing Truck Fleet
- 4.26.2 High North-South Operating-Cost Differential
- 4.26.3 2025 Rail-Works Capacity Crunch on Key Port Corridors
- 4.26.4 Battery-Hazmat Rules Raising EV-Logistics Compliance Cost
- 4.27 Technology Innovations in the Market
- 4.28 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.28.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.28.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.28.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.28.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.28.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode of Transport
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Amazon
- 6.4.2 Arcese Trasporti SpA
- 6.4.3 BRT SpA
- 6.4.4 CMA CGM Group (Including CEVA Logistics)
- 6.4.5 DHL Group
- 6.4.6 DSV A/S (Including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.7 FedEx
- 6.4.8 Fercam SpA
- 6.4.9 International Distributions Services PLC (Including GLS)
- 6.4.10 Grimaldi Group
- 6.4.11 GRUBER Logistics SpA
- 6.4.12 Italsempione
- 6.4.13 Italtrans
- 6.4.14 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.15 Mercitalia Rail
- 6.4.16 MSC Mediterranean Shipping Company S.A.A
- 6.4.17 Poste Italiane
- 6.4.18 Savino Del Bene SpA
- 6.4.19 Transmec Group
- 6.4.20 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment





