 |
市场调查报告书
商品编码
1687851
日本的货运和物流:市场占有率分析、行业趋势和统计、成长预测(2025-2030 年)Japan Freight and Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
价格
※ 本网页内容可能与最新版本有所差异。详细情况请与我们联繫。
简介目录
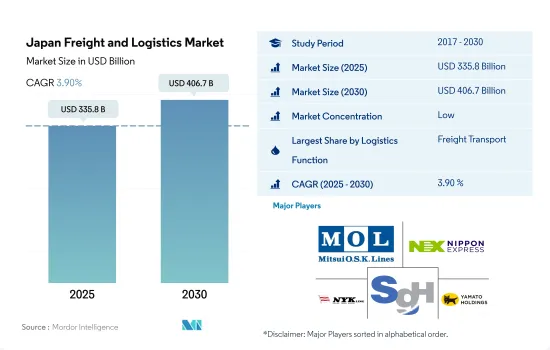
日本的货运和物流市场规模预计在 2025 年将达到 3,358 亿美元,预计到 2030 年将达到 4,067 亿美元,预测期内(2025-2030 年)的复合年增长率为 3.90%。
由于日本电子商务销售额成长和结构变化,对公路货运服务的需求不断增加
- 2023年12月,DHL Express与日本航空(JAL)建立以JAL波音767-300货机为中心的长期伙伴关係关係。此次合作的目的是满足国际快递和电子商务运输领域(特别是东亚地区)快速成长的需求。透过与 DHL 合作,日航将加强利用其波音 767-300ER 货机建立日本、首尔、上海和台北之间的重要连结。特别是,DHL 计划利用日本航空将于 2024 年 2 月开通的航线,扩大其在东亚地区的网路。
- 2023年10月,日本政府透露,将为电动飞机系统拨款306亿日圆(2.1689亿美元),研发活动将于2024年开始。这项决定符合全球鼓励航空公司和政府在2050年实现碳中和的努力。政府计画拨款173亿日圆(1.2262亿美元)用于开发航空氢燃料电池系统,拨款133亿日圆(9,427万美元)用于加强节油引擎控制系统。
日本货运及物流市场的趋势
由于宅配需求不断增加以及劳动力短缺,MILT 正致力于建造自动化货运道路和物流隧道。
- 2024 年 5 月 17 日,在东京车站举行的展览会上,高速客运列车在轻型货运中的应用日益广泛。这一转变是由于商务用驾驶人短缺和新的加班法导致公路运输成本增加高达 20%。从 2023 年 8 月开始,JR 东日本将使用 12 辆车的 E 系列专用列车实施从新舄到东京的当日送货服务。运送的物品包括生鲜食品、糖果零食、饮料、鲜花、精密零件、医疗用品等。 2023 年 9 月,JR 东日本在东北新干线推出货运专用服务,目前在其高速和特快网路中提供「Hako BYUN」品牌货运服务。
- 2024年3月,由于静冈县持续反对环保主张,JR东海放弃了2027年前在东京和名古屋之间运营高速磁浮列车的计划,该计划可能会被推迟到2034年或更晚。中央新干线的目标是以每小时 500 公里的速度连接东京和大阪,但静冈境内的一小段路程却构成了重大障碍。
儘管政府提供补贴,2024 年 7 月燃油价格仍将上涨至 2023 年 10 月以来的最高水平
- 自然资源与能源署于2024年7月宣布,普通汽油零售价格已达每公升1.33美元。这一价格是自2023年10月以来约九个月以来的最高价格,零售价格的上涨是由于批发价格上涨。为了解决这个问题,各国政府正在向炼油精製提供补贴,以降低批发价格。此外,补贴金额也有所增加,6月27日至7月3日期间补贴金额为0.19美元,较前一週增加0.01美元。
- 日本天然气公司预测,由于 2023-24 年天气异常温暖,城市天然气使用量将下降,因此 2024 年 4 月至 2025 年 3 月的财年,城市天然气需求将会增加。日本最大的瓦斯零售商东京瓦斯公司预测,到2025年,其城市瓦斯销售量将增加1.1%至114.22亿立方公尺。其中,居民用气预计增加3.4%至28亿立方米,工业和商务用预计增加0.3%至86亿立方米。
日本货运及物流业概况
日本的货运代理和物流市场较为分散,市场前五大参与者(按字母顺序排列)为商船三井、日本通运控股、日本邮船(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)、SG控股和大和控股。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市场预测 (ME) 表
- 3 个月的分析师支持
目录
第 1 章执行摘要和主要发现
第二章 报告要约
第 3 章 简介
- 研究假设和市场定义
- 研究范围
- 调查方法
第四章 产业主要趋势
- 人口统计
- 按经济活动分類的 GDP 分布
- 经济活动带来的 GDP 成长
- 通货膨胀率
- 经济表现及概况
- 电子商务产业趋势
- 製造业趋势
- 交通运输仓储业生产毛额
- 出口趋势
- 进口趋势
- 燃油价格
- 卡车运输成本
- 卡车持有量(依类型)
- 物流绩效
- 主要卡车供应商
- 模态共享
- 海运能力
- 班轮连结性
- 停靠港和演出
- 货运趋势
- 货物吨位趋势
- 基础设施
- 法律规范(公路和铁路)
- 日本
- 法律规范(海运和空运)
- 日本
- 价值链与通路分析
第五章 市场区隔
- 最终用户产业
- 农业、渔业和林业
- 建设业
- 製造业
- 石油和天然气、采矿和采石
- 批发和零售
- 其他的
- 物流功能
- 快递、快递和小包裹(CEP)
- 目的地
- 国内的
- 国际的
- 货物
- 按运输方式
- 航空
- 海上和内陆水道
- 其他的
- 货物
- 交通方式
- 航空
- 管道
- 铁路
- 路
- 海上和内陆水道
- 仓库存放
- 透过温度控制
- 无温度控制
- 温度管理
- 其他服务
- 快递、快递和小包裹(CEP)
第六章 竞争格局
- 主要策略趋势
- 市场占有率分析
- 业务状况
- 公司简介.
- Deutsche Bahn AG(including DB Schenker)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- Kintetsu Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Mitsui OSK Lines, Ltd.
- Nippon Express Holdings
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
第七章:执行长的关键策略问题
第 8 章 附录
- 世界概况
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球价值链分析
- 市场动态(市场驱动因素、限制因素、机会)
- 技术进步
- 资讯来源和进一步阅读
- 图表清单
- 关键见解
- 资料包
- 词彙表
- 外汇
简介目录
Product Code: 66498
The Japan Freight and Logistics Market size is estimated at 335.8 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 406.7 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 3.90% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Rising demand for road freight services due to increasing e-commerce sales and structural changes in Japan
- In December 2023, DHL Express and Japan Airlines (JAL) forged a long-term partnership centered around JAL's Boeing 767-300 freighters. This collaboration aims to tap into the surging demand in the international express and e-commerce shipping sectors, particularly in East Asia. By teaming up with DHL, JAL is bolstering its efforts to establish key connections between Japan, Seoul, Shanghai, and Taipei, leveraging the Boeing 767-300ER freighters. Notably, DHL plans to expand its intra-East Asia network by leveraging the routes introduced by JAL starting in February 2024.
- In October 2023, Japan's government unveiled its intention to allocate JPY 30.6 billion (USD 216.89 million) toward electric aircraft systems, initiating research and development activities in 2024. This decision aligns with global efforts to push aviation operators and governments toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. The government plans to allocate JPY 17.3 billion (USD 122.62 million) toward hydrogen fuel cell system development for aircraft and JPY 13.3 billion (USD 94.27 million) for the enhancement of fuel-efficient engine control systems.
Japan Freight and Logistics Market Trends
With growing demand for home deliveries & labour shortages, the MILT is focusing on construction of automatic cargo transport roads and logistics tunnels
- On May 17, 2024, a fair at Tokyo Station highlighted the growing use of high-speed passenger trains for light freight. This shift, driven by a shortage of commercial drivers and new overtime laws, has increased road delivery costs by up to 20%. Since August 2023, JR East has been running a same-day delivery service from Niigata to Tokyo using a dedicated 12-car Series E trainset. Items transported include fresh food, confectionery, drinks, flowers, precision components, and medical supplies. In September 2023, JR East launched a freight-only service on the Tohoku Shinkansen and now offers Hakobyun-branded freight services across its high-speed and Limited Express networks.
- In March 2024, Central Japan Railway Co. abandoned its plan to launch a high-speed maglev train between Tokyo and Nagoya by 2027 due to ongoing environmental opposition in Shizuoka Prefecture, possibly delaying the project until 2034 or later. The Linear Chuo Shinkansen aims to connect Tokyo and Osaka with trains reaching speeds of 500 kilometers per hour, but a small section in Shizuoka has been a major obstacle.
Rising prices of fuel in Japan witnessed in July 2024, highest since October 2023, despite government subsidies
- In July 2024, the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy announced that the retail price of regular gasoline reached USD 1.33 per liter, marking an increase of USD 0.006 from June 2024. This price point is the highest observed in nearly nine months, dating back to October 2023. The uptick in retail prices is attributed to surging wholesale prices. To counteract this, the government has been subsidizing oil refiners, ensuring that wholesale prices remain subdued. Moreover, the subsidy amount saw an uptick, rising to USD 0.19 between June 27 and July 3, which is an increase of USD 0.01 from the week prior.
- Japanese gas utilities expect city gas demand to rise in the fiscal year April 2024 to March 2025, following reduced usage in 2023-24 due to unusually warm weather. Tokyo Gas, Japan's largest gas retailer, forecasts city gas sales will increase by 1.1% to 11.422 billion cubic meters by 2025. Household sales are expected to grow by 3.4% to 2.8 billion cubic meters, while supplies to industry and commercial users are projected to rise by 0.3% to 8.6 billion cubic meters.
Japan Freight and Logistics Industry Overview
The Japan Freight and Logistics Market is fragmented, with the major five players in this market being Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd., Nippon Express Holdings, NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line, SG Holdings Co., Ltd. and Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd. (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.11 Trucking Fleet Size By Type
- 4.12 Logistics Performance
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Modal Share
- 4.15 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.16 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.17 Port Calls And Performance
- 4.18 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.19 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.20 Infrastructure
- 4.21 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.21.1 Japan
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.22.1 Japan
- 4.23 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes 1. Market value in USD for all segments 2. Market volume for select segments viz. freight transport, CEP (courier, express, and parcel) and warehousing & storage 3. Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Deutsche Bahn AG (including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 DSV A/S (De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- 6.4.4 Kintetsu Group Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.6 Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Nippon Express Holdings
- 6.4.8 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.9 SG Holdings Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.10 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.11 Yamato Holdings Co., Ltd.
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FREIGHT AND LOGISTICS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (Market Drivers, Restraints & Opportunities)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
- 8.7 Currency Exchange Rate
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219




